当前位置:网站首页>Robot autonomous exploration DSVP: code parsing
Robot autonomous exploration DSVP: code parsing
2022-07-07 22:26:00 【Lift the cement together】
Write it at the front
The paper :DSVP: Dual-Stage Viewpoint Planner for Rapid Exploration by Dynamic Expansion
The article is right “Receding Horizon "Next-Best-View" Planner for 3D Exploration” Improvement
Code parsing :
First of all to see launch file :
<launch> <arg name="enable_bag_record" default="false"/> <arg name="bag_name" default="dsvp_garage"/> <arg name="simulation" default="false"/> <arg name="use_boundary" default="false"/> <arg name="planner_param_file" default="$(find dsvp_launch)/config/exploration.yaml" /> <arg name="octomap_param_file" default="$(find dsvp_launch)/config/octomap.yaml" /> <rosparam command="load" file="$(arg planner_param_file)" /> <rosparam command="load" file="$(arg octomap_param_file)" /> <node name="dsvplanner" pkg="dsvplanner" type="dsvplanner" output="screen" /> <group if="$(arg use_boundary)"> <node pkg="dsvp_launch" type="navigationBoundary" name="navigationBoundary" output="screen" required="true"> <param name="boundary_file_dir" type="string" value="$(find dsvp_launch)/data/boundary.ply" /> <param name="sendBoundary" type="bool" value="true" /> <param name="sendBoundaryInterval" type="int" value="2" /> </node> </group> <node name="exploration" pkg="dsvp_launch" type="exploration" output="screen" > <param name="simulation" type="bool" value="$(arg simulation)" /> </node> <include file="$(find graph_planner)/launch/graph_planner.launch"/> <group if="$(arg enable_bag_record)"> <include file="$(find dsvp_launch)/launch/rosbag_record.launch"> <arg name="bag_name" value="$(arg bag_name)" /> </include> </group> <node pkg="rviz" type="rviz" name="dsvp_rviz" args="-d $(find dsvp_launch)/default.rviz"/> </launch>from launch The document shows that , It mainly implements two node file , So let's look at the first one dsvplanner, Their corresponding cpp File for drrtp_node.cpp
drrtp_node.cpp
In this code , To define a drrtPlanner object planner, The specific implementation of this object is drrtp.cpp in
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Dense>
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <dsvplanner/drrtp.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "nbvPlanner");
ros::NodeHandle nh;
ros::NodeHandle nh_private("~");
dsvplanner_ns::drrtPlanner planner(nh, nh_private);
ros::spin();
return 0;
}drrtp.cpp
First look at the constructor of this object
dsvplanner_ns::drrtPlanner::drrtPlanner(const ros::NodeHandle &nh,
const ros::NodeHandle &nh_private)
: nh_(nh), nh_private_(nh_private) {
manager_ = new volumetric_mapping::OctomapManager(nh_, nh_private_);
grid_ = new OccupancyGrid(nh_, nh_private_);
dual_state_graph_ = new DualStateGraph(nh_, nh_private_, manager_, grid_);
dual_state_frontier_ = new DualStateFrontier(nh_, nh_private_, manager_, grid_);
drrt_ = new Drrt(manager_, dual_state_graph_, dual_state_frontier_, grid_);
init();
drrt_->setParams(params_);
drrt_->init();
ROS_INFO("Successfully launched DSVP node");
}1. The constructor first defines 4 Objects :
1.1 manager_ object
manager_ = new volumetric_mapping::OctomapManager(nh_, nh_private_);namespace volumetric_mapping {
OctomapManager::OctomapManager(const ros::NodeHandle &nh,
const ros::NodeHandle &nh_private)
: nh_(nh), nh_private_(nh_private), world_frame_("map"),
velodyne_cloud_topic_("/velodyne_cloud_topic"), robot_frame_("velodyne"),
use_tf_transforms_(true), latch_topics_(true),
timestamp_tolerance_ns_(10000000), Q_initialized_(false),
Q_(Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity()), map_publish_frequency_(0.0) {
setParametersFromROS();
subscribe();
advertiseServices();
advertisePublishers();
// After creating the manager, if the octomap_file parameter is set,
// load the octomap at that path and publish it.
std::string octomap_file;
if (nh_private_.getParam("octomap_file", octomap_file)) {
if (loadOctomapFromFile(octomap_file)) {
ROS_INFO_STREAM(
"Successfully loaded octomap from path: " << octomap_file);
publishAll();
} else {
ROS_ERROR_STREAM("Could not load octomap from path: " << octomap_file);
}
}
}subscribe():
void OctomapManager::subscribe() {
pointcloud_sub_ = nh_.subscribe(velodyne_cloud_topic_, 1, &OctomapManager::insertPointcloudWithTf, this);
octomap_sub_ = nh_.subscribe("input_octomap", 1, &OctomapManager::octomapCallback, this);
}velodyne_cloud_topic_: /sensor_scan(lidar Point cloud in coordinate system )
Callback function 1:insertPointcloudWithTf( obtain sensor Transformation from coordinate system to world coordinate system , And convert the transformation to the corresponding format )、 Ray tracing updates the map
void OctomapManager::insertPointcloudWithTf(
const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2::ConstPtr &pointcloud) {
// Look up transform from sensor frame to world frame.
