当前位置:网站首页>new和delete的底层原理以及模板
new和delete的底层原理以及模板
2022-07-07 21:59:00 【__cplusplus】
本文主要内容:
- new和delete的底层原理
- 什么是模板
- 模板怎么使用
- 模板可以声明定义在两个文件里面吗?
new和delete的底层原理
前面我们谈了new和delete的使用,以及和C语言里面malloc和free的差别。但是,new和delete对于内置类型的处理却和malloc和free非常类似。那么不免引起我们的思考:这个new和delete的底层是如何实现的?这个底层实现和malloc还有free之间的关系是怎么样的?
首先我们先来看new的底层原理:
int main()
{
int* pa=new int;
return 0;
}
在调试模式下转到反汇编,观察对应的汇编语言: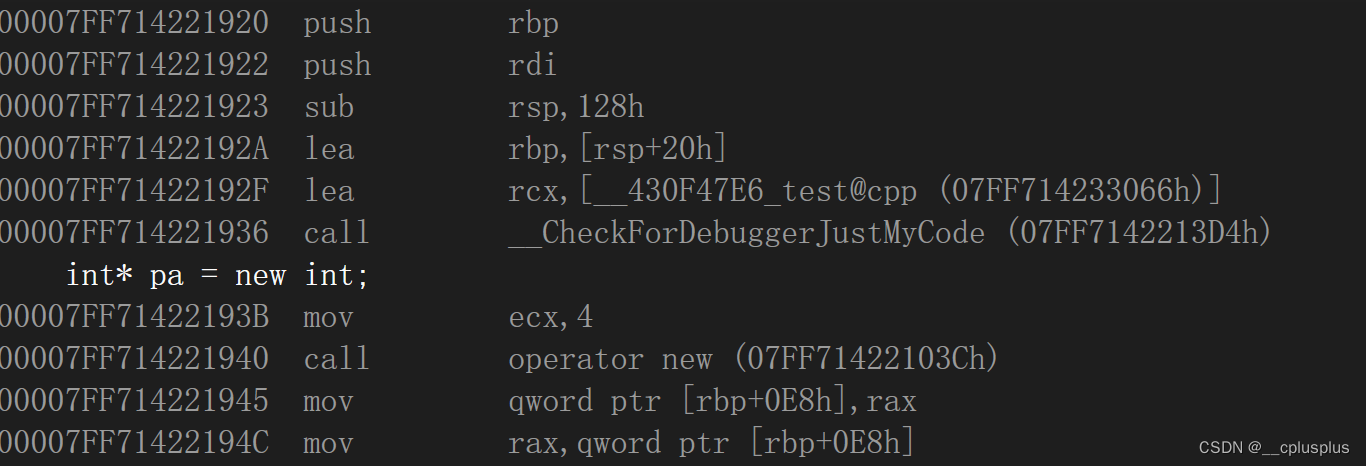
这里我们看到,我们调用了new运算符。而编译器在转换的时候调用了一个函数:opreator new的一个函数,而这个函数恰恰就是new的底层实现!
我们来看一看operator new函数的源代码实现:
void *__CRTDECL operator new(size_t size) _THROW1(_STD bad_alloc)
{
// try to allocate size bytes
void *p;
while ((p = malloc(size)) == 0)
if (_callnewh(size) == 0)
{
// report no memory
static const std::bad_alloc nomem;
_RAISE(nomem);
}
return (p);
}
从这份源代码可以看出,operator new函数本质也是封装了malloc的函数,并且当申请内存空间失败的时候不再是返回NULL,而是抛出异常!可以这么简单认为,operator new函数就是失败抛出异常的malloc!
所以new的工作原理就是这样:
底层调用operator new函数进行空间的申请,申请到空间以后,调用对应的类的构造函数进行初始化
类似的,delete的底层实现原理调用的就是operator delete函数,对应的就是封装了free的函数。
注意:这里的operator new并不是对new的重载!这点经常会误导人!这个operator new是一个单独的函数,如果需要调用就要显式写出opreator new!
