当前位置:网站首页>[Li Kou] the second set of the 280 Li Kou weekly match
[Li Kou] the second set of the 280 Li Kou weekly match
2022-07-06 03:11:00 【Xiao Huang, who likes to knock code】
- Author's brief introduction : Hello everyone , I'm Xiao Huang who likes to knock code , Unicorn enterprise Java Development Engineer ,Java New star creators in the field
- Official account number : Xiao Huang who likes to knock code
- Series column :Java Design patterns 、 Data structures and algorithms
- If there is something wrong with the knowledge of the article , Please correct me. ! Learn with you , Progress together
- If you feel the blogger's article is good , Please support the blogger for the third company
- Bloggers are trying to complete 2022 Planned : Take dreams as horses , Set sail ,2022 Dream catcher
List of articles
One 、 introduction
Today's weekly match is hard to say , Because of a simple long Conversion negligence leads to oneself T3 no A
Two 、 6004. obtain 0 The number of operations
1、 Introduction to the topic

2、 title
- Simulation is enough
- Pay attention to the return condition :
while(num1 != 0 && num2 != 0)
3、 Title code
class Solution {
public int countOperations(int num1, int num2) {
int count = 0;
while(num1 != 0 && num2 != 0){
if(num1 >= num2){
num1 = num1 - num2;
}else{
num2 = num2 - num1;
}
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
3、 ... and 、6005. The minimum number of operands to make an array an alternating array
1、 Introduction to the topic

2、 title
- greedy
- We analyze the topic , In a nutshell , The final result :
Our odd digits are the same number , Even digits are the same number , And the numbers cannot be equal - We use two priority queues to store its number , according to
The most frequent occurrenceJudge - Let's consider the following situations :
- [0]:
Queue 2 is empty - [1,2]:
The size of queue one and queue two is 1 - [1,2,3]:
The size of queue one is 2, The size of queue 2 is 1 - [1,2,3,4]:
The size of queue one is 2, The size of queue 2 is 2
- [0]:
- We compare the priority queue
int value = peek(), The number of times the number appears- If not equal , It means that you need to become
value, Calculate the number of times - If it's equal , We need to compare
valueSize , Big ones stay the same , Small needs becomeThe second largest
- If not equal , It means that you need to become
3、 Title code
class Solution {
public static int minimumOperations(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 1) {
return 0;
}
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();
int count1 = 0;
int count2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i % 2 != 0) {
count1++;
map1.put(nums[i], map1.getOrDefault(nums[i], 0) + 1);
} else {
count2++;
map2.put(nums[i], map2.getOrDefault(nums[i], 0) + 1);
}
}
// Odd number
PriorityQueue<int[]> priorityQueue1 = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o2[1] - o1[1];
}
});
for (Integer key : map1.keySet()) {
priorityQueue1.add(new int[]{
key, map1.get(key)});
}
// even numbers
PriorityQueue<int[]> priorityQueue2 = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o2[1] - o1[1];
}
});
for (Integer key : map2.keySet()) {
priorityQueue2.add(new int[]{
(int) key, (int) map2.get(key)});
}
if (priorityQueue1.size() == 1 && priorityQueue2.size() == 1) {
if (priorityQueue1.peek()[0] != priorityQueue2.peek()[0]) {
return 0;
} else {
return priorityQueue1.peek()[1] >= priorityQueue2.peek()[1] ? priorityQueue2.peek()[1] : priorityQueue1.peek()[1];
}
}else if (priorityQueue1.size() > 1 && priorityQueue2.size() == 1) {
if (priorityQueue1.peek()[0] != priorityQueue2.peek()[0]) {
return count1 - priorityQueue1.peek()[1];
} else {
if (priorityQueue1.peek()[1] >= priorityQueue2.peek()[1]) {
return count2 + count1 - priorityQueue1.peek()[1];
} else {
priorityQueue1.poll();
return count1 - priorityQueue1.peek()[1];
}
}
} else {
if (priorityQueue1.peek()[0] != priorityQueue2.peek()[0]) {
return count1 - priorityQueue1.peek()[1] + count2 - priorityQueue2.peek()[1];
} else {
if (priorityQueue1.peek()[1] >= priorityQueue2.peek()[1]) {
priorityQueue2.poll();
return count1 - priorityQueue1.peek()[1] + count2 - priorityQueue2.peek()[1];
} else {
priorityQueue1.poll();
return count1 - priorityQueue1.peek()[1] + count2 - priorityQueue2.peek()[1];
}
}
}
}
}
Four 、6006. Take out the smallest number of magic beans
1、 Introduction to the topic