Transformation sensor_to_world;
if (lookupTransform(pointcloud->header.frame_id, world_frame_,
pointcloud->header.stamp, &sensor_to_world)) {
insertPointcloud(sensor_to_world, pointcloud);
}
}lookupTransformTf Realization :
1. pointcloud->header.frame_id by :/sensor_at_scan stay sensor_scan_generation Defined in the function package ;
2. world_frame_:/map
bool OctomapManager::lookupTransform(const std::string &from_frame,
const std::string &to_frame,
const ros::Time ×tamp,
Transformation *transform) {
if (use_tf_transforms_) {
return lookupTransformTf(from_frame, to_frame, timestamp, transform);
} else {
return lookupTransformQueue(from_frame, to_frame, timestamp, transform);
}
}bool OctomapManager::lookupTransformTf(const std::string &from_frame,
const std::string &to_frame,
const ros::Time ×tamp,
Transformation *transform) {
tf::StampedTransform tf_transform;
ros::Time time_to_lookup = timestamp;
// If this transform isn't possible at the time, then try to just look up
// the latest (this is to work with bag files and static transform publisher,
// etc).
if (!tf_listener_.canTransform(to_frame, from_frame, time_to_lookup)) {
ros::Duration timestamp_age = ros::Time::now() - time_to_lookup;
if (timestamp_age < tf_listener_.getCacheLength()) {
time_to_lookup = ros::Time(0);
// ROS_WARN("Using latest TF transform instead of timestamp match.");
} else {
// ROS_ERROR("Requested transform time older than cache limit.");
return false;
}
}
try {
tf_listener_.lookupTransform(to_frame, from_frame, time_to_lookup,
tf_transform);
} catch (tf::TransformException &ex) {
ROS_ERROR_STREAM(
"Error getting TF transform from sensor data: " << ex.what());
return false;
}
tf::transformTFToKindr(tf_transform, transform);
return true;
}void transformTFToKindr(const tf::Transform& tf_type,
kindr::minimal::QuatTransformation* kindr) {
CHECK_NOTNULL(kindr);
Eigen::Vector3d position;
Eigen::Quaterniond rotation;
quaternionTFToKindr(tf_type.getRotation(), &rotation);
vectorTFToKindr(tf_type.getOrigin(), &position);
// Enforce positive w.
if (rotation.w() < 0) {
rotation.coeffs() = -rotation.coeffs();
}
*kindr = kindr::minimal::QuatTransformation(rotation, position);
}That is, type conversion (tf_transform--transform( obtain rotation and position))
insertPointcloud(sensor_to_world, pointcloud): The realization is to update by raytracing each point in the current frame point cloud free_cells and occupied_cells
Callback function 2: octomapCallback( Don't look at it for the time being )
1.2 grid_ object
grid_ = new OccupancyGrid(nh_, nh_private_);Implementation of this object :
OccupancyGrid::OccupancyGrid(const ros::NodeHandle &nh, const ros::NodeHandle &nh_private)
: nh_(nh), nh_private_(nh_private) {
initialize();
}bool OccupancyGrid::initialize() {
// Read in parameters
if (!readParameters())
return false;
// Initialize subscriber
odom_sub_.subscribe(nh_, sub_odom_topic_, 1);
terrain_point_cloud_sub_.subscribe(nh_, sub_terrain_point_cloud_topic_, 1);
sync_.reset(new Sync(syncPolicy(100), odom_sub_, terrain_point_cloud_sub_));
sync_->registerCallback( boost::bind(&OccupancyGrid::terrainCloudAndOdomCallback, this, _1, _2));
grid_cloud_pub_ = nh_.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(pub_grid_points_topic_, 1);
map_half_width_grid_num_ = int(kMapWidth / 2 / kGridSize); // 40/2/0.1
map_width_grid_num_ = map_half_width_grid_num_ * 2 + 1;
clearGrid();
ROS_INFO("Successfully launched OccupancyGrid node");
return true;
}Initialize some parameters and subscribe /state_estimation and /terrain_map_ext, Execute callback function terrainCloudAndOdomCallback
void OccupancyGrid::terrainCloudAndOdomCallback(
const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr &odom_msg,
const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2::ConstPtr &terrain_msg) {
terrain_time_ = terrain_msg->header.stamp;
robot_position_[0] = odom_msg->pose.pose.position.x;
robot_position_[1] = odom_msg->pose.pose.position.y;
robot_position_[2] = odom_msg->pose.pose.position.z;
terrain_cloud_->clear();
terrain_cloud_ds->clear();
terrain_cloud_traversable_->clear();
terrain_cloud_obstacle_->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*terrain_msg, *terrain_cloud_);
pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointXYZI> point_ds;
point_ds.setLeafSize(kDownsampleSize, kDownsampleSize, kDownsampleSize);
point_ds.setInputCloud(terrain_cloud_);
// Sampling under terrain message
point_ds.filter(*terrain_cloud_ds);
