What is a process ?
process (Process) It is an execution activity of a program in its own virtual address space . The reason to create a process , Just to make
Multiple programs can be executed concurrently , So as to improve the resource utilization and throughput of the system . Simply put, a process is the execution of a program .
What is the difference between a process and a program ?
Program : Just a static set of instructions ; A process is a dynamic execution process of a program , It has a life cycle , Is the dynamic production and extinction .
process : Is a resource request 、 Dispatch and independent operation unit , therefore , It uses running resources in the system ; And the program cannot apply for system resources 、 Cannot be scheduled by the system 、
Nor can it be used as an independent unit , therefore , It does not occupy the operating resources of the system .
Neither program nor process One correspondence . On the one hand, a program can be shared by multiple processes , That is, when a program is running, multiple processes can be generated ; On the other hand , A process can execute several programs in sequence during its lifetime .
Properties of the process
stay linux There are always many processes running in the system at the same time , Each process has an identification number , be called PID(Process ID), To distinguish different processes . Each process has a ID Number , Can pass ps The order shows
It can be used echo $$, see shell Hezi shell
[[email protected] ~]# echo $$ first $ On behalf of the variable , the second $ A variable's value , this $ On behalf of the current shell The process number of
2943
[[email protected]~]# bash Intron shell
[[email protected]~]# echo $$
2983 The process number is different from that of the parent process
View the system process tree
[[email protected]~]# pstree -p
systemd(1)─┬─ModemManager(909)─┬─{ModemManager}(938)
│ └─{ModemManager}(964)
systemd It is the first process that the system starts , Is the parent of all processes , Its process number is 1.
Usually killing a child process does not affect the parent process , Killing the parent process will affect the child process , and systemd This process cannot be killed , Unless shut down or restart .
Hard disk 、 process 、 Memory 、CPU The relationship between
One of the three illusions of life :QQ、 Storm video 、 Browsers, etc. can be executed together . Are processes executed in parallel . No more than that. . For a single CPU For the system, at a certain moment , Only one process can be in execution , occupy CPU Right to use , Other processes are in other States , Wait for system resources , Each process constantly switches between certain states according to the scheduling algorithm . But because CPU Faster processing efficiency , So that users can't feel the changes .
State of process
R (TASK_RUNNING), Executable state .
S (TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE), An interruptible sleep state
D (TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE), Uninterrupted sleep
T (TASK_STOPPED or TASK_TRACED), Pause state or trace state .
Z (TASK_DEAD - EXIT_ZOMBIE), Exit state , The process becomes a zombie process .
X (TASK_DEAD - EXIT_DEAD), Exit state , The process is about to be destroyed .
R (TASK_RUNNING), Executable state .
Running or ready : Ready status means that the process has applied for CPU All other resources except .
experiment :
Open Firefox browser and use top Command view status
S (TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE), An interruptible sleep state Light sleep
In the waiting line , Wake up when resources are available ( For example, wait for keyboard input 、socket Connect 、 Signals and so on
experiment :
Open Firefox browser and use top Command view status
D (TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE), Uninterrupted sleep Deep sleep
In the waiting line , Wake up when resources are available ( For example, wait for keyboard input 、socket Connect 、 Signals and so on ), But it cannot be awakened by interruption .
experiment :
Open Firefox browser and use top Command view status
T (TASK_STOPPED or TASK_TRACED), Pause state or trace state .
The process was suspended by an external program ( If received SIGSTOP The signal , The process goes into TASK_STOPPED state ), Continue to run when agreed again ( Process received SIGCONT The signal , Get into TASK_RUNNING state ).
Pause jobs Mission
Z (TASK_DEAD - EXIT_ZOMBIE), Exit state , The process becomes a zombie process . A dead state . Process resource user space is freed , But processes in the kernel PCB No release . Wait for the parent process to recycle
X (TASK_DEAD - EXIT_DEAD), Exit state , The process is about to be destroyed . The normal exit
Process scheduling process 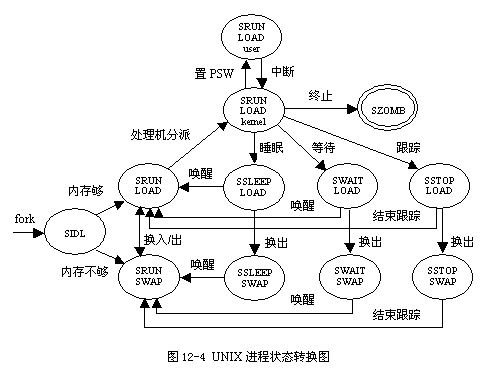
Check the process
The goal of learning process management :
1、 View the current process of the system , Is there a process that uses too much resources
2、 Let the program execute first by adjusting the process priority
3、 How to deal with crashed programs stuck in memory
Common commands
PS: List process information statically
top: List process information dynamically
PS:
ps -l Check yourself bash Program
vim file1 &
ps -l
F: Represents this program tag
4: Indicates that the program permission is root
1: Indicates that the subroutine is only copied fork Without actually executing exec
S: Represents the state of the program STAT, The process status is 5 Kind of .
