当前位置:网站首页>Dynamic planning: robbing families and houses
Dynamic planning: robbing families and houses
2022-07-05 23:24:00 【chenyfan_】
Dynamic programming And raid homes and plunder houses
198. raid homes and plunder houses ●●
You are a professional thief , Plan to steal houses along the street . There is a certain amount of cash in every room , The only constraint on your theft is that the adjacent house is equipped with Interconnected anti-theft system , If two Adjacent houses were broken into by thieves on the same night , The system will automatically alarm .
Given an array of non negative integers representing the storage amount of each house , Count you Without triggering the alarm , The maximum amount that can be stolen overnight .
–
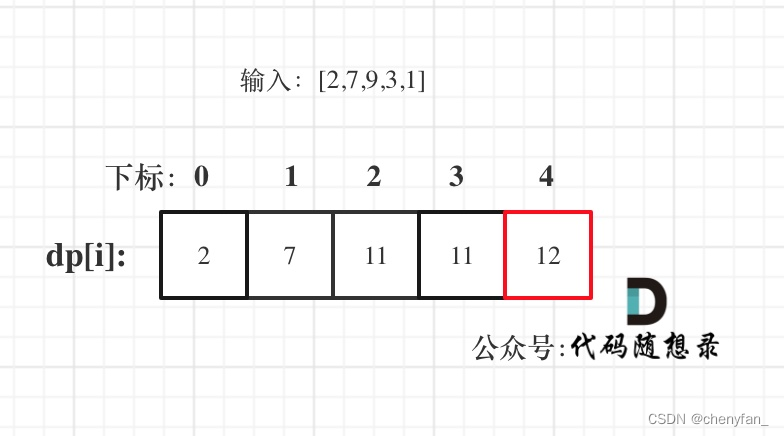
Input :[2,7,9,3,1]
Output :12
explain : Steal 1 House No ( amount of money = 2), Steal 3 House No ( amount of money = 9), Then steal 5 House No ( amount of money = 1). Maximum amount stolen = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12 .
- Dynamic programming , Two dimensional array , Steal or not steal nums[i] Expressed as dp[i][1] and dp[i][0]
class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(2, 0));
dp[0][1] = nums[0];
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i){
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][1]); // Don't steal nums[i]
dp[i][1] = dp[i-1][0] + nums[i]; // steal nums[i]
}
return max(dp[n-1][0], dp[n-1][1]);
}
};
- Dynamic programming , One dimensional array
- dp[j]: Consider Subscripts j( Include j) The houses within , The maximum amount that can be stolen is dp[j].
dp[j] = max(dp[j-1], dp[j-2] + nums[j]);
Consider stealing or not stealing subscripts j- dp[0] = nums[0];
dp[1] = max(nums[0], nums[1]); - Traversing from front to back
class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1) return nums[0];
vector<int> dp(n, 0); // dp[j]
dp[0] = nums[0];
dp[1] = max(nums[0], nums[1]); // 0 and 1 Only one can be stolen
for(int j = 2; j < n; ++j){
// steal or Don't steal nums[j]
dp[j] = max(dp[j-1], dp[j-2] + nums[j]);
}
return dp[n-1];
}
};
213. raid homes and plunder houses II ●●
You are a professional thief , Plan to steal houses along the street , There is a certain amount of cash in every room . All the houses in this place are Make a circle , It means The first house is next to the last house . meanwhile , Adjacent houses are equipped with interconnected anti-theft system , If two adjacent houses are broken into by thieves on the same night , The system will automatically alarm .
Given an array of non negative integers representing the storage amount of each house , Count you Without triggering the alarm device , The maximum amount you can steal tonight .
