当前位置:网站首页>Basic use of MySQL (it is recommended to read and recite the content)
Basic use of MySQL (it is recommended to read and recite the content)
2022-07-06 04:06:00 【'or 1 or improper bubble】
List of articles
Preface
Come out ~ This time, I finally sql A summary of the basic use of , There is a lot of content in it , The problematic part , You can leave a message , I will bring it out alone when I have time ( After all, this orientation is still centered on me , I think I can understand , Most people can understand )
This article is longer , Including common instructions , Concept , It is recommended to read and recite ~
First of all, it's about SQL The classification of sentences ,SQL There are four kinds of sentences ,DDL,DML,DQL,DCL. Next, let's talk about this operation around these .
Read the suggestions in this article , Please read in the following order
Then read this article , Of course, if there is a foundation, just come to review , Let's look at it directly ~
It's still an old suggestion about environmental preparation , If you are Windows Direct installation is not recommended mysql, You can use the inheritance development environment , for example phpstudy Or other database tools , If you are Linux System , It is recommended to install directly , If you have a graphical interface, you can also install integration tools , If not, install it directly mysql, And then use vscode or idea Just connect , Of course, other tools can also be used . You can also use the command line hardware , Suggest pip install mycli( A command line sql Artifact , It is recommended to install first python, If you are Linux Words built python3.x, But there should be no pip Installation tools , So you can consider installing pip Tools or directly apt install It's OK, too )
I've been clamoring to make a summary since summer vacation , Now it's finally here !
DDL
DDL Database definition language , Used to define this database , What does this data sheet look like . How about this table , Database creation .
Database creation
C(create) establish
Create database :create database yourdatabasename;There is judgment
create database if not exists yourdatabasename;Create database , Specify character set
create database name character set utf8;Case study
create database if not exists Huterox character set utf8;R(Retrieve) Inquire about
Query all
show databases;Query the creation statement of a database
show create database name;U(updata) modify
Modify character setalter database name character set Character set ;D(delete) Delete
Deletedrop database name;Judge
drop database if exists name;Use
Enter the database to useuse databasename;Query the currently used database name
select database();
Operate database tables
establish
Format
create table Table name ( Name ( Field name ), Name ( Field name ), Name ( Field name ), ... );Case study
create table student( id int, name varchar(32), age int, score double(4,1), birthdat date, insert_time timestamp );The created table looks like the existing table
create table A like B;Inquire about
Query all data tables
show tables;Check the description of this table
desc tablename;modify
Modify the name of the table
alter table Table name rename to Table name ( new );Modify character set
alter table Table name character set Character set ;Add a column ( Field name )
alter table Table name add Field name ( Name ) data type ;Change column names , type
Revise it together alter table Table name change Field name New field name type ; Just modify the properties alter table Table name modify Field name attributeDelete column
alter table Table name drop Field name ( Name )Delete
Case study
drop table if exists Table name
Antithetical CURD
The words here are actually operations on database tables , But there are two things here. One is DML, It is for database tables
CUD, increase , Change , Delete . The query is called DQL, This is also a complicated point , So it was disassembled separately .
DML
OK, now let's talk about this DML
Add data
insert into Table name ( Name , Name ...) value( value , value ...); insert into Table name value( The values of all fields );Delete data
delete from Table name [ Conditions ]; delete from A where id=1;details
If you want to delete everythingdelete from Table nameBut to do so , It's not good , He deleted one by one , So that's why
truncate table Table nameThis is like this
create table A like B; drop table B;Modifying data
update Table name set Name = value , Name 2= value 2 where Name = value ;for example :
update A set age=20 where name = Huterox;Similarly, if you don't add where Then all will be modified
DQL
This is our more important content ,
Let's first look at the format
select
Field name ,
Field name ,
...
from
Table name ,
Table name
where
Conditions
group by
grouping
having
Conditional operation after grouping
order by
Sort
limit
Sort
This is a complete operation , Of course, let's play with the simplest one first .
Single table operation
The simplest example
select * from A
Remove duplicate result sets
select distinct * from A
Simple operation
stay SQL It supports some simple direct operations , For example, direct summation , Of course, we also have aggregate functions , This, if you've seen that Pandas The basic use of the word should be to know how to play . And actually that Pandas Of DataFrame In fact, the structure of our data table is very similar .
select a,b,c,a+b from A
Suppose our table has a,b,c These three fields .
Of course, there is a detail here , If a,b One of them is null The sum there is null So we need to solve the problem of null value .
select IFNULL(a,0),IFNULL(b,0),c,a+b from A
If it does null, use 0 Instead of .
In addition, you can also give an alias
select IFNULL(a,0),IFNULL(b,0),c,a+b as sum from A
This as You can also use spaces instead of .
Then ours where I don't think I need to say more about this , Remember that one detail is here = No == That's about it , for example
select * from A where id>=20 and id=<30;
select * from A where id between 20 and 30;
Fuzzy query
In addition, we have fuzzy query
It is clear here that _ It's a place holder ,% yes N individual _ It means
Look at the examples and you will see
select * from A where name like '_ Happy %';
select * from A where name like ' Happy %';
select * from A where name like '__ Happy %';
Subquery
Of course, there is a sub query here
select name from student where id in (select id from score where math > 10);
It looks like this .
