当前位置:网站首页>【线程】 理解线程(并行)线程同步的处理(信号量,互斥锁,读写锁,条件变量)
【线程】 理解线程(并行)线程同步的处理(信号量,互斥锁,读写锁,条件变量)
2022-08-02 14:13:00 【白U】
并行是一种特殊的并发
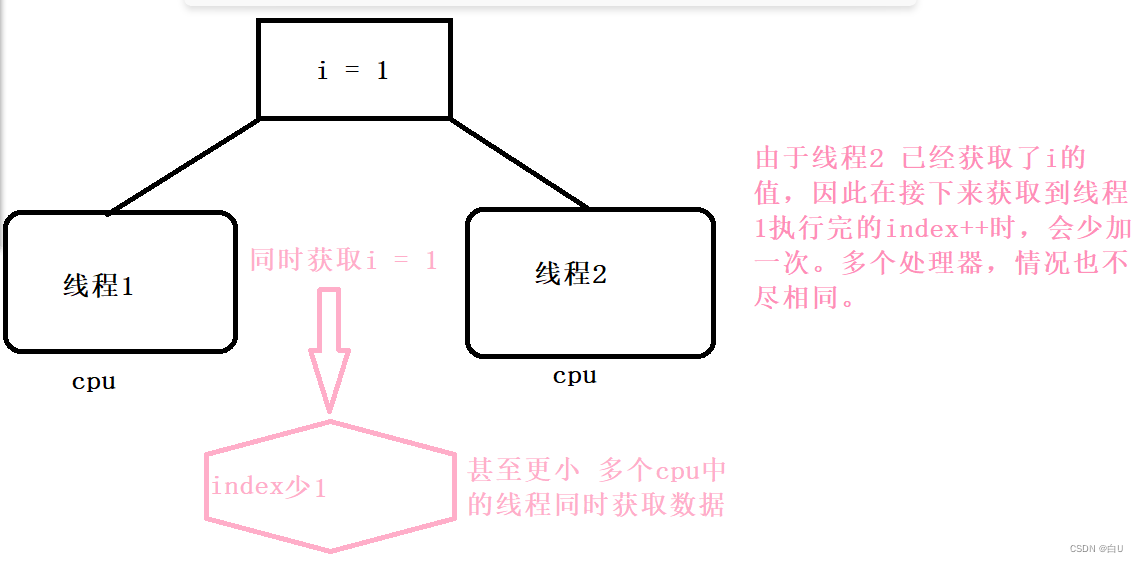
例如:单链表进行尾插,多个处理器中线程同时获得尾部指针,同时插入结点,就可能出现覆盖的情况。因此需要去控制多个处理器同时处理数据带来的问题。
- (线程同步)
- 信号量 (可以使用多个信号量对多个线程就行顺序控制)
- 互斥锁 (只有一个)
- 读写锁
- 条件变量
线程中的信号量: 头文件:
#include <semaphore.h>直接引用信号量初始化
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value)
//传入信号量的地址 \给信号量初始化的值
//信号量是否可以被多个线程共享(0)P操作
int sem_wait(sem_t *sem);V操作
int sem_post(sem_t *sem);删除信号量 (必须销毁)
int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);互斥锁:(不能用于初始值为0的情况,但是信号量可以)
多条执行路径,会产生冲突。
使用多个线程函数,完成不同的功能,并对线程之间进行控制。(线程同步)int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex, pthread_mutexattr_t *attr);
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
thread.c
- 完成index = 5000 的输出。 (收到多个处理器的影响,出现并行答应
#include<pthread.h>
#include<semaphore.h>
sem_t sem;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
int m_index = 1;
void* fun(void* arg)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
// sem_wait(&sem); //p
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); //互斥锁
printf("m_index = %d\n", m_index++);
// sem_post(&sem); //v
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
- main
int main()
{
sem_init(&sem,0,1);
pthread_t id[5];
int i = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
pthread_create(&id[i], NULL, fun, NULL);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
pthread_join(id[i], NULL);
}
// sem_destroy(&sem);
exit(0);
}
- 信号量:
示例2: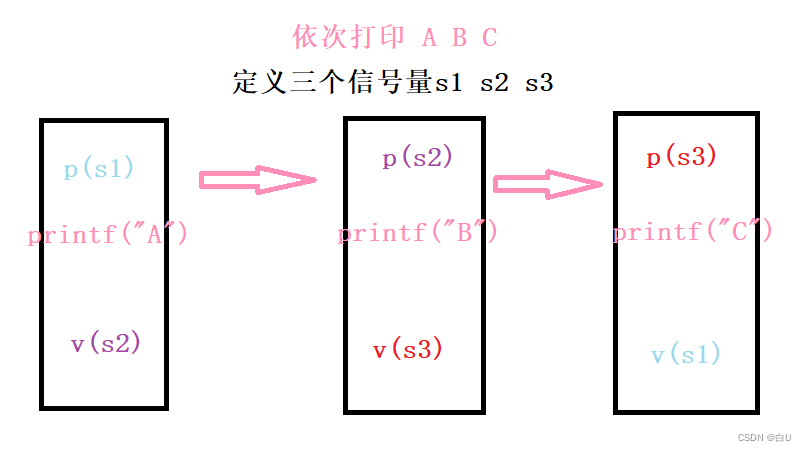
- 引用线程信号量头文件
- 定义全局信号量
- 初始化信号量
- 执行 p v操作
- 销毁信号量
#include<pthread.h>
#include<semaphore.h>
sem_t sema;
sem_t semb;
sem_t semc;
void* funa(void* arg)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
sem_wait(&sema); //p
printf("A");
fflush(stdout);
sem_post(&semb); //v
sleep(1);
}
}
void* funb(void* arg)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
sem_wait(&semb); //p
printf("B");
fflush(stdout);
sem_post(&semc); //v
sleep(1);
}
}
void* func(void* arg)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
sem_wait(&semc); //p
printf("C");
fflush(stdout);
sem_post(&sema); //v
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
sem_init(&sema,0,1);
sem_init(&semb, 0, 0);
sem_init(&semc, 0, 0);
pthread_t id[3];
pthread_create(&id[0], NULL, funa, NULL);
pthread_create(&id[1], NULL, funb, NULL);
pthread_create(&id[2], NULL, func, NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
pthread_join(id[i], NULL);
}
sem_destroy(&sema);
sem_destroy(&semb);
sem_destroy(&semc);
exit(0);
}
- 读写锁:
在读操作时,不能进行写操作。 但是多个读操作可以同时进行。
1. 初始化
pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock, pthread_rwlockattr_t *attr);
