当前位置:网站首页>一万字彻底学会堆和二叉树
一万字彻底学会堆和二叉树
2022-06-11 09:15:00 【命由己造~】
堆
一、堆的基本概念
堆(heap)是计算机科学中一类特殊的数据结构的统称。堆通常是一个可以被看做一棵树的数组对象。
两个性质:
1️⃣堆中某个结点的值总是不大于或不小于其父结点的值;
2️⃣堆总是一棵完全二叉树。
所以堆要么是大堆要么是小堆
1.1完全二叉树
一棵深度为k的有n个结点的二叉树,对树中的结点按从上至下、从左到右的顺序进行编号,如果编号为i(1≤i≤n)的结点与满二叉树中编号为i的结点在二叉树中的位置相同,则这棵二叉树称为完全二叉树。
二、大堆和小堆
根据堆的两个性质可以分为大堆和小堆
大堆(父亲大于孩子):
小堆(父亲小于孩子):
三、堆的公式
假设父亲的下标是parent
leftchild = 2 * parent + 1;
rightchild = leftchild + 1;
假设孩子的下标是child(不管左右)
parent = (child - 1) / 2.
四、向下调整算法
现在我们要调小堆
前提条件:左子树和右子树都是小堆,而整棵树不是小堆
用图来演示过程:
void Swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
//向下调整
//小堆
void AdjustDown(int a[], int n, int parent)
{
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < n)
{
if (child + 1 < n && a[child] > a[child + 1])
{
child++;
}
if (a[child] < a[parent])
{
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int a[] = {
27, 15, 19, 18, 28, 34, 65, 49, 25, 37 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
AdjustDown(a, sz, 0);
return 0;
}
如果要建大堆,就把两个大于小于号逆置
五、建堆
上面的向下调整算法必须要满足左子树和右子树都是小堆,但是如果不满足这个条件就需要建堆
如图右子树就不满足小堆
从下向上建堆:
从倒数第一个非叶子节点(28),从后往前,依次向下调整。
建堆的时间复杂度为O(N)
28处节点求法(n个数字):
(n - 1 - 1)/ 2
//建堆
for (int i = (sz - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(a, sz, i);
}
六、堆排序(易错)️️
排升序建大堆,排降序建小堆
如果反过来时间复杂度就为O(N^2),而且父子关系全乱了
排降序思路:
选小的放数组后面,依次选次小的
方法:
建小堆,交换收尾元素,不把尾元素看成堆里面的,再向下调整(其他都是小堆),就能选出次小的……
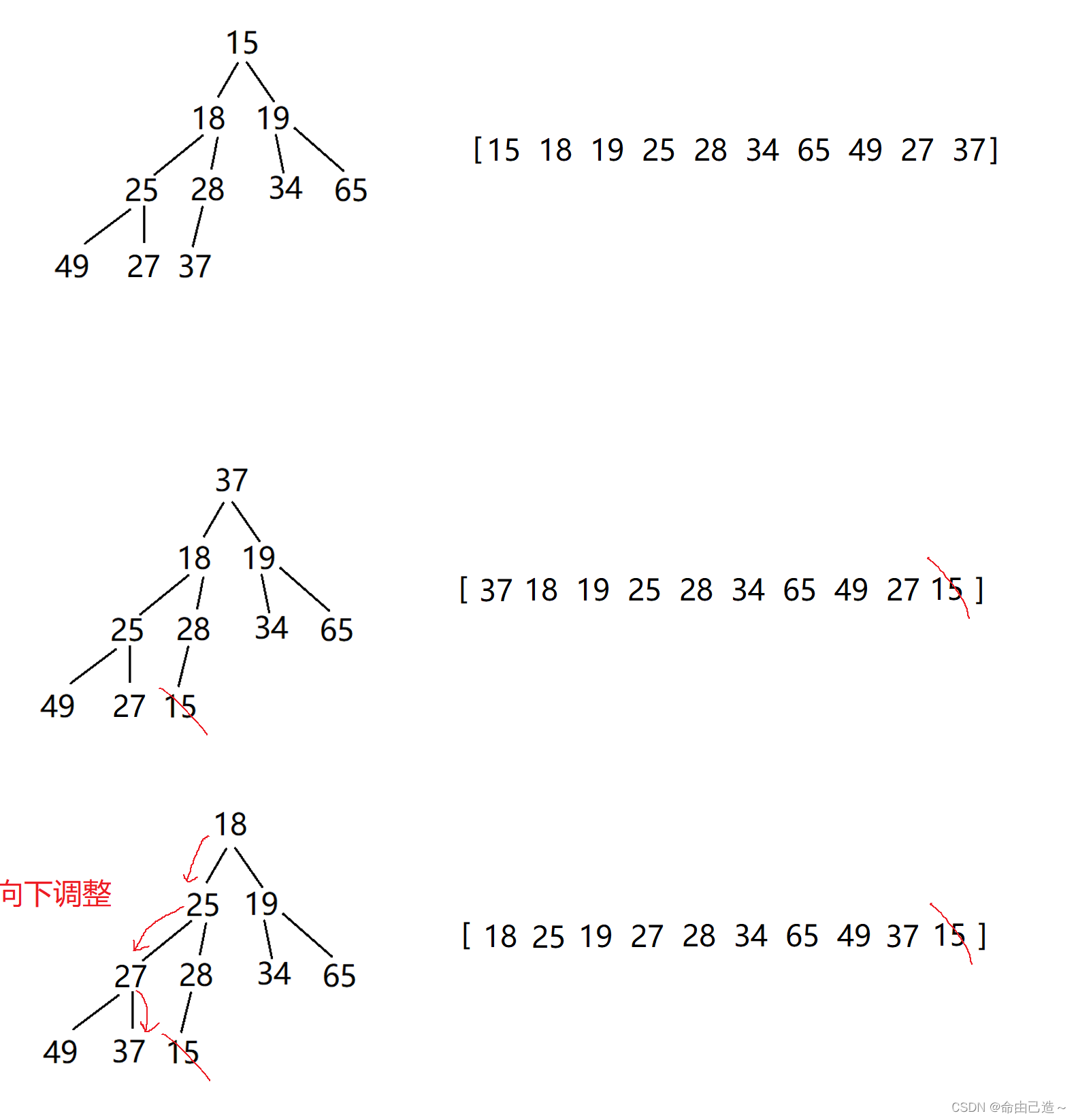
依次把数组元素向前调整,调完以后都是小堆。
这样时间复杂度为O(N * logN),(建堆 * 向下调整)
void HeapSort(int a[], int n)
{
//建小堆(降序)
for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(a, n, i);
}
int end = n - 1;
while (end)
{
Swap(&a[0], a[end]);
AdjustDown(a, end, 0);
end--;
}
}
七、堆的接口实现
接口预览:

