当前位置:网站首页>Kill -9 system call used by PID to kill process
Kill -9 system call used by PID to kill process
2022-07-06 17:53:00 【TABE_】
Here's the catalog title
kill Command Introduction
kill The command sends a signal to the operating system kernel ( Most of them are termination signals ) And target process PID, And then the system kernel depends on the type of signal it receives , Process the specified process .
kill( Options )( Parameters )
-a: When processing the current process , There is no limit to the correspondence between the command name and the process number ;
-l < Information number >: If not add < Information number > Options , be -l Parameter will list all information names ;
-p: Appoint kill The command only prints the process number of the relevant process , Without sending any signals ;
-s < Information name or number >: Specify the message to send ;
-u: Designated user .
Only the first one 9 Signals (SIGKILL) To terminate the process unconditionally , Other signaling processes have the right to ignore , Here are some common signals
HUP 1 Terminal disconnection ( Smooth restart process )
INT 2 interrupt ( Same as Ctrl + C)
QUIT 3 sign out ( Same as Ctrl + \)
TERM 15 End
KILL 9 Mandatory termination
CONT 18 continue ( And STOP contrary , fg/bg command )
STOP 19 Pause ( Same as Ctrl + Z)
Example :
[[email protected].com ~]#ps -ef |grep chronyd
chrony 30365 1 0 19:58 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/chronyd
root 30385 29218 0 19:58 pts/1 00:00:00 grep --color=auto chronyd
[[email protected].com ~]#kill -9 30483
[[email protected].com ~]#ps -ef |grep chronyd
root 30508 29218 0 20:00 pts/1 00:00:00 grep --color=auto chronyd
kill The principle of command
perform kill -9 <PID>, First of all, we need to generate signals . perform kill The program needs a pid, According to this pid Find the process task_struct( This is Linux The following represents the process / Thread structure ), Then write down this signal in the specific member variables of this structure . At this time, the signal is generated but has not been processed by a specific process , be called Pending signal.
Wait until the next time CPU When this process is scheduled , The kernel guarantees to execute first do_signal This function checks whether there is a signal that needs to be processed , If you have any , Then deal with ; If there is no , Then continue the process directly . So we see , stay Linux Next , Signals do not behave asynchronously like interrupts , Instead, every time you schedule this process, you check whether there are unprocessed signals .
Signal transmission
call kill After the command , Signal and target process PID Sent by the user to the kernel .
kill It's a program in itself , Is the source code , Its code can be found in Linux Of coreutils Found in . The code is very long , I won't copy it all , Those who are interested can go and have a closer look .kill The core code of the command is like this :
static int send_signals (int signum, char *const *argv) {
…
kill (pid, signum);
…
}
int main (int argc, char **argv) {
…
send_signals (signum, argv + optind);
…
}
kill Command called send_signals (signum, argv + optind) function ,send_signals (signum, argv + optind) System call is called again kill (pid, signum), The system call is in Linux kernel linux-3.16.3/kernel/signal.c To realize , It describes the structure of the process task_struct To operate , stay task_struct Write down the signals to be transmitted in the specific member variables in .task_struct The signal related parts of the structure are as follows :
struct task_struct {
… /* signal handlers */
struct signal_struct *signal; /* All threads of a process share one signal */
struct sighand_struct *sighand; sigset_t blocked,real_blocked; /* Which signals are blocked */
sigset_t saved_sigmask; /* restored if set_restore_sigmask() was used */
struct sigpending pending; /* Multiple threads in the process have their own pending */
…
}
kill (pid, signum) The core code of the system call is as follows , For ease of understanding , I added comments to the core logic :
SYSCALL_DEFINE2(kill, pid_t, pid, int, sig) {
…
return kill_something_info(sig, &info, pid);
}
static int kill_something_info(int sig, struct siginfo * info, pid_t pid) {
int ret;
// If pid Greater than 0, Send the signal to the specified process
if (pid > 0) {
ret = kill_pid_info(sig, info, find_vpid(pid));
return ret;
}
// If pid <=0 And it's not equal to -1, Send a signal to -pid Specified process group
