当前位置:网站首页>[exercise-7] crossover answers
[exercise-7] crossover answers
2022-07-06 15:56:00 【Flame car】
Description
A crossword puzzle consists of a rectangular grid of black and white squares and two lists of definitions (or descriptions).
One list of definitions is for “words” to be written left to right across white squares in the rows and the other list is for words to be written down white squares in the columns. (A word is a sequence of alphabetic characters.)
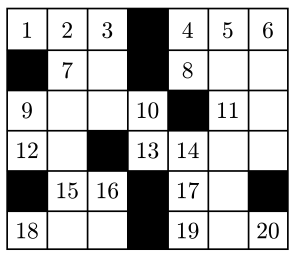
To solve a crossword puzzle, one writes the words corresponding to the definitions on the white squares of the grid.
The definitions correspond to the rectangular grid by means of sequential integers on “eligible” white squares. White squares with black squares immediately to the left or above them are “eligible.” White squares with no squares either immediately to the left or above are also “eligible.” No other squares are numbered. All of the squares on the first row are numbered.
The numbering starts with 1 and continues consecutively across white squares of the first row, then across the eligible white squares of the second row, then across the eligible white squares of the third row and so on across all of the rest of the rows of the puzzle. The picture below illustrates a rectangular crossword puzzle grid with appropriate numbering.
An “across” word for a definition is written on a sequence of white squares in a row starting on a numbered square that does not follow another white square in the same row.
The sequence of white squares for that word goes across the row of the numbered square, ending immediately before the next black square in the row or in the rightmost square of the row.
A “down” word for a definition is written on a sequence of white squares in a column starting on a numbered square that does not follow another white square in the same column.
The sequence of white squares for that word goes down the column of the numbered square, ending immediately before the next black square in the column or in the bottom square of the column.
Every white square in a correctly solved puzzle contains a letter.
You must write a program that takes several solved crossword puzzles as input and outputs the lists of across and down words which constitute the solutions.
Input
Each puzzle solution in the input starts with a line containing two integers r and c (1≤r≤10 and 1≤c≤10), where r (the first number) is the number of rows in the puzzle and c (the second number) is the number of columns.
The r rows of input which follow each contain c characters (excluding the end-of-line) which describe the solution. Each of those c characters is an alphabetic character which is part of a word or the character ‘*’, which indicates a black square.
The end of input is indicated by a line consisting of the single number ‘0’.
Output
Output for each puzzle consists of an identifier for the puzzle (puzzle #1:, puzzle #2:, etc.) and the list of across words followed by the list of down words. Words in each list must be output one-per-line in increasing order of the number of their corresponding definitions.
The heading for the list of across words is ‘Across’. The heading for the list of down words is ‘Down’.
In the case where the lists are empty (all squares in the grid are black), the ‘Across’ and ‘Down’ headings should still appear.
Separate output for successive input puzzles by a blank line.
The main idea of the topic :
Is to output strings in order , The end condition of this string is that * Or to the line ( Column ) Ending . And the number at the first letter position should be output before outputting the string , The rule of row number is the first row and the first column as long as it is not * Just count , Others, if there is * We should also count .
AC CODE:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int r,c;
int main()
{
int time=1;
while(cin>>r && r)
{
char a[15][15]={
0};
int sign[15][15]={
0},ed[15][15]={
0},cnt=0,ord=0;
cin>>c;
for(int i=1;i<=r;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=c;j++)
{
cin>>a[i][j];
if(a[i][j]!='*')
if(i==1||j==1||a[i][j-1]=='*'||a[i-1][j]=='*')
sign[i][j] = ++cnt;
}
cout<<"puzzle #"<<time<<":"<<endl;
cout<<"Across"<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=r;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=c;j++)
{
while(a[i][j]=='*') j++;
if(j>c) continue;
if(sign[i][j]<10) cout<<" "<<sign[i][j]<<".";
else cout<<" "<<sign[i][j]<<".";
while(j<=c && a[i][j]!='*')
{
cout<<a[i][j];
j++;
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<"Down"<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=r;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=c;j++)
{
while(sign[i][j]==0||ed[i][j]) j++;
if(j>c) continue;
if(sign[i][j]<10) cout<<" "<<sign[i][j]<<".";
else cout<<" "<<sign[i][j]<<".";
int ii=i;
while(ii<=r && a[ii][j]!='*')
{
ed[ii][j]=1;
cout<<a[ii][j];
ii++;
}
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
time++;
}
return 0;
}
Break it down :
The first part :
for(int i=1;i<=r;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=c;j++)
{
cin>>a[i][j];
if(a[i][j]!='*')
if(i==1||j==1||a[i][j-1]=='*'||a[i-1][j]=='*')
sign[i][j] = ++cnt;
}
This is to arrange the numbers according to the regulations , Input at the same time you can finish . Pretty simple , Should be able to see .
