当前位置:网站首页>Shell_ 02_ Text three swordsman
Shell_ 02_ Text three swordsman
2022-07-06 16:50:00 【Coke loving w】
Shell_02_ Text three swordsman
cut
cut command : Operate on data in fields
Command format :cut Options File path
| Options | meaning |
|---|---|
| -d | Specify the delimiter of the data |
| -f | Specify the field display |
| -c N | Appoint N The characters are 1 Display units |
1)-d and -f Options together make sense ( Only the delimiter of the specified data , Data can be segmented )
2)-c The value followed by the option “-” There are different meanings in different places
Such as : Show PATH The fifth path in the variable path 
Such as : Display in different character units test1.txt The contents of the document 
sed
sed command : Replace data in behavioral units 、 Delete 、 newly added 、 Selection and other functions
Command format :sed Options ‘ operation ’ File path
1) Options are optional , But the operation must have ;
2)sed Command more than two operations , Need to add -e Options ;
3) The operation must be enclosed in two single quotation marks , And between multiple operations “;” Separate ;
| Options | meaning |
|---|---|
| -n | Only output is sed Processed lines |
| -e | In the command prompt interface sed operation |
| -f | take sed Write to a file |
| -r | Use extended regular expression syntax ( The default is the basic regular expression syntax ) |
| -i | Directly modify the contents of the document ( The default is to only read the file and output it to the terminal ) |
| operation | meaning |
|---|---|
| s | Replace / Delete string ( Usually used with regular expressions ) |
| y | Replace character |
| i | ( Last line ) Insert |
| a | ( The next line ) Insert |
| c | Replacement row |
| d | Delete row |
| p | Print ( Usually cooperate -n Options together make sense ) |
Replace string
s operation : Replace the string specified in the data flow
1) Format :s/ Original string / New string / identification
2) Signs are divided into (p and w It can be used for other operations ):
| identification | explain |
|---|---|