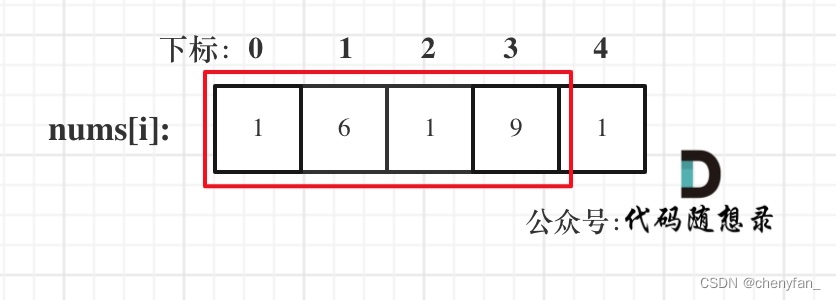
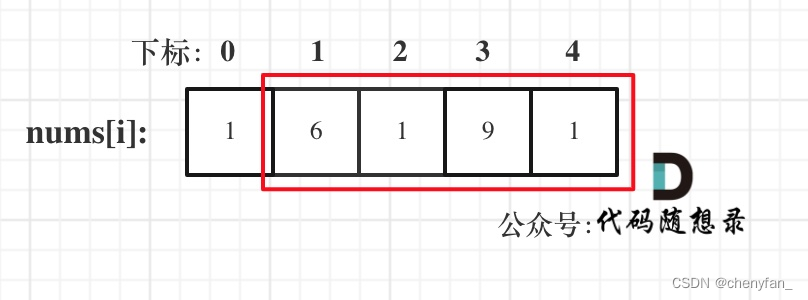
The house in this question End to end connection into a ring 了 , therefore , Divide the house into two situations , Turn into Two non looped The problem of house raiding is calculated separately :
- consider ( But not necessarily ) The first house , Not considering the last house ;
- consider ( But not necessarily ) The last house , Not considering the first house .
class Solution {
public:
int subRob(vector<int>& nums, int strat, int end){
int n = end - strat + 1; // The number of subsets
if(n == 1) return nums[strat];
vector<int> dp(n, 0);
dp[0] = nums[strat];
dp[1] = max(nums[strat], nums[strat + 1]);
for(int j = 2; j < n; ++j){
dp[j] = max(dp[j-1], dp[j-2] + nums[j+strat]);
}
return dp[n-1];
}
int rob(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
if(n == 1) return nums[0];
int strat = subRob(nums, 0, n-2); // [0, n-2]
int end = subRob(nums, 1, n-1); // [1, n-1]
return max(strat, end);
}
};
337. raid homes and plunder houses III ●●
The thief found a new area to steal . There is only one entrance to the area , We call it root .
except root outside , Each house has and only has one “ Father “ The house is connected to it . After some reconnaissance , The clever thief realized that “ All the houses in this place are arranged like a binary tree ”. If Two directly connected houses were robbed the same night , The house will alarm automatically .
Given a binary tree root . return Without triggering the alarm , The maximum amount a thief can steal .
After the sequence traversal , Through the return value of the recursive function to do the next calculation .
If steal The current node , Two children can't move , and Recursion to grandchildren ;
If Don't steal Current node , You can consider stealing around children ( Notice what's going on here “ consider ”)
1. Memory recursive search
Avoid double calculation of nodes , Use the hash table to store the calculated node amount .
- Time complexity : O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
- Spatial complexity : O ( log n ) O(\log n) O(logn), Count the space of the recursive system stack
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<TreeNode*, int> map;
int rob(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) return root->val; // Leaf node , Direct return value
if(map[root]) return map[root]; // Mnemonic search hash
