当前位置:网站首页>Typical use cases for knapsacks, queues, and stacks
Typical use cases for knapsacks, queues, and stacks
2022-07-05 05:35:00 【Raise items】
List of articles
knapsack
The following example is to calculate all double It's worth it The average and Sample standard deviation .
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include "bag.h"
int main()
{
Bag<double> bag;
double d;
while (std::cin >> d) {
bag.Add(d);
}
double sum = 0;
for (auto x : bag) {
sum += x;
}
double mean = sum / bag.Size();
sum = 0;
for (auto x : bag) {
sum += (x - mean) * (x - mean);
}
double std = sqrt(sum / (bag.Size() - 1));
std::cout << mean << std::endl;
std::cout << std << std::endl;
return 0;
}
In order to be able to use Range for Statement traversal bag The elements in the object , You need to add begin() and end() Method (deque The iterator supports ++ operation ).
template <typename Item>
class Bag {
public:
typename std::deque<Item>::iterator begin();
typename std::deque<Item>::iterator end();
// ...
};
template <typename Item>
typename std::deque<Item>::iterator Bag<Item>::begin()
{
return dq_.begin();
}
template <typename Item>
typename std::deque<Item>::iterator Bag<Item>::end()
{
return dq_.end();
}
Running results ( Command line ctrl + D yes EOF):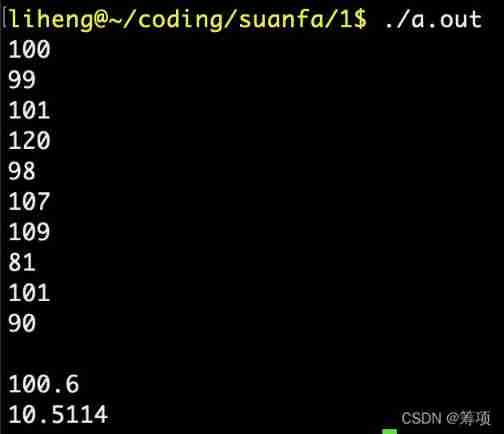
queue
The following example is to input the standard int Value press The order Store in an array , We don't know in advance how much memory to allocate for the array .
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include "queue.h"
int main()
{
Queue<int> qi;
int ele;
while (std::cin >> ele) {
qi.EnQueue(ele);
}
int N = qi.Size();
int arr[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
arr[i] = qi.Dequeue();
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
std::cout << arr[i] << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
Running results (D Is command line input EOF The emergence of ):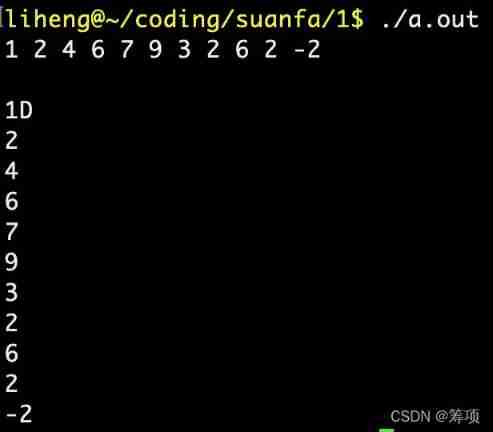
Stack
In the following example , Press the integer in the standard input The reverse Print out .
#include <iostream>
#include "stack.h"
int main()
{
Stack<int> si;
int ele;
while (std::cin >> ele) {
si.Push(ele);
}
while (!si.IsEmpty()) {
std::cout << si.Pop() << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
Running results :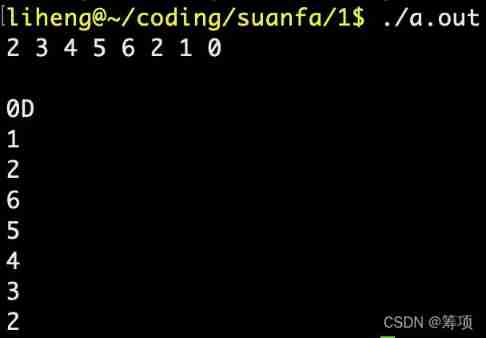
Arithmetic expression evaluation
A classic use case of stack is computation Arithmetic expressions : Enter a string , Output a value .
For the sake of simplicity , expression Do not omit parentheses ( Use parentheses instead of priority rules to do four operations ), Brackets 、 Operands 、 Between operators Space separate .
Input :( 1 + ( 2 + 3 ) * ( 4 * 5 ) )
Output :101
E.W.Dijkstra stay 20 century 60 In the s, a very simple algorithm was invented , The process is as follows :(1) Prepare two stacks : The stack of operands and Operator stack .(2) Traversal arithmetic expression .(3) take The operand is pushed into the operand stack 、 Operator push into operator stack , Ignore left parenthesis .(4) encounter Right bracket when , eject An operator , Again eject Required operands , perform operation , Result Push the The stack of operands .(5) When the last closing bracket is processed , There is only one operand on the stack , That is the expression result .
Code implementation :
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <cmath>
#include "stack.h"
using std::string;
void Calculate(Stack<string> &ops, Stack<double> &vals)
{
string op = ops.Pop();
double a = vals.Pop();
if (op == string("+")) {
double b = vals.Pop();
vals.Push(a + b);
} else if (op == string("-")) {
double b = vals.Pop();
vals.Push(b - a);
} else if (op == string("*")) {
double b = vals.Pop();
vals.Push(a * b);
} else if (op == string("/")) {
double b = vals.Pop();
vals.Push(b / a);
} else if (op == string("sqrt")) {
vals.Push(sqrt(a));
} else {
std::cout << "unknown operator" << std::endl;
}
}
int main()
{
Stack<string> ops; // Operator stack
Stack<double> vals; // The stack of operands
string str;
while (std::cin >> str) {
if (str == string("(")) {
continue;
} else if ((str == string("+")) || (str == string("-")) ||
(str == string("*")) || (str == string("/")) ||
(str == string("sqrt"))) {
ops.Push(str);
continue;
} else if (str == string(")")) {
Calculate(ops, vals);
} else {
vals.Push(atof(str.c_str()));
}
}
std::cout << vals.Pop() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Running results :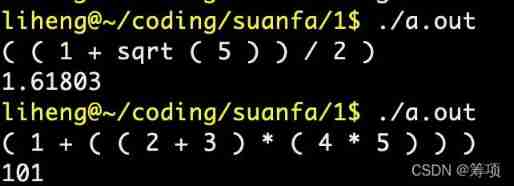
This implementation does not provide Parameter check Mechanism .
边栏推荐
- ALU逻辑运算单元
- Web APIs DOM node
- Chapter 6 data flow modeling - after class exercises
- 注解与反射
- Codeforces round 712 (Div. 2) d. 3-coloring (construction)
- Service fusing hystrix
- object serialization
- kubeadm系列-02-kubelet的配置和启动
- Analysis of backdoor vulnerability in remote code execution penetration test / / phpstudy of national game title of national secondary vocational network security B module
- Annotation and reflection
猜你喜欢
YOLOv5-Shufflenetv2
Sword finger offer 06 Print linked list from beginning to end
Graduation project of game mall
Pointnet++ learning
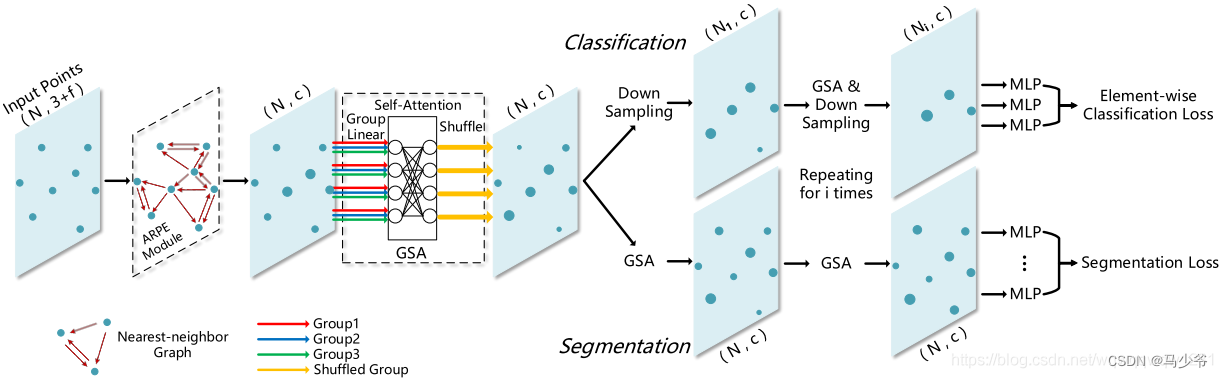
Improvement of pointnet++