pcl::PointXYZI point;
int terrainCloudSize = terrain_cloud_ds->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < terrainCloudSize; i++) {
point.x = terrain_cloud_ds->points[i].x;
point.y = terrain_cloud_ds->points[i].y;
point.z = terrain_cloud_ds->points[i].z;
point.intensity = terrain_cloud_ds->points[i].intensity;
// crop all ground points
// 0.2m To 1m Obstacles between are considered to be obstacle,(kObstacleHeightThre Default 0.2)
if (point.intensity > kObstacleHeightThre && point.intensity < kFlyingObstacleHeightThre) {
terrain_cloud_obstacle_->push_back(point);
} else if (point.intensity <= kObstacleHeightThre) {
terrain_cloud_traversable_->push_back(point);
}
}
clearGrid(); // grid All filled as unknown state
updateGrid();
publishGridMap();
}void OccupancyGrid::updateGrid() {
pcl::PointXYZI point;
for (int i = 0; i < terrain_cloud_obstacle_->points.size(); i++) {
point = terrain_cloud_obstacle_->points[i];
// Convert obstacle points into indexes
// kGridSize = 0.1
int indX = int((point.x - robot_position_[0] + kGridSize / 2) / kGridSize) + map_half_width_grid_num_;
int indY = int((point.y - robot_position_[1] + kGridSize / 2) / kGridSize) + map_half_width_grid_num_;
// Deal with negative rounding
if (point.x - robot_position_[0] + kGridSize / 2 < 0)
indX--;
if (point.y - robot_position_[1] + kGridSize / 2 < 0)
indY--;
if (indX < 0)
indX = 0;
if (indY < 0)
indY = 0;
if (indX > map_width_grid_num_ - 1)
indX = map_width_grid_num_ - 1;
if (indY > map_width_grid_num_ - 1)
indY = map_width_grid_num_ - 1;
if (indX >= 0 && indX < map_width_grid_num_ && indY >= 0 && indY < map_width_grid_num_) {
gridStatus grid_state = occupied;
gridState_[indX][indY] = grid_state;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < terrain_cloud_traversable_->points.size(); i++) {
point = terrain_cloud_traversable_->points[i];
int indX = int((point.x - robot_position_[0] + kGridSize / 2) / kGridSize) + map_half_width_grid_num_;
int indY = int((point.y - robot_position_[1] + kGridSize / 2) / kGridSize) + map_half_width_grid_num_;
if (point.x - robot_position_[0] + kGridSize / 2 < 0)
indX--;
if (point.y - robot_position_[1] + kGridSize / 2 < 0)
indY--;
if (indX < 0)
indX = 0;
if (indY < 0)
indY = 0;
if (indX > map_width_grid_num_ - 1)
indX = map_width_grid_num_ - 1;
if (indY > map_width_grid_num_ - 1)
indY = map_width_grid_num_ - 1;
if (indX >= 0 && indX < map_width_grid_num_ && indY >= 0 && indY < map_width_grid_num_) {
if (gridState_[indX][indY] == 2) {
continue;
}
if (updateFreeGridWithSurroundingGrids(indX, indY) == false) {
gridStatus grid_state = free;
gridState_[indX][indY] = grid_state;
} else {
gridStatus grid_state = near_occupied;
gridState_[indX][indY] = grid_state;
}
}
}
}point.x() - robot_position_[0] Is the vector from the current point to the robot origin
kGridSize The default is 0.1, This vector plus kGridSize/2 Divided by kGridSize And then to int Variable , It means round off ;
That is, assume that the current point is away from the robot 2m, The resolution of the grid is 0.1, Then distance 20 Lattice , Plus map_half_width_grid_num_(200), That is, at this point 220 It's about .
The robot is the center of the map , A point is on the right side of the robot 20 It's about , So in the whole map , It should be on the left 220 Lattice .
void OccupancyGrid::publishGridMap() {
grid_cloud_->clear();
pcl::PointXYZI p1;
geometry_msgs::Point p2;
// typedef Vector2i GridIndex;
GridIndex p3;
for (int i = 0; i < map_width_grid_num_; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < map_width_grid_num_; j++) {
p3[0] = i;
p3[1] = j;
// Return point
p2 = getPoint(p3);
p1.x = p2.x;
p1.y = p2.y;
p1.z = p2.z;
p1.intensity = gridState_[i][j];
grid_cloud_->points.push_back(p1);
}
}
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 gridCloud2;
pcl::toROSMsg(*grid_cloud_, gridCloud2);
gridCloud2.header.stamp = terrain_time_;
gridCloud2.header.frame_id = world_frame_id_;
grid_cloud_pub_.publish(gridCloud2);
}1.2 grid_ Object summary
grid_ The definition is to only initialize subscribers and publishers and clearGrid() function .
subscribe /state_estimation as well as /terrain_map_ext, Execute callback function , The function executes the following : Divide the points in the point cloud into four categories :unknown , free , occupied , near_occupied , And store the information of each point in intensity Properties of the , And take it as a topic /occpancy_grid_map Release it .
