当前位置:网站首页>Analyze "C language" [advanced] paid knowledge [i]
Analyze "C language" [advanced] paid knowledge [i]
2022-07-07 01:49:00 【Choice~】
Program = Algorithm + data structure + Programming method + Language tools and bad environment
inform : Use C Linguistic 7 A step
The first 1 Step : Define the objectives of the program
Before you start writing the program , Have a clear mind . If you want the program to do something, you should first make clear what you want to do , Think about what information your program needs , What calculations and controls are to be carried out , And what information the program should report . In this step , There is no specific computer language involved , The problem should be described in general terms .
The first 2 Step : Design procedure
After having a conceptual understanding of what the program should accomplish , We should consider how to use the program to complete it . for example , What the user interface should look like ? How to organize the program ? Who are the target users ? How long is it going to take to complete this program ?
besides , And we have to decide in the process ( It could be an auxiliary file ) How to represent data in , And how to process the data . Study C The beginning of language , The problems are very simple , There's no choice . however , As the situation to be dealt with becomes more and more complex , There are more and more aspects that need decision-making and consideration . Usually , Choosing an appropriate way to represent information makes it easier to design programs and process data .
Again , The problem should be described in general terms , Instead of using specific code . however , Some of your decisions may depend on the nature of the language . for example , In terms of data representation ,C I'm a better programmer than Pascal There are more options for programmers in the world .
The first 3 Step : Write code
After designing the program , You can write code to implement it . in other words , Translate your program into C Language . Here's what you really need to use C Language place . You can write ideas on paper , But in the end, you have to put the code into the computer . The mechanism of this process depends on the programming environment , We'll talk about some common environments later . generally speaking , Use a text editor to create a source code file . The content of this document is your translation C The language code . Program listing 1.1 It's a C Examples of source code .
Program listing 1.1 C Source code example
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int dogs;
printf("How many dogs do you have?\n");
scanf("%d", &dogs);
printf("So you have %d dog(s)!\n", dogs);
return 0;
}
In this step , You should add text notes to your own programs . The easiest way is to use C The annotation tool in the source code to add the interpretation of the code .
The first 4 Step : compile
The next step is to compile the source code . Again, pay attention to , The details of compilation depend on the programming environment , As mentioned earlier , A compiler is a program that converts source code into executable code . Executable code is the code expressed in the machine language of a computer . This language consists of instructions represented by a numeric code . As mentioned earlier , Different computers use different machine language schemes .C The compiler is responsible for putting C Code is translated into a specific machine language . Besides ,C The compiler also integrates the source code with C library ( The library contains a large number of standard functions for users to use , Such as printf() and scanf()) The code is merged into the final program ( To be more precise , It should be a program called linker that links library functions , But in most systems , The compiler runs the linker ). As a result, , Generate an executable file that users can run , It contains code that a computer can understand .
The compiler also checks C Whether the language program is effective . If C The compiler found an error , No executable file will be generated and an error will be reported . Understanding errors or warnings reported by a particular compiler is another skill for programmers .
The first 5 Step : Run the program
Traditionally , An executable is a program that can run . stay ( Normal mode and Linux Terminal mode ) To run the program in, enter the file name of the executable file , Other environments may have to run commands ( Such as , stay VAX Medium VMS[2]) Or some other mechanism . for example , stay Windows and Macintosh Provides an integrated development environment (IDE) in , Users can go to IDE To edit and execute by selecting an option in the menu or pressing a special key C Program . The final program can be run directly in the operating system by clicking or double clicking the file name or icon .
The first 6 Step : Testing and debugging procedures
It's a good sign that the program works , But sometimes there may be running errors . Next , You should check that the program is running in the way you designed it . You will find some mistakes in your program , Computer jargon is called bug. The process of finding and fixing program errors is called debugging . Mistakes are inevitable in the process of learning , So is learning programming . therefore , When you apply what you've learned to programming , You'd better be prepared for your mistakes .
The first 7 Step : Maintain and modify code
After creating the program , You find something wrong with the program , Or want to extend the purpose of the program , At this time, we need to modify the program . for example , User input to Zz There was an error in the program when the name at the beginning 、 You come up with a better solution 、 Want to add a better new feature , Or modify the program to run in different computer systems , wait . If the program is written with clear notes and reasonable design scheme , These things are very simple .
Many beginners often ignore the second 1 And the first step 2 Step ( Define program goals and design programs ), Go straight to 3 Step ( Write code ). At the beginning of study , The program is very simple , You can conceive the whole process in your mind . Even if it's wrong , And it's easy to find . however , As the program becomes larger and larger 、 More and more complex , You can't use your head without your hands , And the hidden errors in the program are becoming more and more difficult to find . Final , Those who skip the first two steps tend to waste more time , Because the programs they write are ugly 、 Lack of organization 、 It's hard to understand . The larger the program, the more complex it is , The more work it takes to define and design the program in advance .
Sharpening a knife never misses a woodcutter , We should develop a good habit of planning before writing code , Use paper and notes to record the goals and design framework of the program . In this way, it will be easier to write code 、 Clarity of organization .
