当前位置:网站首页>Numpy quick start (I) -- pre knowledge (create array + constant + data type)
Numpy quick start (I) -- pre knowledge (create array + constant + data type)
2022-07-03 10:40:00 【serity】
Catalog
One 、 What is? Numpy?
NumPy yes Python The basic package of scientific computing in . It's a Python library , Provide multidimensional array objects , Derived objects and various... For quick array operations API, Including mathematics 、 Logic 、 Shape operation 、 Sort 、 choice 、 Input and output 、 Basic linear algebra , Basic statistical operation and random simulation, etc .
NumPy At the heart of yes ndarray(n-dimensional array) object , namely n Dimension group , It is associated with Python The differences between lists are as follows :
- NumPy Arrays are created with a fixed size , and Python The list of can dynamically grow or shorten . change ndarray The size of will create a new array and delete the original array .
- NumPy Elements in an array need to have the same data type , and Python The list of can have elements of different data types .
- NumPy Arrays help with advanced mathematics and other types of operations on large amounts of data , Usually these operations are performed more efficiently , Than using Python The list has less code .
- More and more based on Python Science of / Math package use NumPy Array , Although these tools usually support Python As a parameter , But they will still convert the input list into NumPy Array of , And it's usually output as NumPy Array .
Two 、 install Numpy
stay Command line Use the following commands to install :
pip install numpy
about conda user , Available
conda install numpy
After the installation , We can import Numpy 了 , We usually use the following code to import :
import numpy as np
np yes numpy Abbreviation , The purpose is to make the program more concise and convenient , Use at the same time np Will not lose readability , And this abbreviation is also the choice of the vast majority of people .
3、 ... and 、ndarray and matrix Which one to use ?
We already know ,ndarray yes Numpy Medium n Dimensional array object , But beyond that ,Numpy A special matrix type is also provided :matrix, It is ndarray Of Subclass .
ndarray and matrix Can complete the operation of matrix , So which one is better ?
Let's start with the answer : Use ndarray.
The reasons are as follows :
- ndarray yes Numpy The standard vector in / matrix / Tensor type , many Numpy function It's an array , Not the matrix .
- Use ndarray Than using matrix It is more convenient to build a matrix .
- ndarray Can handle high-dimensional arrays , and matrix Only two-dimensional arrays can be processed .
- stay ndarray in , Operator
*Represents multiplying by elements ( It can also be used. multiply()), Operator@Representation matrix multiplication ( It can also be used. dot()); And in the matrix in ,*It represents matrix multiplication , Multiplying by elements requires multiply().
Four 、 establish n Dimension group
You must have been right about Numpy Medium n Dimensional array object ndarray Have a general understanding , So how do we create n And the dimension group ?
There are two common methods :
- Put the existing Python list 、 Tuple to ndarray
- Use Numpy The built-in array creation function ( Such as arange、linspace etc. )
4.1 Put the existing list 、 Tuple to n Dimension group
It's easy , Just put one on the outside np.array() that will do .
For a list of :
A = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(A)
print(type(A))
# [1 2 3]
# <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
For tuples :
A = np.array((1, 2, 3))
print(A)
print(type(A))
# [1 2 3]
# <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
4.2 Use Numpy The built-in array creation function
We will only make a brief introduction here , About the creation of arrays 、 See the next article in this series for details of modifications and so on .
| function | describe |
|---|---|
| np.arange([start], stop, [step]) | Create one in [start, stop) In the interval , In steps of step Array of ;start When omitted, the default is 0,step When omitted, the default is 1 |
| np.linspace(start, stop, num) | Create one in [start, stop] In the interval , The size is num Array of |
for example , To create [ 0 , 10 ] [0, 10] [0,10] All even arrays in , We can use arange function , Just set the step size to 2:
A = np.arange(0, 11, 2)
print(A)
# [ 0 2 4 6 8 10]
You can also use linspace function , But we need to know in advance [ 0 , 10 ] [0, 10] [0,10] How many even numbers in :
A = np.linspace(0, 10, 6)
print(A)
# [ 0. 2. 4. 6. 8. 10.]
look arange and linspace The result is the same , But the reality is different , I won't go into details here , See the next article for details .
4.3 Yes ndarray Index and slice
Of course , We can treat as Python Like the list , Yes Numpy Medium n Dimension groups are indexed and sliced :
A = np.arange(10)
print(A[3])
print(A[1:])
print(A[:-2])
print(A[::-1])
print(A[::2])