Then there is our order , Group query , Of course, there are paging , This part is in
SQL Injection problem Yes , Here is our aggregate function .
Aggregate functions : Calculate a column of data as a whole .
for example : Number of Statistics
select count(name) from A;
In addition, we have these functions ( Remember that these functions exclude null)
count
max
min
sum
avg
Then let's take a look at this constraint .
This is also more important .
constraint
First of all, our constraints are also divided into several categories .
Primary key constraint :primary key
Non empty constraint not null
Unique constraint unique
Foreign key constraints foreign key
There are also two ways to add constraints , One is to add
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(32) not null,
)charset=utf8;
The above three constraints are actually very simple , But we should pay attention to this foreign key operation , Because this foreign key involves our entire multi table operation , It is also a complex part of database operation .
Foreign keys
First of all, there are two ways to create this foreign key. One is to write it directly , What's more, it's added later
create table student
(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(32) not null,
constrain Name of the foreign key foreign key Foreign key column name references The name of another table ( Name )
)charset=utf8
First of all, we have to create two tables .
create table student(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(128),age int)charset=utf8;
create table class(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(128))charset=utf8;
Now we have created the table , So let's talk about cascading , These two operations are one .
Cascade concept
First of all, let's talk about , In the actual operation process , According to Alibaba's development manual, cascading of tables is forbidden , All related operations should be logically cascaded in the code . This is actually for safety , Of course, I just know now , Which of mine White Hole I don't know how many cascades are used .
The so-called cascade is actually very simple , Take an old example to understand . Student list and class list .
There must be a field in the student table for the class ID, So this class ID Whether the field needs to be constrained .
Use this constraint to limit the classes stored in the student table Id The content of the field . for example : In the class table ID There's no “A”, So obviously, the class is stored in the student table ID You can't appear in the field of “A” This value !
Next, let's demonstrate this specific operation .
Now let's create one class_id As our foreign key
alter table student add class_id int;
Then upgrade to foreign key
alter table student add constraint fg_class_id foreign key(class_id) references class(id);
Of course, if you want to delete it, do so
alter table student drop constraint fg_class_id;
Speaking of this, I'm going to talk about , Table relations , Now we actually implement a one to many relationship of a table
In fact, there are many to many , One-to-one relationship , These can be achieved through our foreign key cascade operation .
Table relations
One to many
Here we can directly use Django Of ORM As an example . stay sql Just set a foreign key directly in the statement .
One of its models is like this . That is our example here .
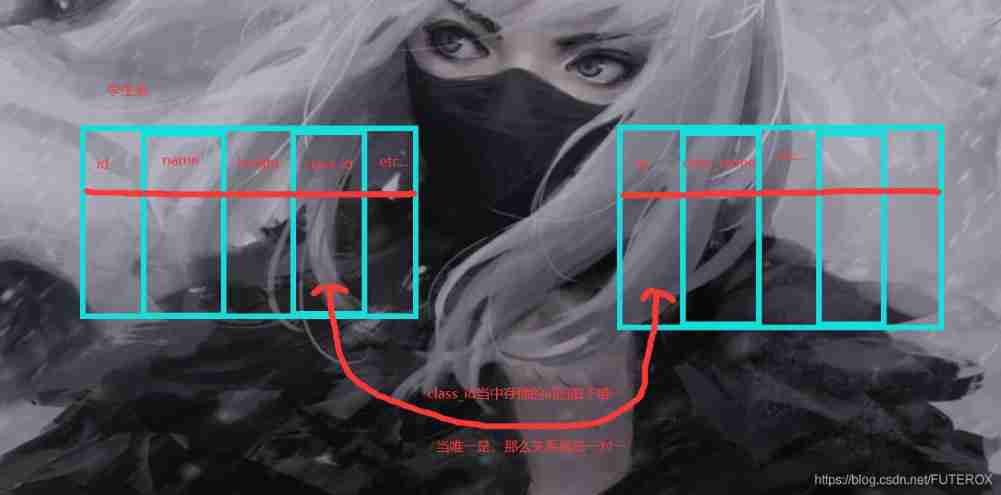

Besides, we are directly in Django Just do it inside ( Is it better than mybatis This semi-automatic frame is much more powerful )
Look at the code :
class Grade(models.Model):
g_name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
class Student(models.Model):
s_name = models.CharField(max_length=16)
s_grade = models.ForeignKey(Grade) # Add a foreign key constraint
one-on-one
Now use the relationship between ID card and people as an analogy  .
.
In our sql If you want to realize this function, you can do it like this
alter table student add constraint fg_class_id foreign key(class_id) references class(id);
alter table student add constraint fg_class_id_un unique(fg_class_id );
stay Django This is the case .
class Person(models.Model):
p_name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
class Person_id(models.Model):
p_id = models.CharField(max_length=32)
p_person = models.OneToOne(Person)
Many to many
We should pay attention to this , Because the operation is different .