if (pid != -1) {
ret = __kill_pgrp_info(sig, info, pid ? find_vpid( - pid) : task_pgrp(current));
}
else {
// Otherwise, it sends a signal to all processes except its own process
int retval = 0,
count = 0;
struct task_struct * p;
for_each_process(p) {
if (task_pid_vnr(p) > 1 && !same_thread_group(p, current)) {
int err = group_send_sig_info(sig, info, p); ++count;
if (err != -EPERM) retval = err;
}
}
ret = count ? retval: -ESRCH;
}
return ret;
}
kill (pid, signum) Would call kill_something_info(sig, &info, pid),kill_something_info(sig, &info, pid) Will be based on pid To determine whether to send to a specific process or a process group , Let's mainly look at the situation of sending to a specific process , That is to call kill_pid_info(sig, info, find_vpid(pid)), The code for this function is as follows :
int kill_pid_info(int sig, struct siginfo * info, struct pid * pid) {
int error = -ESRCH;
struct task_struct * p;
p = pid_task(pid, PIDTYPE_PID);
if (p) {
error = group_send_sig_info(sig, info, p);
}
return error;
}```
kill_pid_info(sig, info, find_vpid(pid)) We mentioned above task_strcut, This is Linux The following represents each process / Thread structure , according to struct pid Find this structure , It's called group_send_sig_info(sig, info, p), The code for this function is as follows :
int group_send_sig_info(int sig, struct siginfo * info, struct task_struct * p) {
int ret;
ret = do_send_sig_info(sig, info, p, true);
return ret;
}
int do_send_sig_info(int sig, struct siginfo * info, struct task_struct * p, bool group) {
unsigned long flags;
int ret = -ESRCH;
if (lock_task_sighand(p, &flags)) {
ret = send_signal(sig, info, p, group);
unlock_task_sighand(p, &flags);
}
return ret;
}
static int send_signal(int sig, struct siginfo * info, struct task_struct * t, int group) {
int from_ancestor_ns = 0;
#ifdef CONFIG_PID_NS from_ancestor_ns = si_fromuser(info) && !task_pid_nr_ns(current, task_active_pid_ns(t));
#endif
return __send_signal(sig, info, t, group, from_ancestor_ns);
}
static int __send_signal(int sig, struct siginfo * info, struct task_struct * t, int group, int from_ancestor_ns) {
struct sigpending * pending;
struct sigqueue * q;
int override_rlimit;
int ret = 0,result; // The difference between sending to a process and a thread is here , If it's a process , be &t->signal->shared_pending, otherwise &t->pending pending = group ? &t->signal->shared_pending : &t->pending;
/* * fast-pathed signals for kernel-internal things like SIGSTOP * or SIGKILL. */
if (info == SEND_SIG_FORCED) goto out_set;
…
out_set: // Notify the signal listening
signalfd. signalfd_notify(t, sig); // take sig Add to the signal bitmap of the target process , Next time CPU Read when scheduling
sigaddset(&pending->signal, sig); // Used to determine which process / The thread processes the signal , then wake_up This process / Threads
complete_signal(sig, t, group);
ret:
trace_signal_generate(sig, info, t, group, result);
return ret;
}
You can see , Finally call to __send_signal, Set the data structure of the signal , Wake up processes that need to process signals , The whole signal transmission process is over . At this time, the signal has not been processed by the process , Or a pending signal.
signal processing ( kernel )
When the kernel schedules the process , Would call do_notify_resume() To process the signals in the signal queue , Then this function will call do_signal(), Call again handle_signal(), No code is needed to explain the specific process , Finally, we will find the processing function of each signal , The problem is how to find the signal processing function ?
Remember what I mentioned above task_struct Do you , There's a member variable in it sighand_struct It is used to store the processing function of each signal .
struct sighand_struct {
atomic_t count; /* Reference count */
struct k_sigaction action[_NSIG]; /* Store the structure of the processing function */
spinlock_t siglock; /* spinlocks */
wait_queue_head_t signalfd_wqh; /* Waiting in line */
};
struct k_sigaction {
struct sigaction sa;
}
struct sigaction {
__sighandler_t sa_handler;
}
among sa_handler It points to the signal processing program .
边栏推荐
- 编译原理——预测表C语言实现
- PyTorch 提取中间层特征?
- Pytest learning ----- detailed explanation of the request for interface automation test
- adb常用命令
- Nodejs 开发者路线图 2022 零基础学习指南
- The art of Engineering
- The easycvr platform reports an error "ID cannot be empty" through the interface editing channel. What is the reason?