The second part :
for(int i=1;i<=r;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=c;j++)
{
while(a[i][j]=='*') j++;
if(j>c) continue;
if(sign[i][j]<10) cout<<" "<<sign[i][j]<<".";
else cout<<" "<<sign[i][j]<<".";
while(j<=c && a[i][j]!='*')
{
cout<<a[i][j];
j++;
}
cout<<endl;
}
Traverse the output ... I feel this step is relatively easy to understand .
The third part :
for(int i=1;i<=r;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=c;j++)
{
while(sign[i][j]==0||ed[i][j]) j++;
if(j>c) continue;
if(sign[i][j]<10) cout<<" "<<sign[i][j]<<".";
else cout<<" "<<sign[i][j]<<".";
int ii=i;
while(ii<=r && a[ii][j]!='*')
{
ed[ii][j]=1;
cout<<a[ii][j];
ii++;
}
cout<<endl;
}
This part may be more difficult , In fact, it's still two floors for The output of the loop , But if you find the starting position of the string , Keep looking down , And mark , Then when you scan this character again, it will not be output repeatedly .
details :
① Remember the label puzzle Changes
② Finally, output one more carriage return
③ It's strange that I use OJ The superscript should keep three positions , Such as :()()1.AB ()10.WUD
边栏推荐
- Nodejs+vue online fresh flower shop sales information system express+mysql
- 洛谷P1102 A-B数对(二分,map,双指针)
- Accounting regulations and professional ethics [5]
- Truck History
- 渗透测试 ( 3 ) --- Metasploit Framework ( MSF )
- Opencv learning log 16 paperclip count
- Cost accounting [17]
- 用C语言写网页游戏
- Opencv learning log 19 skin grinding
- B - 代码派对(女生赛)
猜你喜欢
Matlab comprehensive exercise: application in signal and system
Learning record: how to perform PWM output
信息安全-安全编排自动化与响应 (SOAR) 技术解析
Learning record: use STM32 external input interrupt
信息安全-威胁检测-NAT日志接入威胁检测平台详细设计

STM32 how to use stlink download program: light LED running light (Library version)

动态规划前路径问题优化方式
用C语言写网页游戏
![MySQL import database error [err] 1273 - unknown collation: 'utf8mb4_ 0900_ ai_ ci’](/img/e6/f4a696179282fe1f4193410c5a493a.png)
MySQL import database error [err] 1273 - unknown collation: 'utf8mb4_ 0900_ ai_ ci’
![[analysis of teacher Gao's software needs] collection of exercises and answers for level 20 cloud class](/img/3b/dc43564a36f82e73826b08f39c935e.png)
[analysis of teacher Gao's software needs] collection of exercises and answers for level 20 cloud class
随机推荐
China's salt water membrane market trend report, technological innovation and market forecast
Cost accounting [22]
【练习-10】 Unread Messages(未读消息)
Market trend report, technical innovation and market forecast of geosynthetic clay liner in China
信息安全-威胁检测引擎-常见规则引擎底座性能比较
Opencv learning log 12 binarization of Otsu method
Market trend report, technical innovation and market forecast of lip care products in China and Indonesia
Accounting regulations and professional ethics [3]
Research Report of cylindrical grinder industry - market status analysis and development prospect forecast
Shell脚本编程
【练习-9】Zombie’s Treasure Chest
Record of brushing questions with force deduction -- complete knapsack problem (I)
CEP used by Flink
Cost accounting [21]
渗透测试 ( 4 ) --- Meterpreter 命令详解
STM32 learning record: LED light flashes (register version)
mysql导入数据库报错 [Err] 1273 – Unknown collation: ‘utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci’
差分(一维,二维,三维) 蓝桥杯三体攻击
Research Report on market supply and demand and strategy of China's Medical Automation Industry
China's PCB connector market trend report, technological innovation and market forecast