当前位置:网站首页>A taste of node JS (V), detailed explanation of express module
A taste of node JS (V), detailed explanation of express module
2022-07-04 12:46:00 【Makabaka's making】
List of articles
Express modular
First time to know Express
Express brief introduction
Concept :Express Function and Node.js Medium http The module is similar to , It's designed to create Web The framework of the server .
Express Chinese official website : http://www.expressjs.com.cn/
Express What can be done :
- Web Web server : Specialized in providing Web Web resource server .
- API Interface server : Specialized in providing API Interface server .
- Use Express, We can easily and quickly create Web Web server and API Interface server .
Express Basic use of
- install :
npm install express - monitor GET request
adopt app.get() Method , Can listen to the client's GET request , The specific format is as follows :
app.get(' request URL Address ',function(req,res){
// Processing function
})
- monitor POST request
app.post(' request URL Address ',function(req,res){
// Processing function
})
- Respond the content to the client
app.get('/user',(req,res)=>{
// Send to the client JSON object
res.send(name:' Xiao Wang ',age:18)
})
app.post('/user',(req,res)=>{
// Send text content to the client
res.send(' The request is successful ')
})
- obtain URL Parameters carried in
app.get('/',(req,res)=>{
//req.query The default is an empty object
// Client side usage ?name= Xiao Wang &age=18 This query is in the form of a string , Parameters sent to the server
// Can pass req.query Object access to , for example :
//req.query.name req.query.age
console.log(req.query)
})
- obtain URL Dynamic parameters in
//URL In the address , Can pass : The form of parameter name , Match dynamic parameter values
app.get('/user/:id',(req,res)=>{
//req.params The default is an empty object
// There is... In it : Dynamically matched parameter values
console.log(req.params)
})
Hosting static resources
express.static()
express Provides a very useful function , be called express.static(), Through it , We can easily create a static resource server , for example , With the following code, you can public Pictures under the directory 、CSS file 、JavaScript The document is open to the public :
app.use(express.static('public'))Now you can visit public All the files in the directory
http://localhost:3000/images/bg.jpg http://localhost:3000/css/style.css http://localhost:3000/js/login.jsBe careful :Express Find the file in the specified static Directory , And provide access path to resources . therefore , The directory name where the static file is stored will not appear in URL in .
Hosting multiple static resource directories
If you want to host multiple static resource directories , Can be called multiple times express.static() function
app.use(express.static('public'))
app.use(express.static('files'))
When accessing a static resource file ,express.static() The function will query the required files according to the order of adding directories .
- Mount path prefix
If you want to be ahead of the managed static resource access path , Mount path prefix , You can use the following method :
app.use('/public',express,static('public'))
nodemon Use
- Why use nodemon
Writing debugging Node.js When the project is , If you change the project code , It requires frequent manual close fall , Then restart , Is cumbersome .
Now? , We can use nodemon(https://www.npmjs.com/package/nodemon) This tool , It can monitor changes in project files , When the code is modified ,nodemon Will automatically help us restart the project , It is very convenient for development and debugging .
- install nodemon
npm install -g nodemon
- Use nodemon
nodemon app.js // It used to be node app.js
Express route
The concept of routing
- What is routing
Routing is a mapping relationship
Express The routing
- stay Express in , Routing refers to the mapping between client requests and server processing functions .
- Express The routes in are divided into 3 part , The types of requests , Requested URL Address , Processing function , The format is as follows :
app.method(path,handler())Express Examples of routing in
What we said above get,post All requests are routed
- Routing matching process
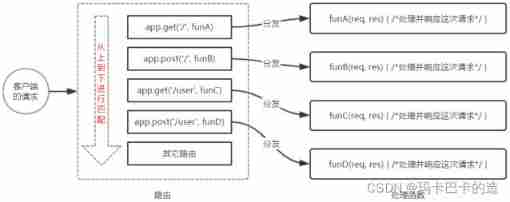
Use of routes
- The simplest use
stay Express The easiest way for the middle way is to mount to app On :
const express=require('express')
const app=express()
// Mount route
app.get('/',(req,res)=>{
res.send('Hello Express!')
})
- Modular routing
In order to facilitate the modular management of routing ,Express It is not recommended to mount the route directly to app On , Instead, it's recommended to pull the route out into a separate module .
The steps to extract a route into a separate module are as follows :
- Create the routing module corresponding to .js file
- call express.Router() Function to create a routing object
- Mount the specific route to the routing object
- Use module.exports Share routing objects out
- Use app.use() Function registration routing module
The code is as follows :
Create routing module :
var express=require('express') // Import express
var router=express.Router() // Create routing objects
route.get('/user/list',(req,res)=>{
// Mount route
res.send("Get user list")
})
module.exports=router // Export routing objects out
Register routing module :
const userRouter=require('./router/user.js') // Import routing module
app.use('/api',userRouter) // Use app.use() Register routing module , And add the prefix /api
Express middleware
Middleware concept
- What is Middleware
middleware (Middleware ), It refers to the intermediate process of business process .