//显示调用operator new
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int* pa = new int;
//显式调用必须这样!
void* pa = operator new(sizeof(int));
return 0;
}
operator delete的源码:
void operator delete(void* pUserData)
{
_CrtMemBlockHeader* pHead;
RTCCALLBACK(_RTC_Free_hook, (pUserData, 0));
if (pUserData == NULL)
return;
_mlock(_HEAP_LOCK); /* block other threads */
__TRY
/* get a pointer to memory block header */
pHead = pHdr(pUserData);
/* verify block type */
_ASSERTE(_BLOCK_TYPE_IS_VALID(pHead->nBlockUse));
_free_dbg(pUserData, pHead->nBlockUse);
__FINALLY
_munlock(_HEAP_LOCK); /* release other threads */
__END_TRY_FINALLY
return;
}
C++官方库对应还有operator new[]函数,感兴趣的可以自行去了解,这里不再多提。
什么是模板
我们知道C++具有面向对象程序设计的思想,其中最经典的就是C++的泛型编程,而模板就是实现泛型编程的前提条件。那么我们先来想一想什么是模板?
首先,我们日常做实验报告。对应的老师都会要求我们按照一定的格式进行书写。通常老师都会发一份样例给我们进行参考,这个样例就是模板
模板的使用
在联系我们在学习C语言的时候,C语言的一些不足之处。
首先C语言第一点不足的地方就是不支持重载,比如我们写一个swap函数,我们就要为不同的类型起不同的名字
而C++语言提供了函数重载的机制,解决了我们不用再为函数起名字的苦恼.。但是这样仍然还是需要写很多冗余重复的代码。为了解决这样的问题。C++引入了模板的机制,把生成对应函数的工作交给了编译器而非程序员。
//模板的语法---->template关键字
//使用模板写swap函数
template<typename T>
void swap(T& a,T& b)
{
T tmp=a;
a=b;
b=tmp;
}
int main()
{
int a=2,b=1;
swap(a,b);
double c=1.0,d=2.0;
swap(c,d);
return 0;
}
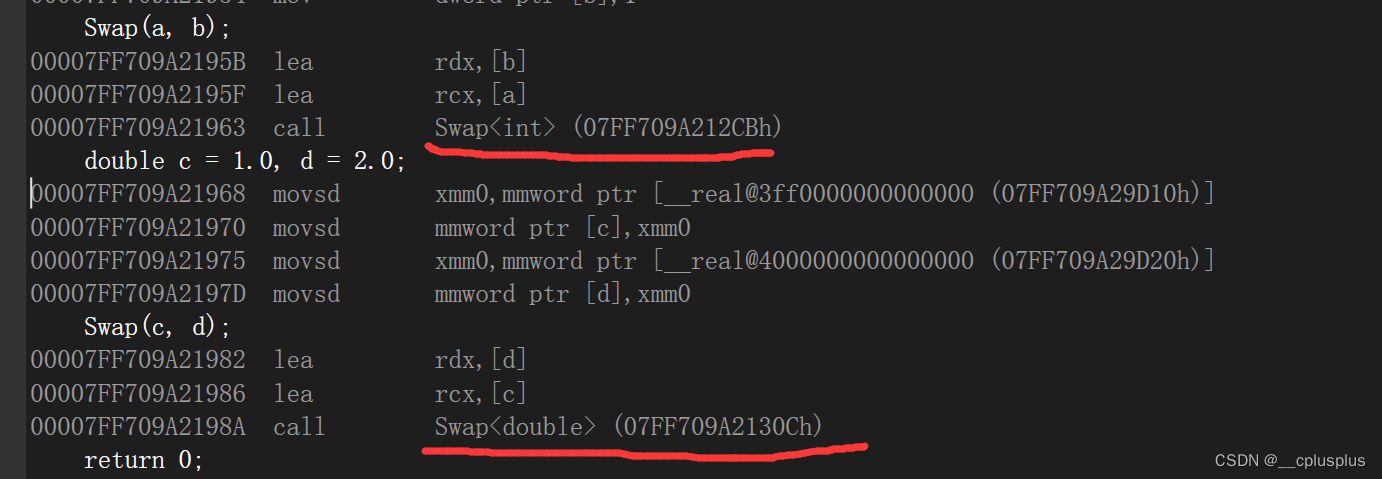
不难可以看出,编译器自动根据参数的类型推导出来了对应的Swap函数的版本!这里使用的模板是函数模板,可以根据参数类型自动推导需要生成的函数
那么在来看这么一个代码
int Add(const int x, const int y)
{
return x + y;
}
template<typename T>