The simplest C Code
int main(void){
return 0;
}
Determine floating point variables x Whether the value of is zero
if(|x-0.000001|<=0.000001)
printf(" zero ");
else
printf(" It's not zero ")
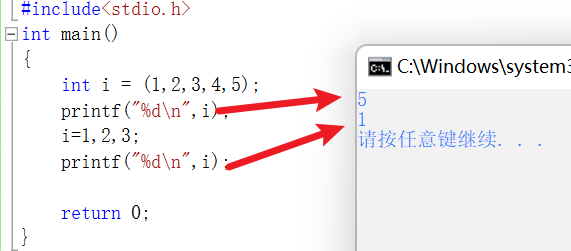
Comma expression
The first output : Because the comma expression , Only the last value of the comma will be assigned to i
the second :i The assignment is 1, Then execute the constant 2 Arithmetic , The calculation result is discarded . Final ,i The result is 1 instead of 2.
Seeking position
Percentile :n/00;
ten :n/10%100 or (n-a*100)/10
bits :n%10
Control line number :if(++n%5==0)// Five in a row
printf("\n");
Loop statement
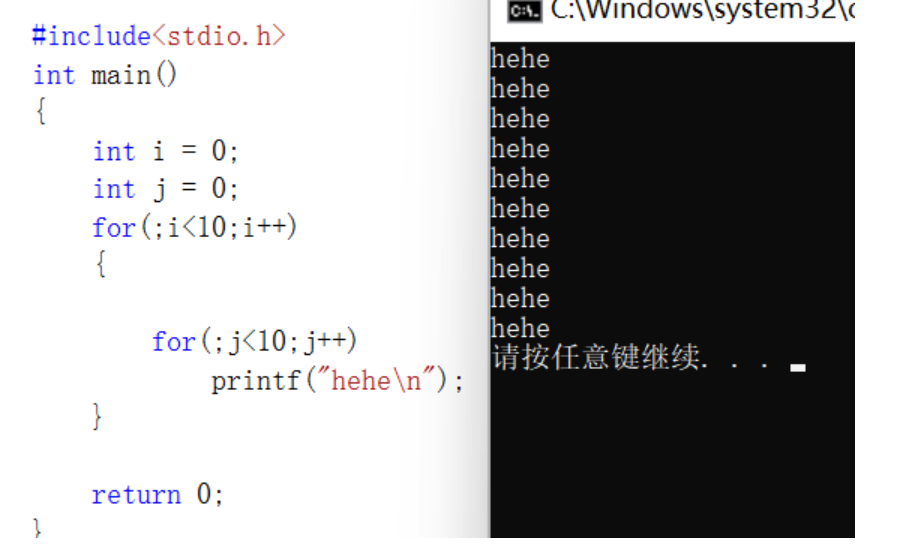
Look at the code below , How many sentences do you think you will print ”hehe“?
- for variant 1
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for(;i<10;i++)
{
for(;j<10;j++)
printf("hehe\n");
}
return 0;
}
The answer is to output only 10 sentence ;
//j++ =0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10;j=10;
// Execute the outer layer for when ,i be equal to 1 了 , Enter internal circulation ,j Not reinitialized , Lead to j The value of the or 10;i++ be equal to 2 when ,j Still 10 Start .… Exit directly if the inner loop is not satisfied , Print 10 Time hehe
for variant 2
Go straight to the code
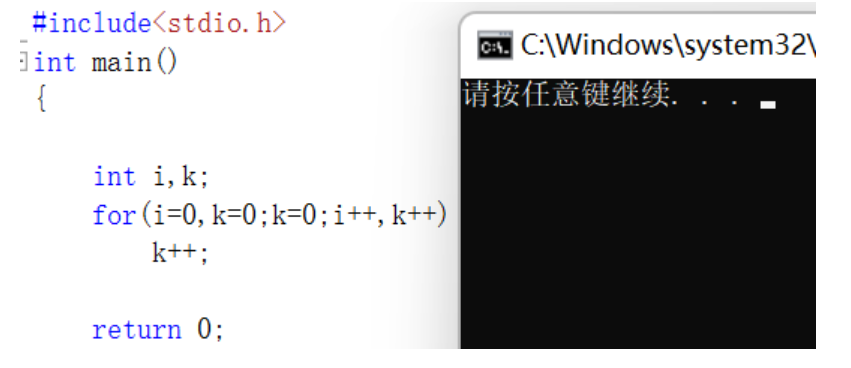
for Yes 0 Time , because k Assigned a value to 0, For false , So don't execute
Branch statement
int day = 0;
int n = 1;
scanf("%d",&day);
switch(day)
{
case 1+0://ok
printf(" Monday ");
case 1.0://error , Can only be integer constants
case n://error
break;// At the end of the case Add a statement break, Add... For later case Branch and easy to maintain
}
if Code specification
int num = 4;
if(5 == num)// When comparing constants and variables , The constant is placed to the left of the dependent variable
//if(5 = num);// Compile failed , Intuitive error
printf("hehe");
function
The actual parameter ( Actual parameters )
The parameters that are actually passed to the function , It's called the actual parameter , The argument can be : Constant , Variable , expression , Functions, etc . Whatever the type of argument is , When making a letter call , They all have to have certain values , To pass these values to the formal parameters .
Formal parameters ( Shape parameter )
Formal parameters refer to the variables in brackets after the function name , Because formal parameters are only instantiated when the function is called ( Allocate memory units ), So it's called formal parameter , Formal parameters are automatically destroyed when the function call is completed , So formal parameters are only valid in functions
Time function
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
int main ()
{
time_t rawtime;
struct tm * timeinfo;
time ( &rawtime );
timeinfo = localtime ( &rawtime );
printf ( " The current local time is : %s", asctime (timeinfo) );
return 0;
}
Function call
#include<stdio.h>
void Swap2(int* pa,int* pb)
{
int tmp = 0;
tmp = *pa;
*pa = *pb;
*pb = tmp;
}
//void Swap1(int x,int y)
//{
//
// int tmp = 0;
// tmp = x;
// x = y;
// y = x;
//}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
printf(" Exchange before :a = %d b = %d\n",a,b);
//Swap1(a, b);// Value transfer call
Swap2(&a, &b);// Address call
printf(" After exchanging :a = %d,b = %d\n",a,b);
return 0;
}
Value transfer call :
Function parameters and arguments occupy different memory blocks , Modification of a parameter does not affect the argument .