// Steal the parent node , Recursively traverse grandchildren
int val1 = root->val;
if(root->left != nullptr) val1 += rob(root->left->left) + rob(root->left->right);
if(root->right != nullptr) val1 += rob(root->right->left) + rob(root->right->right);
// Don't steal the parent node , Recursive traversal of child nodes
int val2 = rob(root->left) + rob(root->right);
// Taking the maximum , And store memory
map[root] = max(val1, val2);
return map[root];
}
};
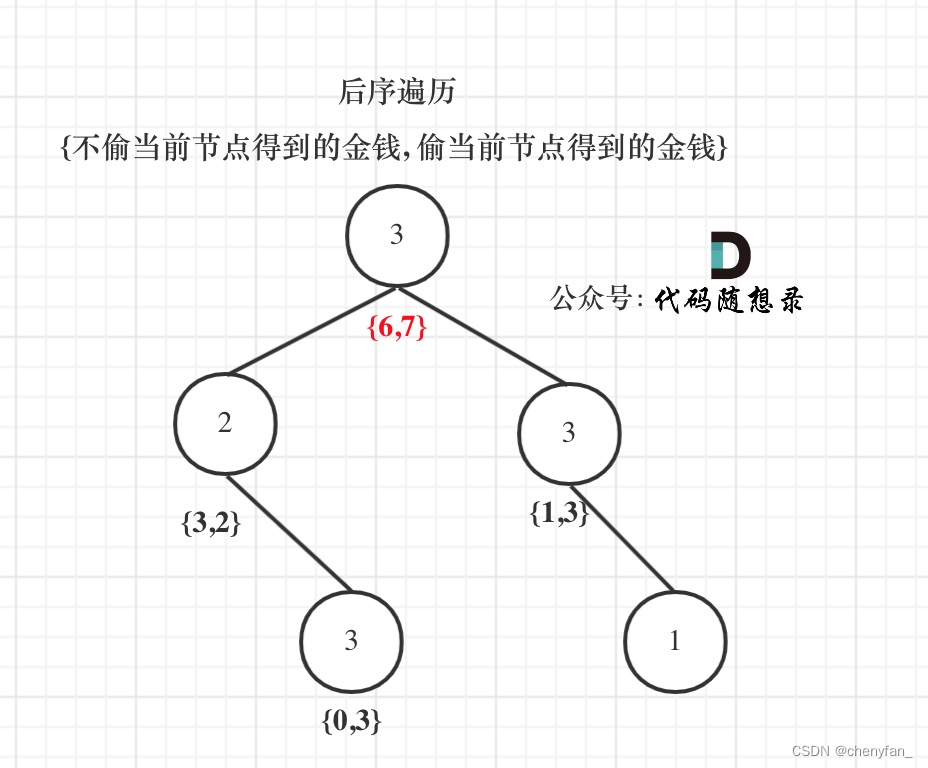
2. Dynamic programming ( Tree form dp)
The above memory search is for a node Steal and don't steal The biggest money you get is not recorded , It requires real-time calculation and comparison .
Dynamic programming is actually using state transition container array dp[] To record changes in state ,dp[0] Indicates the maximum amount obtained by not stealing this node ,dp[1] Indicates the maximum amount obtained by stealing this node .
- Time complexity : O ( n ) O(n) O(n), Each node is traversed only once
- Spatial complexity : O ( log n ) O(\log n) O(logn), Count the space of the recursive system stack
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> robTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return {
0, 0};
vector<int> dp(2, 0);
// Consider the child node
vector<int> left = robTree(root->left);
vector<int> right = robTree(root->right);
// Do not steal this node , Subscript to be 0, Child nodes can be stolen, not stolen
dp[0] = max(left[0], left[1]) + max(right[0], right[1]);
// Steal this node , Subscript to be 1, You can't steal children's nodes
dp[1] = root->val + left[0] + right[0];
return dp;
}
int rob(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ans = robTree(root);
return max(ans[0], ans[1]);
}
};
边栏推荐
- 14种神笔记方法,只需选择1招,让你的学习和工作效率提高100倍!
- Composition of interface
- C Primer Plus Chapter 9 question 9 POW function
- What is the process of building a website
- Practice of concurrent search
- poj 2762 Going from u to v or from v to u? (infer whether it is a weak link diagram)
- 代码农民提高生产力
- LeetCode145. Post order traversal of binary tree (three methods of recursion and iteration)
- Data type, variable declaration, global variable and i/o mapping of PLC programming basis (CoDeSys)
- 两数之和、三数之和(排序+双指针)
猜你喜欢
![[original] what is the core of programmer team management?](/img/11/d4b9929e8aadcaee019f656cb3b9fb.png)
[original] what is the core of programmer team management?