堆的结构
typedef int HPDataType;
struct Heap
{
HPDataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
};
typedef struct Heap HP;
7.1堆的初始化
void HeapInit(HP* php, HPDataType* a, int n)
{
assert(php);
php->a = (HPDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HPDataType) * n);
if (php->a == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
memcpy(php->a, a, n * sizeof(HPDataType));
php->size = php->capacity = n;
//建堆
for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(php->a, php->size, i);
}
}
7.2堆的销毁
void HeapDestroy(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
free(php->a);
php->a = NULL;
php->size = 0;
php->capacity = 0;
}
7.3堆的插入
插入的时候注意判断是否满
void HeapPush(HP* php, HPDataType x)
{
assert(php);
if (php->size == php->capacity)
{
HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->a, sizeof(HPDataType) * php->capacity * 2);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
php->a = tmp;
php->capacity *= 2;
}
php->a[php->size] = x;
php->size++;
//向上调整
AdjustUp(php->a, php->size - 1);
}
插入完后要调整为小堆(或大堆),采取向上调整算法
void AdjustUp(int* a, int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child)
{
if (a[parent] > a[child])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
7.4堆的删除
删除首先把首尾元素交换,删除尾,再把首元素向下调整
void HeapPop(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
assert(php->size > 0);
Swap(&php->a[0], &php->a[php->size - 1]);
php->size--;
AdjustDown(php->a, php->size, 0);
}
7.5返回堆顶元素
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
assert(php->size > 0);
return php->a[0];
}
7.6堆的大小
int HeapSize(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
return php->size;
}
7.7判断是否为空
bool HeapEmpty(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
return php->size == 0;
}
7.8打印堆
打印堆用条件控制形状
void HeapPrint(HP* php)
{
assert(php);
int row = 0;
for (row = 1; row < php->size; row++)
{
if ((int)(pow(2, row) - 1) / php->size != 0)
{
break;
}
}
int col = (int)pow(2, row - 1);
int i = 0;
int k = 0;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
int j = 0;
//打印空格
for (j = 0; j < (col / 2) - i - 1; j++)
{
printf(" ");
}
for (j = 0; j < (int)pow(2, i); j++)
{
if (k >= php->size)
{
break;
}
printf("%d ", php->a[k++]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
效果图:
八、TopK问题️️