2. 读锁pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
3.写锁pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
4.解锁pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);
5.摧毁pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock)
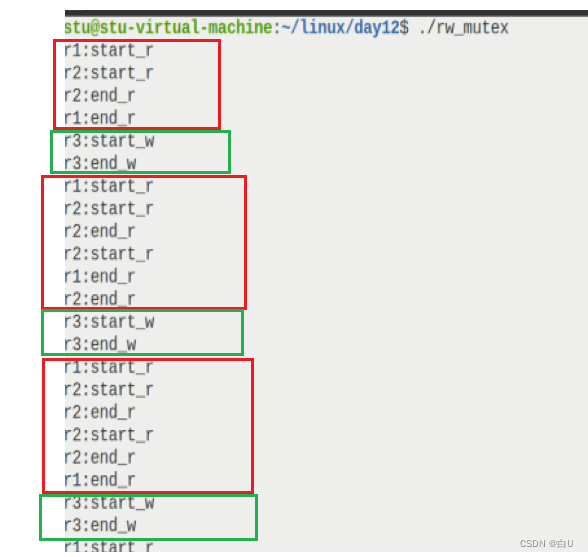
两个读操作是可以同时进行的(因此看谁读的快,结束的快),但是读和写不能同时进行,等读完,读锁释放,才能写。
两个读线程,一个写线程
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<semaphore.h>
pthread_rwlock_t rwlock;
- 读
void* fun_read(void* arg)
{
char* s = (char*)arg;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock); //读锁
printf("%s:start_r\n",s);//进入临界区要尽可能快,把事情办完
int n = rand() % 3;
sleep(n);
printf("%s:end_r\n", s); //标识读结束
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock); //开锁
n = rand() % 3;
sleep(n);
}
}
- 读
void* funb_read(void* arg)
{
for(int i = 0;i<5;i++)
{
char* s = (char*)arg;
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock); //读锁
printf("%s:start_r\n", s);
int n = rand() % 3;
sleep(n);
printf("%s:end_r\n", s); //标识读结束
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock); //开锁
n = rand() % 3;
sleep(n);
}
}
- 写
void* fun_write(void* arg)
{
for(int i = 0;i<5;i++)
{
char* s = (char*)arg;
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock); //写锁
printf("%s:start_w\n", s);
int n = rand() % 3;
sleep(n);
printf("%s:end_w\n", s); //标识读结束
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock); //开锁
n = rand() % 3;
sleep(n);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL);
pthread_t id[3];
pthread_create(&id[0], NULL, fun_read, "r1");
pthread_create(&id[1], NULL, fun_read, "r2");
pthread_create(&id[2], NULL, fun_write, "r3");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
pthread_join(id[i], NULL);
}
exit(0);
}
- 用户级线程 //优点:创建开销小 。缺点:无法使用多个处理器的资源,因为
内核无法感知到线程的存在,所以即便有空闲的cpu,也不会把这些线程放入cpu中。(无法实现并行,只有一条执行路径) - 内核级线程 :前提:系统必须支持多线程。结果:可以实现并行,
可以使用多处理器的资源。 - 组合级线程
《操作系统精髓与设计原理》第四章第五章- 生产者,消费者看看
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
许多代码……

饥荒联机版Mod开发——准备工具(一)
软件测试基础知识(背)
UnityAPI-Ray-Physics
数学工具-desmos 图形曲线

光学好书推荐
Based on the matrix calculation in the linear regression equation of the coefficient estimates
implement tcp bbr on ns3 (在ns3上实现TCP BBR)
Introduction to MATLAB drawing functions ezplot explanation
Detailed introduction to the hierarchical method of binary tree creation
随机推荐
shader入门精要3
implement tcp copa on ns3
第三十一章:二叉树的概念与性质
What are IPV4 and IPV6?
Unity-编辑器扩展(Editor)
Unity-3D数学
1.开发社区首页,注册
unity-shader(入门)
Redis common interview questions
Unity-存档与读档
测试用例练习
shader入门精要2
富文本编辑
光波导应用中的真实光栅效应
Introduction to C language function parameter passing mode
mininet hosts talk to real internet
Unity插件-NGUI
第三十章:普通树的存储和遍历
Manifest merger failed : Attribute [email protected] value=
2021-06-06