# 3
# [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
# [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7]
# [9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0]
# [0 2 4 6 8]
5、 ... and 、Numpy Constant in
| Constant | describe |
|---|---|
| np.inf | representative + ∞ +\infty +∞ |
| np.NINF | representative − ∞ -\infty −∞ |
| np.nan | For non numeric |
| np.e | Represents the natural base |
| np.pi | representative π \pi π |
| np.euler_gamma | Represents Euler constant |
| np.newaxis | representative None |
Be careful : As mentioned above 7 Of the constants , The first six are all floating-point , namely <class 'float'>, Only the last one is Nonetype type :<class 'NoneType'>.
The first six constants must be familiar to everyone , And it is often used in practical programming tasks . For the seventh constant :np.newaxis, We will explain it in detail in the following article .
6、 ... and 、Numpy Data types in
Numpy Support than Python More types of data , This section will cover that common Data type of , And how to modify n Data type of dimension group .
6.1 Boolean type
| name | describe |
|---|---|
| np.bool8(np.bool_) | Boolean data type (True perhaps False) |
6.2 integer
| name | describe |
|---|---|
| np.int8 | byte (-128 to 127) |
| np.int16 | Integers (-32768 to 32767) |
| np.int32 | Integers (-2147483648 to 2147483647) |
| np.int64(np.int_) | Integers (-9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807) |
| np.uint8 | Unsigned integer (0 to 255) |
| np.uint16 | Unsigned integer (0 to 65535) |
| np.uint32 | Unsigned integer (0 to 4294967295) |
| np.uint64 | Unsigned integer (0 to 18446744073709551615) |
6.3 floating-point
| name | describe |
|---|---|
| np.float16 | Semi precision floating point number , Include :1 Sign bits ,5 One digit ,10 One last digit |
| np.float32 | Single-precision floating-point , Include :1 Sign bits ,8 One digit ,23 One last digit |
| np.float64(np.float_) | Double precision floating point , Include :1 Sign bits ,11 One digit ,52 One last digit |
6.4 Plural
| name | describe |
|---|---|
| np.complex64 | The plural , By two 32 Bit floating point ( Real and imaginary parts ) form |
| np.complex128(np.complex_) | The plural , By two 64 Bit floating point ( Real and imaginary parts ) form |
6.5 dtype
6.5.1 View data type
Be careful :Numpy The default data type in is float_, Double precision floating-point number
dtype Can be used to view ndarray The data type of the element in . Let's do some experiments first :
Experiment 1
A = np.array([1, 1])
print(A.dtype)
# int32
Visible for n Dimensional integer array ,Numpy The default data type is int32.
in fact , If the value of an element in the array is greater than 2147483647 when , The data type will be converted to
int64.
Experiment two
A = np.array([1., 1.])
print(A.dtype)
# float64
Visible for n Dimensional floating-point array ,Numpy The default data type is float_.
Experiment three
A = np.array([1j, 1j])
print(A.dtype)
# complex128
Visible for n Dimensional complex array ,Numpy The default data type is complex_.
6.5.2 Set the data type of the array
To set the data type of the array , We can do that :
A = np.array([1, 2, 3], dtype=np.float64)
print(A)
# [1. 2. 3.]
You can find that integer arrays have been converted to floating-point arrays .
Of course, we have simpler methods :
A = np.float64([1, 2, 3])
print(A)
# [1. 2. 3.]
The two methods mentioned above are both in Set the data type while creating the array , We can also use astype() Method Change the data type of the existing array :
A = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(A.dtype)
A = A.astype(np.float64)
print(A.dtype)
# int32
# float64
Most of the time , We all declare data types while creating arrays , In fact, we can use it more succinctly dtype:
| A more concise form | Original form |
|---|---|
| dtype=int | Equivalent to dtype=np.int32 |
| dtype=float | Equivalent to dtype=np.float64 |
| dtype=complex | Equivalent to dtype=np.complex128 |
for example :
A = np.array([1, 1], dtype=int)
print(A.dtype)
# int32
6.5.3 Spillover problem
If the data type is set improperly , May cause data overflow . for example , When creating an array like this :
A = np.array([3333443333, 4444334444], dtype=np.int32)
Will report a mistake : OverflowError, This is because the value of an element in the array is greater than int32 The scope of , We need to use int64 To continue creating .
A = np.array([3333443333, 4444334444], dtype=np.int64)
print(A)
# [3333443333 4444334444]
边栏推荐
- Hou Jie -- STL source code analysis notes
- Leetcode skimming ---1
- Leetcode刷题---10
- 【SQL】一篇带你掌握SQL数据库的查询与修改相关操作
- Ind FXL first week
- Leetcode skimming ---217
- High imitation bosom friend manke comic app
- Leetcode skimming ---44
- [LZY learning notes dive into deep learning] 3.4 3.6 3.7 softmax principle and Implementation
- Linear regression of introduction to deep learning (pytorch)
猜你喜欢
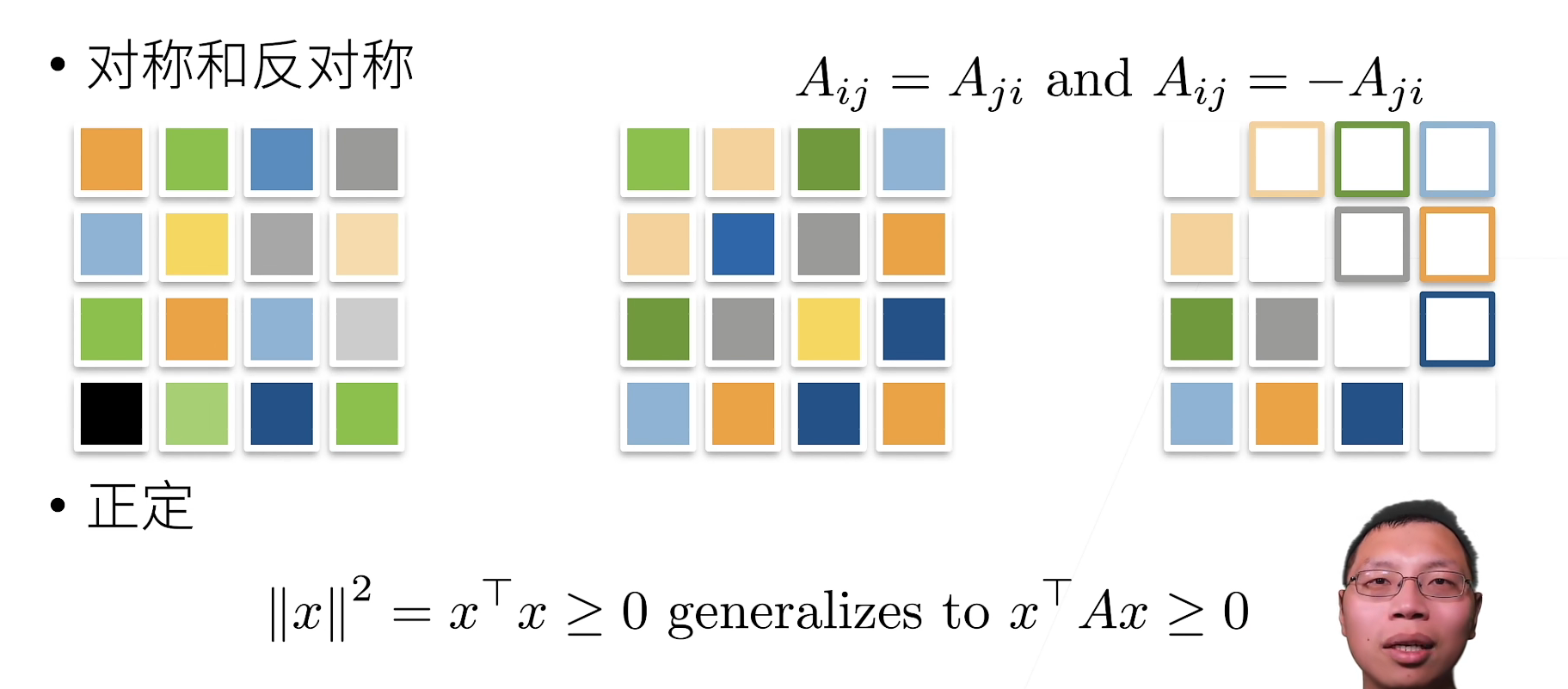
Introduction to deep learning linear algebra (pytorch)