第六章 数据流建模—课后习题

【实战技能】如何做好技术培训?
挂起等待锁 vs 自旋锁(两者的使用场合)

CF1634E Fair Share
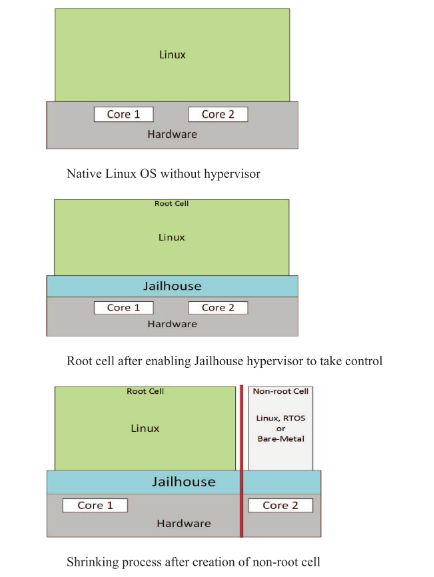
【Jailhouse 文章】Performance measurements for hypervisors on embedded ARM processors
随机推荐
软件测试 -- 0 序
智慧工地“水电能耗在线监测系统”
After setting up the database and website When you open the app for testing, it shows that the server is being maintained
Use of room database
Educational Codeforces Round 107 (Rated for Div. 2) E. Colorings and Dominoes
CF1634E Fair Share
Haut OJ 1350: choice sends candy
常见的最优化方法
用STM32点个灯
Haut OJ 1218: maximum continuous sub segment sum
[to be continued] [UE4 notes] L3 import resources and project migration
Codeforces Round #715 (Div. 2) D. Binary Literature
On-off and on-off of quality system construction
Sword finger offer 05 Replace spaces
Palindrome (csp-s-2021-palin) solution
Demonstration of using Solon auth authentication framework (simpler authentication framework)
kubeadm系列-02-kubelet的配置和启动
Light a light with stm32
Developing desktop applications with electron
kubeadm系列-01-preflight究竟有多少check