So how is it realized , Let's start with an example , The relationship between shopping cart and people , This is a typical many to many .
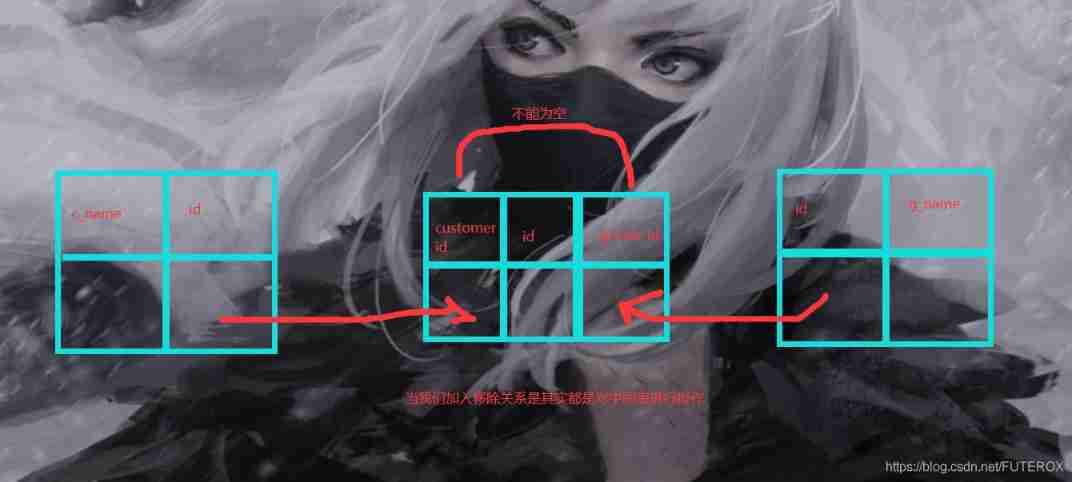
We need an intermediate table to realize .
Then there is the binding of foreign keys .
This is my one
SpringBoot + Vue( Blog upload with front and back end separation ) There are cases , How is that watch designed .
Of course, now that thing will be a demo play , Refactoring ~( This time I have to use all my skills java Technology stack ,python Technology stack , Later, based on flink Create a push system , As for which distributed system to choose springcloud Rely on , still k8s Well , This has to wait for me to make a good pit of the distribution , I don't believe I can't finish my sophomore next semester , When the time comes, it should be OK Of , Then we will focus on artificial intelligence ( In case it's not done , Take this as a backup solution ))
class Customer(model.Model):
c_name = models.CharField(max_length=16)
class Goods(models.Model):
g_name = models.CharField(max_length=16)
g_customer = models.MangToMangField(Customer)
Now we have built the model , So let's operate the model first , Later, let's talk about how this thing is made .
The query part is still the same as before , But there's an added relationship here , For example, we added a product in our shopping cart .
Phone = Goods()
Phone.g_name="iPhone12"
Phone.save()
Me = Customer.objects.get(c_name="xiaoming")
Me.goods_set.add(Phone)
.remove(Phone)
.set(Phone1,Phone2,...)
Of course, we can also turn the other way around , But in fact, these effects are the same , The reason is shown in the figure below .
So if you want to implement it yourself, you can also design it in this way , Even more complicated .
Master slave table
Having said that , The one with more mouth is the one with Django The problem in this table .
Every time this multi table relationship is involved, the problem of joint table relationship will appear , stay django For example, the ID card table in the relationship between person and ID card is from the table , When the main table is deleted , It will also be deleted from the table (delete on cascade), This is the default , So sometimes for data security , We should set up , For example, only when the corresponding data in the table is deleted , Then the main table can be deleted .( In fact, this is cascade operation )
class Person_id(models.Model):
p_id = models.CharField(max_length=32)
p_person = models.OneToOne(Person,ondetele=models.PROTECT)
Of course, there are other models
SETNULL
SET_DEFAULT()
SET()
Cascade operation
This thing is our master-slave table just now sql The embodiment inside , In fact, it is also our cascade operation . That's it ,
This is easy to understand, that is, the class Of ID Changed , Then the corresponding student's class ID Do you want to change , Of course, it can be implemented directly in the database , You can also use code , However, code implementation is recommended here , That is, put it in java Do it inside
Then add something to the database
alter table student add constraint fg_class_id foreign key(class_id) references class(id) on delete cascade on update cascade;
Use with caution ! Use with caution ! Use with caution ! The default is empty , That is, there will be no operation .
League table query
This joint table query actually integrates the contents of the two data tables , In fact, it is more vivid, that is, the relationship between the intersection and union of two sets , If we treat the results of each query statement as a collection .
There are three kinds of words here , inline , league of the left-wing writers , Right couplet .