T Add(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
Add(3, 2);
Add(3.0, 2.0);
return 0;
}
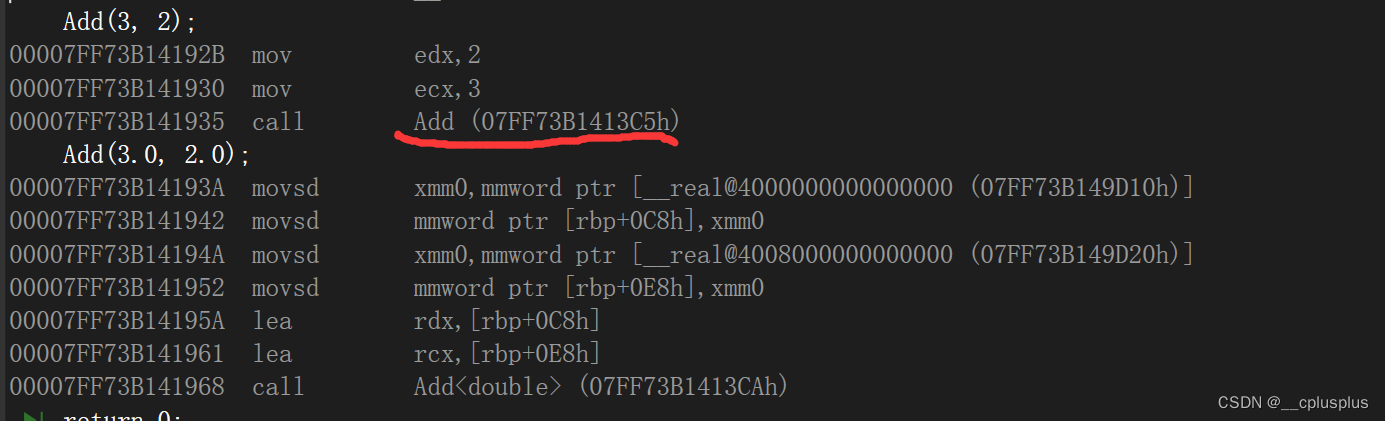
可以看到这里的第一个调用调用的是已经有的函数Add,而不是推演出来的。
也就是说,如果现有函数已经有可以满足调用需求的函数,编译器优先调用匹配的!找不到才会去考虑推演代码。
如果想要编译器推演,改造这样调用即可。
int Add(const int x, const int y)
{
return x + y;
}
template<typename T>
T Add(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
Add<int>(3, 2);//编译器就会去推演版本
Add(3.0, 2.0);
return 0;
}
这种模板叫做函数模板,还有一种模板叫做类模板。类模板在我们学习STL的时候会接触得更多!我们先来看类模板得语法定义
//类模板的使用
#include<iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
//尖括号里面也可以用class,但是绝对不能用struct
template<typename T>
class vector
{
public:
vector(size_t capacity=10)
: _a(new T[capacity])
,_size(0)
,_capacity(capacity)
{
}
private:
T* _a;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
};
int main()
{
//类模板必须显示提供推导的类型!
vector<int>v;
return 0;
}
那么有的时候也可以把声明和定义分离,不过这里的声明和定义分离仅限于声明和定义在同一个文件里面,这时候我们来看应该怎么处理
//同一个文件里面声明和定义分离
#include<iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
template<typename T>
class vector
{
public:
vector(size_t capacity=10)
: _a(new T[capacity])
,_size(0)
,_capacity(capacity)
{
}
void push_back(const T& e);
private:
T* _a;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
};
//分离定义还需要带上模板声明,
//并且所属的类域变成了vector<T>
template<typename T>
void vector<T>::push_back(const T& e)
{
_a[_size++] = e;
}
int main()
{
vector<int>v;
return 0;
}
模板可以声明定义在两个文件里面吗?
首先,先给出明确的答案:模板类的声明和定义不要放在两个文件里面!
