当前位置:网站首页>Extended tree (I) - graphic analysis and C language implementation
Extended tree (I) - graphic analysis and C language implementation
2022-07-07 23:27:00 【Life needs depth】
Summary
This chapter introduces extended trees . It and " Binary search tree " and "AVL Trees " equally , Are special binary trees . In understanding " Binary search tree " and "AVL Trees " after , Learning to stretch trees is quite easy . As usual , This article will first give a brief introduction to the theoretical knowledge of extended trees , Then give C The realization of language . The following sequence will be given separately C++ and Java Implementation of version ; this 3 The principle of each implementation method is the same , Choose one of them to learn . If there are mistakes or deficiencies in the article , I hope you can point out !
Catalog
1. Introduction to the stretch tree
2. Stretching the tree C Realization
3. Stretching the tree C The test program
Reprint please indicate the source : Stretch the tree ( One ) And Graphic analysis and C The realization of language - If the sky doesn't die - Blog Garden
More : Data structure and algorithm series Catalog
(01) Stretch the tree ( One ) And Graphic analysis and C The realization of language
(02) Stretch the tree ( Two ) And C++ The implementation of the
(03) Stretch the tree ( 3、 ... and ) And Java The implementation of the
Introduction to the stretch tree
Stretch the tree (Splay Tree) It's a binary sort tree , It can be in O(log n) Insert inside complete 、 Search and delete operations . It consists of Daniel Sleator and Robert Tarjan create .
(01) Stretch tree belongs to binary search tree , That is, it has the same properties as binary search tree : hypothesis x Is any node in the tree ,x Nodes contain keywords key, node x Of key Value to key[x]. If y yes x A node in the left subtree of , be key[y] <= key[x]; If y yes x A node of the right subtree of , be key[y] >= key[x].
(02) In addition to the properties of binary search tree , Another feature of stretch trees is : When a node is accessed , Stretching the tree will make the node become the root of the tree by rotation . The advantage of this is , The next time you want to access this node , Can quickly access the node .
Suppose you want to perform a series of lookup operations on a binary lookup tree . In order to make the whole search time smaller , The items that are checked frequently should always be near the root of the tree . So I thought of designing a simple method , Refactoring the tree after each lookup , Move the searched items closer to the root of the tree . Stretch tree came into being , It is a self-adjusting binary search tree , It follows the path from a node to the root of the tree , Move this node to the root of the tree through a series of rotations .
Compared with " Binary search tree " and "AVL Trees ", When learning to stretch a tree, you need to focus on " Rotation algorithm of extended tree ".
Stretching the tree C Realization
1. Node definition
typedef int Type;
typedef struct SplayTreeNode {
Type key; // keyword ( Key value )
struct SplayTreeNode *left; // Left the child
struct SplayTreeNode *right; // The right child
} Node, *SplayTree; The nodes of the extension tree include several constituent elements :
(01) key -- Is the key word , It is used to sort the nodes of the extended tree .
(02) left -- The left child. .
(03) right -- It's the right child .
External interface

// The former sequence traversal " Stretch the tree " void preorder_splaytree(SplayTree tree); // In the sequence traversal " Stretch the tree " void inorder_splaytree(SplayTree tree); // After the sequence traversal " Stretch the tree " void postorder_splaytree(SplayTree tree); // ( Recursive implementation ) lookup " Stretch the tree x" The middle key value is key The node of Node* splaytree_search(SplayTree x, Type key); // ( Non recursive implementation ) lookup " Stretch the tree x" The middle key value is key The node of Node* iterative_splaytree_search(SplayTree x, Type key); // Find the smallest node : return tree The smallest node of an extended tree that is the root node . Node* splaytree_minimum(SplayTree tree); // Find the largest node : return tree The largest node of the extended tree that is the root node . Node* splaytree_maximum(SplayTree tree); // rotate key The corresponding node is the root node . Node* splaytree_splay(SplayTree tree, Type key); // Insert the node into the extended tree , And return the root node Node* insert_splaytree(SplayTree tree, Type key); // Delete node (key Is the value of the node ), And return the root node Node* delete_splaytree(SplayTree tree, Type key); // Destroy the stretch tree void destroy_splaytree(SplayTree tree); // Print stretch tree void print_splaytree(SplayTree tree, Type key, int direction);

