当前位置:网站首页>In depth analysis of kubebuilder
In depth analysis of kubebuilder
2022-07-07 04:41:00 【chenxy02】
Refer to the website :
Introduction - The Kubebuilder Book
In depth analysis of Kubebuilder: Let's write CRD Make it easier - You know
Reading guide
I recommend you to read the official documents above .
I forwarded a blog earlier be based on Kubebuilder Development Operator( Get started with )_chenxy02 The blog of -CSDN Blog The record of kubebuilder To get started with , This paper aims to deepen the understanding of kubebuilder Shenzhen , Further familiarity kubebuilder Project code .
The core concept
GVKs & GVRs
GVK = GroupVersionKind,GVR = GroupVersionResource
- During coding , Resource data is stored in structures ( be called Go type)
- Due to multiple versions version The existence of (alpha1, beta1, v1 etc. ), There are differences in storage structures in different versions , But we will all give it the same Kind name ( such as Deployment)
- therefore , We are coding Only kind name ( Such as Deployment), It is impossible to accurately obtain which version structure it uses
- therefore , use GVK Get a specific storage structure , That is to say GVK The three messages of (group/version/kind) Confirm one Go type( Structure )
How to get it ? —— adopt Scheme,Scheme Store GVK and Go Type The mapping relation of
- In the process of creating resources , We write yaml, Submit a request :
- To write yaml In the process , We will write apiversion and kind, In fact, that is GVK
- And the client ( That's us ) And apiserver Communication is http form , Is to send a request to a http path
To which http path Well ?—— This http path In fact, that is GVR
- /apis/batch/v1/nampspaces/default/job This means default Namespace job resources
- We kubectl get po when It is also the path of the request , It can also be called GVR
- Actually GVR By GVK Transformed —— adopt REST The mapping of RESTMappers Realization
Scheme
Each group Controllers You need one Scheme, Provides Kinds With the corresponding Go types Mapping , in other words Given Go type I knew him GVK, Given GVK I knew him Go type
Manager
Kubebuilder Core components , have 3 A duty :
Responsible for running all Controllers;
Initialize share cashes, contain listAndWath function
initialization clients Used with Api Server signal communication
Cache
Kubebuilder Core components , Responsible for Controller According to Scheme Sync Api Server All of the Controller Care for GVKs Of GVRs, Its core is GVK->Informer Mapping ,Informer Will be responsible for monitoring the corresponding GVK Of GVRs The creation of / Delete / update operation , To trigger Controller Of Reconcile Logic .
Controller
Kubebuilder Scaffolding files generated for us , We just need to achieve Reconcile The method can .
Clients
In the realization of Controller Inevitably, some resource types need to be created / Delete / to update , Through this Clients Realized , The query function is local Cache, Write direct access Api Server
Index
because Controller Always be right Cache The query ,Kubebuilder Provide Index utility to Cache Picasso reference improves query efficiency .
Finalizer
In general , If the resource is deleted , Although we can trigger the deletion event , But this time from Cache It can't read any information of the deleted object , thus , A lot of garbage cleaning work can not be carried out due to lack of information .
K8s Of Finalizer Fields are used to handle this situation . stay K8s in , As long as the object ObjectMeta Inside Finalizers Not empty , For this object delete The operation will change to update operation , Specifically update deletionTimestamp Field , Its meaning is to tell K8s Of GC“ stay deletionTimestamp After this moment , as long as Finalizer It's empty , Delete the object immediately “.
So the general use of posture is to create objects when Finalizers Set it up ( arbitrarily string), Then process DeletionTimestamp Not empty update operation ( the truth is that delete), according to Finalizers The value of does all pre-delete hook( You can do it in Cache It reads any information of the deleted object ) After the Finalizers Leave blank .
OwnerReference
k8s GC When deleting an object , whatever ownerReference All objects that are objects of this object will be cleared , meanwhile ,kubebuilder Support the change of all objects Will trigger Owner object controller Of Reconcile Method .