Address call
- Address call is a way to call a function by passing the memory address of the created variable outside the function to the function parameter .
- This parameter transfer method can establish a real relationship between the function and the variables outside the function , In other words, the variables outside the function can be directly manipulated inside the function .
Addressing calls can save memory , Because if the value is transferred , We need to copy , The system overhead of parameter stack pressing is relatively large , Performance degradation
Nested function
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%d",printf("%d",printf("%d",printf("%d",4))));// Print 4111
// Because the last one printf Print 4, second to last printf Print call printf The number of outputs is 1( Including Spaces ), successively ... See in detail printf Function documentation
printf("%d",printf("%d",printf("%d",43))//4321
return 0;
}
Function recursion ( Hand it back )
Two necessary conditions for recursion
- There are restrictions , When this constraint is met , Recursion doesn't continue
- Getting closer to this limit after each recursive call
Misuse recursive
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
main();//err
return 0;
}
Use recursion correctly
#include<stdio.h>
void print(int n)// In turn, print 1 2 3 4
{
if(n>9)
print(n/10);
printf("%d ",n%10);
}
int main()
{
int num = 0;
scanf("%d",&num);//1234
print(num);
}
Callback function
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
//void qsort(void *base, //base The address of the first object in the data to be sorted is stored in
// size_t num, // Number of sorted data elements
// size_t size,// Sort the size of an element in the data , Unit is byte
// int (*cmp)(const void*,const void*)// It is used to compare... In the data to be sorted 2 An element of ( One ) function
// );
int cmp_int(const void* e1,const void* e2)
{
return *(int *)e1-*(int *)e2;// Because the parameter type is void, We use it (*int) Cast
/* Return value significance <0 The element pointed to is before the element pointed to p1p2 0 The element pointed to is equivalent to Pointing elements p1p2 >0 The element pointed to is located in After the element pointed to p1p2 */
}
void print(int arr[],int sz)
{
int i= 0;
for(i=0;i<sz;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void test1()
{
// Sorting of shaping data
int arr[]={
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0};
int sz=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
// Sort
qsort(arr,sz,sizeof(arr[0]),cmp_int);
// Print
print(arr,sz);
}
struct Stu
{
char name[20];
int age;
};
int sort_by_age(const void* e1,const void* e2)
{
return ((struct Stu*)e1)->age - ((struct Stu*)e2)->age;// Convert structure type pointer ,e1 Point to age member
}
void test2()
{
// Sort structure data
struct Stu s[3]={
{
"zhangsang",30},{
"lisi",34},{
"wangwu",20}};
int sz=sizeof(s)/sizeof(s[0]);
// Sort by age
qsort(s,sz,sizeof(s[0]),sort_by_age);
}
int sort_by_name(const void* e1,const void* e2)
{
return strcmp(((struct Stu*)e1)->name ,((struct Stu*)e2)->name);
}
void test3()
{
// Sort structure data
struct Stu s[3]={
{
"zhangsang",30},{
"lisi",34},{
"wangwu",20}};
int sz=sizeof(s)/sizeof(s[0]);
// Sort by name
qsort(s,sz,sizeof(s[0]),sort_by_name);
}
int main()
{
//test1();
//test2();
test3();
return 0;
}
Array
- The unit of length of an array is a constant expression representing
- Arrays are stored continuously in memory ,
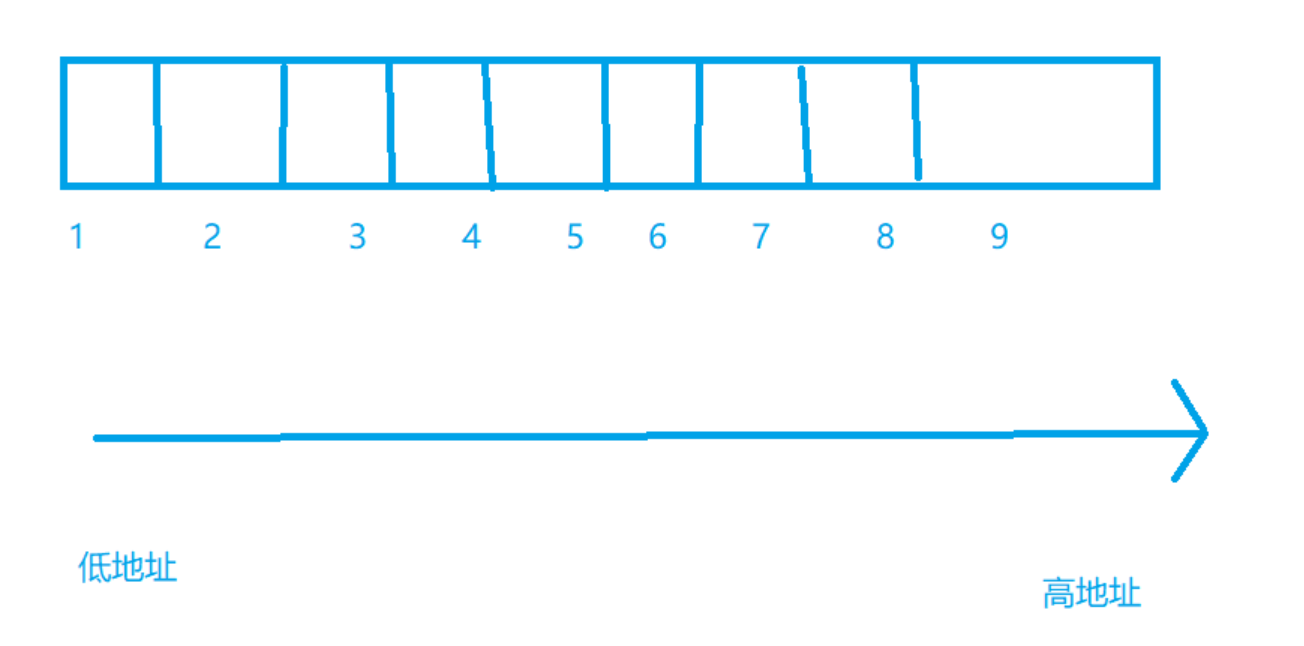
int n =10;
int arr[n]={
1,2,3,4,4,};//error
Subscript
If the subscript is calculated from those known correct values , Then there is no need to check its value . If a value used as a subscript is generated from the data entered by the user according to some method , Then you must check it before using it , Make sure they are within the valid range .