Registration of Electrical Engineering (elementary) examination in 2022 and the latest analysis of Electrical Engineering (elementary)
进击的技术er——自动化

LeetCode102. Sequence traversal of binary tree (output by layer and unified output)
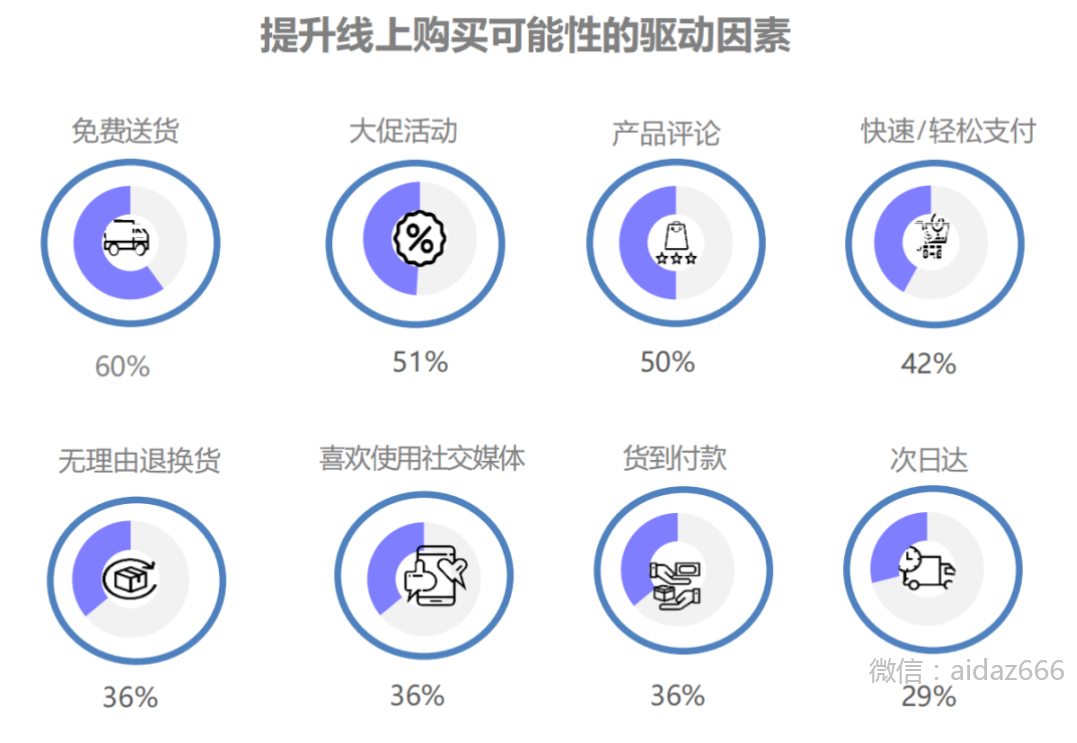
东南亚电商指南,卖家如何布局东南亚市场?

Dynamic memory management (malloc/calloc/realloc)
![Development specification: interface unified return value format [resend]](/img/3e/8751b818147cabbe22e4ce44af7d24.jpg)
Development specification: interface unified return value format [resend]
无刷驱动设计——浅谈MOS驱动电路
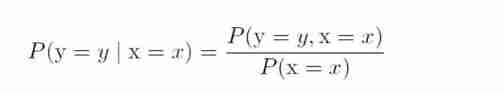
Marginal probability and conditional probability

动态规划 之 打家劫舍
随机推荐
2022 G3 boiler water treatment simulation examination and G3 boiler water treatment simulation examination question bank
两数之和、三数之和(排序+双指针)
(4)UART应用设计及仿真验证2 —— RX模块设计(无状态机)
Neural structured learning - Part 2: training with natural graphs
二叉树递归套路总结
There are 14 God note taking methods. Just choose one move to improve your learning and work efficiency by 100 times!
poj 2762 Going from u to v or from v to u? (infer whether it is a weak link diagram)
UVA11294-Wedding(2-SAT)
Go language implementation principle -- lock implementation principle
grafana工具界面显示报错influxDB Error
Thoroughly understand JVM class loading subsystem
Alibaba Tianchi SQL training camp task4 learning notes
idea 连接mysql ,直接贴配置文件的url 比较方便
The method and principle of viewing the last modification time of the web page
Multi camera stereo calibration
Krypton Factor purple book chapter 7 violent solution
Fix the memory structure of JVM in one article
TypeError: this. getOptions is not a function
424. 替换后的最长重复字符 ●●
Simple and beautiful method of PPT color matching