- Express Call process of Middleware
When a request arrives Express After the server of , Multiple middleware can be called continuously , To preprocess this request .
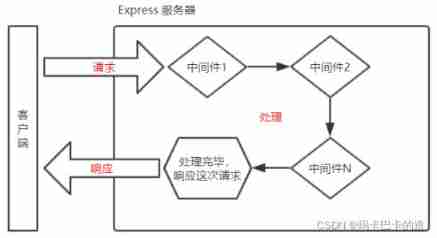
- Express Middleware format
Express Middleware , It's essentially one function Processing function ,Express The format of middleware is as follows :
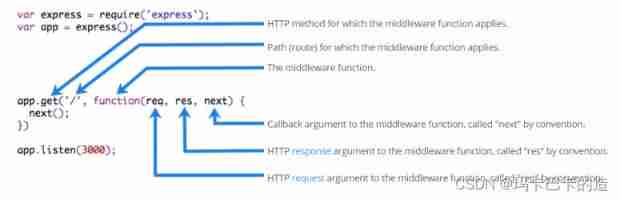
Be careful : In the formal parameter list of middleware functions , Must contain next Parameters . The routing processing function only contains req and res.
- next Function function
next Function is the key to realize the continuous call of multiple middleware , It means transferring the flow relationship to the next middleware or routing .
The first experience of middleware
- Define middleware functions
Let's define the simplest middleware function :
const mw=function(req,res,next){
console.log(' This is the simplest middleware function ')
next() // After the business processing of the current middleware is completed , Must call next() function , It means that the flow relationship is handed over to the next middleware or routing
}
- Globally effective middleware
Any request from the client , After arriving at the server , Will trigger middleware , It's called globally effective middleware .
By calling app.use( Middleware function ), You can define a middleware that works globally , The sample code is as follows :
const mw=function(req,res,next){
console.log(' This is the simplest middleware function ')
next() // After the business processing of the current middleware is completed , Must call next() function , It means that the flow relationship is handed over to the next middleware or routing
}
// Register middleware globally
app.use(mw)
- Define a simplified form of global middleware
app.use(function(req,res,next){
console.log(' This is the simplest middleware function ')
next()
})
- The role of middleware
Between multiple middleware , Share the same req and res. Based on this characteristic , We can in the upstream middleware , Uniform for req or res Object to add custom properties or methods , For downstream middleware or routing . It will be transmitted from one level to another .
- Define multiple global middleware
have access to app.use() Continuously define multiple global middleware . After the client request arrives at the server , It will be called in the order defined by the middleware .
- Partially effective middleware
Don't use app.use() Defined middleware , Middleware called local validation , The sample code is as follows :
const mw=function(req,res,next){
console.log(' This is the simplest middleware function ')
next()
}
//mw This middleware is only used in the current routing , This usage belongs to Partially effective middleware
app.get('/',mw,function(req,res){
res.send('Hello Express')
})
//mw This middleware will not affect the following routes
app.get('/user'funciton(req,res){
res.send('User page')
})
- Define multiple local middleware
In routing , Through the following two equivalent ways , Use multiple local middleware :
app.get('/',mw1,mw2,(req,res)=>{
res.send()})
app.get('/',[mw1,mw2],(req,res)=>{
res.send()})
- Learn about middleware 5 There are two points for attention
- Be sure to register middleware before routing ;
- The request sent by the client , Multiple middleware can be called continuously for processing ;
- After executing the business code of middleware , Don't forget to call next() function ;
- In order to prevent code logic confusion , call next() Don't write extra code after the function ;
- When calling multiple Middleware in succession , Between multiple middleware , share req and res object .
Classification of middleware
Express The official use of common middleware , Divided into 5 Categories: , Namely :
- Application level middleware :
adopt app.use() or app.get() or app.post() , Bound to the app Middleware on instance , It's called application level middleware . It is the global and local middleware we registered ourselves .
- Routing level middleware :
Bound to the express.Router() Middleware on instance , It's called routing level middleware . There is no difference between its usage and application level middleware . It's just , Application level middleware is bound to app For instance , The routing level middleware is bound to router For instance .
Error level middleware :
- The role of error level middleware : It's designed to catch unexpected errors in the entire project , So as to prevent the abnormal collapse of the project .
- Format : Error level middleware function In the processing function , There has to be 4 Parameters , The order of formal parameters is from front to back , Namely (err, req, res, next).
