当前位置:网站首页>Number theoretic function and its summation to be updated
Number theoretic function and its summation to be updated
2022-07-05 04:45:00 【Strezia】
Mainly record the relevant topics , Skip knowledge explanation .
List of articles
Example 1 Number theory is divided into blocks
Title Description
if x x x The result of decomposing the prime factor is x = p 1 k 1 p 2 k 2 ⋯ p n k n x=p_1^{k_1}p_2^{k_2}\cdots p_n^{k_n} x=p1k1p2k2⋯pnkn, Make f ( x ) = ( k 1 + 1 ) ( k 2 + 1 ) ⋯ ( k n + 1 ) f(x)=(k_1+1)(k_2+1)\cdots (k_n+1) f(x)=(k1+1)(k2+1)⋯(kn+1), seek ∑ i = l r f ( i ) \sum_{i=l}^rf(i) ∑i=lrf(i) Yes 998 244 353 998\,244\,353 998244353 Results of die taking .
Time complexity O ( n ) O(\sqrt n) O(n).
Ideas
The first thing to know is f ( x ) f(x) f(x) In fact, that is x x x The approximate number of .( Every prime factor has k i k_i ki Then you can take 0 , 1 , . . . , k i 0,1,...,k_i 0,1,...,ki altogether k i + 1 k_i+1 ki+1 Sort and combine , From the unique decomposition theorem, it is obvious that the products are different ) Because the topic requires interval and , Then it is normally transformed into prefix and form a n s = ∑ i = 1 r f ( x ) − ∑ i = 1 l − 1 f ( x ) ans=\sum_{i=1}^rf(x)-\sum_{i=1}^{l-1}f(x) ans=∑i=1rf(x)−∑i=1l−1f(x) , set up S ( n ) = ∑ i = 1 n f ( x ) S(n) = \sum_{i=1}^nf(x) S(n)=∑i=1nf(x), The problem is transformed into seeking S ( n ) S(n) S(n) , That is to say seek 1 − n 1-n 1−n this n n n The sum of the number of factors .
1 − n 1-n 1−n There are factors i i i There are a total of ⌊ n i ⌋ \lfloor\frac ni\rfloor ⌊in⌋ , Directly use number theory to divide into blocks .
Code
int ll, rr, n;
int cal(int l, int r) {
int ansr = 0, ansl = 0;
n = rr;
for(int l=1,r;l<=n;l=r+1){
r=n/(n/l);
ansr+=(n/l)*(r-l+1) % P;
ansr %= P;
}
n = ll;
for(int l=1,r;l<=n;l=r+1){
r=n/(n/l);
ansl+=(n/l)*(r-l+1) % P;
ansl %= P;
}
ansr = (ansr - ansl + P) % P;
return ansr;
}
void solve() {
cin >> ll >> rr;
ll--;
cout << cal(ll, rr) << endl;
}
Example 2 Number theory is divided into blocks
P2303 [SDOI2012] Longge The problem of
Title Description
Given an integer n n n, You need to figure out ∑ i = 1 n gcd ( i , n ) \sum\limits_{i=1}^n \gcd(i, n) i=1∑ngcd(i,n), n < 1 0 9 n<10^9 n<109
Ideas
be aware g c d ( i , n ) gcd(i,n) gcd(i,n) The maximum value of is n n n The approximate number of , So consider classification by value , And it appears g c d gcd gcd Problems often need to find a way to figure out g c d ( i , j ) = 1 gcd(i,j)=1 gcd(i,j)=1, So we change the original formula into ∑ d ∣ n d ∑ i = 1 n [ g c d ( i , n ) = d ] = ∑ d ∣ n d ∑ i = 1 n d [ g c d ( i , n d ) = 1 ] = ∑ d ∣ n d ϕ ( n d ) \sum_{d|n}d\sum_{i=1}^n[gcd(i,n)=d ]=\sum_{d|n}d\sum_{i=1}^{\frac nd}[gcd(i,\frac nd)=1]=\sum_{d|n}d\phi(\frac nd) d∣n∑di=1∑n[gcd(i,n)=d]=d∣n∑di=1∑dn[gcd(i,dn)=1]=d∣n∑dϕ(dn)
You can enumerate n n n Directly find the divisor of , Time complexity O ( n ) O(\sqrt n) O(n).