1.3 Define the global graph
dual_state_graph_ = new DualStateGraph(nh_, nh_private_, manager_, grid_);dual_state_graph_ Constructors :
namespace dsvplanner_ns {
DualStateFrontier::DualStateFrontier(
const ros::NodeHandle &nh, const ros::NodeHandle &nh_private,
volumetric_mapping::OctomapManager *manager, OccupancyGrid *grid)
: nh_(nh), nh_private_(nh_private) {
manager_ = manager;
grid_ = grid;
initialize();
}initialize() function :
1. Initialize some parameters
2. Define some subscribers and publishers
// Initialize subscriber
// sub_keypose_topic_: state_estimation_at_scan
key_pose_sub_ = nh_.subscribe<nav_msgs::Odometry>(sub_keypose_topic_, 5, &DualStateGraph::keyposeCallback, this);
// sub_path_topic_ : /graph_planner_path
graph_planner_path_sub_ = nh_.subscribe<nav_msgs::Path>(sub_path_topic_, 1, &DualStateGraph::pathCallback, this);
// sub_graph_planner_status_topic_ : /graph_planner_status
graph_planner_status_sub_ = nh_.subscribe<graph_planner::GraphPlannerStatus>(sub_graph_planner_status_topic_, 1,
&DualStateGraph::graphPlannerStatusCallback, this);
// Initialize publishers
// pub_local_graph_topic_: /local_graph
local_graph_pub_ = nh_.advertise<graph_utils::TopologicalGraph>(pub_local_graph_topic_, 2);
// pub_global_graph_topic_ : /global_graph
global_graph_pub_ = nh_.advertise<graph_utils::TopologicalGraph>(pub_global_graph_topic_, 2);
// pub_global_points_topic_ : /global_points
graph_points_pub_ = nh_.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(pub_global_points_topic_, 2);released /global_graph Display only .
One . Subscribe to the topic /state_estimation_at_scan( Equate to /state_estimation), Execute callback function keyposeCallback
void DualStateGraph::keyposeCallback(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr &msg) {
geometry_msgs::Pose keypose;
keypose.position.x = msg->pose.pose.position.x;
keypose.position.y = msg->pose.pose.position.y;
keypose.position.z = msg->pose.pose.position.z;
keypose.orientation.y = 0;
addNewGlobalVertexWithKeypose(keypose);
}That is, the current posture of each robot , Is executed addNewGlobalVertexWithKeypose() Callback function
void DualStateGraph::addNewGlobalVertexWithKeypose(geometry_msgs::Pose &vertex_msg) {
// Same as addNewLocalVertex but only adds vertex if a similar vertex doesn't already exist
// Extract the point
geometry_msgs::Point new_vertex_location;
new_vertex_location = vertex_msg.position;
// Check if a similar vertex already exists
bool already_exists = false;
bool too_long = false;
double distance = -1;
int closest_vertex_idx = -1;
if (!global_graph_.vertices.empty()) {
closest_vertex_idx = graph_utils_ns::GetClosestVertexIdxToPoint(global_graph_, new_vertex_location);
auto &closest_vertex_location = global_graph_.vertices[closest_vertex_idx].location;
distance = misc_utils_ns::PointXYZDist(new_vertex_location, closest_vertex_location);
if (distance < kMinVertexDist / 2) {
already_exists = true;
}
if (distance > kMaxLongEdgeDist || fabs(new_vertex_location.z - closest_vertex_location.z) > kMaxVertexDiffAlongZ) {
too_long = true;
}
}
}1. This callback function accepts the current pose of the robot , Extract the current position information of the robot , And extract global_graph_ Index of the point closest to the current point in closest_vertex_idx, And its location information closest_vertex_location,
2. Judge the distance between the current point and the nearest point , If the distance is too small or too large , Then ignore the current point . If the distance is right , Then execute the following function :
// If not, add a new one
if (!already_exists && !too_long) {
prev_track_vertex_idx_ = closest_vertex_idx;
addNewGlobalVertex(vertex_msg);
addGlobalEdgeWithoutCheck(prev_track_keypose_vertex_idx_, track_globalvertex_idx_, true);
prev_track_keypose_vertex_idx_ = track_globalvertex_idx_;
}1. Will be closest to the current point global_graph_ Index of points in closest_vertex_idx Assign to prev_track_vertex_idx_,
2. perform addNewGlobalVertex(vertex_msg) function :
2.1 Set the current point position、vertex_id(global_graph_.vertices.size()) and information_gain Add to global_graph_ in , obtain At present vertex The index of track_globalvertex_idx_, And the pointer vertex_new
2.2 When global_graph_ in vertex Is greater than 1 when , Define the current vertex Of parrent_idx by prev_track_vertex_idx_, Execute function addGlobalEdgeWithoutCheck(prev_track_vertex_idx_, track_globalvertex_idx_, false).
2.3 addGlobalEdgeWithoutCheck() The functionality :( In two vertex Add... Between edge)
2.3.1 First of all, from the global_graph_ According to the index of the passed parameter prev_vertex as well as At present vertex And are respectively defined as start_vertex and end_vertex.
2.3.2 Then check two vertex Whether there is edge, If not , Add
2.3.3 First calculate two vertex Distance between dist_diff, Then define two edge object :graph_utils::Edge edge_to_start as well as graph_utils::Edge edge_to_end;
2.3.4 Add two edge : edge_to_start.vertex_id_end = start_vertex_idx,edge_to_end.vertex_id_end = end_vertex_idx; among start_vertex_idx by prev_track_vertex_idx_,end_vertex_idx by track_globalvertex_idx_
2.3.5 Calculation traversal cost:edge_to_start.traversal_costs = dist_diff,edge_to_end.traversal_costs = dist_diff;
2.3.6 edge_to_start.keypose_edge = trajectory_edge,edge_to_end.keypose_edge = trajectory_edge; here trajectory_edge Pass for reference false.
