当前位置:网站首页>[JS] - [sort related] - Notes
[JS] - [sort related] - Notes
2022-07-04 23:17:00 【Interesting learning】
【js】-【 Sort - relevant 】- note
API relevant
stay javascript in , sort Method is used to sort array elements according to certain conditions . If the sort() Method without passing parameters , Then press Alphabetical order Sort the elements in the array ; If you provide a function parameter , Then sort the elements in the array according to the order provided by this function .
sort It uses Insertion sort and Quick sort Combined sorting algorithm .
Array length not more than 10 when , Use Insertion sort .
The length exceeds 10 Use Quick sort .
When the array is short Insertion sort More efficient
function swap(arr, i, j) {
[arr[i], arr[j]] = [arr[j], arr[i]]
}
Find... In the unsorted array The first k individual Largest element . Please note that , What you need to look for is the number after array sorting k The biggest element , Not the first. k A different element .
Input : [3,2,1,5,6,4] and k = 2
Output : 5
Input : [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] and k = 4
Output : 4
Descending
const findKthLargest = function(nums, k) {
// Reverse the array order
const sorted = nums.sort((a,b)=> {
return b-a
})
# Take the first place k Big elements
return sorted[k-1]
};;
1 Bubble sort ( Stable ,O(n2))
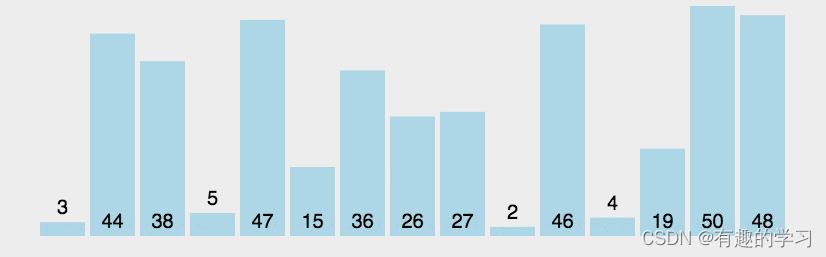
- Just start with the first element , Repeatedly compare two adjacent items , If the first item is larger than the second , Then swap the positions of the two ; On the contrary, do not move .
- Each round of operation , Will put the largest element in this round at the end of the array . If the length of the array is n, So when we finish repeating n When the wheel , The whole array is in order .
Outer layer length Time , Inner layer length-i-1 Time
var sortArray = function (nums) {
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < nums.length - i -1; j++) {
if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {
//swap(nums, j, j + 1);
[nums[j],nums[j+1]]=[nums[j+1],nums[j]];
}
}
}
return nums;
};
improvement , Add a flag , Flag bits can help us locate whether the array is completely ordered at the first bubble , And then save unnecessary judgment logic , Optimize the time complexity in the best case as O(n)
var sortArray = function (nums) {
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
#1 The difference is here , We added a flag bit
let flag = false;
for (let j = 0; j < nums.length - i -1; j++) {
if (nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) {
#2 Sign a
flag=true;
[nums[j],nums[j+1]]=[nums[j+1],nums[j]];
}
}
if(flag==false) return;
}
return nums;#3 If an exchange doesn't happen , The array is ordered , Let it go
};
2 Selection sort ( unstable ,O(n2))
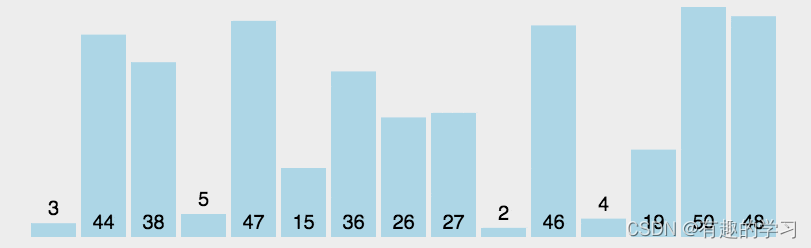
Select sorted Keywords are “ minimum value ”: Loop through groups , Find the minimum value in the current range every time , Put it at the head of the current range ; Then narrow the sorting range , Continue to repeat the above operation , Until the array is completely ordered .