2. rotate
Rotating code

/*
* rotate key The corresponding node is the root node , And return the root node .
*
* Be careful :
* (a): There are in the stretching tree " The key value is key The node of ".
* take " The key value is key The node of " Rotate to root node .
* (b): It doesn't exist in the stretched tree " The key value is key The node of ", also key < tree->key.
* b-1 " The key value is key The node of " If the precursor node of exists , take " The key value is key The node of " The precursor node of is rotated to the root node .
* b-2 " The key value is key The node of " If the precursor node of exists , Means that the ,key Smaller than any key value in the tree , So at this time , Rotate the smallest node to the root node .
* (c): It doesn't exist in the stretched tree " The key value is key The node of ", also key > tree->key.
* c-1 " The key value is key The node of " If the successor node of exists , take " The key value is key The node of " The subsequent node of is rotated to the root node .
* c-2 " The key value is key The node of " If the successor node of does not exist , Means that the ,key Larger than any key value in the tree , So at this time , Rotate the largest node to the root node .
*/
Node* splaytree_splay(SplayTree tree, Type key)
{
Node N, *l, *r, *c;
if (tree == NULL)
return tree;
N.left = N.right = NULL;
l = r = &N;
for (;;)
{
if (key < tree->key)
{
if (tree->left == NULL)
break;
if (key < tree->left->key)
{
c = tree->left; /* 01, rotate right */
tree->left = c->right;
c->right = tree;
tree = c;
if (tree->left == NULL)
break;
}
r->left = tree; /* 02, link right */
r = tree;
tree = tree->left;
}
else if (key > tree->key)
{
if (tree->right == NULL)
break;
if (key > tree->right->key)
{
c = tree->right; /* 03, rotate left */
tree->right = c->left;
c->left = tree;
tree = c;
if (tree->right == NULL)
break;
}
l->right = tree; /* 04, link left */
l = tree;
tree = tree->right;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
l->right = tree->left; /* 05, assemble */
r->left = tree->right;
tree->left = N.right;
tree->right = N.left;
return tree;
}
The function of the above code : take " The key value is key The node of " Rotate to root node , And return the root node . Its handling includes :
(a): There are in the stretching tree " The key value is key The node of ".
take " The key value is key The node of " Rotate to root node .
(b): It doesn't exist in the stretched tree " The key value is key The node of ", also key < tree->key.
b-1) " The key value is key The node of " If the precursor node of exists , take " The key value is key The node of " The precursor node of is rotated to the root node .
b-2) " The key value is key The node of " If the precursor node of exists , Means that the ,key Smaller than any key value in the tree , So at this time , Rotate the smallest node to the root node .
(c): It doesn't exist in the stretched tree " The key value is key The node of ", also key > tree->key.
c-1) " The key value is key The node of " If the successor node of exists , take " The key value is key The node of " The subsequent node of is rotated to the root node .
c-2) " The key value is key The node of " If the successor node of does not exist , Means that the ,key Larger than any key value in the tree , So at this time , Rotate the largest node to the root node .
The following are examples of a To illustrate .
Look in the stretched tree below 10, Including " Right hand " --> " Right link " --> " Combine " this 3 Step .

