当前位置:网站首页>[exercise 4-1] cake distribution
[exercise 4-1] cake distribution
2022-07-06 15:57:00 【Flame car】
List of articles
A . Cake Distribution
Description
You are about to have a birthday and you would like to prepare a birthday cake that weighs anywhere between 1 and 1018 grams inclusive. You know that there will be A,B or C guests at the party. You would like to cut this cake into pieces such that:
The weight of each piece is a positive integer number of grams.
No matter how many guests arrive, the pieces can be distributed between the guests in such a way that each guest gets the same amount of cake. Note that some guests might get more than one piece.
You don’t want to spend too much time cutting the cake, so you would like to have at most 5,000 pieces. Let’s do it!
Input
The only line of input contains the 3 numbers A,B,C, all positive integers not more than 1000.
Output
On the first line, output one number K, the number of pieces. On each of the next K lines, output a description of each piece, consisting of 4 numbers, wi,ai,bi,ci, where wi is the weight of the piece in grams and ai,bi,ci are indices of the person who will get this piece if A,B, or C guests arrive, respectively. The indices should satisfy 1≤ai≤A, 1≤bi≤B, 1≤ci≤C. The sum of all wis must be less than or equal to 1018.
Samples
Input
1 2 3
Output
4
2 1 1 1
1 1 1 2
1 1 2 2
2 1 2 3
1. Source of topic
The question is Waterloo Local Contest 2019 Fall Inside A topic .
Official title link : Click on
Official solutions and data : Click on
2. Topic translation
At first, I didn't understand what I said , Later on N Many translators have learned such a situation :
You have a biggest 1e18 The cake , There may be A Or B Or C personal ( One of them ) Come and eat cake , When distributing cakes , Everyone must be assigned to the cake Same quality ( The number can vary , But the quality must be the same ), Because you are lazy , At most 5000 block ( This determines that you cannot run with violence ).
Then explain the example :
First output how many pieces you divided N( It's up to you , There is a special judgment , No more than 5000 block )
And then down N That's ok , Each row
The first one is to output the quality of this cake .
The second output, if any A How many people will get this cake .
Third output, if any B How many people will get this cake .
The fourth output, if any C How many people will get this cake .
Code
Error model ( Ignore most 5000 block )
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
const int N = 1e6+5;
int main()
{
ll a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
ll t = a*b*c;
cout<<t<<endl;
ll na=1,nb=1,nc=1;
ll cnta=0,cntb=0,cntc=0;
ll moda,modb,modc;
moda = b*c;
modb = a*c;
modc = a*b;
for(ll i=1;i<=t;i++) {
printf("1 %lld %lld %lld\n",na,nb,nc);
if(++cnta%moda==0)
na++;
if(++cntb%modb==0)
nb++;
if(++cntc%modc==0)
nc++;
}
return 0;
}
This is the assumption that every piece is 1g Calculated , It also depends on the time limit 15s Dare to write like this .
Correct demonstration
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
const int N = 1e6+5;
int cnt;
map<ll,int> mp;
ll num[N];
int main()
{
ll a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
for(int i = 1;i <= a; i++)
if(!mp[b*c*i])
num[++cnt]=b*c*i,mp[b*c*i]=1;
for(int i = 1;i <= b; i++)
if(!mp[a*c*i])
num[++cnt]=a*c*i,mp[a*c*i]=1;
for(int i = 1;i <= c; i++)
if(!mp[b*a*i])
num[++cnt]=b*a*i,mp[b*a*i]=1;
sort(num+1,num+1+cnt);
ll last = 0;
cout << cnt << endl;
for (int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) {
cout<<num[i]-last<<' '<<(last/(b*c) + 1)<<' '<<(last/(a*c)+1)<<' '<<(last/(b*a)+1)<<'\n';
last = num[i];
}
return 0;
}
Simple version
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
const int N = 1e6+5;
set<ll> st;
int main()
{
ll a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
for(int i = 1;i <= a; i++)
st.insert(b*c*i);
for(int i = 1;i <= b; i++)
st.insert(a*c*i);
for(int i = 1;i <= c; i++)
st.insert(b*a*i);
ll last = 0;
cout << st.size() << endl;
for (auto x : st) {
cout<<x-last<<' '<<(last/(b*c) + 1)<<' '<<(last/(a*c)+1)<<' '<<(last/(b*a)+1)<<'\n';
last = x;
}
return 0;
}
The concise version actually uses set Instead of using map Duplicate check , as well as sort Sorting steps , because set It will automatically check the duplicate and sort .
auto x : st
set<int>::iterator it = st.begin();it!=st.end();it++
Both are acceptable , Obviously, the former is simpler .auto Is to get the type automatically .