Boston house price forecast (tensorflow2.9 practice)

Raspberry pie 4B deploys lnmp+tor and builds a website on dark web
Leetcode刷题---367

【吐槽&脑洞】关于逛B站时偶然体验的弹幕互动游戏魏蜀吴三国争霸游戏的一些思考

Hands on deep learning pytorch version exercise solution - 2.5 automatic differentiation

A complete mall system

The imitation of jd.com e-commerce project is coming

Raspberry pie 4B installs yolov5 to achieve real-time target detection
![[LZY learning notes -dive into deep learning] math preparation 2.5-2.7](/img/57/579357f1a07dbe179f355c4a80ae27.jpg)
[LZY learning notes -dive into deep learning] math preparation 2.5-2.7
随机推荐
What useful materials have I learned from when installing QT
Leetcode刷题---832
Softmax 回归(PyTorch)
Timo background management system
[untitled]
Install yolov3 (Anaconda)
Leetcode刷题---217
Configure opencv in QT Creator
多层感知机(PyTorch)
mysql5.7安装和配置教程(图文超详细版)
Matrix calculation of Neural Network Introduction (pytoch)
[LZY learning notes dive into deep learning] 3.1-3.3 principle and implementation of linear regression
Judging the connectivity of undirected graphs by the method of similar Union and set search
Leetcode skimming ---852
Common scenarios in which Seata distributed transactions fail and do not take effect (transactions do not rollback)
High imitation wechat
Classification (data consolidation and grouping aggregation)
Leetcode skimming ---283
深度学习入门之线性代数(PyTorch)
Free online markdown to write a good resume