R (running): The program is running :
S(sleep): The program is in sleep idle, Can be awakened (signal)
D: A sleep state that cannot be awakened , Usually this program may be waiting I/O.
T: Stop state (stop), May be jobs A background program or traced Tracking status
Z(Zombie): Zombie state , The program has terminated but cannot be removed from memory .
UID/PID/PPID: owner / process ID/ The parent process of this program ID
C:cpu Usage rate , The unit is percentage
PRI/NI :priority/Nice Abbreviation , The representative program is cpu Priority of execution , The smaller it is , The first to be executed
ADDR/SZ/WCHAN:ADDR Memory related , If the status is a running program running, General display - .SZ Represents how much memory the program uses .WCHAN Indicates whether the program is running , If it is to use - Express .
TTY: Login terminal location
TIME: cost cpu Running program time
CMD:
ps -ef List all processes and trust information Than ps -l detailed
ps -A Show all processes
ps -e And the effect of this parameter is specified "A" Parameters are the same .
f Display in the form of a process tree
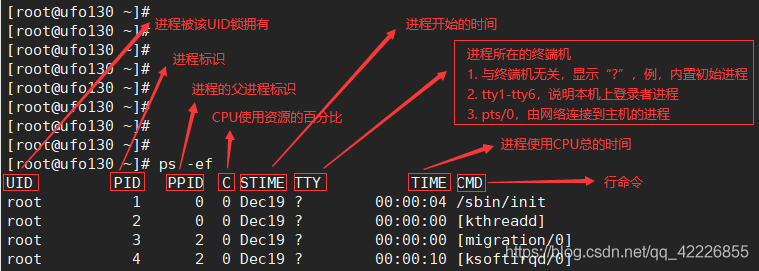
[[email protected]~]$ ps -ef
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 1 0 0 22:39 ? 00:00:03 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switche
root 2 0 0 22:39 ? 00:00:00 [kthreadd]
ps aux Check all system running programs
a Display all programs under the current terminal , Including other users' programs .
u Display program status in a user oriented format .
x Show all programs , Do not differentiate by terminal .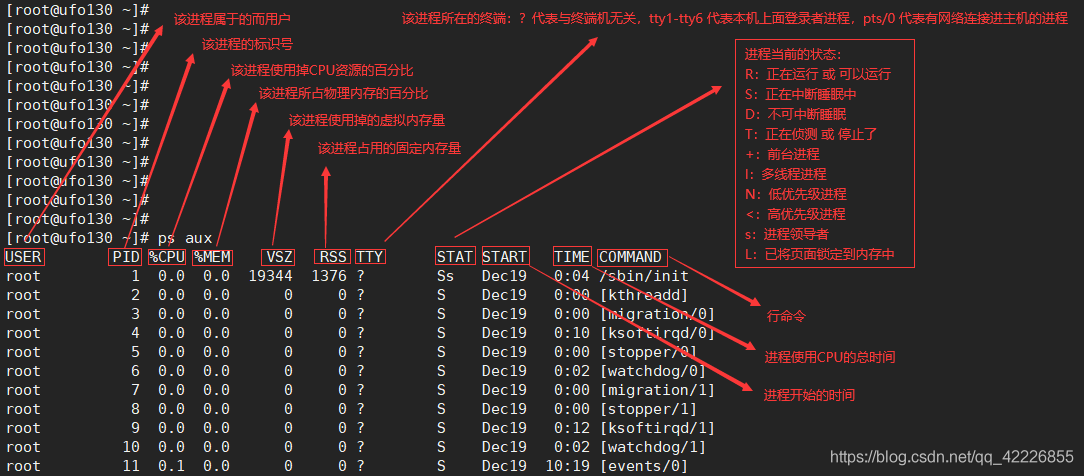
yum repolist all
yum install -y httpd
systemctl start httpd
systemctl status httpd
ps aux
ps aux | grep httpd
top:
1、 Command options :
-d: Screen refresh interval top -d second
2、 Shortcut keys in commands :
h Show shortcut help
k terminate a process Process number 9
q Exit procedure
r Rearrange a priority for progress
s Change refresh interval , Unit second
l Switch to display the average load and start-up time information
m Toggle display memory information
t Toggle display progress and CPU State information
c Toggle display command name and full command line
M Sort by memory usage
P according to CPU Sort usage ( Default sort )
T According to time / Sort in progressive time
1 Unfold multicore cpu Show
3、top Content description
top- Current system time
How long has the system been powered on
Current number of users
load average cpu Average load , The three values are ,1 minute ,5 minute ,15 minute
Current process number of task system , A total of : The total number of processes , function : Number of running processes , sleep : The number of sleep processes , Has stopped : Number of processes stopped , Corpse : Number of zombie processes
%Cpu(s)cpu Usage rate , We : The user to use cpu One hundred percent ,sy: The system kernel uses cpu One hundred percent ,id: remainder cpu One hundred percent
Mem Memory usage information , A total of : Total memory size , You can use : Cached memory , Already used : Used memory ,buff / cache: The size of the cache memory
Exchange virtual memory information