| g | All occurrences of the original string in the data stream are replaced |
| p | Print out the line where the string is operated |
| w File path | Write the result of the operation to the specified file |
| The number N | Specify the number of... That the string successfully matches in this line N Time , To replace |
3) By default, only the first string that is successfully matched is replaced ;
4) If the new string is empty , Then you can delete the original string ;
Such as : Replace the specified string 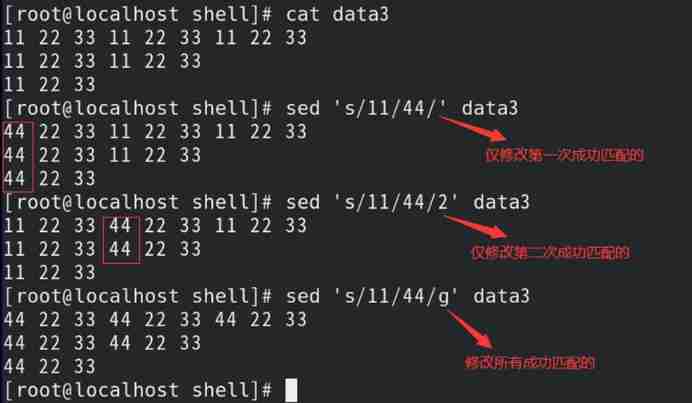
Such as : Only print out by sed Command replacement line 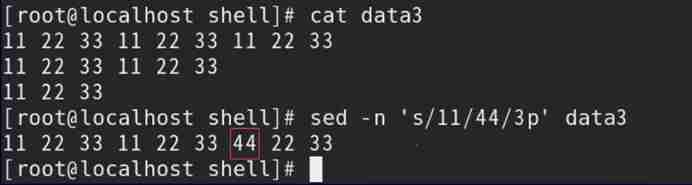
Such as : adopt s Operation deletes the specified string 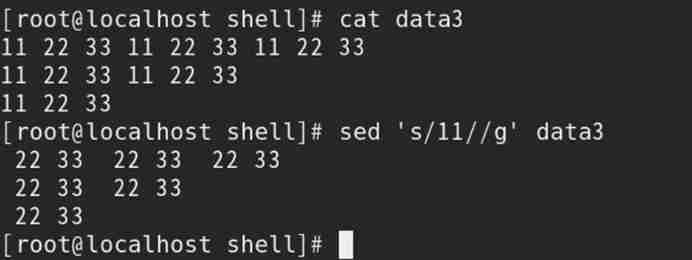
y operation : Replace a single character in the data stream
1) Format :y/ Original character / New character /
2) The number of original characters should be consistent with the number of new characters ;
3) By default, it works on all strings in the data flow ( The range cannot be specified by addressing )
Such as : Replace specified characters 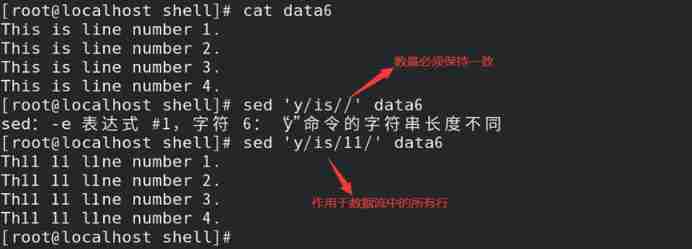
Addressing
Row addressing (Line Addressing): Appoint sed The scope of the operation of the command line
1)sed The operation of the command works on all data lines by default ;
2) Row addressing is divided into : Digital addressing 、 Text addressing
(1) Digital addressing
1)sed By default, the row number is assigned from the first row of data 1( Including the empty line );
2) Digital addressing is divided into : That's ok 、 Row interval
3) Digital addressing format :‘ Values and operations ’
// When specifying a row interval , Use between multiple values “,” Separate ( The interval contains the value itself )
Such as : Through digital addressing , Replace specified data 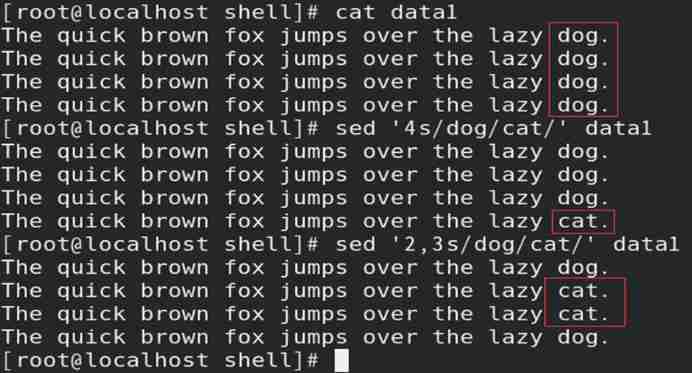
(2) Text addressing
1) Select the line containing the specified string ;
2) Text addressing format :‘/ character string / operation ’
Such as : Through text addressing , Replace specified data 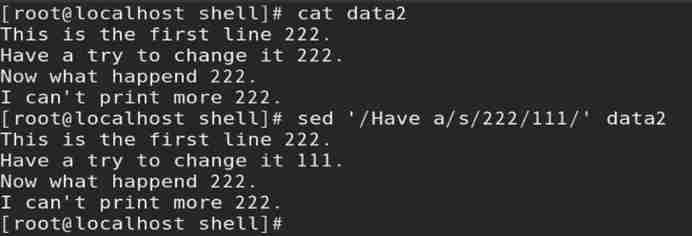