Code
void solve() {
cin >> n;
ll ans = 0;
for(ll i = 1; i * i <= n; i++) {
if(n % i == 0) {
ans += i * phi(n/i);
if(n/i!=i) {
ans += (n/i) * phi(i);
}
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
Mobius function
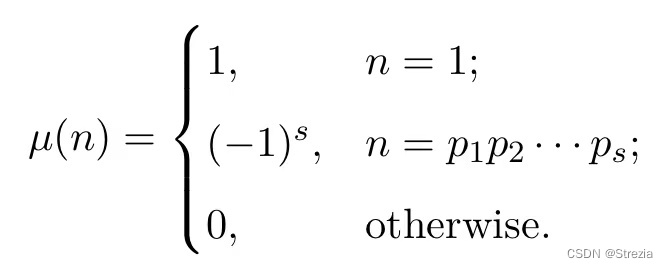
Convolution is often used
ϵ = μ ∗ 1 , I d = ϕ ∗ 1 \epsilon=\mu *1, Id=\phi*1 ϵ=μ∗1,Id=ϕ∗1 .
namely ϵ ( n ) = ∑ d ∣ n μ ( d ) \epsilon(n) = \sum_{d|n}\mu(d) ϵ(n)=∑d∣nμ(d) . among ϵ ( n ) = 1 \epsilon(n)= 1 ϵ(n)=1 If and only if n = 1 n=1 n=1, otherwise = 0 =0 =0 .
Cited example
Given n , m n, m n,m, Find two tuples ( x , y ) (x,y) (x,y) The number of , Satisfy 1 ≤ x ≤ n 1\leq x\leq n 1≤x≤n , 1 ≤ y ≤ m 1\leq y\leq m 1≤y≤m , And g c d ( x , y ) = 1 gcd(x,y)=1 gcd(x,y)=1 . n , m ≤ 1 0 7 n,m\leq 10^7 n,m≤107 , at most 1 0 4 10^4 104 Group data .
Ideas
∑ x = 1 n ∑ y = 1 m [ g c d ( x , y ) = 1 ] = ∑ x = 1 n ∑ y = 1 m ϵ ( g c d ( x , y ) ) = ∑ x = 1 n ∑ y = 1 m ∑ d ∣ g c d ( x , y ) μ ( d ) \sum_{x=1}^n\sum_{y=1}^m[gcd(x,y)=1]=\sum_{x=1}^n\sum_{y=1}^m\epsilon (gcd(x,y))=\sum_{x=1}^n\sum_{y=1}^m\sum_{d|gcd(x,y)}\mu(d) x=1∑ny=1∑m[gcd(x,y)=1]=x=1∑ny=1∑mϵ(gcd(x,y))=x=1∑ny=1∑md∣gcd(x,y)∑μ(d)
= ∑ x = 1 n ∑ y = 1 m ∑ d ∣ x , d ∣ y μ ( d ) = = ∑ d = 1 m i n ( n , m ) μ ( d ) ⌊ n d ⌋ ⌊ m d ⌋ =\sum_{x=1}^n\sum_{y=1}^m\sum_{d|x,d|y}\mu(d)==\sum_{d=1}^{min(n,m)}\mu(d)\lfloor\frac nd\rfloor\lfloor\frac md\rfloor =x=1∑ny=1∑md∣x,d∣y∑μ(d)==d=1∑min(n,m)μ(d)⌊dn⌋⌊dm⌋
Pretreatment of the above formula μ \mu μ And its prefix and , Press ⌊ n d ⌋ ⌊ m d ⌋ \lfloor\frac nd\rfloor\lfloor\frac md\rfloor ⌊dn⌋⌊dm⌋ The value segment of , You can ask each group O ( n ) O(\sqrt n) O(n) solve the problem .
Example 3 Mobius inversion
Title Description
set up d ( x ) d(x) d(x) by x x x The approximate number of , Given n , m n,m n,m, seek
∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 m d ( i j ) \sum_{i=1}^n\sum_{j=1}^md(ij) i=1∑nj=1∑md(ij)
【 Data range 】
about 100 % 100\% 100% The data of , 1 ≤ T , n , m ≤ 50000 1\le T,n,m \le 50000 1≤T,n,m≤50000.