2.3.7 take edge Add to vertex in :start_vertex.edges.push_back(edge_to_end),end_vertex.edges.push_back(edge_to_start).
2.4 For the current vertex Nearby vertex add to edge: Calculation global_graph_ Every one of them vertex Distance from the present vertex Subgrade , If less than a certain threshold , execute addGlobalEdge(graph_vertex.vertex_id, vertex_new.vertex_id) function .
2.4.1 Function declaration :void DualStateGraph::addGlobalEdge(int start_vertex_idx, int end_vertex_idx), namely start_vertex_idx To meet the threshold condition nearby_vertex And current vertex.
2.4.2 Calculate two vertex Distance between dist_edge
2.4.3 Then call ShortestPathBtwVertex(path, global_graph_, start_vertex_idx, end_vertex_idx) function :Function for getting the shortest path on a graph between two vertexes;Output a sequence of vertex ids as the path-->path
2.4.4 And then calculate path The length of dist_path
2.4.5 Carry out the formula in the paper 6 The judgment of the , If the conditions are met , At the same time, collision detection , Those who meet the conditions , call addGlobalEdgeWithoutCheck(), Add edge .
2.5 perform addGlobalEdgeWithoutCheck(prev_track_keypose_vertex_idx_, track_globalvertex_idx_, true);
Then prev_track_keypose_vertex_idx_ = track_globalvertex_idx_;
void DualStateGraph::addNewGlobalVertex(geometry_msgs::Pose &vertex_msg) {
// Extract the point
geometry_msgs::Point new_vertex_location;
new_vertex_location = vertex_msg.position;
// Create a new vertex
graph_utils::Vertex vertex;
vertex.location = new_vertex_location;
vertex.vertex_id = (int)global_graph_.vertices.size();
vertex.information_gain = vertex_msg.orientation.y;
// Add this vertex to the graph
global_graph_.vertices.push_back(vertex);
track_globalvertex_idx_ = (int)global_graph_.vertices.size() - 1;
auto &vertex_new = global_graph_.vertices[track_globalvertex_idx_];
// If there are already other vertices
if (global_graph_.vertices.size() > 1) {
// Add a parent backpointer to previous vertex
vertex_new.parent_idx = prev_track_vertex_idx_;
// Add an edge to previous vertex
addGlobalEdgeWithoutCheck(prev_track_vertex_idx_, track_globalvertex_idx_, false);
// Also add edges to nearby vertices
for (auto &graph_vertex : global_graph_.vertices) {
// If within a distance
float dist_diff = misc_utils_ns::PointXYZDist(graph_vertex.location, vertex_new.location);
if (dist_diff < kConnectVertexDistMax) {
// Add edge from this nearby vertex to current vertex
addGlobalEdge(graph_vertex.vertex_id, vertex_new.vertex_id);
}
}
} else {
// This is the first vertex -- no edges
vertex.parent_idx = -1;
}
}void DualStateGraph::addGlobalEdgeWithoutCheck(int start_vertex_idx, int end_vertex_idx, bool trajectory_edge) {
// Add an edge in the graph from vertex start_vertex_idx to vertex end_vertex_idx
// Get the two vertices
auto &start_vertex = global_graph_.vertices[start_vertex_idx];
auto &end_vertex = global_graph_.vertices[end_vertex_idx];
// Check if edge already exists -- don't duplicate
for (auto &edge : start_vertex.edges) {
if (edge.vertex_id_end == end_vertex_idx) {
// don't add duplicate edge
edge.keypose_edge = trajectory_edge;
for (auto &edge : end_vertex.edges) {
if (edge.vertex_id_end == start_vertex_idx) {
// don't add duplicate edge
edge.keypose_edge = trajectory_edge;
break;
}
}
return;
}
}
// Compute the distance between the two points
float dist_diff = misc_utils_ns::PointXYZDist(start_vertex.location, end_vertex.location);
// Create two edge objects
graph_utils::Edge edge_to_start;
graph_utils::Edge edge_to_end;
// Join the two edges
edge_to_start.vertex_id_end = start_vertex_idx;
edge_to_end.vertex_id_end = end_vertex_idx;
// Compute the traversal cost
// For now, this is just Euclidean distance
edge_to_start.traversal_costs = dist_diff;
edge_to_end.traversal_costs = dist_diff;
edge_to_start.keypose_edge = trajectory_edge;
edge_to_end.keypose_edge = trajectory_edge;
// Add these two edges to the vertices
start_vertex.edges.push_back(edge_to_end);
end_vertex.edges.push_back(edge_to_start);
globalEdgeSize_++;
}void DualStateGraph::addGlobalEdge(int start_vertex_idx, int end_vertex_idx) {
if (start_vertex_idx == end_vertex_idx) {
return;
}
// Get the edge distance
float dist_edge = misc_utils_ns::PointXYZDist(
global_graph_.vertices[start_vertex_idx].location,
global_graph_.vertices[end_vertex_idx].location);
if (dist_edge > kMaxLongEdgeDist) {
// VERY long edge. Don't add it
} else {
// Get the path distance
std::vector<int> path;
graph_utils_ns::ShortestPathBtwVertex(path, global_graph_, start_vertex_idx, end_vertex_idx);
bool path_exists = true;
float dist_path = 0;
// Check if there is an existing path
if (path.empty()) {
// No path exists
path_exists = false;
} else {
// Compute path length