PID process ID
User process owner
PR priority
NI nice value , Negative value indicates high priority , A positive value indicates a low priority
VIRT The amount of virtual memory used by the process
RES The amount of physical memory used by the process
SHR Shared memory size
S Process status ,D: Uninterrupted sleep ,R: function ,S: sleep ,T: track / stop it ,Z: Zombie process
%CPU Used by process CPU Percentage occupied
%MEM Percentage of physical memory used by the process
TIME + Progress used CPU Total time
COMMAND Command name
Kill process :
kill Signal number PID
-1: Reload
-9: Force to kill
-15: The normal exit
[[email protected] mnt]# ps aux | grep vim
root 7258 0.0 0.4 33972 8152 pts/1 T 22:18 0:00 vim file
root 7490 0.0 0.0 12320 1076 pts/0 S+ 22:32 0:00 grep --color=auto vim
[[email protected] mnt]# kill -9 7258
[[email protected] mnt]# ps aux | grep vim
root 7504 0.0 0.0 12320 1056 pts/0 R+ 22:32 0:00 grep --color=auto vim
killall Process name
[[email protected] mnt]# ps aux | grep httpd
root 6424 0.0 0.6 273848 10816 ? Ss 21:47 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
apache 6426 0.0 0.4 286064 8312 ? S 21:47 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
apache 6429 0.0 0.5 1474980 9652 ? Sl 21:47 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
apache 6430 0.0 0.5 1343852 9652 ? Sl 21:47 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
apache 6431 0.0 0.5 1343852 9652 ? Sl 21:47 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
root 7544 0.0 0.0 12320 1028 pts/0 R+ 22:32 0:00 grep --color=auto httpd
[[email protected] mnt]# killall httpd
[[email protected] mnt]# ps aux | grep httpd
root 7570 0.0 0.0 12320 1072 pts/0 R+ 22:34 0:00 grep --color=auto httpd
[[email protected] mnt]# pgrep vim | xargs kill -9
remarks :
Linux Medium buff/cache Memory
We use it free、top And other related commands that can query the current memory usage , There is always one buff/cache Let's be confused .
buffer
When writing to disk , Save to disk buffer first (buffer), Then write to disk .
cache
That is, when reading the disk , After the data is read from the disk , Stay in the buffer (cache), Prepare for the use of subsequent procedures .
How to divide buffer/cache( Already used or Free )
Operating system perspective : This memory is indeed used by the operating system .
User perspective : If the user wants to use , This memory can be quickly recycled and used by user space programs , Therefore, from the user's point of view, this memory should be classified as idle state .
Linux The benefits of this mechanism
This is a Linux A very excellent design , The purpose is to upgrade the disk IO Performance of , Data read from low-speed block devices is temporarily stored in memory , Even though the data was no longer needed at the time , But the next time the application accesses that data , It can be read directly from memory , Bypassing low-speed block devices , So as to improve the overall performance of the system .
In order to improve system performance and not waste memory ,linux Make more memory cache, In order to improve the io Speed . Your memory is not occupied .