All the concepts are put together as shown in the figure below :
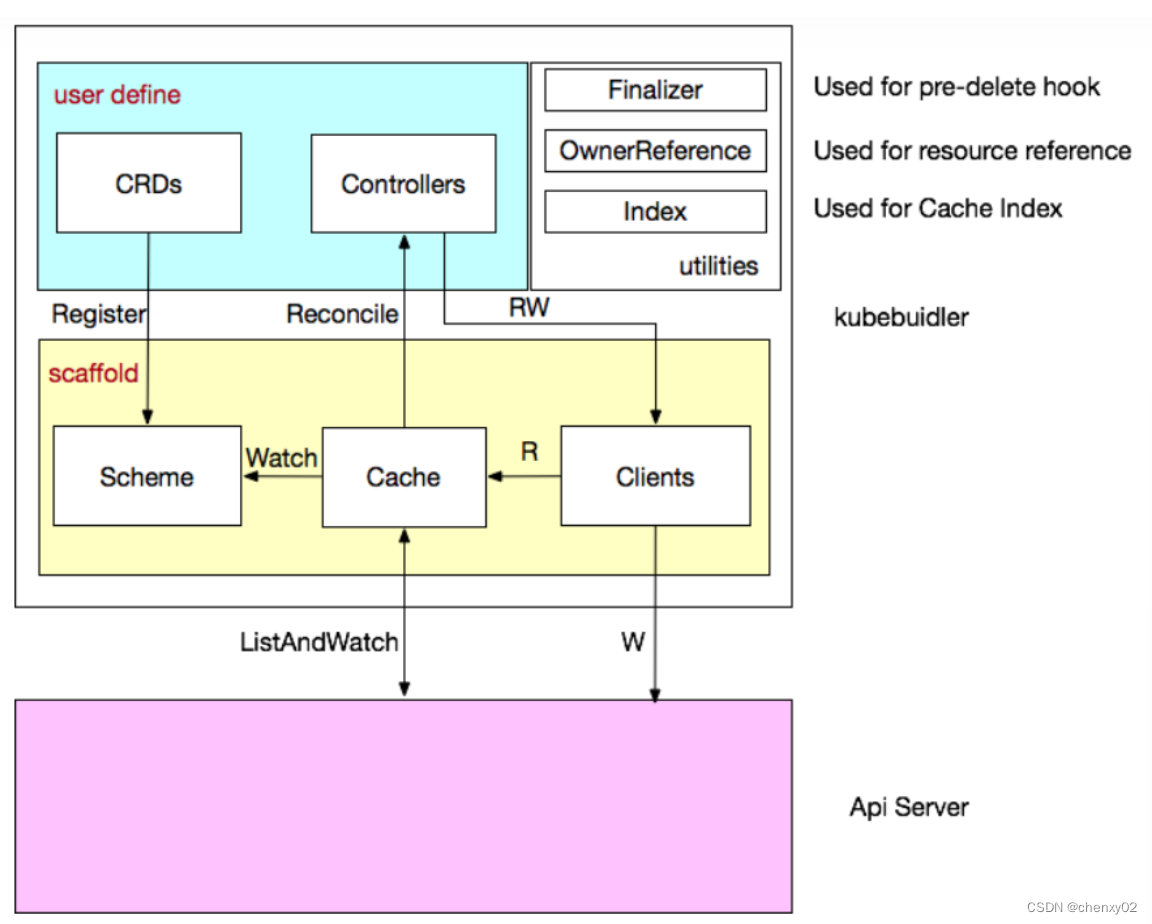
Source code reading
The following code comes from be based on Kubebuilder Development Operator( Get started with )_chenxy02 The blog of -CSDN Blog
from main.go Start
Kubebuilder Created main.go It's the entrance to the whole project , The logic is very simple :
var (
scheme = runtime.NewScheme()
setupLog = ctrl.Log.WithName("setup")
)
func init() {
utilruntime.Must(clientgoscheme.AddToScheme(scheme))
utilruntime.Must(webappv1.AddToScheme(scheme))
//+kubebuilder:scaffold:scheme
}
func main() {
...
// 1、Manager
mgr, err := ctrl.NewManager(ctrl.GetConfigOrDie(), ctrl.Options{
Scheme: scheme,
MetricsBindAddress: metricsAddr,
Port: 9443,
HealthProbeBindAddress: probeAddr,
LeaderElection: enableLeaderElection,
LeaderElectionID: "ecaf1259.my.domain",
})
...
// 2、init Reconciler(Controller)
if err = (&controllers.GuestbookReconciler{
Client: mgr.GetClient(),
Scheme: mgr.GetScheme(),
}).SetupWithManager(mgr); err != nil {
setupLog.Error(err, "unable to create controller", "controller", "Guestbook")
os.Exit(1)
}
...