dist_path = graph_utils_ns::PathLength(path, global_graph_);
// ROS_WARN("path exists of edge of length %f, where path exists of length
// %f", dist_edge, dist_path);
}
// Check if ratio is beyond threshold
// bool collision = false;
// The formula in the paper 6 Defined constraint check
if ((!path_exists || (path_exists && ((dist_path / dist_edge) >= kExistingPathRatioThresholdGlobal))) &&
(!zCollisionCheck(start_vertex_idx, end_vertex_idx, global_graph_))) {
Eigen::Vector3d origin;
Eigen::Vector3d end;
origin.x() = global_graph_.vertices[start_vertex_idx].location.x;
origin.y() = global_graph_.vertices[start_vertex_idx].location.y;
origin.z() = global_graph_.vertices[start_vertex_idx].location.z;
end.x() = global_graph_.vertices[end_vertex_idx].location.x;
end.y() = global_graph_.vertices[end_vertex_idx].location.y;
end.z() = global_graph_.vertices[end_vertex_idx].location.z;
// Make sure that the wires do not collide ( Ray tracing for collision detection )
if (volumetric_mapping::OctomapManager::CellStatus::kFree == manager_->getLineStatusBoundingBox(origin, end, robot_bounding)) {
addGlobalEdgeWithoutCheck(start_vertex_idx, end_vertex_idx, false);
}
}
}
}Two . subscribe /graph_planner_path as well as /graph_planner_status, And execute the callback function . These two topics are from graph_planner Node published , Not for now .
1.4 dual_state_frontier object
// Define a global boundary solver
dual_state_frontier_ = new DualStateFrontier(nh_, nh_private_, manager_, grid_);
DualStateFrontier::DualStateFrontier(
const ros::NodeHandle &nh, const ros::NodeHandle &nh_private,
volumetric_mapping::OctomapManager *manager, OccupancyGrid *grid)
: nh_(nh), nh_private_(nh_private) {
manager_ = manager;
grid_ = grid;
initialize();
}The constructor only executes initialize() function
bool DualStateFrontier::initialize() {
// Read in parameters
if (!readParameters())
return false;
// Initialize subscriber
// /global_points
graph_points_sub_ = nh_.subscribe(sub_graph_points_topic_, 1, &DualStateFrontier::graphPointsCallback, this);
// /state_estimation
odom_sub_.subscribe(nh_, sub_odom_topic_, 1);
// /terrain_map_ext
terrain_point_cloud_sub_.subscribe(nh_, sub_terrain_point_cloud_topic_, 1);
sync_.reset(new Sync(syncPolicy(10), odom_sub_, terrain_point_cloud_sub_));
sync_->registerCallback(boost::bind(&DualStateFrontier::terrainCloudAndOdomCallback, this, _1, _2));
// /octomap_unknown
unknown_points_pub_ = nh_.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(pub_unknown_points_topic_, 1);
// /global_frontier
global_frontier_points_pub_ = nh_.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(pub_global_frontier_points_topic_, 1);
// /local_frontier
local_frontier_points_pub_ = nh_.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(pub_local_frontier_points_topic_, 1);
terrain_elev_cloud_pub_ = nh_.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/elevation_map", 1);
if (kExecuteFrequency_ > 0.0) {
executeTimer_ = nh_private_.createTimer(ros::Duration(1.0 / kExecuteFrequency_), &DualStateFrontier::execute, this);
}
for (int i = 0; i < kTerrainVoxelWidth * kTerrainVoxelWidth; i++) {
terrain_voxel_elev_.push_back(robot_position_.z());
terrain_voxel_points_num_.push_back(0);
terrain_voxel_min_elev_.push_back(1000);
terrain_voxel_max_elev_.push_back(-1000);
}
boundaryLoaded_ = false;
ROS_INFO("Successfully launched DualStateFrontier node");
return true;
}First, at a certain frequency , Keep executing execute() function , and execute() Function is to call getFrontiers() function .
executeTimer_ = nh_private_.createTimer(ros::Duration(1.0 / kExecuteFrequency_), &DualStateFrontier::execute, this);
void DualStateFrontier::execute(const ros::TimerEvent &e) { getFrontiers(); }
void DualStateFrontier::getFrontiers() {
// search_bounding[0] = 40
// search_bounding[1] = 40
// search_bounding[2] = 0.5
// Given a range , And location center , Get the point cloud around it that belongs to the boundary , And save the obtained boundary point set to local_frontier_ in
getUnknowPointcloudInBoundingBox(robot_position_, search_bounding);
// Check and update local boundary points
localFrontierUpdate(robot_position_);
// Check and update global boundary points
gloabalFrontierUpdate();
// Down sampling of global sampling points
globalFrontiersNeighbourCheck();
// Release of various contents , Including local boundary points , Global boundary points , Point cloud in unknown state
publishFrontiers();
}1. First call getUnknowPointcloudInBoundingBox() function :
1.1 First, adjust the center position , Adjust center Parameters
1.2 Traverse the... In a given range in turn x,y,z; call octomap, Get the index value according to the point coordinates , And get the specific node according to the index value .