The pointer
The pointer , Indirect access and variables
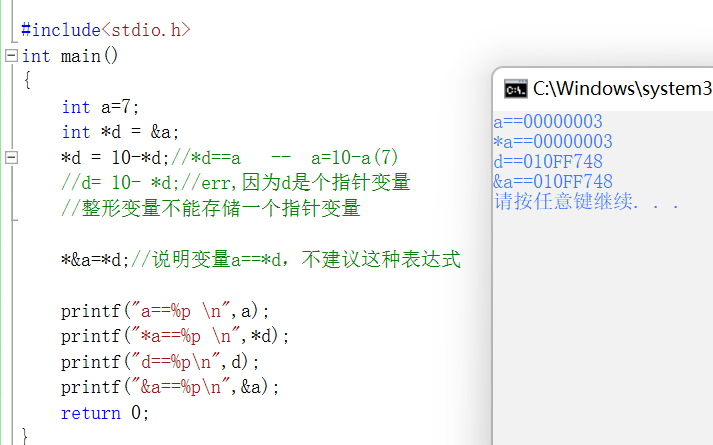
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a=7;
int *d = &a;
*d = 10-*d;//*d==a -- a=10-a(7)
//d= 10- *d;//err, because d It's a pointer variable
// An integer variable cannot store a pointer variable
*&a=*d;// Explanatory variable a==*d, This expression is not recommended
printf("a==%p \n",a);
printf("*a==%p \n",*d);
printf("d==%p\n",d);
printf("&a==%p\n",&a);
return 0;
}
A function pointer
void test(int **p2)
{
**p2=20;
}
int test_p(int x,int y)
{
return x+y;
}
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a =10;
int * pa=&a;//pa Is the first level pointer
int **ppa=&pa;//ppa It's a secondary pointer
// The secondary pointer transmits parameters
test(ppa);
test(&pa);// Pass the address of the first level pointer
int* arr[10]={
0};
test(arr);
printf("%d ",a);
//pf Function pointer variable
int (*pf)(int ,int )=&test_p;
return 0;
}
int Add(int x,int y)
{
return x+y;
}
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
//int (*pf)(int,int )=&Add;
int (*pf)(int,int )=Add;//Add == pf
//int ret=(Add)(3,5);//3
//int ret=(*pf)(3,5)//1 ;* It's furnishings , Sure int ret=(*****pf)(3,5) The results are still correct
//int ret=*pf(3,5)//err; priority pf I'll start with (3,5) combination , whatever * Return value to function 8 Dereference is bound to be wrong
int ret = pf(3,5);//2
printf("%d ",ret);//
return 0;
}
Function pointer array
int add(int x,int y)
{
return x+y;
}
int sub(int x,int y)
{
return x-y;
}
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int (*pf1)(int ,int)=add;
int (*pf2)(int ,int)=sub;
int (*pfarr[2])(int ,int )={
add,sub};//pfarr It's an array of function pointers ,{} Inside can be pf1,pf2,* Notice the curly braces
//add Functions and sub The formal parameters of the function are the same , Memory storage is the same , The premise of array is that the memory type is the same ;
// So it can be stored in the function pointer with the array , So it's called function pointer array .