In addition, it can be subdivided , Look at the picture below 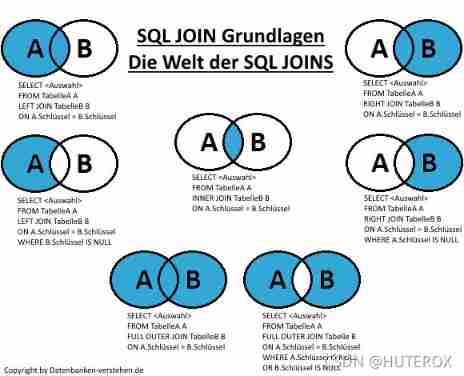
Here we mainly talk about the first three , Because the rest is nothing more than adding some conditions later .
Here's a formula
1. Specify the data to be queried ( Field )
2. Specify which tables to query
3. Define the screening criteria
Here's an example .
Suppose there is a class in the class A its Id yes 1
Query now A The name and age of the class .
select s.name,s.age
from student as s
inner join class as c
on s.class_id = c.id
where s.id=1;
Left / Right linked table
This is actually very simple , But the difference is actually the difference in the previous picture .
select s.name,s.age c.name
from student as s
left join class as c
on s.class_id = c.id
where s.id=1;
Suppose a classmate is not divided into classes , That is, there is no class ID that , At this point, we will find a c.name The value of is empty
That's it 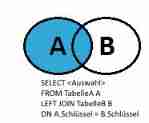
So the right couplet is also 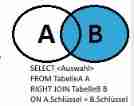
In fact, they are all very simple things , But it's important !
Multiple tables associated query
This is still the same , Let's assume that there is still a table
create table grade(id int primary key auto_increment
grade float,
student_id int,
foreign key(student_id) references student(id) )charset = utf8;
Now I need to find out the student's name , Age , Achievements in A In the class
select name,age,grade
from student as s inner join
class as c on s.class_id = c.id
inner join grade as g
where g.student_id = s.id and c.id=1;
Did you see? , The result of the left to right pairwise query is a left set
Here is the basic query . Want to see specific examples? There are also
Vue+SpringBoot Front and rear end separation practice (mybatisplus Multi table paging query + Blogs show ) ( Now? python,java There are all examples , Next time I'll have a look Go How do you play? )
Do you think this is over ?NO,NO, Here you guess to learn the most basic use , There's something else in the back , I'll say everything here .
Normal form constraint
Say something reasonable. , When designing database tables , Suggested constraints , requirement , Suggest .
Here you are 6 Big paradigm
- First normal form (1NF)
- Second normal form (2NF)
- Third normal form (3NF)
- buss - The COD paradigm (BCNF)
- Fourth normal form (4NF)
- The fifth paradigm (5NF, Also called perfect paradigm )
Like us, we basically follow the first three .
So let's talk about these paradigms
- First normal form (1NF) : Each column is indivisible
- Second normal form (2NF) : stay 1NF Based on the elimination of partial functional dependence on the main code
- Third normal form (3NF) : stay 2NF On the basis of , Any non primary attribute does not depend on other primary attributes
Case study
First normal form
First of all, this kind of graph is not satisfied with the first normal form
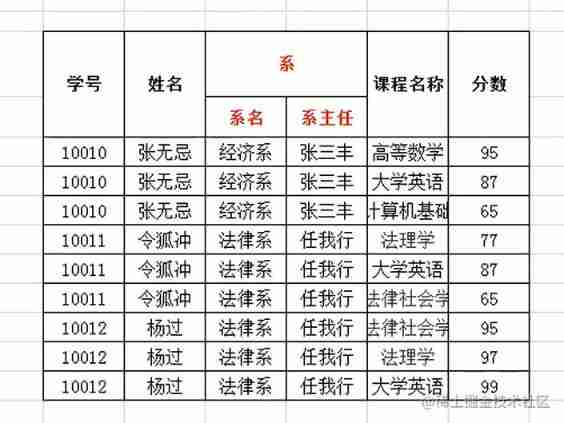
This column must be inseparable, so I have to change it like this
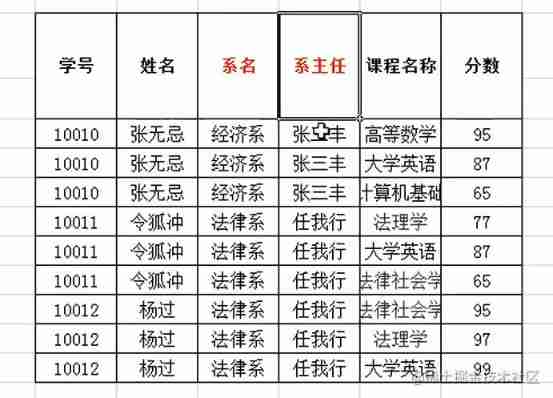
Second normal form
This is more abstract , Here we have to explain clearly the problem of functional dependency , for example A–> B
Student number Sure Confirm the name
( Student number , Course name ) Can be determined fraction
Use letters to indicate
A -> B Some functional dependencies
(A,B)->C Complete functional dependencies
Then the code here is ours (A),(A,B) Attribute group
Now if we want to conform to the second normal form, we need to remove the column that does not conform to this complete functional dependency , Put it somewhere else .