- There is a gap in traditional home decoration. VR panoramic home decoration allows you to experience the completion effect of your new house
- QT中Model-View-Delegate委托代理机制用法介绍
- sql语句优化,order by desc速度优化
猜你喜欢
基于STM32+华为云IOT设计的智能路灯
EasyCVR接入设备开启音频后,视频无法正常播放是什么原因?

Unity粒子特效系列-闪星星的宝箱
kivy教程之在 Kivy 中支持中文以构建跨平台应用程序(教程含源码)
EasyCVR平台通过接口编辑通道出现报错“ID不能为空”,是什么原因?
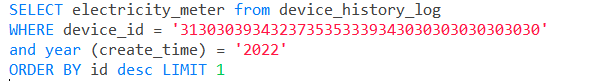
SQL statement optimization, order by desc speed optimization
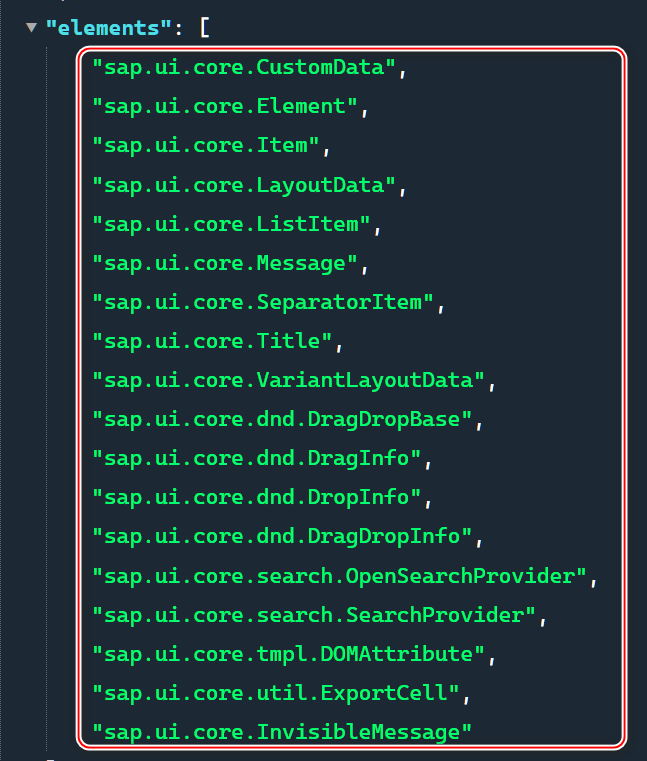
SAP UI5 框架的 manifest.json
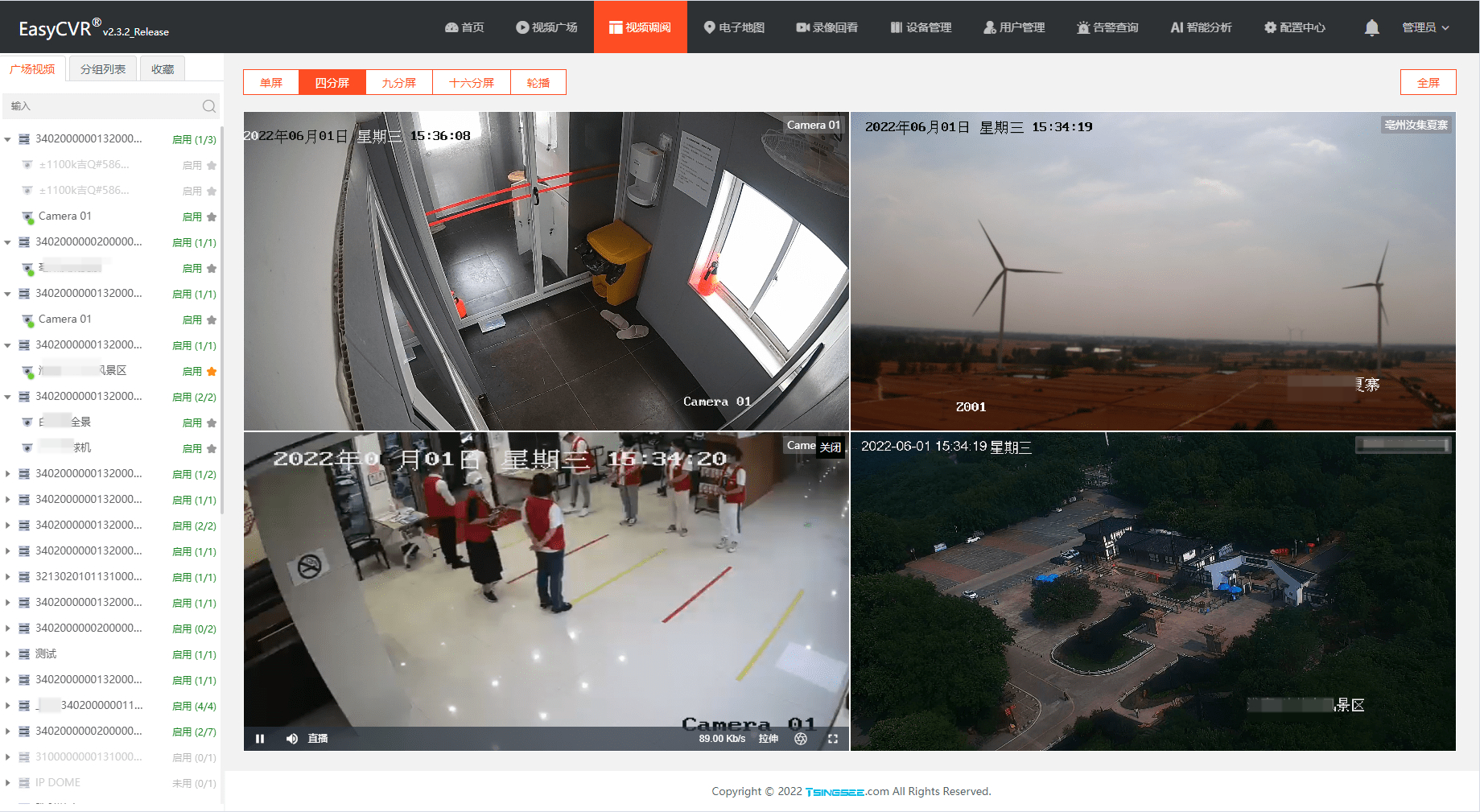
视频融合云平台EasyCVR增加多级分组,可灵活管理接入设备
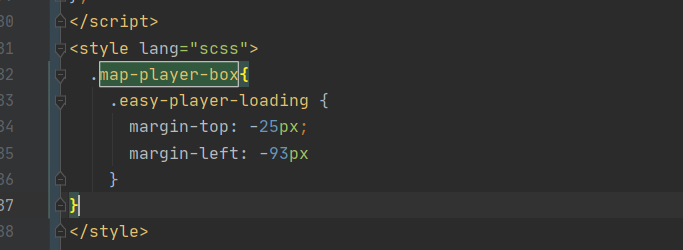
EasyCVR电子地图中设备播放器loading样式的居中对齐优化

Smart street lamp based on stm32+ Huawei cloud IOT design
随机推荐
Grafana 9 is officially released, which is easier to use and more cool!
EasyCVR平台通过接口编辑通道出现报错“ID不能为空”,是什么原因?
遠程代碼執行滲透測試——B模塊測試
HMS Core 机器学习服务打造同传翻译新“声”态,AI让国际交流更顺畅
Run xv6 system
scratch疫情隔离和核酸检测模拟 电子学会图形化编程scratch等级考试三级真题和答案解析2022年6月
面试突击62:group by 有哪些注意事项?
微信小程序获取手机号
容器里用systemctl运行服务报错:Failed to get D-Bus connection: Operation not permitted(解决方法)
MSF横向之MSF端口转发+路由表+SOCKS5+proxychains
BearPi-HM_ Nano development environment
高精度运算
1700C - Helping the Nature
Mysqlimport imports data files into the database
面试突击63:MySQL 中如何去重?
Growth of operation and maintenance Xiaobai - week 7
sql语句优化,order by desc速度优化
《ASP.NET Core 6框架揭秘》样章发布[200页/5章]
Flet教程之 13 ListView最常用的滚动控件 基础入门(教程含源码)
Smart street lamp based on stm32+ Huawei cloud IOT design