return 0;
}
Use of function pointer array
#include<stdio.h>
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Mul(int x, int y)
{
return x * y;
}
int Div(int x, int y)
{
return x / y;
}
void menu()
{
printf("**************************\n");
printf("**** 1. add 2. sub ****\n");
printf("**** 3. mul 4. div ****\n");
printf("**** 0. exit ****\n");
printf("**************************\n");
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
// Calculator - Calculates the addition of an integer variable 、 reduce 、 ride 、 except
//a&b a^b a|b a>>b a<<b a>b
do {
menu();
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int ret = 0;
printf(" Please select :>");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
printf(" Please enter 2 Operands >:");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
ret = Add(x, y);
printf("ret = %d\n", ret);
break;
case 2:
printf(" Please enter 2 Operands >:");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
ret = Sub(x, y);
printf("ret = %d\n", ret);
break;
case 3:
printf(" Please enter 2 Operands >:");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
ret = Mul(x, y);
printf("ret = %d\n", ret);
break;
case 4:
printf(" Please enter 2 Operands >:");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
ret = Div(x, y);
printf("ret = %d\n", ret);
break;
case 0:
printf(" Exit procedure \n");
break;
default:
printf(" Wrong choice , To choose !\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
Optimized code :
#include<stdio.h>
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
int Mul(int x, int y)
{
return x * y;
}
int Div(int x, int y)
{
return x / y;
}
void menu()
{
printf("**************************\n");
printf("**** 1. add 2. sub ****\n");
printf("**** 3. mul 4. div ****\n");
printf("**** 0. exit ****\n");
printf("**************************\n");
}