- First traversal 1-n The smallest in the range , Exchange with the first position
- Again from 2-n The smallest in the range , And the second exchange
- It's all over , It's in order
var sortArray = function (nums) {
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
let minIndex = i;
// Sorted range [0, i) , Unordered range [i+1 , len)
# Traverse i+1 The next element finds the index of the smallest element
for (let j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[j] < nums[min]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
if(minIndex!=i)
[nums[i],nums[minIndex]]=[mums[minIndex],mums[i]];
}
return nums;
};
3 Insertion sort ( Stable ,O(n2))
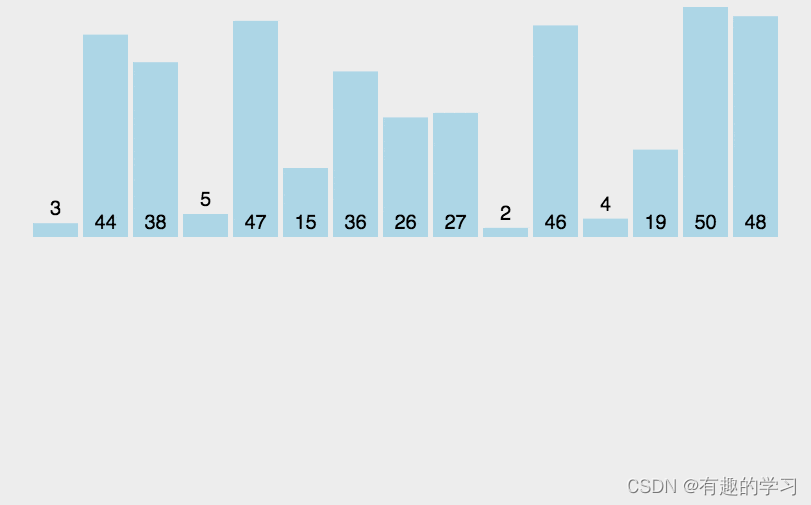
The core idea of insertion sort is “ Find the correct position of the element in the sequence before it ”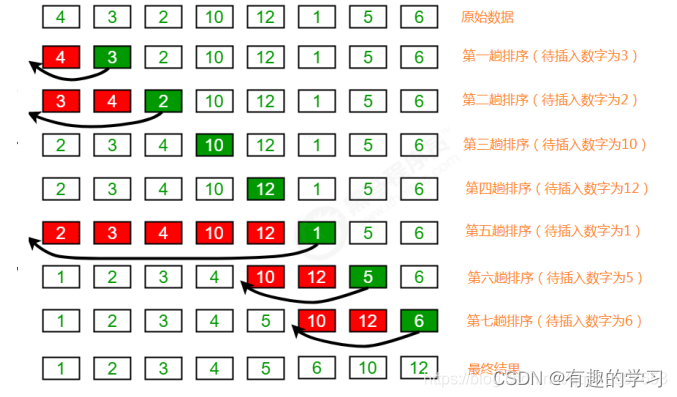
var sortArray = function (nums) {
// From the subscript for 1 Element to start selecting the appropriate position to insert , Because the index is zero 0 There's only one element , The default is ordered
// Sorted range [0, i) , Unordered range [i , len)
// take nums[i] Insert into interval [0, i) Make it an ordered array
for (let i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
// Traverse from right to left
for (let j = i; j > 0 && nums[j] < nums[j - 1]; j--) {
// as long as nums[j] Than the previous element nums[j-1] Small , Just exchange these two elements
[nums[j],nums[j-1]]=[nums[j-1],nums[j]];
}
}
return nums;
};
4 Merge sort ( Stable ,O(nlog(n)))
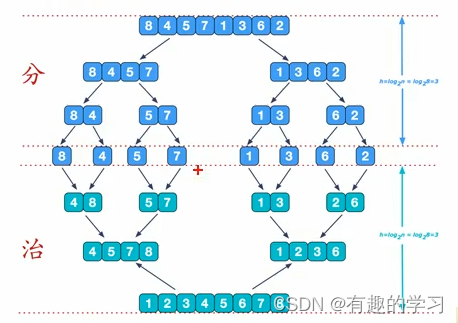
function mergeSort(arr) {