为了验证这个做法,我们写两个文件vector.h ,vector.cpp来验证一下能否分离:
//vector.h 放声明
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
template<typename T>
class vector
{
public:
vector(size_t capacity = 10)
: _a(new T[capacity])
, _size(0)
, _capacity(capacity)
{
}
void push_back(const T& e);
private:
T* _a;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
};
//vector.cpp
#include "vector.h"
template<typename T>
void vector<T>::push_back(const T& e)
{
_a[_size++] = e;
}
template<typename T>
vector<T>::~vector()
{
delete[] _a;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
//main.cpp
#include "vector.h"
int main()
{
vector<int>v1;
vector<double>v2;
v1.push_back(1);
v2.push_back(2.0);
return 0;
}
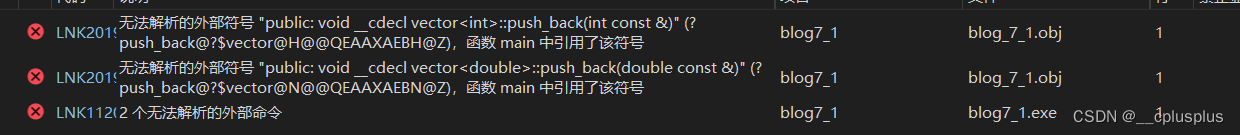
我们发现,发生了链接错误,我们来看一看为什么会出现链接错误
我们从调用的地方来看,函数调用最终在汇编代码层面会变成call一个地址,这个地址就是先前编译生成的符号表里面的函数地址。然而,模板只是一个空壳,**在编译完以后,vector.h和vector.cpp的符号表是空的!**因此,找不到对应的符号表里面函数的地址,所以发生链接错误!
解决方案:在vector.cpp文件里面显示实例化!
//显式实例化--->告诉编译器这么推导
template void vector<int>::push_back(const int& e);
//显式实例化
template void vector<double>::push_back(const double& e);
//显示实例化类
template class vector<int>;
template class vector<double>;
因为声明和定义分离在两个文件的成本很高,所以我们的推荐是不把模板类的声明和定义分离在两个文件里面,而且习惯把.h改成.hpp
总结:
- new和delete的底层原理是operator new/delete,这个是库函数而不是对new/delete的重载,可以理解成是失败抛出异常的malloc/free。
- 模板是泛型编程的基础
- 模板的语法
- 模板不支持声明和定义分离在两个文件里,成本非常高!
希望大家可以共同进步,如有不足之处还望指出。
边栏推荐
- Aitm3.0005 smoke toxicity test
- Codeworks 5 questions per day (average 1500) - day 8
- archery安装测试
- Introduction knowledge system of Web front-end engineers
- P1067 [noip2009 popularity group] polynomial output (difficult, pit)
- Chisel tutorial - 00 Ex.scala metals plug-in (vs Code), SBT and coursier exchange endogenous
- Magic fast power
- [leetcode] 20. Valid brackets
- [programming problem] [scratch Level 2] December 2019 flying birds
- QT and OpenGL: load 3D models using the open asset import library (assimp)
猜你喜欢
![[question de programmation] [scratch niveau 2] oiseaux volants en décembre 2019](/img/5e/a105f8615f3991635c9ffd3a8e5836.png)
[question de programmation] [scratch niveau 2] oiseaux volants en décembre 2019

BSS 7230 航空内饰材料阻燃性能测试

Data Lake (XV): spark and iceberg integrate write operations

Install sqlserver2019

HB 5469民用飞机机舱内部非金属材料燃烧试验方法
自动化测试:Robot FrameWork框架90%的人都想知道的实用技巧

如何衡量产品是否“刚需、高频、痛点”
Basic learning of SQL Server -- creating databases and tables with the mouse
PostGIS learning

UIC564-2 附录4 –阻燃防火测试:火焰的扩散
随机推荐
Kubectl 好用的命令行工具:oh-my-zsh 技巧和窍门
C - linear table
Robomaster visual tutorial (0) Introduction
【編程題】【Scratch二級】2019.12 飛翔的小鳥
关于组织2021-2022全国青少年电子信息智能创新大赛西南赛区(四川)复赛的通知
Install sqlserver2019
ROS from entry to mastery (IX) initial experience of visual simulation: turtlebot3
[the most detailed in history] statistical description of overdue days in credit
P1055 [noip2008 popularization group] ISBN number
Go learning notes (2) basic types and statements (1)
P1308 [noip2011 popularity group] count the number of words
C - Fibonacci sequence again
Database interview questions + analysis
Common selectors are
【编程题】【Scratch二级】2019.09 制作蝙蝠冲关游戏
Is it safe to buy funds online?
BSS 7230 flame retardant performance test of aviation interior materials
串联二极管,提高耐压
80% of the people answered incorrectly. Does the leaf on the apple logo face left or right?
PostGIS learning