int main()
{
int input = 0;
// Calculator - Calculates the addition of an integer variable 、 reduce 、 ride 、 except
//a&b a^b a|b a>>b a<<b a>b
do {
menu();
//pfArr It's an array of function pointers
// Transfer table - 《C And a pointer 》
int (*pfArr[5])(int, int) = {
NULL, Add, Sub, Mul, Div };
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int ret = 0;
printf(" Please select :>");
scanf("%d", &input);//2
if (input >= 1 && input <= 4)
{
printf(" Please enter 2 Operands >:");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
ret = (pfArr[input])(x, y);
printf("ret = %d\n", ret);
}
else if(input == 0)
{
printf(" Exit procedure \n");
break;
}
else
{
printf(" Wrong choice \n");
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
Callback function _qsort Use of functions
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
//void qsort(void *base, //base The address of the first object in the data to be sorted is stored in
// size_t num, // Number of sorted data elements
// size_t size,// Sort the size of an element in the data , Unit is byte
// int (*cmp)(const void*,const void*)// It is used to compare... In the data to be sorted 2 An element of ( One ) function
// );
int cmp_int(const void* e1,const void* e2)
{
return *(int *)e1-*(int *)e2;// Because the parameter type is void, We use it (*int) Cast
/* Return value significance <0 The element pointed to is before the element pointed to p1p2 0 The element pointed to is equivalent to Pointing elements p1p2 >0 The element pointed to is located in After the element pointed to p1p2 */
}
void print(int arr[],int sz)
{
int i= 0;
for(i=0;i<sz;i++)
{
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void test1()
{
// Sorting of shaping data
int arr[]={
9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0};
int sz=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