// Dealing with border situations
if(arr.length <= 1) return arr
# Calculate the split point
const mid = Math.floor(arr.length/ 2)
#1 Recursive segmentation left 、 Right subarray , Then merge into an ordered array
const leftArr = mergeSort(arr.slice(0, mid))
const rightArr = mergeSort(arr.slice(mid,arr.length))
#2 Merge the left and right ordered arrays
arr = mergeArr(leftArr, rightArr)
return arr
}
# This part is merging ordered arrays
function mergeArr(arr1, arr2) {
# Initialize two pointers , Point to respectively arr1 and arr2
let i = 0, j = 0
const res = []
# Merge two subarrays , Which one is small , Which one to add first
while(i < arr1.length && j < arr2.length ) {
if(arr1[i] < arr2[j]) {
res.push(arr1[i])
i++
} else {
res.push(arr2[j])
j++
}
}
# Which one is left , Directly splice the rest
if(i<len1) {
return res.concat(arr1.slice(i))
} else {
return res.concat(arr2.slice(j))
}
}
5 Quick sort ( unstable ,O(nlog(n)))
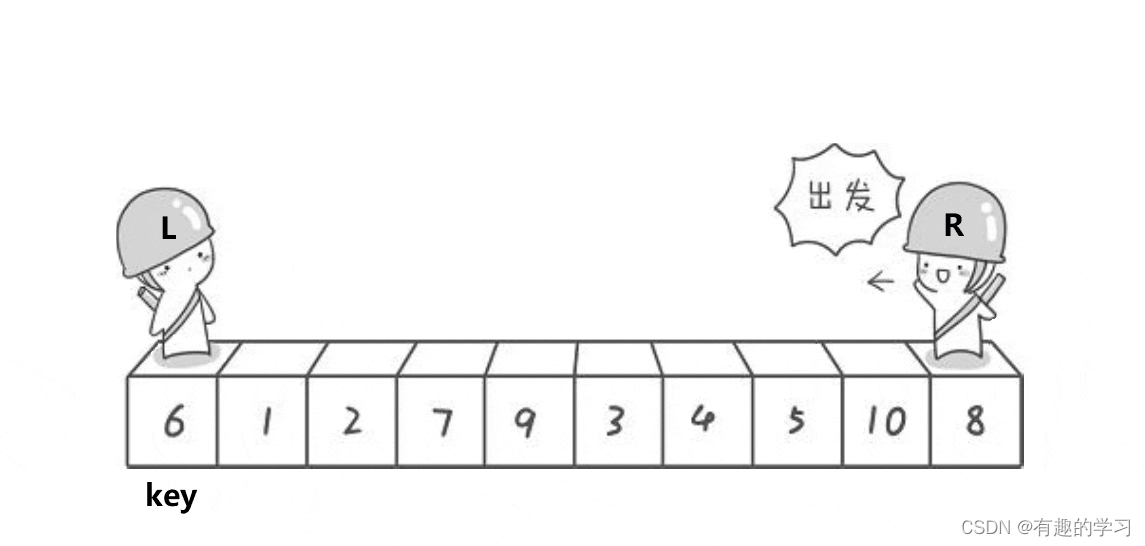
Calling code
var sortArray = function (nums) {
const N = nums.length;
quickSort(nums, 0, N - 1);
return nums;
};
Quick line up
function quickSort(nums, left, right) {
if (right <= left) {
return;
}
let pIndex = partition(nums, left, right);
quickSort(nums, left, pIndex - 1);
quickSort(nums, pIndex + 1, right);
}
Take the reference value as the axis , The process of dividing left and right subarrays
function partition(nums, left, right) {
let pivot = nums[left];
// Define a pointer for each of the two arrays
let i = left + 1;
let j = right;
while (true) {
while (i <= right && nums[i] <= pivot) {
i++;
}