Linux Work scheduling jobs
because linux It is a multi person and multi task operating system , So users are using linux There will be some work that we need to watch the progress of completion , And we can just put some work directly in the background , Here we are concerned with the front and back stage implementation of the task , So how to put a task into the background for execution ?
[[email protected] ~]# firefox & #& The symbol is to put the process into the background for execution
[1] 9283
[[email protected] ~]# jobs # View background tasks
[1]+ Running firefox &
Conclusion , The program runs in the background , Does not affect the command prompt
Work management job control
adopt job control In a bash Perform multiple tasks in the environment .
We can't put tty1 The task of tty2 Execute below .
Suppose we have only one terminal interface . Therefore, the command prompt interface can appear, which we call foreground foreground, As for other work, you can put it in the background background Take a pause or work . Work put into the background, such as vim It can't be carried out , You can't use ctrl+c To terminate .
Something to watch out for :
These work starting procedures must come from you shell The subroutine of ( Only manage your own bash);
prospects : The environment in which you can control and give orders is called foreground work (foreground);
background : Work that can operate on its own , You can't use ctrl+c Stop it , have access to bg/fg Call the job ;
In the background :‘ perform ’ Your program can't wait terminal/shell Output input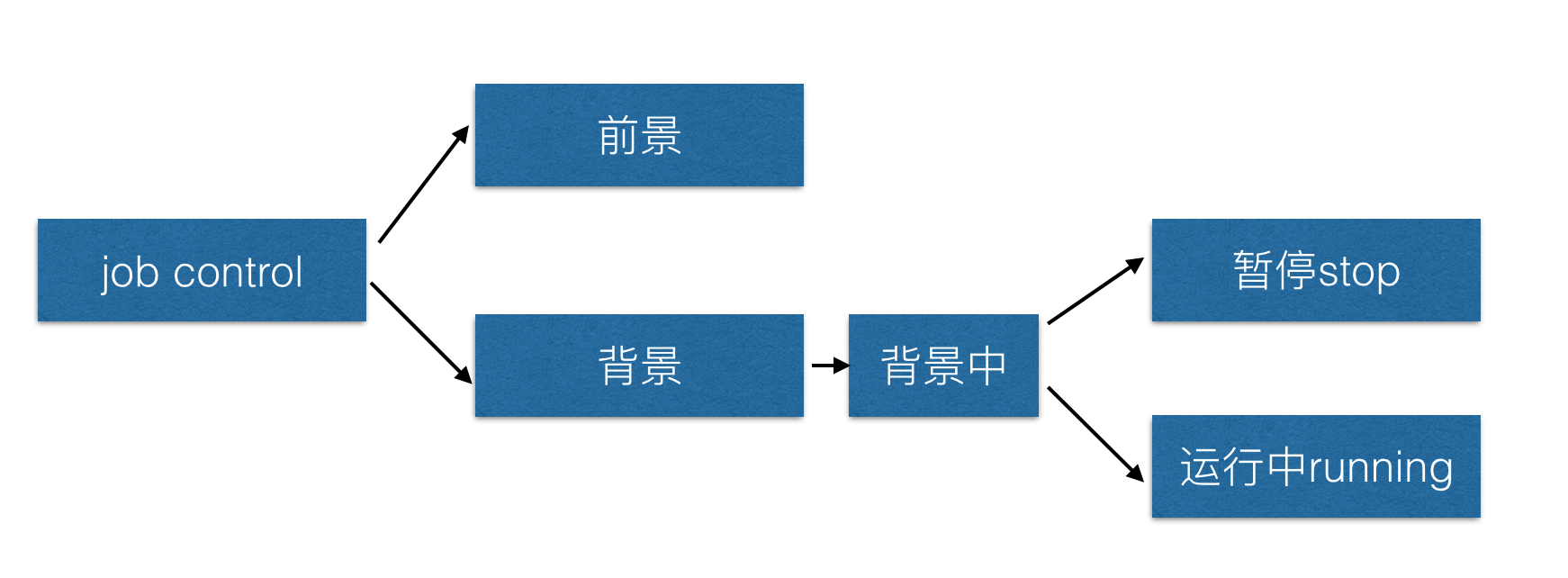
Example :
1、tar -zpcf /tmp/etc.tar.gz /etc &
[[email protected] desktop ]# tar -zpcf /tmp/etc.tar.gz /etc &
[1] 10502 1 Is the job number ,10502 Is a process,
[1]+ Done tar -zpcf /tmp/etc.tar.gz /etc appear Done Represents this task to complete
Put the tasks in the work into the background jobs
Execute two orders
vim ~/.bashrc After implementation ctrl+z
find / print Press after execution ctrl+z
jobs View the tasks in the background
Options :
-l Show PID
-r Display in progress running The task of
-s Show stop The task of
fg % Task number Transfer the backstage to the front desk
bg % Task number Let the tasks in the background run in the background
kill -9 % Task number
[[email protected] ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/bigfile bs=1M count=4000 # Press ctrl+z Manually cut into the background
^Z
[4]+ Has stopped dd if=/dev/zero of=/bigfile bs=1M count=4000
[[email protected] ~]# jobs
[1] Running firefox &
[2] Has stopped vim 1.sh
[3]- Has stopped vim 2.sh
[4]+ Has stopped dd if=/dev/zero of=/bigfile bs=1M count=4000 # The task of manual entry will be suspended
[[email protected] ~]# jobs -l