1.3 If octomap There is no such node in , Add this point to the set of unknown points unknown_points_ in , If the point is within a given range , And it is indeed a boundary point ( If this point is indeed a boundary point , Then there should be both free and unknown around this point ), Then join local_frontier_temp in
1.4 Yes local_frontier_temp Filter to get local_frontier_
2. Then call localFrontierUpdate(robot_position_) function :
2.1 Traverse local_frontier Every point in the
2.2 inSensorRangeofRobot() Function analysis : Only its parameter transmission distance from the current position of the robot is within a certain threshold , And the pitch angle of its vector is less than 15 degree , And the currently unknown grid cells for ray tracing of robots are free state , Then return to TRUE
2.3 collisionCheckByTerrainWithVector(center, checkedPoint) function : Given a starting point and an end point , Judge whether there are obstacles on the connection between the two
2.4 inSensorRangeofGraphPoints(checkedPoint): Enter a point , utilize kd Trees , Find the nearest set of points in the global , As long as there is one that can be normally observed by the position of the formal parameter , And there are no obstacles , Think it is true
2.5 Boundary points satisfying certain conditions are added to local_frontier_pcl_ as well as global_frontier_ in , Also on local_frontier_pcl_ Conduct downsampling to obtain local_frontier_
3. call gloabalFrontierUpdate() function : extract global_frontier_ Every point in the , If the point belongs to the cleared boundary point , Then jump out of this cycle , Get that point in octomap Index value in , If the point belongs to the boundary point, it is added to global_frontier_pcl_ in , And filter it to get global_frontier_
4. globalFrontiersNeighbourCheck();: Traverse global_frontier_ Every point in the , adopt KD The tree searches for boundary points near it , If there is , Then only one boundary point is saved . It is equivalent to a down sampling of global boundary points , And save the result to global_frontier_pcl_ and global_frontier_ in
5. Release /global_frontier as well as /local_frontier ,/global_frontier Than /local_frontier Check whether it belongs to the cleared boundary point again , Then the filter is carried out twice
execute() Function summary : Traverse the points within a certain range of the current robot position , And find the boundary points , Subsequently, the boundary points are obtained by downsampling and published
2. perform init() function ( Read parameters and determine subscribers and publishers )
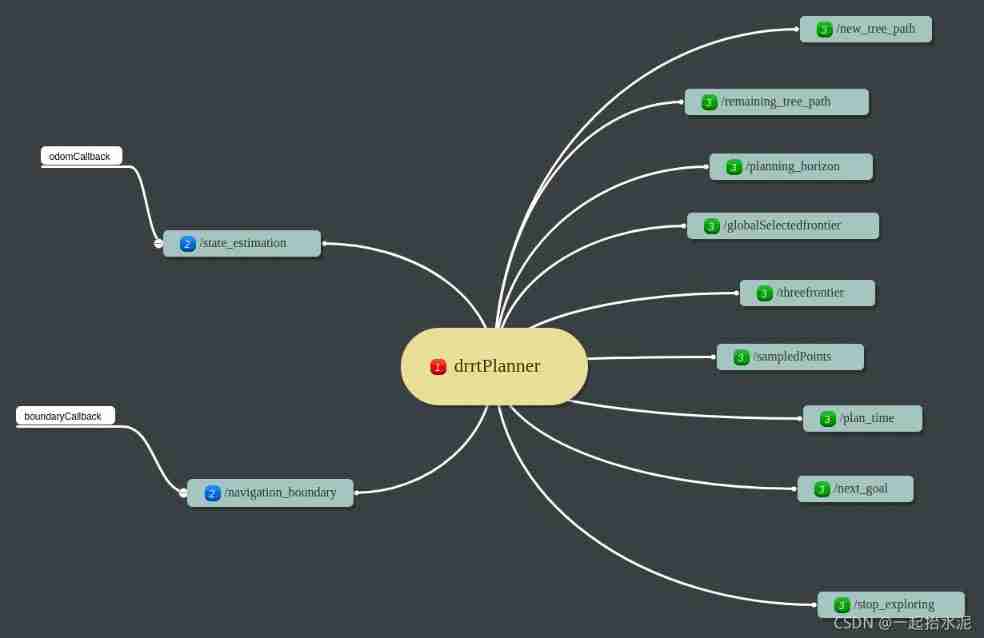
bool dsvplanner_ns::drrtPlanner::init() {
if (!setParams()) {
ROS_ERROR("Set parameters fail. Cannot start planning!");
}
odomSub_ = nh_.subscribe(odomSubTopic, 10, &dsvplanner_ns::drrtPlanner::odomCallback, this);
boundarySub_ = nh_.subscribe(boundarySubTopic, 10, &dsvplanner_ns::drrtPlanner::boundaryCallback, this);
params_.newTreePathPub_ = nh_.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>(newTreePathPubTopic, 1000);
params_.remainingTreePathPub_ = nh_.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>(remainingTreePathPubTopic, 1000);
params_.boundaryPub_ = nh_.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>(boundaryPubTopic, 1000);
params_.globalSelectedFrontierPub_ = nh_.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(globalSelectedFrontierPubTopic, 1000);
params_.localSelectedFrontierPub_ = nh_.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(localSelectedFrontierPubTopic, 1000);
params_.randomSampledPointsPub_ = nh_.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>(randomSampledPointsPubTopic, 1000);
params_.plantimePub_ = nh_.advertise<std_msgs::Float32>(plantimePubTopic, 1000);