The former uses x Substitute value , The latter uses *it.
analysis
At first glance, it may feel messy , In fact, if you look carefully, you can understand the truth :
This is actually a super optimization of violence , The time complexity is directly from O(1e9) drop to O(1e3). In terms of ideology, it is exactly the same . Traversal just merges some that can be merged , In fact, the total quality M = a×b×c There is no change
① The first three times for What does cycle mean ?
Take one for example ( With A For example ), Every time b×c Gram belongs to one person ( The total quality a×b×c, common a Share , each b×c)
② Why use This time x- Last time x?
Or the reason above , The quality of everyone is a( or b or c), We pause once ( Do one operation ) There is At least one group needs to be replaced . Due to the accumulation of a( or b or c) Gram's cake was given to one person , You need to change someone , So this operation is to output how many cakes are separated in this small step .(x Is the cumulative value )
③last/(b×c) + 1) What does that mean? ?
Replacement operation , When last It's you insert At the time of the i×b×c when , Now the one who is sharing the cake is last/(b×c) + 1 Number
Give me a demonstration :
1 2 3
↓
1 --> 6
2 --> 3 6
3 --> 2 4 6
That is, accumulated to 6g when A substitutions
Accumulate to 3g ,6g when B substitutions
Accumulate to 2g , 4g, 6g when C substitutions
After checking and sorting --> 2 3 4 6
That is, it is accumulating to 2,3,4,6g When you need to change people .
The first size 2-0=2 ,1 1 1 , here C substitutions .
The second size 3-2=1 ,1 1 2 , here B substitutions .
The third size 4-3=1 ,1 2 2 , here C substitutions .
The fourth size 6-4=2, 1 2 3 , here A,B,C Change people .
So in fact, this is the optimization of violence .
Violence is :
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 2
1 1 2 2
1 1 2 3
1 1 2 3
A Every time 6 Change one at a time ,B Every time 3 Change one at a time ,C Every time 2 Change one at a time .( The focus is the replacement of a combination )
Optimization is :
2 1 1 1
1 1 1 2
1 1 2 2
2 1 2 3
The optimized version is to put the repeated quality together ( The focus is on the replacement of each combination )
边栏推荐
- 用C语言写网页游戏
- 基于web的照片数码冲印网站
- Truck History
- Find 3-friendly Integers
- C语言必背代码大全
- Printing quality inspection and verification system Industry Research Report - market status analysis and development prospect forecast
- Cost accounting [13]
- 力扣刷题记录--完全背包问题(一)
- Cost accounting [21]
- Learning record: use STM32 external input interrupt
猜你喜欢
力扣刷题记录
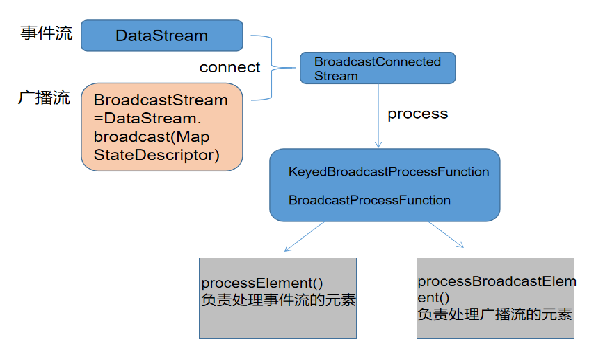
Information security - threat detection - Flink broadcast stream broadcaststate dual stream merging application in filtering security logs