// 3、start Manager
setupLog.Info("starting manager")
if err := mgr.Start(ctrl.SetupSignalHandler()); err != nil {
setupLog.Error(err, "problem running manager")
os.Exit(1)
}
}You can see in the init In the method, we will webappv1 Sign up to Scheme It went to the , thus Cache You know watch Who is that? ,main The logic in the method is basically Manager Of :
- I've initialized one Manager;
- take Manager Of Client Pass to Controller, And call SetupWithManager Methods the incoming Manager Conduct Controller The initialization ;
- start-up Manager
Manager initialization
Manager The initialization code is as follows :
// New returns a new Manager for creating Controllers.
func New(config *rest.Config, options Options) (Manager, error) {
// Set default values for options fields
options = setOptionsDefaults(options)
cluster, err := cluster.New(config, func(clusterOptions *cluster.Options) {
clusterOptions.Scheme = options.Scheme
clusterOptions.MapperProvider = options.MapperProvider
clusterOptions.Logger = options.Logger
clusterOptions.SyncPeriod = options.SyncPeriod
clusterOptions.Namespace = options.Namespace
clusterOptions.NewCache = options.NewCache
clusterOptions.ClientBuilder = options.ClientBuilder
clusterOptions.ClientDisableCacheFor = options.ClientDisableCacheFor
clusterOptions.DryRunClient = options.DryRunClient
clusterOptions.EventBroadcaster = options.EventBroadcaster
})
...
return &controllerManager{
cluster: cluster,
recorderProvider: recorderProvider,
resourceLock: resourceLock,
metricsListener: metricsListener,
metricsExtraHandlers: metricsExtraHandlers,
logger: options.Logger,
elected: make(chan struct{}),
port: options.Port,
host: options.Host,
certDir: options.CertDir,
leaseDuration: *options.LeaseDuration,
renewDeadline: *options.RenewDeadline,
retryPeriod: *options.RetryPeriod,
healthProbeListener: healthProbeListener,
readinessEndpointName: options.ReadinessEndpointName,
livenessEndpointName: options.LivenessEndpointName,
gracefulShutdownTimeout: *options.GracefulShutdownTimeout,
internalProceduresStop: make(chan struct{}),
leaderElectionStopped: make(chan struct{}),
}, nil
}You can see Mainly to create Cache And Clients And so on :
establish Cache
Cache The initialization code is as follows :
// New initializes and returns a new Cache.
func New(config *rest.Config, opts Options) (Cache, error) {
opts, err := defaultOpts(config, opts)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
im := internal.NewInformersMap(config, opts.Scheme, opts.Mapper, *opts.Resync, opts.Namespace)
return &informerCache{InformersMap: im}, nil
}
// NewInformersMap creates a new InformersMap that can create informers for
// both structured and unstructured objects.
func NewInformersMap(config *rest.Config,
scheme *runtime.Scheme,
mapper meta.RESTMapper,
resync time.Duration,
namespace string) *InformersMap {
return &InformersMap{
structured: newStructuredInformersMap(config, scheme, mapper, resync, namespace),
unstructured: newUnstructuredInformersMap(config, scheme, mapper, resync, namespace),
metadata: newMetadataInformersMap(config, scheme, mapper, resync, namespace),
Scheme: scheme,
}
}You can see Cache The main thing is to create InformersMap, Scheme Each of them GVK All created corresponding Informer, adopt informersByGVK This map do GVK To Informer Mapping , Every Informer Will be based on ListWatch The function pair corresponds to GVK Conduct List and Watch.
establish Clients
establish Clients It's simple :
// defaultNewClient creates the default caching client
func defaultNewClient(cache cache.Cache, config *rest.Config, options client.Options) (client.Client, error) {
// Create the Client for Write operations.
c, err := client.New(config, options)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &client.DelegatingClient{
Reader: &client.DelegatingReader{
CacheReader: cache,
ClientReader: c,
},
Writer: c,
StatusClient: c,
}, nil
}The read operation uses the Cache, Write operation use K8s go-client Direct connection .
Controller initialization
Let's see below. Controller Start of :
// SetupWithManager sets up the controller with the Manager.
func (r *GuestbookReconciler) SetupWithManager(mgr ctrl.Manager) error {
return ctrl.NewControllerManagedBy(mgr).
For(&webappv1.Guestbook{}).
Complete(r)
}In use Builder Pattern ,NewControllerManagerBy and For Give me all the methods Builder The ginseng , The most important thing is the last way Complete, The logic is :
func (blder *Builder) Build(r reconcile.Reconciler) (manager.Manager, error) {
...