直接建堆用堆排序就可以做, 但是如果数据特别多,就会malloc非常多的节点,会出现问题。
所以我们可以只选前k个数建大堆,拿后边的所有数比较,如果堆顶元素大于后边的数,就让堆顶为这个数,再向下调整为大堆。最后的堆就是最小的k个数
/** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */
void Swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int tmp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = tmp;
}
//大堆
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)
{
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while(child < n)
{
if(child + 1 < n && a[child] < a[child + 1])
{
child++;
}
if(a[parent] < a[child])
{
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
int* getLeastNumbers(int* arr, int arrSize, int k, int* returnSize){
if(k == 0)
{
*returnSize = 0;
return NULL;
}
//取数前k个数
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * k);
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
a[i] = arr[i];
}
//建大堆
for(int i = (k - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(a, k, i);
}
for(int i = k; i < arrSize; i++)
{
if(a[0] > arr[i])
{
a[0] = arr[i];
AdjustDown(a, k, 0);
}
}
*returnSize = k;
return a;
}
二叉树
一、四种遍历顺序
1.1前序遍历
根→左→右
A→B→C→NULL→NULL→D→NULL→NULL→E→NULL→F→NULL→NULL
1.2中序遍历
左→根→右
NULL→C→NULL→B→NULL→D→NULL→A→NULL→E→NULL→F→NULL
1.3后序遍历
左→右→根
NULL→NULL→C→NULL→NULL→D→B→NULL→NULL→NULL→F→E→A
1.4层序遍历
一层一层走
A→B→E→C→D→F
二、二叉树的接口实现
2.1前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%c ", root->val);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}
2.2中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->val);
InOrder(root->right);
}
2.3后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->val);
}
2.4求节点个数
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
2.5求叶子节点个数
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
2.6求第K层节点️️
求当前树的第K层的节点可以看成求(从第二层看)第K-1层的节点个数……求(从第K层看)第1层节点个数
int TreeLevelSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
return TreeLevelSize(root->left, k - 1) + TreeLevelSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
2.7寻找目标节点️️
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (root->val == x)
{
return root;
}
BTNode* left = TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (left)
{
return left;
}
BTNode* right = TreeFind(root->right, x);
if (right)
{
return right;
}
return NULL;
}
2.8二叉树的销毁️️
后序遍历销毁节点:先销毁左树再销毁右树再销毁自己
2.8.1一级指针
void TreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
TreeDestroy(root->left);
TreeDestroy(root->right);
free(root);
}
A = NULL;
如果用一级指针就要在调用销毁函数后边把指针置空。
2.8.2二级指针
void TreeDestroy(BTNode** pproot)
{
if (*pproot == NULL)
{
return;
}
TreeDestroy(&(*pproot)->left);
TreeDestroy(&(*pproot)->right);
free(*pproot);
*pproot = NULL;
}
三、深度优先广度优先遍历️️
3.1深度优先遍历
就是从图中一个未访问的顶点开始,沿着一条路一直走到底,然后从这条路尽头的节点回退到上一个节点,再从另一条路开始走到底…,不断递归重复此过程,直到所有的顶点都遍历完成,它的特点是不撞南墙不回头,先走完一条路,再换一条路继续走。
二叉树的前中后序遍历就是深度优先遍历
3.2广度优先遍历
广度优先遍历,指的是从图的一个未遍历的节点出发,先遍历这个节点的相邻节点,再依次遍历每个相邻节点的相邻节点。
二叉树的层序遍历就是广度优先遍历
3.3层序遍历的实现
首先确定用队列实现
1.先把根入队列

2.出队头数据,带入下一层数据

先引入写好的队列:一万字彻底学会栈和队列
void TreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%c ", front->data);
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
3.4判断是否为完全二叉树
用两个二叉树来总结规律:
可以看出完全二叉树层序遍历只要出现NULL,后边的都为NULL;
不是完全二叉树的NULL后边会有不为NULL的节点
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front == NULL)
{
break;
}
else
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* cur = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (cur)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
边栏推荐
- Talk about reading the source code
- Flask (I) - quick start
- [scheme design] scheme of household oximeter based on single chip microcomputer
- Résumé de la méthode d'examen des mathématiques
- 2161. 根据给定数字划分数组
- ESP8266_SNTP(Simple Network Time Protocol)
- [scheme development] sphygmomanometer scheme pressure sensor sic160
- 报错ModularNotFoundError: No module named ‘find_version’
- Customize PCBA scheme and develop wrist sphygmomanometer scheme
- Flask (VI) - template
猜你喜欢

Day44 database

Blinn Phong reflection model

Method (common method), method execution memory analysis, method overloading mechanism, method recursion

Talk about how to customize data desensitization
affair

The first TOF related data set available for deep learning: deep learning for confidence information in stereo and TOF data fusion (iccv 2017)

keyboard entry.
报错Version mismatch between installed depthai lib and the required one by the scrip.

Version mismatch between installed deeply lib and the required one by the script

How do we connect to WiFi?
随机推荐
js中关键字this的理解
MySQL:Got a packet bigger than ‘max_ allowed_ packet‘ bytes
12.5 concurrent search + violent DFS - [discovery ring]
Type-C Bluetooth speaker single port rechargeable OTG solution
MSF SMB based information collection
document对象
Output image is bigger (1228800b) than maximum frame size specified in properties (1048576b)
[image processing] spatial domain image enhancement
报错[DetectionNetwork(1)][warning]Network compiled for 6 shaves,maximum available 10,compiling for 5 s
When the enterprise makes a decision, which part should lead the ERP project?
关于原型及原型链
[software] ten skills to maximize the value of ERP system
ESP8266_接入百度物联网核心套件、使用MQTT协议通信
Method (common method), method execution memory analysis, method overloading mechanism, method recursion
[share] how do enterprises carry out implementation planning?
[scheme development] scheme of infrared thermometer
Analysis of Kube scheduler disk scheduling source code
ESP8266_通过MQTT协议连接阿里云
考研數學 【數列極限證明題】題型方法總結
Openstack explanation (24) -- registration of neutron service