So after the transformation, it's like this
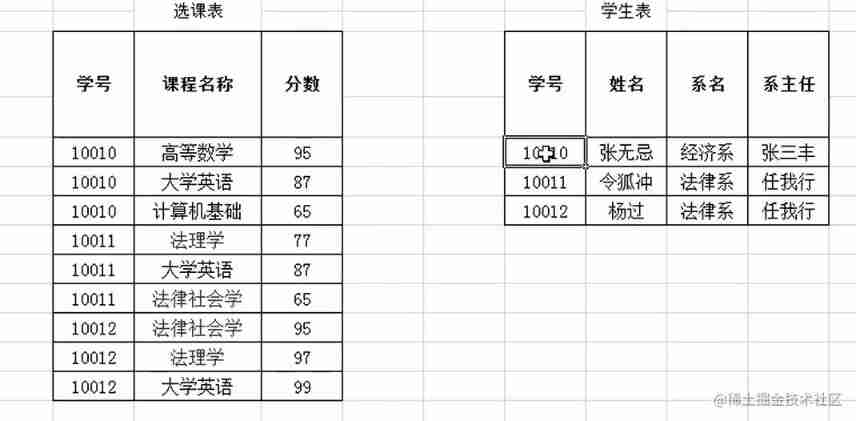
because full name , Department name , The dean of the Department
stay
(A,B)->C Among them, only A, or B Satisfaction is established , So we must split .
Third normal form
On the basis of the second paradigm , We split the course schedule , But there are still problems with the student table
Student number –> The dean of the Department
Department name –> The dean of the Department
That is to say
A–>C
B–>C
(A,B)->C
There was a previous problem , So we have to dismantle
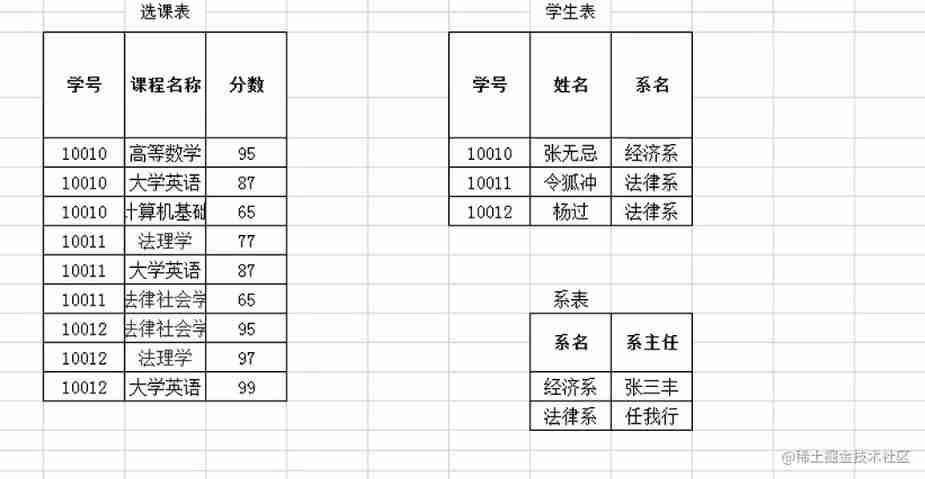
Now look at the student list
A,B,C It means the student number , full name , Department name
A->B
A->C
B,C It doesn't matter.
The removed tie table is also
So this satisfies the third paradigm , This is actually very complicated , But in fact, I think this convenient problem should be considered when designing , If for no other , I don't want redundant information when I check users , In this way, we have to deal with it in the code .
Backup and restore of database
Now let's talk about the backup and restore of this database , This also has tools or direct instructions
This and Redis The same backup is actually a backup statement .
mysqldump -u user name -p password The database that needs to be backed up > route ( preservation )
Restore
source Your one sql file
Then this is the backup and restore of the database , In fact, it's very simple , Then there are a few more operations for the database , One is that matter , Another is the view , There is also the one that writes sql Function stuff , Finally, it's our DCL, There is not much content in this part , Absolutely not DQL complex .
Business (trans action)
This transaction is actually an atomic operation , Some things cannot be separated , For example, having children , You have to have a girlfriend , Then you can have a wife , Then we can have children ( Of course, it's OK in theory to have no wife, but you have to have a woman , We speak according to normal ethics )
This baby , None of the above links can be omitted , One but less , Then this thing will fail , Then you have to start again , We call this rollback , So this matter is two , operation , Failure rollback .
( It is worth mentioning that it seems to be Redis There is no rollback of transactions )
Here to talk about , The four characteristics of affairs , And the things of transaction isolation .
It's tight , The business is : A series of things either all succeed , Or all gg.