毕业才知道IT专业大学生毕业前必做的1010件事

Record of force deduction and question brushing

信息安全-史诗级漏洞Log4j的漏洞机理和防范措施
Penetration test (8) -- official document of burp Suite Pro
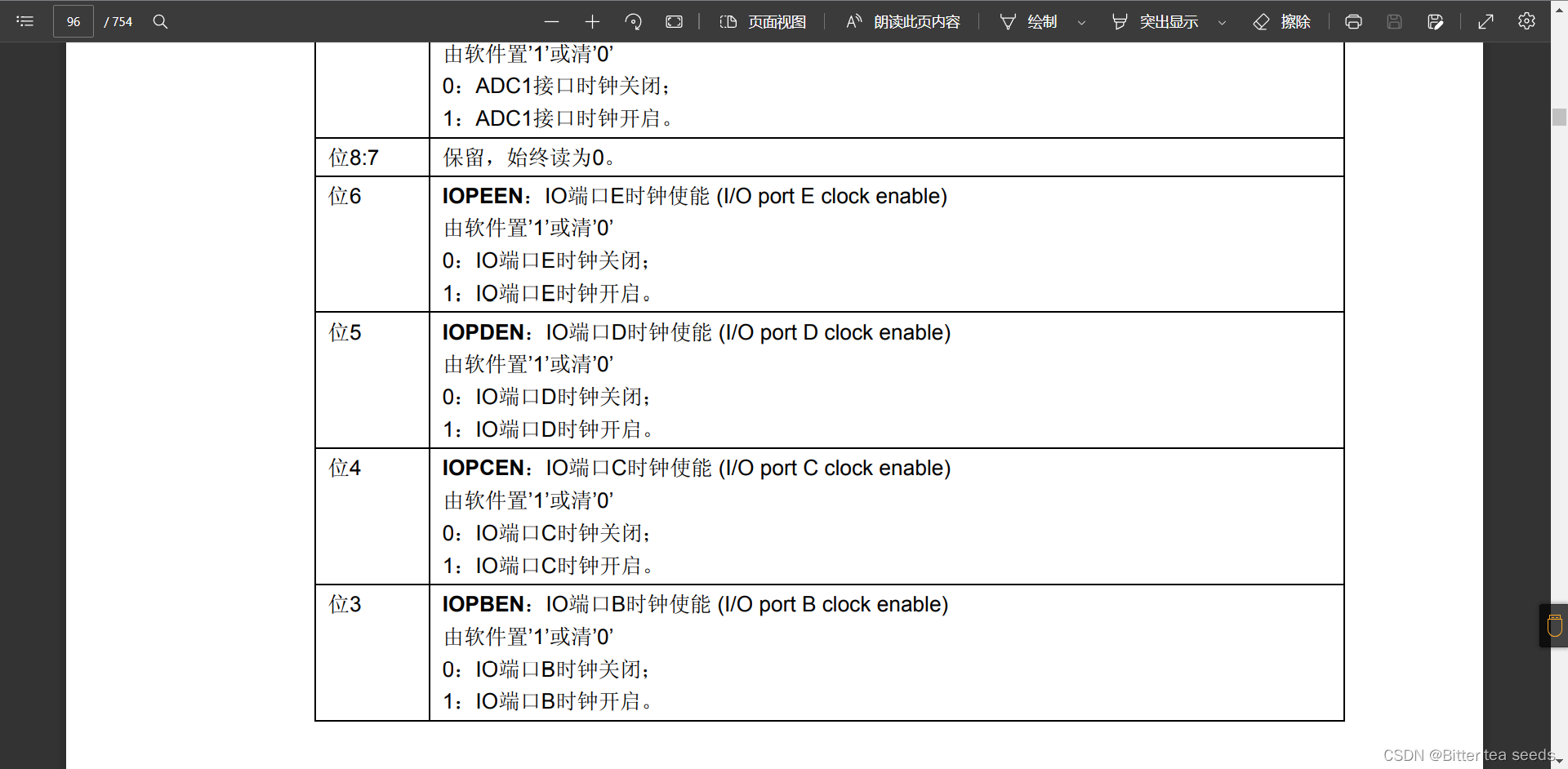
STM32 learning record: LED light flashes (register version)
Penetration test (7) -- vulnerability scanning tool Nessus
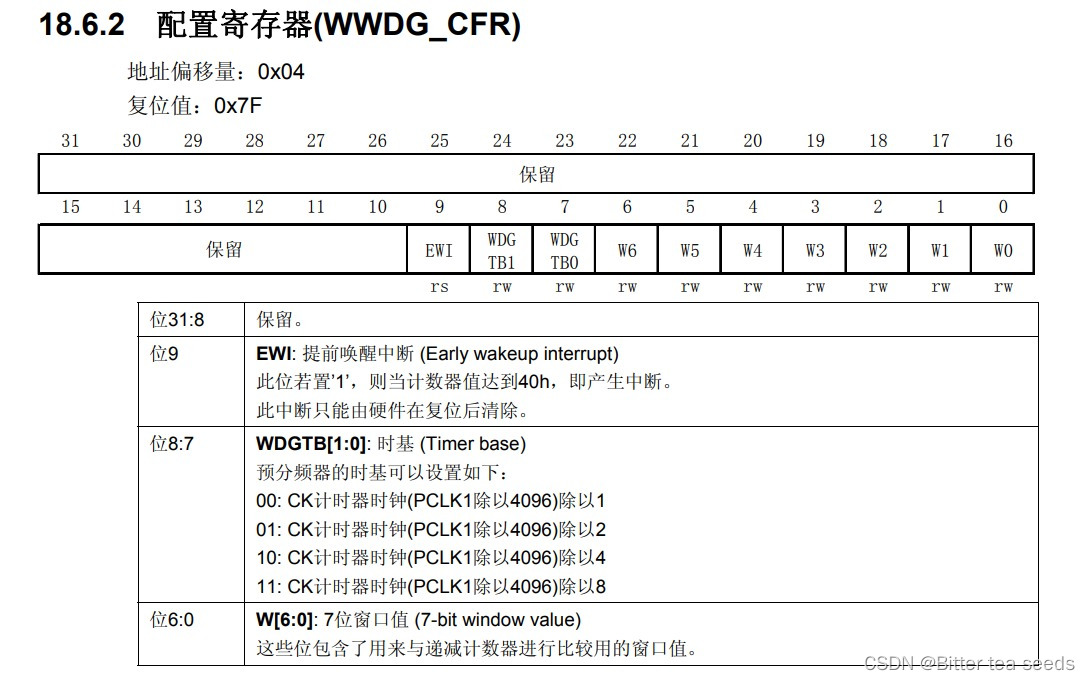
Learning record: use stm32f1 watchdog
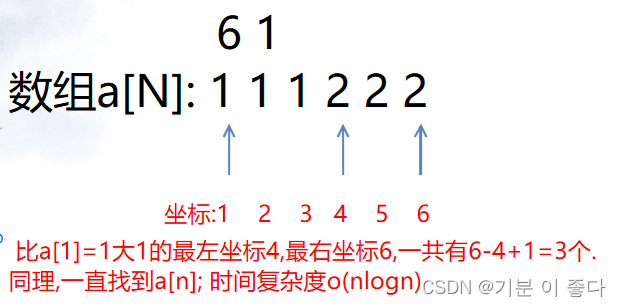
洛谷P1102 A-B数对(二分,map,双指针)
随机推荐
Determine the Photo Position
Information security - threat detection engine - common rule engine base performance comparison
信息安全-威胁检测-flink广播流BroadcastState双流合并应用在过滤安全日志
[analysis of teacher Gao's software needs] collection of exercises and answers for level 20 cloud class
China chart recorder market trend report, technology dynamic innovation and market forecast
Learning record: USART serial communication
cs零基础入门学习记录
Web based photo digital printing website
China's earthwork tire market trend report, technical dynamic innovation and market forecast
Accounting regulations and professional ethics [3]
Ball Dropping
Opencv learning log 13 corrosion, expansion, opening and closing operations
C语言数组的概念
E. Breaking the Wall
China's salt water membrane market trend report, technological innovation and market forecast
Cost accounting [14]
Truck History
0-1背包问题(一)
MySQL授予用户指定内容的操作权限
C语言必背代码大全