[1] 9283 Running firefox &
[2] 9689 stop it (tty Output ) vim 1.sh
[3]- 9808 stop it vim 2.sh
[4]+ 9839 stop it dd if=/dev/zero of=/bigfile bs=1M count=4000
[[email protected] ~]# jobs -r
[1] Running firefox &
[[email protected] ~]# jobs -s
[2] Has stopped vim 1.sh
[3]- Has stopped vim 2.sh
[4]+ Has stopped dd if=/dev/zero of=/bigfile bs=1M count=4000
[[email protected] ~]# bg %4 # The background task continues to run
[4]+ dd if=/dev/zero of=/bigfile bs=1M count=4000 &
[[email protected] ~]# jobs
[1] Running firefox &
[2]- Has stopped vim 1.sh
[3]+ Has stopped vim 2.sh
[4] Running dd if=/dev/zero of=/bigfile bs=1M count=4000 &
[[email protected] ~]# Recorded 4000+0 Read in of
Recorded 4000+0 Write
4194304000 bytes (4.2 GB, 3.9 GiB) copied, 178.781 s, 23.5 MB/s
[4] Completed dd if=/dev/zero of=/bigfile bs=1M count=4000
[[email protected] ~]# fg %2 # The background task is transferred to the foreground
vim 1.sh
[[email protected] ~]# jobs
[1]- Running firefox &
[3]+ Has stopped vim 2.sh
[[email protected] ~]# kill -9 %3 # Kill the background task
[3]+ Have killed vim 2.sh
[[email protected] ~]# jobs
[1]+ Running firefox &
nice value
PRI: The priority given by the system cannot be manually modified
NI:nice value , It can be considered that the scope of change -20~19
1 root You can change your own or others' programs Nice Range of values -20~19
2、 General users can only adjust their own Nice Range of values 0-19
3、 General users can only nice The higher the value, the higher
Finally, the priority formula :PRI( new )=PRI( used )+nice value
The lower the priority, the first to execute
adjustment nice Value instruction :
System settings nice Value to use :nice command
There are already assigned nice Value to use :renice command
grammar :
nice -n Numbers command
-n A number range can be followed -20~19
nice -n -5 vi & Start a process and set nice value
renice 10 20485 Modify an already running program
Example :
nice -n -5 vi &
[[email protected] desktop ]# ps -l
F S UID PID PPID C PRI NI ADDR SZ WCHAN TTY TIME CMD
4 S 0 18949 18947 0 80 0 - 1719 - pts/0 00:00:00 bash
4 T 0 20485 18949 0 75 -5 - 1700 - pts/0 00:00:00 vi
0 T 0 20490 18949 0 80 0 - 1700 - pts/0 00:00:00 vi
4 R 0 20491 18949 0 80 0 - 1624 - pts/0 00:00:00 ps
renice 10 Process number , Then the modified value directly becomes the default value 80+10
[[email protected] desktop ]# renice 10 20485
20485: old priority -5, new priority 10
[[email protected] desktop ]# ps -l
F S UID PID PPID C PRI NI ADDR SZ WCHAN TTY TIME CMD
4 S 0 18949 18947 0 80 0 - 1719 - pts/0 00:00:00 bash
4 T 0 20485 18949 0 90 10 - 1700 - pts/0 00:00:00 vi
0 T 0 20490 18949 0 80 0 - 1700 - pts/0 00:00:00 vi
4 R 0 20778 18949 3 80 0 - 1625 - pts/0 00:00:00 ps