while (j > left && nums[j] > pivot) {
j--;
}
if (i >= j) {
break;
}
swap(nums, i, j);
i++;
j--;
}
swap(nums, left, j);
return j;
}
6 Heap sort ( Stable ,O(nlog(n)))
/** * Heap sort * @param {*} nums * @returns */
function sortArray(nums) {
const N = nums.length;
// Building the heap Find the first non leaf node , Traversal up
for (let i = Math.floor(N / 2 - 1); i >= 0; i--) {
// Yes i Location node Adjust the heap
heapify(nums, i, N);
}
// Sorting process Each cycle finds the current maximum ( The root node ), Array length minus one
for (let i = N - 1; i > 0; i--) {
// The root node exchanges positions with the last node ( Move the largest element at this time to the end of the array )
swap(nums, 0, i);
// Yes At this time, the root node Adjust the heap The last element does not need to be adjusted
heapify(nums, 0, i);
}
return nums;
}
/** * The node i Conduct Adjust the heap * Satisfy :i The sub heap below the node is a large top heap * Adjustment range [i, length) * @param {*} nums * @param {*} i * @param {*} length */
function heapify(nums, i, length) {
// take i The value of the node is saved , This process is to temp Find the right place
let temp = nums[i]
// j Point to i Left child node of
let j = 2 * i + 1;
// Loop traversal [i, length)
while (j < length) {
if (j + 1 < length && nums[j] < nums[j + 1]) {
// The parent node has a right child also The left child is smaller than the right child take j Point to the right child
j++;
}
// here j Point to i The larger of the child nodes
if (temp < nums[j]) {
// If The parent node is less than j node
// In exchange for i,j The elements of