(3) When multiple operations are performed under the same address , Operations need to be specified by branches
// It can also be written on the same line , However, you need to specify addressing multiple times and use “;” Separation operation
Such as : In the specified row , Replace multiple data at the same time 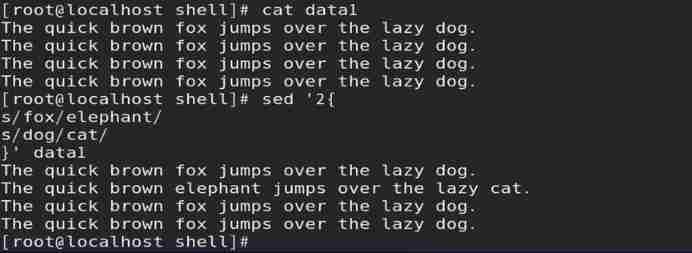
Delete
d operation : Delete the specified row in the data flow
1) Format : Match format d
2) If no string is specified , Then the string of all lines is deleted by default ;
3) Use two text addressing , It can realize the opening and closing of the deletion function ;
// Enable the deletion function when matching to the first text addressing , Close when the second one is matched
Such as : Delete specified row 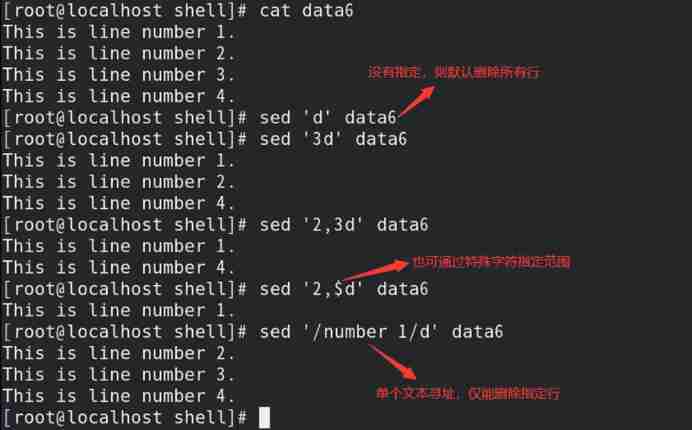
Such as : Addressing through two texts , Realize the opening and closing of the deletion function 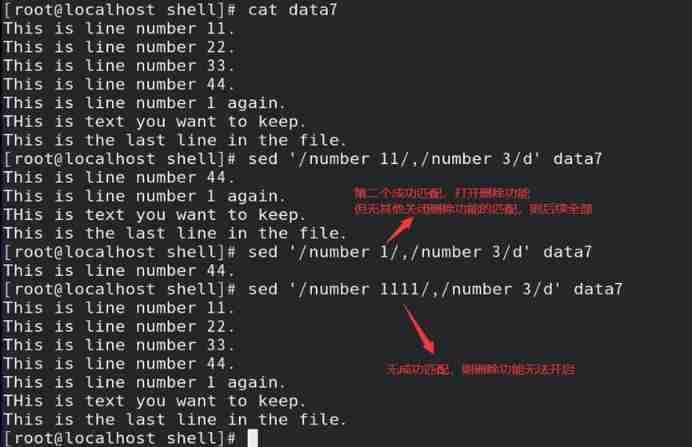
Insert
i operation : Insert a row of data into the previous row of the specified row in the data flow
1) Format : Addressing i\ insert data
2)i Operation must be coordinated with addressing , And row interval addressing cannot be used ;
// If addressing is not specified , By default, the specified data is inserted in the previous row of all rows
3)a Operation and i Same operation ( The difference lies in : Insert );
Such as : Read data6 In the file data stream , The first 3 Insert the specified data in the previous row of the row 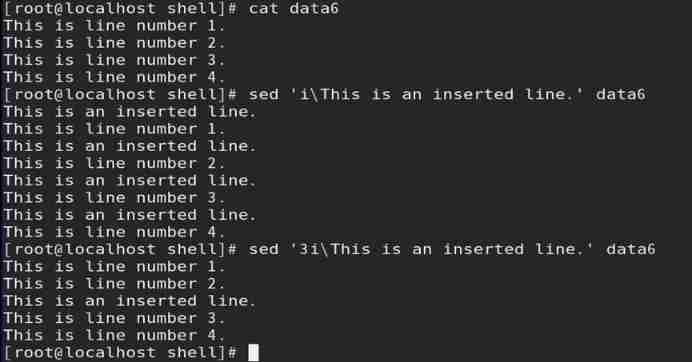
Replacement row
c operation : The new row replaces the specified row in the data flow
1) Format : Addressing c\ New line
2)c Operation must be coordinated with addressing ( If row interval addressing , Then the interval is replaced by a new line );
// If addressing is not specified , Replace all rows in the data flow by default
Such as : The new line replaces the specified line 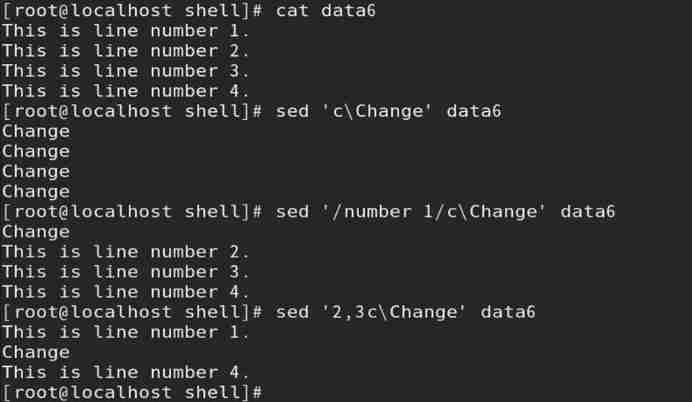
gawk
gawk Program :Unix in awk programmatic GNU edition , It has the following functions
1) Variables can be defined to store data ;