Ideas
First, there are conclusions :
d ( i j ) = ∑ x ∣ i ∑ y ∣ j [ g c d ( x , y ) = 1 ] d(ij)=\sum_{x|i}\sum_{y|j}[gcd(x,y)=1] d(ij)=x∣i∑y∣j∑[gcd(x,y)=1]
Then the original formula :
∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 m d ( i j ) = ∑ i = 1 n ∑ j = 1 m ∑ x ∣ i ∑ y ∣ j [ g c d ( x , y ) = 1 ] = ∑ x = 1 n ∑ y = 1 m [ g c d ( x , y ) = 1 ] ⌊ n x ⌋ ⌊ m y ⌋ \sum_{i=1}^n\sum_{j=1}^md(ij)=\sum_{i=1}^n\sum_{j=1}^m\sum_{x|i}\sum_{y|j}[gcd(x,y)=1]=\sum_{x=1}^n\sum_{y=1}^m[gcd(x,y)=1]\lfloor\frac nx\rfloor\lfloor\frac my\rfloor i=1∑nj=1∑md(ij)=i=1∑nj=1∑mx∣i∑y∣j∑[gcd(x,y)=1]=x=1∑ny=1∑m[gcd(x,y)=1]⌊xn⌋⌊ym⌋
Bring the conclusion of the cited example into :
= ∑ d = 1 m i n ( n , m ) μ ( d ) ∑ x = 1 ⌊ n d ⌋ ∑ y = 1 ⌊ m d ⌋ ⌊ n x d ⌋ ⌊ m y d ⌋ = ∑ d = 1 m i n ( n , m ) μ ( d ) ∑ x = 1 ⌊ n d ⌋ ∑ y = 1 ⌊ m d ⌋ ⌊ ⌊ n d ⌋ x ⌋ ⌊ ⌊ m d ⌋ y ⌋ =\sum_{d=1}^{min(n,m)}\mu(d)\sum_{x=1}^{\lfloor\frac nd\rfloor}\sum_{y=1}^{\lfloor\frac md \rfloor}\lfloor\frac n{xd}\rfloor\lfloor\frac m{yd}\rfloor=\sum_{d=1}^{min(n,m)}\mu(d)\sum_{x=1}^{\lfloor\frac nd\rfloor}\sum_{y=1}^{\lfloor\frac md \rfloor}\lfloor\frac{\lfloor\frac nd\rfloor}x\rfloor\lfloor\frac {\lfloor \frac md\rfloor}y\rfloor =d=1∑min(n,m)μ(d)x=1∑⌊dn⌋y=1∑⌊dm⌋⌊xdn⌋⌊ydm⌋=d=1∑min(n,m)μ(d)x=1∑⌊dn⌋y=1∑⌊dm⌋⌊x⌊dn⌋⌋⌊y⌊dm⌋⌋
Make f ( n ) = ∑ i = 1 n ⌊ n i ⌋ f(n)=\sum_{i=1}^n\lfloor\frac ni\rfloor f(n)=∑i=1n⌊in⌋ , be
= ∑ d = 1 m i n ( n , m ) μ ( d ) f ( ⌊ n d ⌋ ) f ( ⌊ m d ⌋ ) =\sum_{d=1}^{min(n, m)}\mu(d)f(\lfloor\frac nd\rfloor)f(\lfloor\frac md\rfloor) =d=1∑min(n,m)μ(d)f(⌊dn⌋)f(⌊dm⌋)
also f ( n ) = ∑ i = 1 n ⌊ n i ⌋ = ∑ k = 1 n d ( k ) f(n)=\sum_{i=1}^n\lfloor\frac ni\rfloor=\sum_{k=1}^nd(k) f(n)=∑i=1n⌊in⌋=∑k=1nd(k)
Therefore, it can pass the Euler sieve O ( n ) O(n) O(n) Preprocessing d ( n ) d(n) d(n), By prefix and, we get f ( n ) f(n) f(n), You can ask every time O ( n ) O(\sqrt n) O(n) answer .
Code
int mu[maxn], prim[maxn], sum[maxn], cnt;
int g[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
void get_mu(int n)
{
mu[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!vis[i]){
prim[++cnt]=i;mu[i]=-1;}
for(int j=1;j<=cnt&&prim[j]*i<=n;j++)
{
vis[prim[j]*i]=1;
if(i%prim[j]==0)break;
else mu[i*prim[j]]=-mu[i];
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)sum[i]=sum[i-1]+mu[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
long long ans=0;
for(int l=1,r;l<=i;l=r+1)
{
r=(i/(i/l));
ans+=1ll*(r-l+1)*1ll*(i/l);
}
g[i]=ans;
}
}
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int ans = 0;
int mn = min(n, m);
for(int l = 1, r; l <= mn; l = r + 1){
r = min(n/(n/l), m/(m/l));
ans += (sum[r] - sum[l-1]) * g[n/l] * g[m/l];
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
边栏推荐
- 直播預告 | 容器服務 ACK 彈性預測最佳實踐
- Label exchange experiment
- Qt蓝牙:搜索蓝牙设备的类——QBluetoothDeviceDiscoveryAgent
- [Chongqing Guangdong education] National Open University 2047t commercial bank operation and management reference test in autumn 2018
- 2022-2028 global and Chinese virtual data storage Market Research Report
- WeNet:面向工业落地的E2E语音识别工具
- 取余操作是一个哈希函数
- Leetcode hot topic Hot 100 day 33: "subset"
- 【acwing】528. cheese
- 3 minutes learn to create Google account and email detailed tutorial!