- Be careful : Error level middleware must be registered after all routes .
app.get('/',function(req,res)=>{ throw new Error(' An error occurred inside the server !') res.send('Home Page') }) app.use(function(req,res,next){ console.log(' Something went wrong ',arr.message) // Print an error message on the server res.send('Error'+err.message) // Respond to the client about the error })Express Built-in middleware :
express.staticBuilt in middleware for fast hosting static resources , for example : HTML file 、 picture 、CSS Patterns, etc ( No compatibility )express.jsonanalysis JSON Request body data in format ( Compatibility , Only in 4.16.0+ Available in version )express.urlencodedanalysis URL-encoded Request body data in format ( Compatibility , Only in 4.16.0+ Available in version )
Configuration analysis application/json Built in middleware for formatted data app.use(express.json()) // Configuration analysis application/x-www/form-urlencoded Built in middleware for formatted data app.use(express,urlencoded({ extended:false}))Third party middleware :
Not Express The official built-in , It's middleware developed by a third party , It's called third-party middleware . In the project , You can download and configure third-party middleware as needed , So as to improve the development efficiency of the project .
Use Express Write the interface
Create a basic server
const express=require('express')
const app=require()
app.listen(5000,function(){
console.log(' Server created successfully !')
})
establish API Routing module
//apiRouter.js Routing module
const express=require('express')
const apiRouter=express.Router()
module.exports=apiRouter
//app.js Import and register routing module
const apiRoutetr=require('./apiRouter.js')
app.use('./api',apiRouter)
To write GET Interface
apiRouter.get('/get',(req,res)=>{
// Get the client through the query string , Data sent to server
const query=req.query
// call res.send() Method , Respond data to client
res.send({
status:0,
msg:'GET The request is successful ',
data:query
})
})
To write POST Interface
apiRouter.get('/post',(req,res)=>{
// Get the client through the request body , Send to the server URL-encoded data
const body=req.body
// call res.send() Method , Respond data to client
res.send({
status:0,
msg:'POST The request is successful ',
data:body
})
})
Be careful : If you want to get URL-encoded Request body data in format , Middleware must be configured app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: false }))
CORS Cross-domain resource sharing
- It was written just now GET and POST Interface , There is a very serious problem : Cross domain requests are not supported .
There are two main solutions to interface cross domain problems :
- CORS( Mainstream solutions , Recommended )
- JSONP( Flawed solutions : Only support GET request )
- Use cors Middleware solves cross domain problems
- function npm install cors Install middleware
- Use const cors = require(‘cors’) Import Middleware
- Call before routing app.use(cors()) Configuration middleware
边栏推荐
- In 2022, financial products are not guaranteed?
- Star leap plan | new projects are continuously being recruited! MSR Asia MSR Redmond joint research program invites you to apply!
- When synchronized encounters this thing, there is a big hole, pay attention!
- [solve the error of this pointing in the applet] SetData of undefined
- 轻松玩转三子棋
- 《天天数学》连载57:二月二十六日
- C language array
- BCD code Baidu Encyclopedia
- [the way of programmer training] - 2 Perfect number calculation
- Openssl3.0 learning 20 provider KDF
猜你喜欢

VIM, another program may be editing the same file If this is the solution of the case
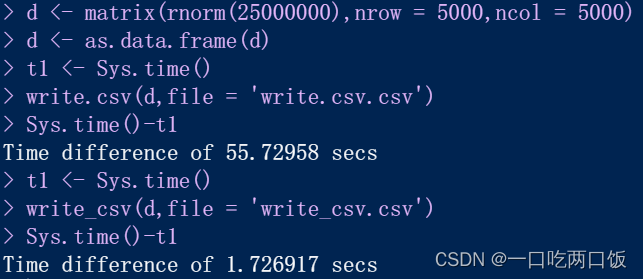
R language -- readr package reads and writes data
22 API design practices
ArgMiner:一个用于对论点挖掘数据集进行处理、增强、训练和推理的 PyTorch 的包
MySQL advanced review
Introduction to the button control elevatedbutton of the fleet tutorial (the tutorial includes the source code)
![[the way of programmer training] - 2 Perfect number calculation](/img/fd/4bb8560f601daddaa8895f20215be4.jpg)
[the way of programmer training] - 2 Perfect number calculation
C fonctions linguistiques

Leetcode day 17

It's hard to hear C language? Why don't you take a look at this (V) pointer
随机推荐
Transformer principle and code elaboration (tensorflow)
Concepts and theories related to distributed transactions
Show recent errors only command /bin/sh failed with exit code 1
Awk getting started to proficient series - awk quick start
17.内存分区与分页
Global and Chinese markets for soluble suture 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
DC-5靶机
A few words explain redis cache penetration, breakdown, avalanche, and redis sentinel
Abnormal mode of ARM processor
It's hard to hear C language? Why don't you take a look at this (V) pointer
R language -- readr package reads and writes data
16. Memory usage and segmentation
Argminer: a pytorch package for processing, enhancing, training, and reasoning argument mining datasets
Daily Mathematics Series 57: February 26
Mongodb vs mysql, which is more efficient
Star leap plan | new projects are continuously being recruited! MSR Asia MSR Redmond joint research program invites you to apply!
Can Console. Clear be used to only clear a line instead of whole console?
The latest idea activation cracking tutorial, idea permanent activation code, the strongest in history
The most robust financial products in 2022
MPLS experiment