First step : Right hand
Corresponding to "rotate right" part

The second step : Right link
Corresponding to "link right" part

The third step : Combine
Corresponding to "assemble" part

Tips : If you look in the stretched tree above "70", Is exactly the same as " Example 1" symmetry , The corresponding operations are "rotate left", "link left" and "assemble".
Other things , for example " lookup 15 yes b-1 The situation of , lookup 5 yes b-2 The situation of " wait , These are relatively simple , You can analyze by yourself .
3. Insert

Uploading … Re upload cancel
/*
* Insert the node into the extended tree ( No rotation )
*
* Parameter description :
* tree Extend the root node of the tree
* z Inserted node
* Return value :
* The root node
*/
static Node* splaytree_insert(SplayTree tree, Node *z)
{
Node *y = NULL;
Node *x = tree;
// lookup z Where to insert
while (x != NULL)
{
y = x;
if (z->key < x->key)
x = x->left;
else if (z->key > x->key)
x = x->right;
else
{
printf(" Inserting the same node is not allowed (%d)!\n", z->key);
// Release the requested node , And back to tree.
free(z);
return tree;
}
}
if (y==NULL)
tree = z;
else if (z->key < y->key)
y->left = z;
else
y->right = z;
return tree;
}
/*
* Create and return the extended tree node .
*
* Parameter description :
* key Is the key value .
* parent Is the parent node .
* left The left child. .
* right It's the right child .
*/
static Node* create_splaytree_node(Type key, Node *left, Node* right)
{
Node* p;
if ((p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node))) == NULL)
return NULL;
p->key = key;
p->left = left;
p->right = right;
return p;
}
/*
* New node (key), Then insert it into the extended tree , And rotate the inserted node into the root node
*
* Parameter description :
* tree Extend the root node of the tree
* key Insert the key value of the node
* Return value :
* The root node
*/
Node* insert_splaytree(SplayTree tree, Type key)
{
Node *z; // New node
// If the new node fails , Then return to .
if ((z=create_splaytree_node(key, NULL, NULL)) == NULL)
return tree;
// Insert node
tree = splaytree_insert(tree, z);
// The nodes (key) Rotate to root node
tree = splaytree_splay(tree, key);
}
External interface : insert_splaytree(tree, key) It is an interface provided to the outside , Its function is to create new nodes ( The key value of the node is key), And insert the node into the extended tree ; then , Rotate this node to the root node .
Internal interface : splaytree_insert(tree, z) It's the internal interface , Its function is to connect nodes z Insert into tree in .splaytree_insert(tree, z) Will be z Insert into tree In the middle of the day , Only will tree Think of it as a binary search tree , And it is not allowed to insert the same node .
4. Delete
Delete interface

/*
* Delete node (key Is the key value of the node ), And return the root node .
*
* Parameter description :
* tree Extend the root node of the tree
* z Deleted nodes
* Return value :
* The root node ( The root node is the precursor node of the deleted node )
*
*/
Node* delete_splaytree(SplayTree tree, Type key)
{
Node *x;
if (tree == NULL)
return NULL;
// The search key value is key The node of , If it cannot be found, return directly .
if (splaytree_search(tree, key) == NULL)
return tree;
// take key The corresponding node is rotated to the root node .
tree = splaytree_splay(tree, key);
if (tree->left != NULL)
{
// take "tree The precursor node of " Rotate to root node
x = splaytree_splay(tree->left, key);
// remove tree node
x->right = tree->right;
}
else
x = tree->right;
free(tree);
return x;
}
Uploading … Re upload cancel
delete_splaytree(tree, key) The role of is : Delete the key value of key The node of .
It will first find the key value of key The node of . If not found , Then return directly . If found , Then rotate the node to the root node , Then delete the node .
Be careful : About stretching trees " The former sequence traversal "、" In the sequence traversal "、" After the sequence traversal "、" Maximum "、" minimum value "、" lookup "、" Print "、" The destruction " Equal interface and " Binary search tree " Is essentially the same , These operations are in " Binary search tree " Has been introduced in , Here is no longer a separate introduction . Of course , The complete source code of the extended tree given later , Have given these API Implementation code . These interfaces are simple ,Please RTFSC(Read The Fucking Source Code)!
Stretching the tree C Realization ( Complete source code )
Stretch the header file of the tree (splay_tree.h)
View Code
Implementation file of extension tree (splay_tree.c)
View Code
Test program of stretching tree (splaytree_test.c)
View Code
Stretching the tree C The test program
The test program running results of the extended tree are as follows :