// Set the Manager
if err := blder.doManager(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Set the ControllerManagedBy
if err := blder.doController(r); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Set the Watch
if err := blder.doWatch(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
...
return blder.mgr, nil
}Mainly to see doController and doWatch Method :
doController Method
func NewUnmanaged(name string, mgr manager.Manager, options Options) (Controller, error) {
...
// Inject dependencies into Reconciler
if err := mgr.SetFields(options.Reconciler); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Create controller with dependencies set
return &controller.Controller{
Do: options.Reconciler,
MakeQueue: func() workqueue.RateLimitingInterface {
return workqueue.NewNamedRateLimitingQueue(options.RateLimiter, name)
},
MaxConcurrentReconciles: options.MaxConcurrentReconciles,
CacheSyncTimeout: options.CacheSyncTimeout,
SetFields: mgr.SetFields,
Name: name,
Log: options.Log.WithName("controller").WithName(name),
}, nil
}This method initializes a Controller, Some important parameters are passed in :
- Do: Reconcile Logic ;
- Cache: look for Informer register Watch
- Queue:Watch Resources CUD Event cache
doWatch Method
func (blder *Builder) doWatch() error {
// Reconcile type
typeForSrc, err := blder.project(blder.forInput.object, blder.forInput.objectProjection)
if err != nil {
return err
}
src := &source.Kind{Type: typeForSrc}
hdler := &handler.EnqueueRequestForObject{}
allPredicates := append(blder.globalPredicates, blder.forInput.predicates...)
if err := blder.ctrl.Watch(src, hdler, allPredicates...); err != nil {
return err
}
// Watches the managed types
for _, own := range blder.ownsInput {
typeForSrc, err := blder.project(own.object, own.objectProjection)
if err != nil {
return err
}
src := &source.Kind{Type: typeForSrc}
hdler := &handler.EnqueueRequestForOwner{
OwnerType: blder.forInput.object,
IsController: true,
}
allPredicates := append([]predicate.Predicate(nil), blder.globalPredicates...)
allPredicates = append(allPredicates, own.predicates...)
if err := blder.ctrl.Watch(src, hdler, allPredicates...); err != nil {
return err
}
}
// Do the watch requests
for _, w := range blder.watchesInput {
allPredicates := append([]predicate.Predicate(nil), blder.globalPredicates...)
allPredicates = append(allPredicates, w.predicates...)
// If the source of this watch is of type *source.Kind, project it.
if srckind, ok := w.src.(*source.Kind); ok {
typeForSrc, err := blder.project(srckind.Type, w.objectProjection)
if err != nil {
return err
}
srckind.Type = typeForSrc
}
if err := blder.ctrl.Watch(w.src, w.eventhandler, allPredicates...); err != nil {
return err
}
}
return nil
}You can see that this method is right for this Controller conscientious CRD the watch, At the same time, there will be watch Ben CRD Other resources managed , This managedObjects Can pass Controller initialization Builder Of Owns Methods the incoming , Speaking of Watch We care about two logics :
1、 Registered handler
type EnqueueRequestForObject struct{}
// Create implements EventHandler
func (e *EnqueueRequestForObject) Create(evt event.CreateEvent, q workqueue.RateLimitingInterface) {
...
q.Add(reconcile.Request{NamespacedName: types.NamespacedName{
Name: evt.Meta.GetName(),
Namespace: evt.Meta.GetNamespace(),
}})
}
// Update implements EventHandler
func (e *EnqueueRequestForObject) Update(evt event.UpdateEvent, q workqueue.RateLimitingInterface) {
if evt.MetaOld != nil {
q.Add(reconcile.Request{NamespacedName: types.NamespacedName{
Name: evt.MetaOld.GetName(),
Namespace: evt.MetaOld.GetNamespace(),
}})
} else {
enqueueLog.Error(nil, "UpdateEvent received with no old metadata", "event", evt)
}
if evt.MetaNew != nil {
q.Add(reconcile.Request{NamespacedName: types.NamespacedName{
Name: evt.MetaNew.GetName(),
Namespace: evt.MetaNew.GetNamespace(),
}})
} else {
enqueueLog.Error(nil, "UpdateEvent received with no new metadata", "event", evt)
}
}
// Delete implements EventHandler
func (e *EnqueueRequestForObject) Delete(evt event.DeleteEvent, q workqueue.RateLimitingInterface) {
...
q.Add(reconcile.Request{NamespacedName: types.NamespacedName{
Name: evt.Meta.GetName(),
Namespace: evt.Meta.GetNamespace(),
}})
}You can see Kubebuilder Registered Handler Is the object of the change NamespacedName Queue entry , If in Reconcile Logic needs judgment to create / to update / Delete , We need to have our own judgment logic .