// Sort
qsort(arr,sz,sizeof(arr[0]),cmp_int);
// Print
print(arr,sz);
}
struct Stu
{
char name[20];
int age;
};
int sort_by_age(const void* e1,const void* e2)
{
return ((struct Stu*)e1)->age - ((struct Stu*)e2)->age;// Convert structure type pointer ,e1 Point to age member
}
void test2()
{
// Sort structure data
struct Stu s[3]={
{
"zhangsang",30},{
"lisi",34},{
"wangwu",20}};
int sz=sizeof(s)/sizeof(s[0]);
// Sort by age
qsort(s,sz,sizeof(s[0]),sort_by_age);
}
int sort_by_name(const void* e1,const void* e2)
{
return strcmp(((struct Stu*)e1)->name ,((struct Stu*)e2)->name);
}
void test3()
{
// Sort structure data
struct Stu s[3]={
{
"zhangsang",30},{
"lisi",34},{
"wangwu",20}};
int sz=sizeof(s)/sizeof(s[0]);
// Sort by name
qsort(s,sz,sizeof(s[0]),sort_by_name);
}
int main()
{
//test1();
//test2();
test3();
return 0;
}
imitation qsort General algorithm of function
void Swap(char*buf1,char*buf2,int width)
{
int i = 0;
for(i=0;i<width;i++)
{
char tmp = *buf1;
*buf1=*buf2;
*buf2=tmp;
buf1++;
buf2++;
}
}
// imitation qsort Implement a general algorithm for bubble sorting
void bubbble_sort(void *base,
int sz,
int width,
int (*cmp)(const void*e1,const void*e2)
)
{
int i =0;
for(i=0;i<sz-1;i++){
int j = 0;
for(j=0;j<sz-1-i;j++)
{
if(cmp((char*)base+j*width,(char *)base+(j+1)*width)>0)//( Merger and acquisition (m&a) ) fit int Type and character type , If it is to use int Words , Then I sort that byte with characters + A few is to skip 4 Bytes , A single
{
Swap((char*)base+j*width,(char*)base+(j+1)*width,width);
}
}
}
}
边栏推荐
- The use of video in the wiper component causes full screen dislocation
- 糊涂工具类(hutool)post请求设置body参数为json数据
- Google released a security update to fix 0 days that have been used in chrome
- 修改px4飞控的系统时间
- Drag to change order