swap(nums, i, j);
// take i and j All move down one bit
i = j;
j = 2 * i + 1;
} else {
// Parent node Greater than The largest element in the child node , Just exit the loop
break;
}
}
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
MariaDB的Galera集群-双主双活安装设置

PS style JS webpage graffiti board plug-in

Why does infographic help your SEO
Intelligence test to see idioms guess ancient poems wechat applet source code
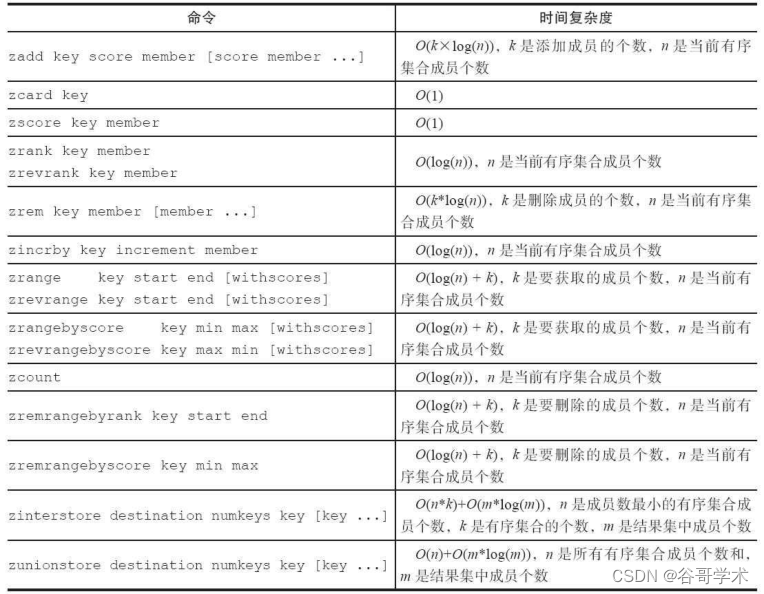
Redis introduction complete tutorial: detailed explanation of ordered collection
位运算符讲解
【kotlin】第三天
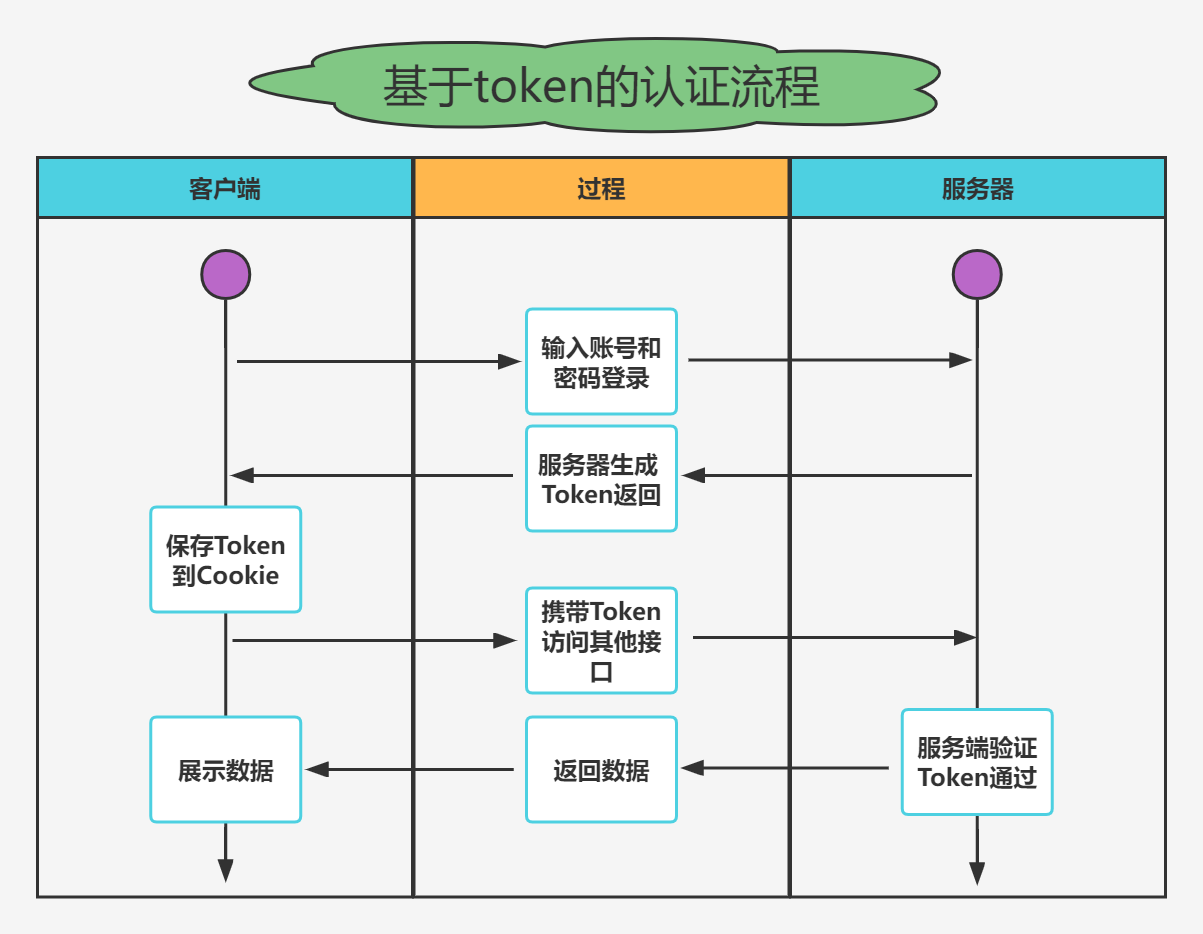
Actual combat simulation │ JWT login authentication
Redis getting started complete tutorial: publish and subscribe
The difference between debug and release
随机推荐
qt绘制网络拓补图(连接数据库,递归函数,无限绘制,可拖动节点)
C语言快速解决反转链表
vim编辑器知识总结
VIM editor knowledge summary
Redis getting started complete tutorial: Key Management
Complete tutorial for getting started with redis: bitmaps
heatmap. JS picture hotspot heat map plug-in
企业里Win10 开启BitLocker锁定磁盘,如何备份系统,当系统出现问题又如何恢复,快速恢复又兼顾系统安全(远程设备篇)
Wechat official account solves the cache problem of entering from the customized menu
Galera cluster of MariaDB - dual active and dual active installation settings
【图论】拓扑排序
Redis: redis transactions
Phpcms paid reading function Alipay payment
SHP data making 3dfiles white film
Question brushing guide public
金融市场,资产管理与投资基金
The initial trial is the cross device model upgrade version of Ruijie switch (taking rg-s2952g-e as an example)
Photoshop批量给不同的图片添加不同的编号
蓝天NH55系列笔记本内存读写速度奇慢解决过程记录
实战模拟│JWT 登录认证