2、 Registration process
// Watch implements controller.Controller
func (c *Controller) Watch(src source.Source, evthdler handler.EventHandler, prct ...predicate.Predicate) error {
...
log.Info("Starting EventSource", "controller", c.Name, "source", src)
return src.Start(evthdler, c.Queue, prct...)
}
// Start is internal and should be called only by the Controller to register an EventHandler with the Informer
// to enqueue reconcile.Requests.
func (is *Informer) Start(handler handler.EventHandler, queue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface,
...
is.Informer.AddEventHandler(internal.EventHandler{Queue: queue, EventHandler: handler, Predicates: prct})
return nil
}our Handler Actual registration to Informer above , So the whole logic is strung up , adopt Cache We created all Scheme Inside GVKs Of Informers, Then corresponding GVK Of Controller registered Watch Handler To the corresponding Informer, This corresponds to GVK Any changes to the resources in it will trigger Handler, Write the change event to Controller In the event queue , Then trigger our Reconcile Method .
边栏推荐
- Comment les tests de logiciels sont - ils effectués sur le site Web? Testez la stratégie!
- 深耕开发者生态,加速AI产业创新发展 英特尔携众多合作伙伴共聚
- How do test / development programmers get promoted? From nothing, from thin to thick
- NFT meta universe chain diversified ecosystem development case
- 微信能开小号了,拼多多“砍一刀”被判侵权,字节VR设备出货量全球第二,今日更多大新闻在此
- Detect when a tab bar item is pressed
- Unit test asp Net MVC 4 Application - unit testing asp Net MVC 4 apps thoroughly
- Oracle -- 视图与序列
- 1.19.11. SQL client, start SQL client, execute SQL query, environment configuration file, restart policy, user-defined functions, constructor parameters
- 架构实战训练营|课后作业|模块 6
猜你喜欢

The easycvr platform is connected to the RTMP protocol, and the interface call prompts how to solve the error of obtaining video recording?
Practice Guide for interface automation testing (middle): what are the interface testing scenarios

Case reward: Intel brings many partners to promote the innovation and development of multi domain AI industry