猜你喜欢

【acwing】240. food chain

How can CIOs use business analysis to build business value?

直播预告 | 容器服务 ACK 弹性预测最佳实践
Function (error prone)

取余操作是一个哈希函数
windows下Redis-cluster集群搭建
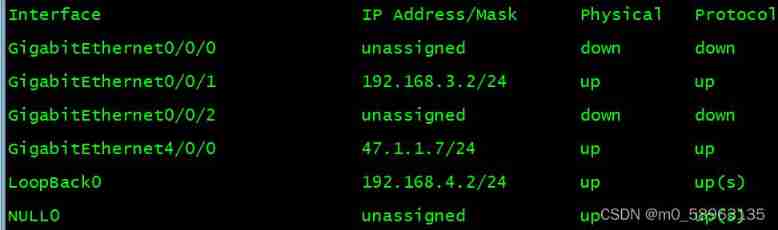
Label exchange experiment
About the prompt loading after appscan is opened: guilogic, it keeps loading and gets stuck. My personal solution. (it may be the first solution available in the whole network at present)
The 22nd Spring Festival Gala, an immersive stage for the yuan universe to shine into reality

Looking at Chinese science and technology from the Winter Olympics: what is the mystery of the high-speed camera that the whole people thank?
随机推荐
Thinking of 2022 American College Students' mathematical modeling competition
Private collection project practice sharing [Yugong series] February 2022 U3D full stack class 006 unity toolbar
Thematic information | carbon, carbon neutrality, low carbon, carbon emissions - 22.1.9
2021 Higher Education Club Cup mathematical modeling national tournament ABCD problem - problem solving ideas
CSDN body auto generate directory
程序员应该怎么学数学
首席信息官如何利用业务分析构建业务价值?
[goweb development] Introduction to authentication modes based on cookies, sessions and JWT tokens
Neural networks and deep learning Chapter 6: Circular neural networks reading questions
自动语音识别(ASR)研究综述
质量体系建设之路的分分合合
Introduction to RT thread kernel (4) -- clock management
[illusory engine UE] method to realize close-range rotation of operating objects under fuzzy background and pit recording
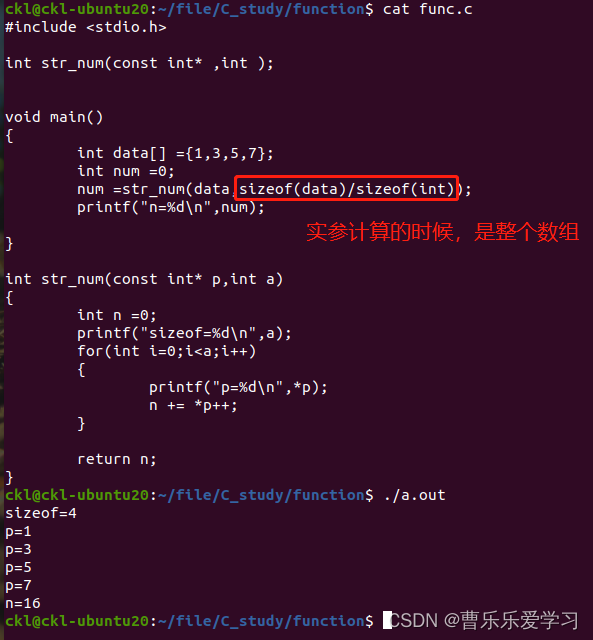
函数(易错)
Leetcode 222 number of nodes of complete binary tree
Wenet: E2E speech recognition tool for industrial implementation
Manually implement heap sorting -838 Heap sort
Cookie learning diary 1
Special information | real estate and office buildings - 22.1.9
Qt蓝牙:搜索蓝牙设备的类——QBluetoothDeviceDiscoveryAgent