Use format :
statrt transaction Open transaction
rollback Roll back
commit Submit
Now let's take a specific example , Suppose we have a banking system , Now I want to transfer money ( Zhang San , Li Si , Their amount is enough )
So let's do it first
start transaction; Use here begin; It's the same
update account set monery=monery-500 where name=' Zhang San ';
update account set monery=monery+500 where name=' Li Si ';
commit; If no exception is submitted
rollback; Otherwise, roll back
Here we use it again python Let's demonstrate .
import pymysql
# Establishing a connection
conn=pymysql.connect(
host='127.0.0.1',port=3306,user='Huterox',
passwd='865989840',db='huterox',charset='utf8'
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
try:
Sqlcomm = """insert into hello(name) value(%s)"""
cursor.execute(Sqlcomm,(" Xiaogang "))
conn.commit()# Submit
except pymysql.Error as err:
conn.rollback()# Roll back
print(err)
finally:
conn.close()
This completes our basic transaction operations (java It's too troublesome , It's directly used here python demonstration )
Transaction submission details
Here's a point to note , That is, we are implementing DML At the time of statement ,MYSQL It helps us automatically commit 了 , stay Oracle There is no default .

You can set up
Submit manually by yourself
set @@autocommit =0;
Then add one after each statement commit.
The four characteristics of affairs
Atomicity
The smallest non separable operating unit , All or nothing , Or fail all
persistence
commit rollback Are persistent
Isolation,
Transactions are independent of each other
Uniformity
The total amount of data before and after the transaction operation remains unchanged (A Transfer money to B, The total amount of money remains unchanged )
The isolation level of the transaction
Multiple transactions are independent of each other , However, if multiple transactions operate on the same batch of data at the same time, some problems will occur , You need to set the isolation level between transactions to solve the problem .
The following problems will arise here
- Dirty reading : A business , Read the uncommitted data in another transaction ( Data is not submitted but there is data cache )
- It can't be read repeatedly ( Virtual reading ): In the same transaction , The data read twice is different .
- Fantasy reading : A transaction operation (DML) All records in the data sheet , Another transaction adds a piece of data , As a result, the first query cannot be modified ( Missed reading )
stay mysql There are four isolation levels ( In fact, it is the strategy of multiple transaction submission , The reason for this problem is that we have multiple clients , It can be imagined as multithreading , In addition, the more problems solved , The slower the speed , for example serializable They locked the watch directly )
Isolation level :
- read uncommitted Read uncommitted
A strategy that arises from all three problems , But the processing efficiency is the highest - read committed After reading the submission (Oracle Default )
2,3 The problem can't be solved - repeatable read Repeatable (mysql Default )
Unreal reading cannot solve - serializable Serial call
all can ok
These are related to efficiency , It depends on what strategy you want to adopt .
Level operation
In this case, there are only two instructions
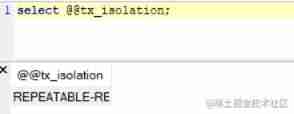
Query level
select @@tx_isolation;
Set up
set global transcation isolation level Level string ;
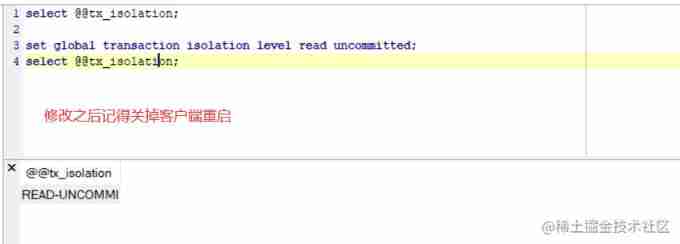
There will be no demonstration here , Considering the length , Then you can call Leaving a message. , I'm talking about this , Otherwise, that's it ~
So these are the parts about affairs
View
Then next is the part of our database view ~ How to understand this , In fact, that's what , Save our query results , In this case, you can take it directly next time , In addition, it can also play a role of permission isolation ( Say DCL You will know when ) This is actually a watch .
create view View name as Yours DQL sentence ;
And then in show tables; You can simply create it when view 了 , How to use this is actually a special watch , Improve your code efficiency . But there is one characteristic , That is, if the original data changes , Then your view table will also change ( Corresponding data ), It looks like this
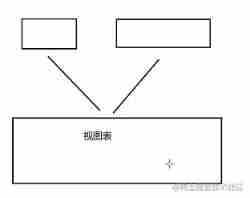
If you change the view chart, the original linked table will also be modified .
Delete words , Just directly
drop view View table name
stored procedure
This is what we said at the beginning about how to implement aggregate functions by ourselves , This thing (Stored Procedure) It's a complex program stored in a database , A database object that can be called by an external program , Stored procedures are designed to accomplish specific functions SQL Statements set , After compilation and creation, it is saved in the database ! Then the user calls the name of the stored procedure to execute the call .
To put it bluntly, it is actually equivalent to a function , however CURD The programmer , This should not be used often , I haven't used much , It may be my little demo It's too simple .
Before how to play , Let's talk about , Why this sql Statements are always ; The end can run , I don't want this ; Is the end ok . The answer is yes .
delimiter ; Set up ; For statement Terminator ( Default )
delimiter && Set up && For statement Terminator
Ok , This is easy to do .
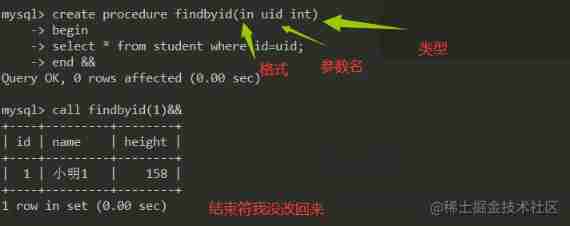
Now let's write a simple stored procedure .