2) Use arithmetic and string operators to process data ;
3) Use structured programming concepts to add processing logic to data processing ;
4) By extracting the data elements in the data file , Format it and output ;
gawk command : The fields in each row are used to replace the data 、 Delete 、 newly added 、 Selection and other functions
Command format :gawk Options ‘ key word 1{ operation 1} key word 2{ operation 2}’ File path
| Options | meaning |
|---|---|
| -F character | Specifies the separator for the field |
| -f File path | Specify storage gwak Files for operation |
| -v Variable name = value | Define variables and variable values |
| -mf | Specify the maximum number of processing fields in the data flow |
1)gawk Unit by behavior , Take the field as the processing unit ;
2)gwak The built-in variables for each field in are :
| Variable name | explain |
|---|---|
| $0 | Represents the whole row of data |
| $1 | On behalf of the 1 A field |
| $2 | On behalf of the 2 A field |
| $N | On behalf of the N A field |
3)gawk Other built-in variables
| Variable name | meaning |
|---|---|
| NF | The total number of fields per row |
| NR | gawk What line of data is being processed |
| FS | Input field separator ( Default is space ) |
| RS | Enter the delimiter of the data row |
| OFS | Separator for output field |
| ORS | Separator of output data row |
// Built in variables in gawk When used inside , There is no need to add variable symbols before “$”
4)gawk in 3 Key words :BEGIN( The first to perform )、pattern、END( Finally, execute )
// When specifying split characters , Need to use BEGIN key word , otherwise gawk When the split character has not been replaced , Other operations have already been processed
// The default is omitted pattern key word ( Use less )
Such as : Format output 
// When there are multiple commands in an operation , Need to use “;” Separate
Such as : Store by calling gwak Files for operation , Output /etc/passwd The user name of the file and UID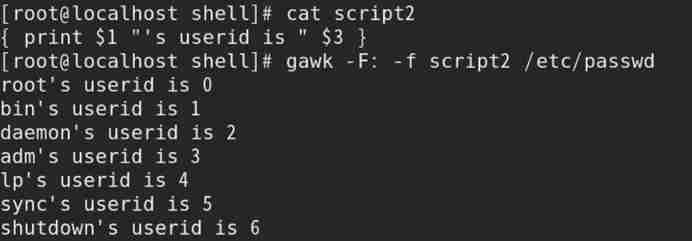