== Add... In turn : 10 50 40 30 20 60 == The former sequence traversal : 60 30 20 10 50 40 == In the sequence traversal : 10 20 30 40 50 60 == After the sequence traversal : 10 20 40 50 30 60 == minimum value : 10 == Maximum : 60 == Tree details : 60 is root 30 is 60's left child 20 is 30's left child 10 is 20's left child 50 is 30's right child 40 is 50's left child == Rotate nodes (30) Root node == Tree details : 30 is root 20 is 30's left child 10 is 20's left child 60 is 30's right child 50 is 60's left child 40 is 50's left child

Uploading … Re upload cancel
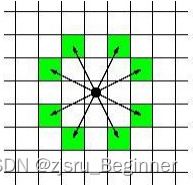
The main flow of the test program is : Create a new stretch tree , Then insert into the extended tree one by one 10,50,40,30,20,60. After inserting these data , The nodes of the extended tree are 60; here , Then rotate the node , bring 30 Become the root node .
Insert... In turn 10,50,40,30,20,60 The schematic diagram is as follows :

take 30 The schematic diagram of rotating to root node is as follows :

边栏推荐
- Cloud native data warehouse analyticdb MySQL user manual
- B_QuRT_User_Guide(40)
- Adrnoid Development Series (XXV): create various types of dialog boxes using alertdialog
- 云原生数据仓库AnalyticDB MySQL版用户手册
- USB (XVI) 2022-04-28
- Coreseek: the second step is index building and testing
- V-for traversal object
- CAIP2021 初赛VP
- sql 数据库执行问题
- USB (十七)2022-04-15
猜你喜欢
![[compilation principle] lexical analysis design and Implementation](/img/8c/a3a50e6b029c49caf0d791f7d4513a.png)
[compilation principle] lexical analysis design and Implementation
PCI-Express接口的PCB布线规则
高效的S2B2C电商系统,是这样帮助电子材料企业提升应变能力的

Adults have only one main job, but they have to pay a price. I was persuaded to step back by personnel, and I cried all night
Installing spss25
七月第一周
![Ros2 topic (03): the difference between ros1 and ros2 [01]](/img/20/39d47c93400050a7bc8ad7efea51b3.png)
Ros2 topic (03): the difference between ros1 and ros2 [01]
![Ros2 topic (03): the difference between ros1 and ros2 [02]](/img/12/244ea30b5b141a0f47a54c08f4fe9f.png)
Ros2 topic (03): the difference between ros1 and ros2 [02]

B / Qurt Utilisateur Guide (36)

Unity3d Learning Notes 6 - GPU instantiation (1)
随机推荐
Mysql索引优化实战一
三问TDM
VS扩展工具笔记
Live-Server使用
Install a new version of idea. Double click it to open it
Tree background data storage (using webmethod) [easy to understand]
LeeCode -- 6. Z 字形变换
【编译原理】词法分析设计实现
Unity3D学习笔记4——创建Mesh高级接口
Add data analysis tools in Excel
The 19th Zhejiang Provincial College Programming Contest VP record + supplementary questions
PCI-Express接口的PCB布线规则
生鲜行业数字化采购管理系统:助力生鲜企业解决采购难题,全程线上化采购执行
js 获取对象的key和value
Opencv scalar passes in three parameters, which can only be displayed in black, white and gray. Solve the problem
Home appliance industry channel business collaboration system solution: help home appliance enterprises quickly realize the Internet of channels
高效的S2B2C电商系统,是这样帮助电子材料企业提升应变能力的
Talk about the design and implementation logic of payment process
B_QuRT_User_Guide(36)
MySQL Index Optimization Practice I