There is such a watch
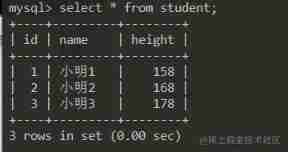
Now I want to write a function that can directly help me check the information of this table .
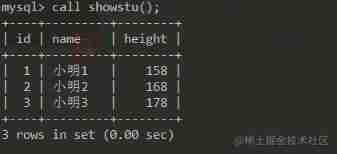
So I do this
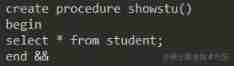
delimiter &&
create procedure showstu()
begin
select * from student;
end &&
delimiter ;
call showstd();
Then deleted
drop procedure showstu;
That's it .
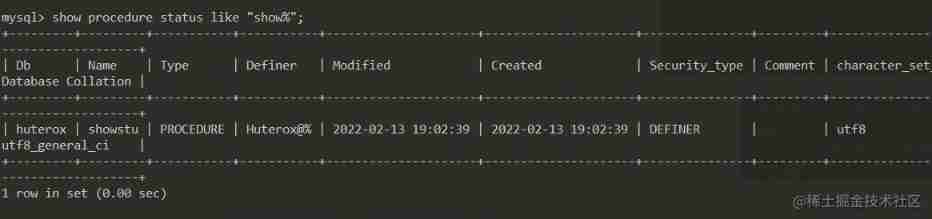
Looking for stored procedures
This is simple
show procedure status like "show%";
It also supports this fuzzy query
Besides
show create procedure showstu;
You can see what's inside
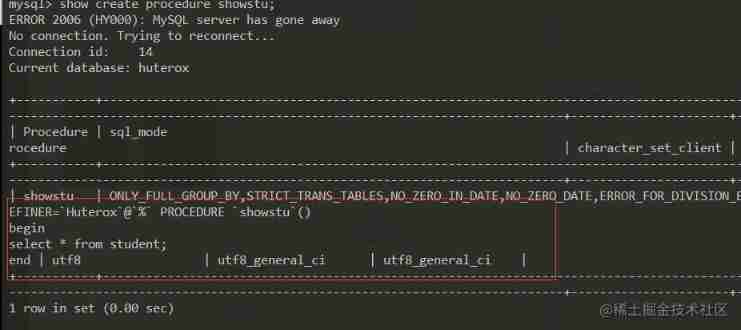
You can see that
The ginseng
This is not enough , What if I want to get information about a single classmate , Pass a id I can get a message . This is also very simple
Let's write a findbyid() This function
DCL
Finally, it's our last one , This is the management of our database , Permission statement , Of course, there are user created things , Just like the one at the beginning
mariadb(sql) Basic operation
Create user .
This is mainly for DBA Database administrator .
The content of this piece is actually us mariadb(sql) Basic operation Contents of user operation
User creation
The format of the basic instruction created is as follows :
create users 'usrname'@' Specify the user login address ' identified by'password';
# To view the user
select * from mysql.user;
for example :
create users 'Hello'@'localhost' identified by'abc123';
there 'localhost' It's local IP
'%' It means any IP
If you want to create a user who can connect remotely in the future, you can do this
create users 'Hello'@'%' identified by'abc123';
Change user password
If you accidentally forget your password , You can use another account with sufficient permissions to log in to the database to modify that account .
set password for 'Hello'@'%' = password('abcd123');
User deletion
drop usr 'Hello'@'%';
User permissions
When we create a user, we can use
show grants for 'Hello'@'localhost';
see
for example ;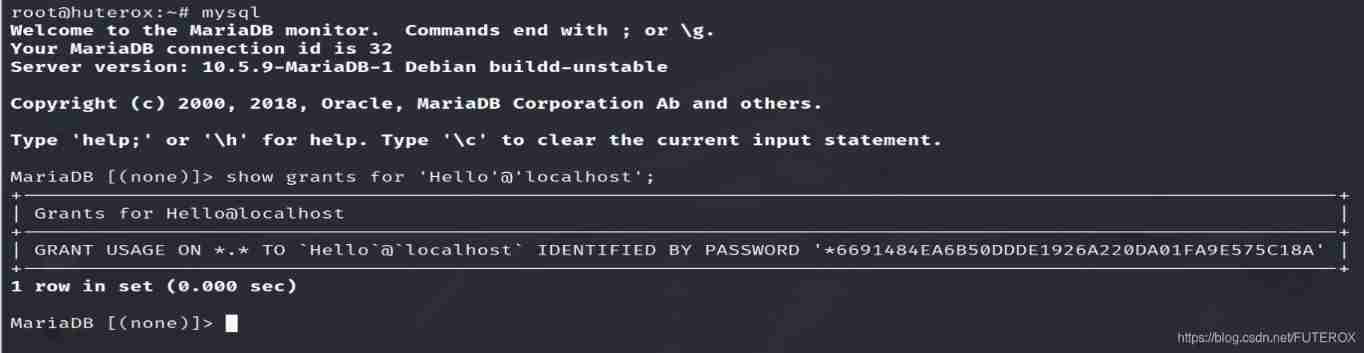
Authority modification
First, let's talk about the permissions ;
SELECT
INSERT
CREATE
DELECT
DROP
UPDATE
CRANT OPITON Permission to give other users permission ( The right to be someone else's father )
Now we give it except CREATEOPTION The right to
grant all privileges on *.* to Hello@localhost;
revoke GRANT OPTION on *.* from Hello@localhost;
flush privileges; Make the configuration work

Here I copied it directly .