Such as : Inquire about /etc/passwd In the file UID Less than 10 Users of , And pass awk Format output 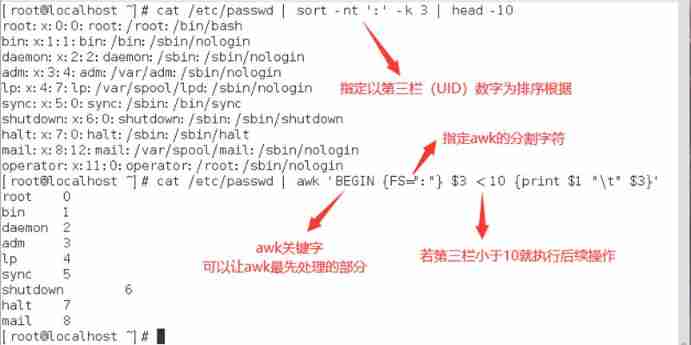
//gawk Operation selection can be realized by logical operation , And awk and gawk Universal
Such as : adopt gawk Format output
1) To write 3.sh Script files 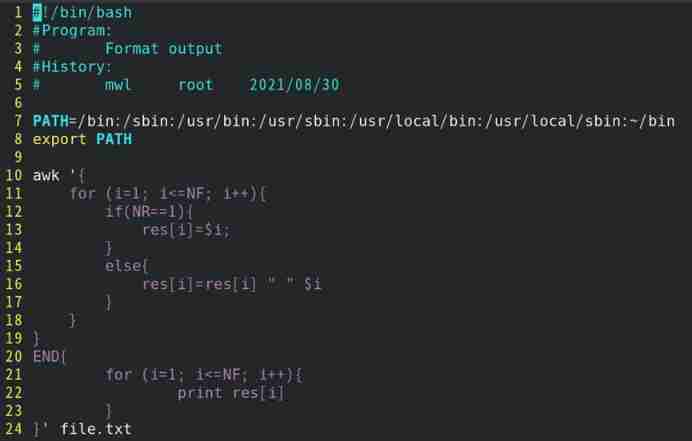
2) call 3.sh Script files 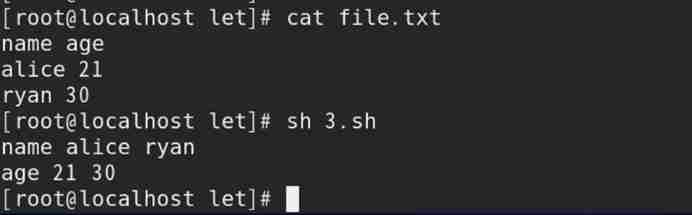
边栏推荐
- Chapter 1 overview of MapReduce
- LeetCode 1558. Get the minimum number of function calls of the target array
- Chapter 6 datanode
- 第一章 MapReduce概述
- ~Introduction to form 80
- LeetCode 1447. Simplest fraction
- Data config problem: the reference to entity 'useunicode' must end with ';' delimiter.
- Chapter 2 shell operation of hfds
- Error: case label `15 'not within a switch statement
- 第2章 HFDS的Shell操作
猜你喜欢
Spark独立集群动态上线下线Worker节点

字节跳动开源GAN模型压缩框架,算力最高节省97.8%丨ICCV 2021

我走過最迷的路,是字節跳動程序員的腦回路

业务系统兼容数据库Oracle/PostgreSQL(openGauss)/MySQL的琐事
Chapter 5 detailed explanation of consumer groups
我在字节跳动「修电影」

~Introduction to form 80
Gridhome, a static site generator that novices must know

字节跳动新程序员成长秘诀:那些闪闪发光的宝藏mentor们
Chapter 5 yarn resource scheduler
随机推荐
Detailed explanation of FLV format
~83 form introduction
Solr standalone installation
~74 JD top navigation bar exercise
Li Kou leetcode 280 weekly match
Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of China's four seasons tent industry
字节跳动开源GAN模型压缩框架,算力最高节省97.8%丨ICCV 2021
Educational Codeforces Round 122 (Rated for Div. 2)
Market trend report, technological innovation and market forecast of desktop electric tools in China
【锟斤拷】的故事:谈谈汉字编码和常用字符集
图像处理一百题(1-10)
~68 Icon Font introduction
The concept of spark independent cluster worker and executor
One hundred questions of image processing (1-10)
Data config problem: the reference to entity 'useunicode' must end with ';' delimiter.
JS time function Daquan detailed explanation ----- AHAO blog
业务系统从Oracle迁移到openGauss数据库的简单记录
Saw local status change event StatusChangeEvent [timestamp=1644048792587, current=DOWN, previous=UP]
~85 transition
第三章 MapReduce框架原理