![[team learning] [34 sessions] Alibaba cloud Tianchi online programming training camp](/img/50/bfe7229d380a514c40f9f6822381c7.jpg)
[team learning] [34 sessions] Alibaba cloud Tianchi online programming training camp
DFS和BFS概念及实践+acwing 842 排列数字(dfs) +acwing 844. 走迷宫(bfs)
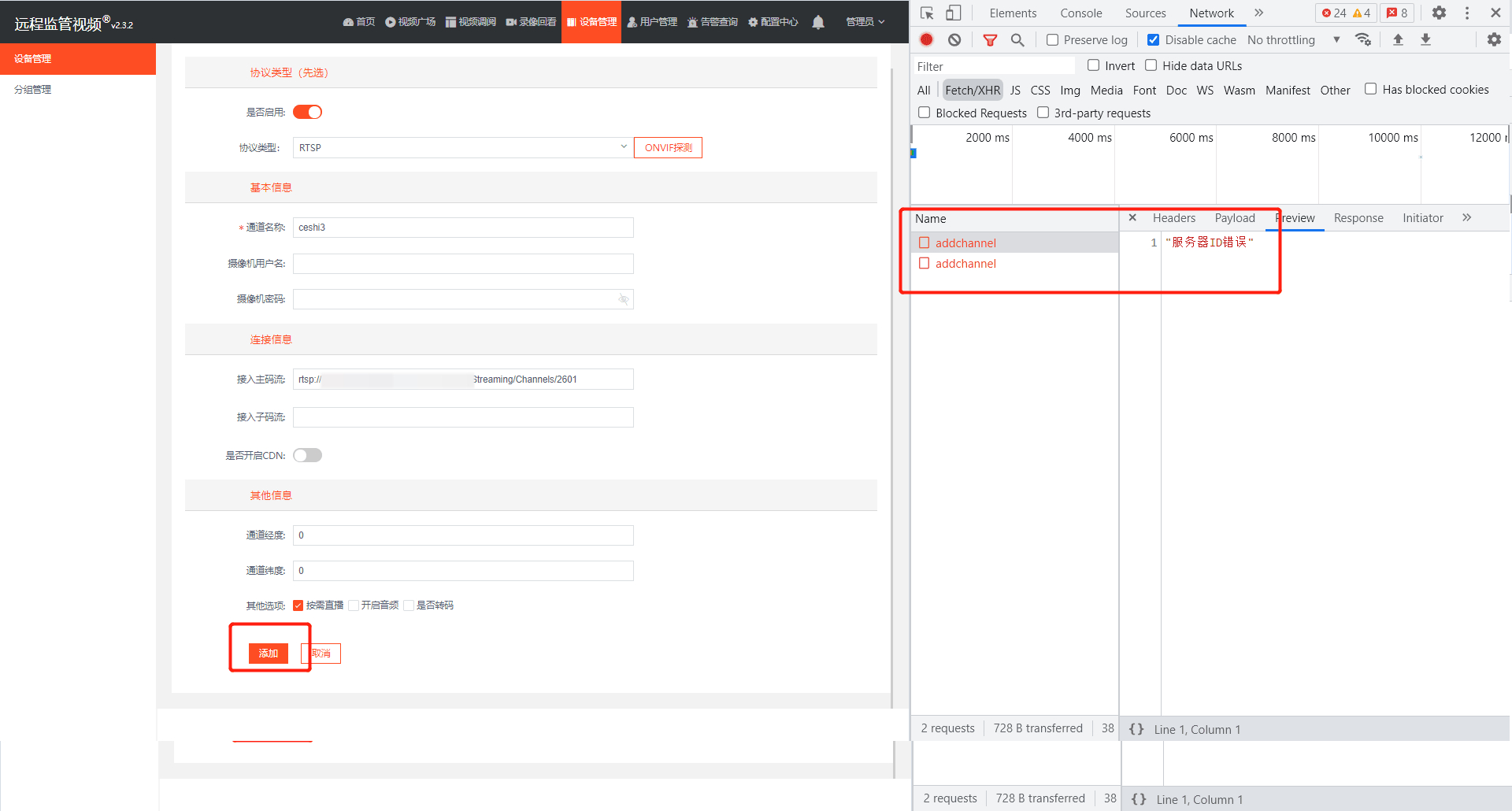
EasyCVR集群版本添加RTSP设备提示服务器ID错误,该如何解决?

Intel and Xinbu technology jointly build a machine vision development kit to jointly promote the transformation of industrial intelligence
System framework of PureMVC

Dab-detr: dynamic anchor boxes are better queries for Detr translation

EasyCVR平台接入RTMP协议,接口调用提示获取录像错误该如何解决?
随机推荐
Win11玩绝地求生(PUBG)崩溃怎么办?Win11玩绝地求生崩溃解决方法
Nanopineo use development process record
微信能开小号了,拼多多“砍一刀”被判侵权,字节VR设备出货量全球第二,今日更多大新闻在此
Up to 5million per person per year! Choose people instead of projects, focus on basic scientific research, and scientists dominate the "new cornerstone" funded by Tencent to start the application
【实践出真理】import和require的引入方式真的和网上说的一样吗
Highly paid programmers & interview questions. Are you familiar with the redis cluster principle of series 120? How to ensure the high availability of redis (Part 1)?
1.19.11. SQL client, start SQL client, execute SQL query, environment configuration file, restart policy, user-defined functions, constructor parameters
mpf2_ Linear programming_ CAPM_ sharpe_ Arbitrage Pricin_ Inversion Gauss Jordan_ Statsmodel_ Pulp_ pLU_ Cholesky_ QR_ Jacobi
AI landing new question type RPA + AI =?
EasyCVR无法使用WebRTC进行播放,该如何解决?
Implementation of JSTL custom function library
Fix the problem that the highlight effect of the main menu disappears when the easycvr Video Square is clicked and played
sscanf,sscanf_s及其相关使用方法「建议收藏」
案例大赏:英特尔携众多合作伙伴推动多领域AI产业创新发展
JS form get form & get form elements
Zero knowledge private application platform aleo (1) what is aleo
Easycvr cannot be played using webrtc. How to solve it?
[team learning] [34 sessions] Alibaba cloud Tianchi online programming training camp
This "advanced" technology design 15 years ago makes CPU shine in AI reasoning
Lecture 3 of "prime mover x cloud native positive sounding, cost reduction and efficiency enhancement lecture" - kubernetes cluster utilization improvement practice