- Baidu flying general BMN timing action positioning framework | data preparation and training guide (Part 2)
- POJ 3177 redundant paths POJ 3352 road construction (dual connection)
- 永久的摇篮
- The cradle of eternity
- Add PDF Title floating window
猜你喜欢
JVM memory model

454 Baidu Mianjing 1
Can't you understand the code of linked list in C language? An article allows you to grasp the secondary pointer and deeply understand the various forms of parameter passing in the function parameter
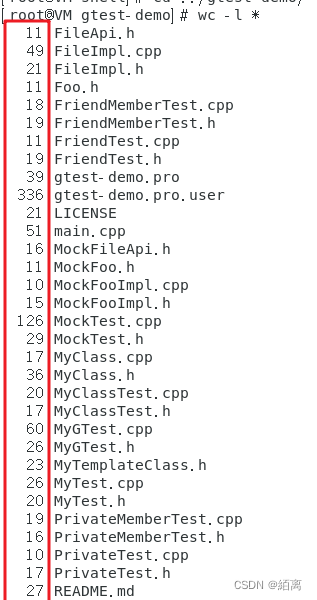
Shell script quickly counts the number of lines of project code
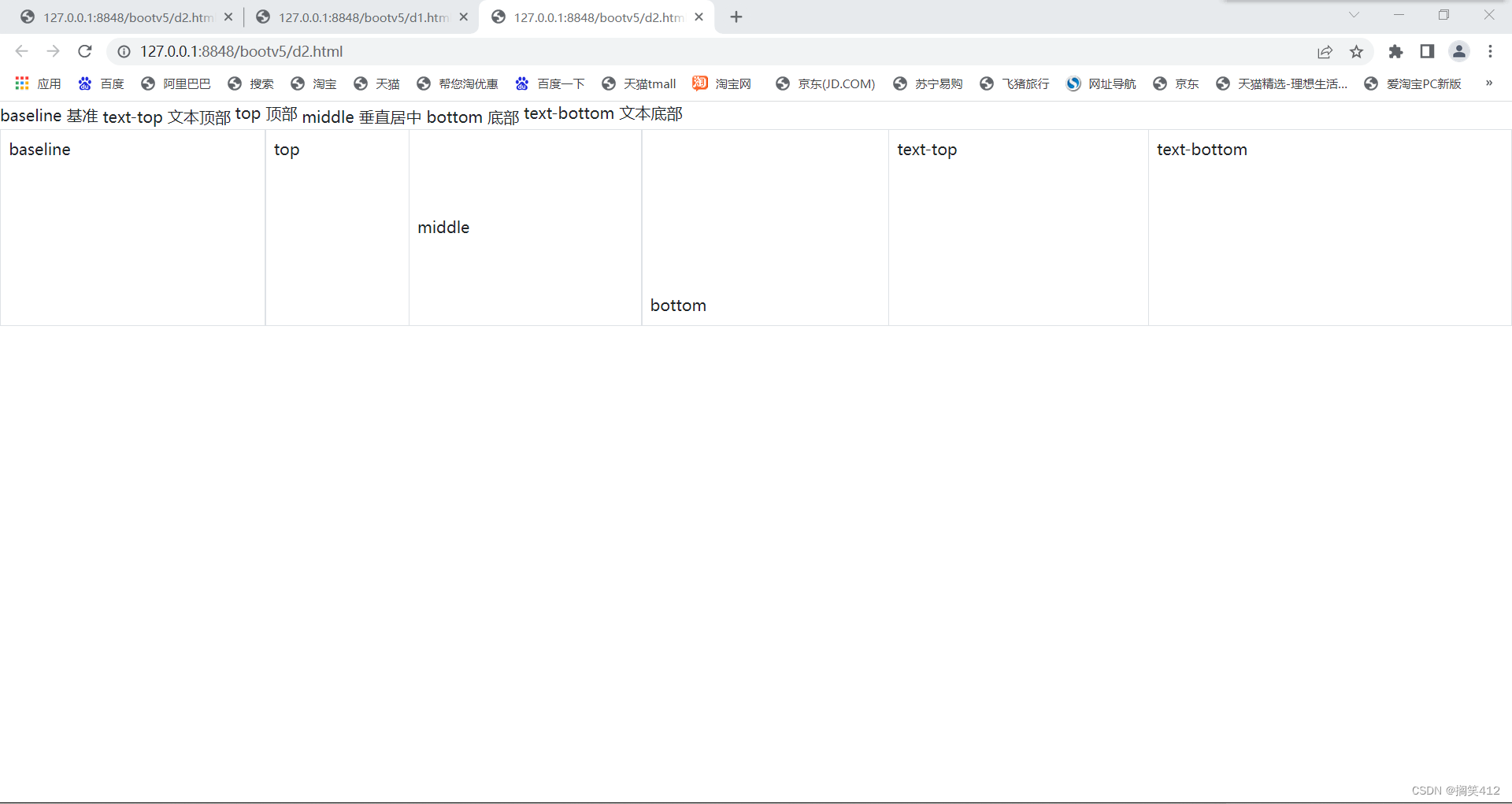
2022/0524/bookstrap
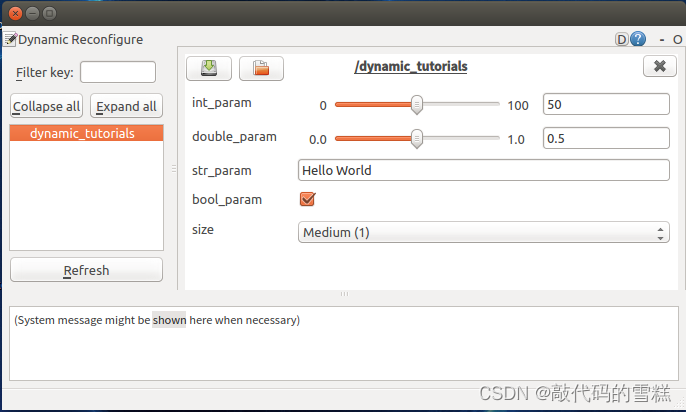
ROS学习(26)动态参数配置
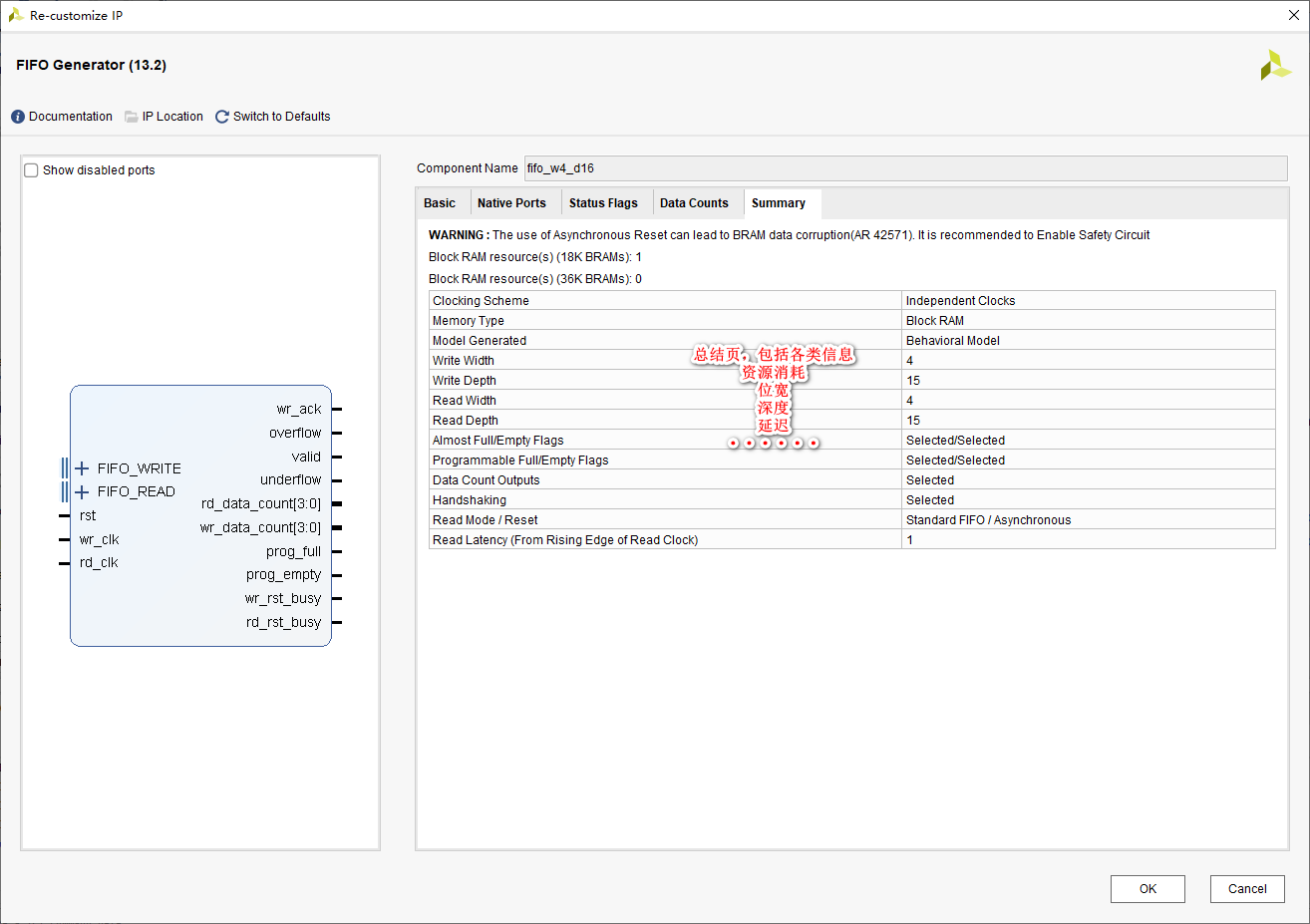
Start from the bottom structure to learn the customization and testing of fpga---- FIFO IP
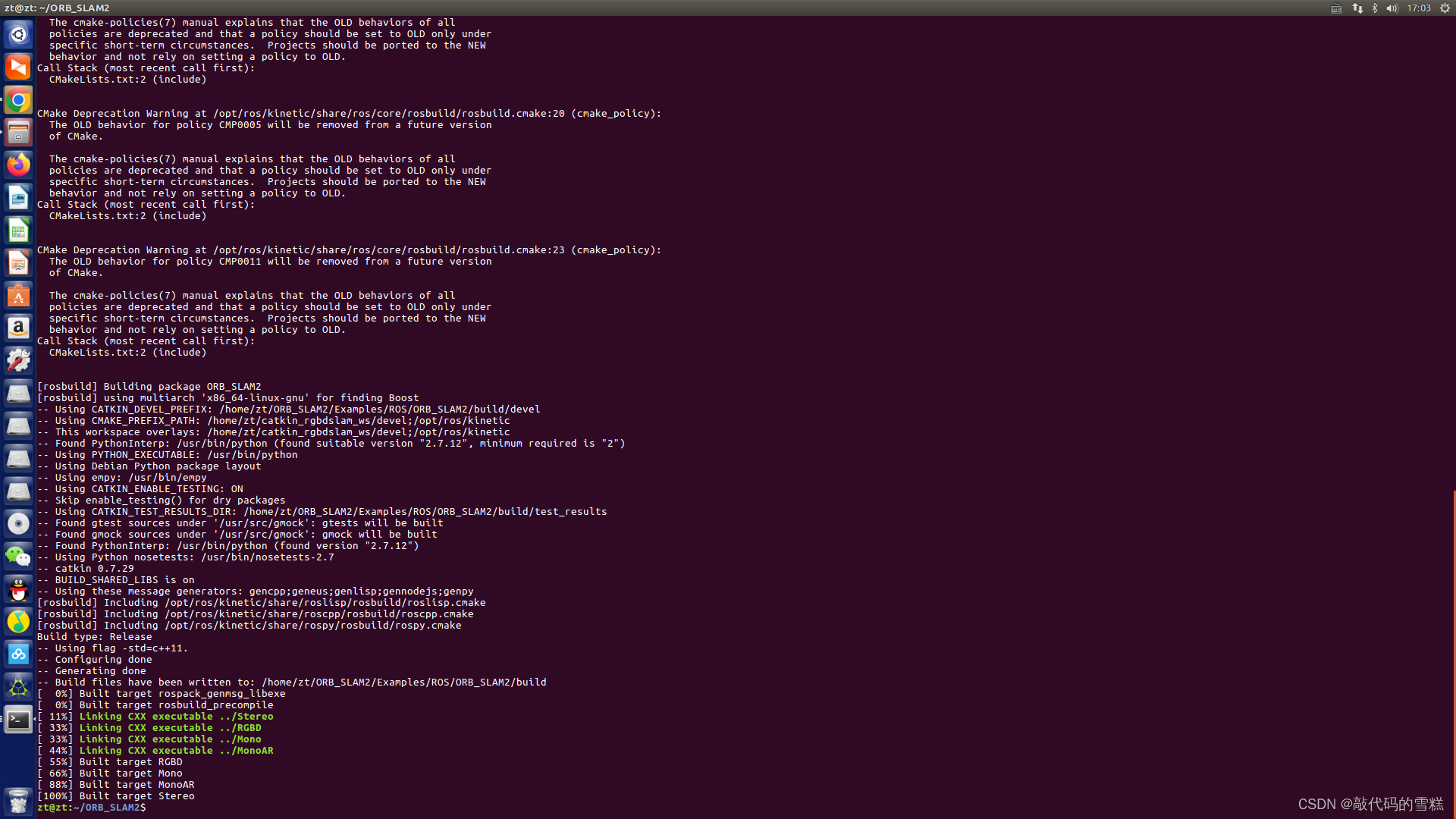
ROS学习(21)机器人SLAM功能包——orbslam的安装与测试
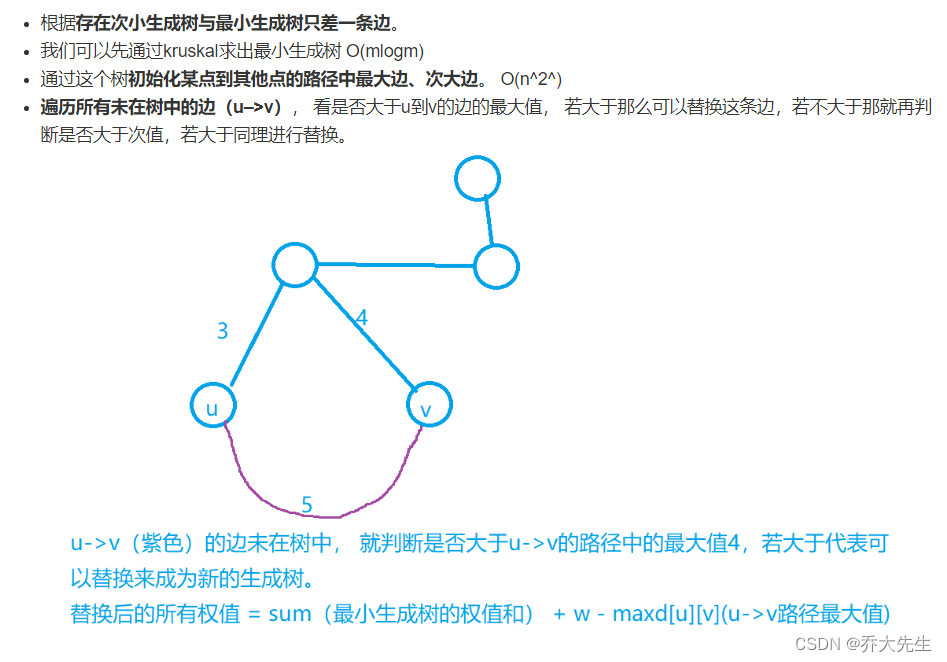
AcWing 1148. Secret milk transportation problem solution (minimum spanning tree)
Gin 入门实战
随机推荐
Gin introduction practice
2022/0524/bookstrap
AcWing 904. 虫洞 题解(spfa求负环)
JS ES5也可以創建常量?
LeetCode. Sword finger offer 62 The last remaining number in the circle
AcWing 345. Cattle station solution (nature and multiplication of Floyd)
Set up [redis in centos7.x]
Basic introduction and use of dvajs
Related programming problems of string
What does security capability mean? What are the protection capabilities of different levels of ISO?
AcWing 1140. Shortest network (minimum spanning tree)
mysqlbackup 还原特定的表
Curl command
How can I code for 8 hours without getting tired.
Appium基础 — Appium Inspector定位工具(一)
Baidu flying general BMN timing action positioning framework | data preparation and training guide (Part 1)
蓝桥杯2022年第十三届省赛真题-积木画
刨析《C语言》【进阶】付费知识【完结】
MySQL's most basic select statement
grep查找进程时,忽略grep进程本身