2、 title
- We found that , We want to make magic beans equal , Need to find one
critical point, According to this critical point :Less than his all become 0, More than his whole becomes it - Sort first
- We use
[1,4,5,6]As an example- Suppose the current critical point is
5, So our1、4Need to become0,6become5, The final result is :7 - Because our magic beans can't be increased , Can only reduce
- When we traverse its value , We will
Overall sum - The number of subsequent data * The current value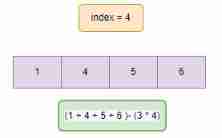
- Be careful , When we are evaluating , Don't forget to change the type to
long - This topic can also be used
The prefix and
- Suppose the current critical point is
3、 Title code
class Solution {
public long minimumRemoval(int[] beans) {
int len = beans.length;
Arrays.sort(beans);
long sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
sum = sum + beans[i];
}
long minSum = Long.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
// Attention turns to long
minSum = Math.min(minSum, sum - (len - i) * (long)beans[i]);
}
return minSum;
}
}
5、 ... and 、 summary
The result of this week's race is still not ideal , I hope the next week's race will be better ~
Next time, be sure to pay attention to the conversion of types
Come on ~~~
边栏推荐
- [Chongqing Guangdong education] higher mathematics I reference materials of Southwest Petroleum University
- How to do function test well
- Elimination games
- ERA5再分析资料下载攻略
- 不赚钱的科大讯飞,投资价值该怎么看?
- 【若依(ruoyi)】设置主题样式
- 如何做好功能测试
- Leetcode problem solving -- 108 Convert an ordered array into a binary search tree
- 微服务注册与发现
- Reverse repackaging of wechat applet
猜你喜欢
1. Dynamic parameters of function: *args, **kwargs
Eight super classic pointer interview questions (3000 words in detail)
Maturity of master data management (MDM)
IPv6 jobs
下一个行业风口:NFT 数字藏品,是机遇还是泡沫?

JS regular filtering and adding image prefixes in rich text
【概念】Web 基础概念认知
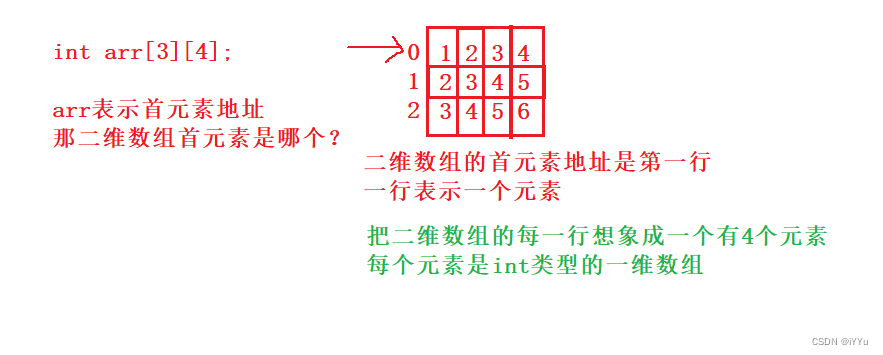
深入探究指针及指针类型
![[concept] Web basic concept cognition](/img/27/14bcd73ca70d136436a4382a1b4bd1.jpg)
[concept] Web basic concept cognition
如何做好功能测试
随机推荐
ERA5再分析资料下载攻略
MySQL advanced notes
Redis SDS principle
SD卡報錯“error -110 whilst initialising SD card
【若依(ruoyi)】设置主题样式
Introduction to robotframework (I) brief introduction and use
IPv6 jobs
codeforces每日5题(均1700)-第六天
Detailed use of dbutils # yyds dry goods inventory #
Mysql database operation
【指针训练——八道题】
张丽俊:穿透不确定性要靠四个“不变”
OCR文字識別方法綜述
. Net 6 and Net core learning notes: Important issues of net core
Derivation of anti Park transform and anti Clarke transform formulas for motor control
C language - Blue Bridge Cup - promised score
华为、H3C、思科命令对比,思维导图形式从基础、交换、路由三大方向介绍【转自微信公众号网络技术联盟站】
不赚钱的科大讯飞,投资价值该怎么看?
JS regular filtering and adding image prefixes in rich text
Software design principles