summary
This is what I finally summed up after spending an afternoon mysql Basic use of , Basically, these are the common ones , There are still a lot of things , It is suitable for taking it to review , Or it's good to preview .
边栏推荐
- MySQL transaction isolation level
- Align items and align content in flex layout
- Prime protocol announces cross chain interconnection applications on moonbeam
- Use js to complete an LRU cache
- 颠覆你的认知?get和post请求的本质
- ESP32_ FreeRTOS_ Arduino_ 1_ Create task
- cookie,session,Token 这些你都知道吗?
- 10个 Istio 流量管理 最常用的例子,你知道几个?
- Record the pit of NETCORE's memory surge
- Detailed explanation of serialization and deserialization
猜你喜欢

Web components series (VII) -- life cycle of custom components

STC8H开发(十二): I2C驱动AT24C08,AT24C32系列EEPROM存储
C#(二十九)之C#listBox checkedlistbox imagelist
![[Key shake elimination] development of key shake elimination module based on FPGA](/img/47/c3833c077ad89d4906e425ced945bb.png)
[Key shake elimination] development of key shake elimination module based on FPGA
Record the pit of NETCORE's memory surge
《2022年中国银行业RPA供应商实力矩阵分析》研究报告正式启动
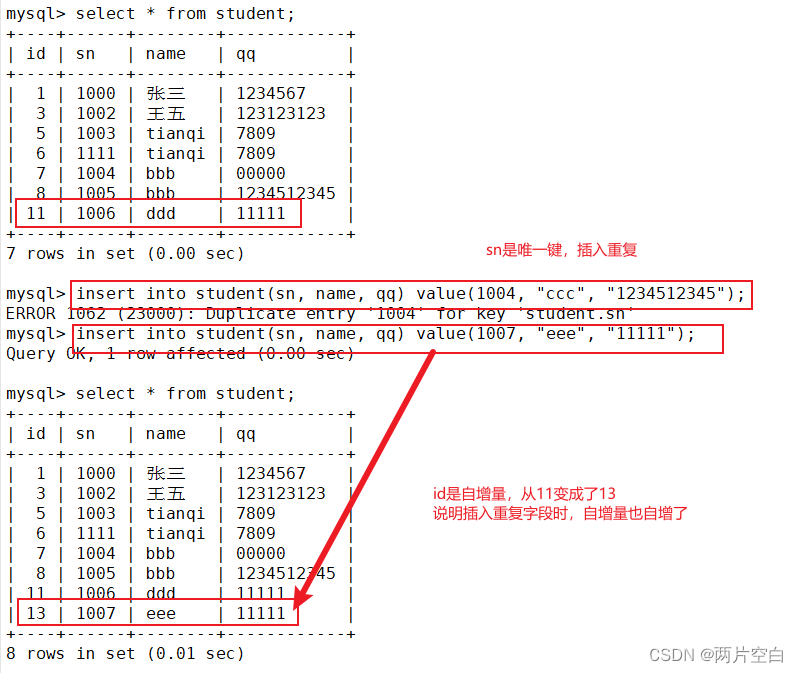
MySQL about self growth

C#(三十)之C#comboBox ListView treeView

食品行业仓储条码管理系统解决方案
Alibaba testers use UI automated testing to achieve element positioning
随机推荐
Oracle ORA error message
Python book learning notes - Chapter 09 section 01 create and use classes
KS003基于JSP和Servlet实现的商城系统
How can programmers resist the "three poisons" of "greed, anger and ignorance"?
Facebook and other large companies have leaked more than one billion user data, and it is time to pay attention to did
Simple blog system
【可调延时网络】基于FPGA的可调延时网络系统verilog开发
Blue Bridge Cup - Castle formula
2/10 parallel search set +bfs+dfs+ shortest path +spfa queue optimization
Web components series (VII) -- life cycle of custom components
Comprehensive ability evaluation system
[introduction to Django] 11 web page associated MySQL single field table (add, modify, delete)
How to standardize the deployment of automated testing?
在 .NET 6 中使用 Startup.cs 更简洁的方法
Codeforces Round #770 (Div. 2) B. Fortune Telling
MySQL about self growth
[FPGA tutorial case 11] design and implementation of divider based on vivado core
Cf464e the classic problem [shortest path, chairman tree]
What is the difference between gateway address and IP address in tcp/ip protocol?
MySQL transaction isolation level