params_.nextGoalPub_ = nh_.advertise<geometry_msgs::PointStamped>(nextGoalPubTopic, 1000);
params_.shutdownSignalPub = nh_.advertise<std_msgs::Bool>(shutDownTopic, 1000);
plannerService_ = nh_.advertiseService(plannerServiceName, &dsvplanner_ns::drrtPlanner::plannerServiceCallback,this);
cleanFrontierService_ = nh_.advertiseService(cleanFrontierServiceName, &dsvplanner_ns::drrtPlanner::cleanFrontierServiceCallback, this);
return true;
}
2.1 subscribe /state_estimation, perform odomCallback() Callback function ( The current pose of the robot is passed to drrt solver )
void dsvplanner_ns::drrtPlanner::odomCallback(const nav_msgs::Odometry &pose) {
drrt_->setRootWithOdom(pose);
// Planner is now ready to plan.
drrt_->plannerReady_ = true;
}void dsvplanner_ns::Drrt::setRootWithOdom(const nav_msgs::Odometry &pose) {
root_[0] = pose.pose.pose.position.x;
root_[1] = pose.pose.pose.position.y;
root_[2] = pose.pose.pose.position.z;
}2.3 Defining services :
Service type :dsvplanner_srv
Header header
-------
geometry_msgs/Point[] goal
std_msgs/Int32 modeplannerService_ = nh_.advertiseService(plannerServiceName, &dsvplanner_ns::drrtPlanner::plannerServiceCallback,this);
cleanFrontierService_ = nh_.advertiseService(cleanFrontierServiceName, &dsvplanner_ns::drrtPlanner::cleanFrontierServiceCallback, this);graph_planner_node.cpp
1. Define a GraphPlanner object
2. perform execute() function
graph_planner_ns::GraphPlanner graph_planner(node_handle); graph_planner.execute();
graph_planner.cpp
This function is graph_planner The implementation function of , First look at its constructor
GraphPlanner::GraphPlanner(const ros::NodeHandle &nh) { nh_ = nh; initialize(); }
1. initialize()
bool GraphPlanner::initialize() {
if (!readParameters())
return false;
// Initialize target waypoint
waypoint_ = geometry_msgs::PointStamped();
waypoint_.point.x = -1.0;
waypoint_.point.y = -1.0;
waypoint_.point.z = 0.0;
// world_frame_id_ : map
waypoint_.header.frame_id = world_frame_id_;
// Initialize subscribers
// /local_graph
graph_sub_ = nh_.subscribe(sub_graph_topic_, 1, &GraphPlanner::graphCallback, this);
// /graph_planner_command
graph_planner_command_sub_ = nh_.subscribe(graph_planner_command_topic_, 1, &GraphPlanner::commandCallback, this);
// /state_estimation
odometry_sub_ = nh_.subscribe(sub_odometry_topic_, 1, &GraphPlanner::odometryCallback, this);
// /terrain_map_ext
terrain_sub_ = nh_.subscribe(sub_terrain_topic_, 1, &GraphPlanner::terrainCallback, this);
// Initialize publishers
// /way_point
waypoint_pub_ = nh_.advertise<geometry_msgs::PointStamped>(pub_waypoint_topic_, 2);
// /graph_planner_status
graph_planner_status_pub_ = nh_.advertise<graph_planner::GraphPlannerStatus>(graph_planner_status_topic_, 2);
// /graph_planner_path
graph_planner_path_pub_ = nh_.advertise<nav_msgs::Path>(pub_path_topic_, 10);
ROS_INFO("Successfully launched graph_planner node");
return true;
}First look at the subscription function /state_estimation
1. subscribe /state_estimation, perform odometryCallback() Callback function :
Put the robot currently (x,y,z) The position is passed to robot_pos_, as well as yaw Information to robot_yaw_
void GraphPlanner::odometryCallback(
const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr &odometry_msg) {
double roll, pitch, yaw;
geometry_msgs::Quaternion geo_quat = odometry_msg->pose.pose.orientation;
tf::Matrix3x3(tf::Quaternion(geo_quat.x, geo_quat.y, geo_quat.z, geo_quat.w))
.getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
robot_yaw_ = yaw;
robot_pos_ = odometry_msg->pose.pose.position;
}2. subscribe /terrain_map_ext, Execute callback function terrainCallback:
Accept the local point cloud message , Greater than 0.2, Less than 1.2 The point cloud of is judged to cause obstacles to robot action , And save the point cloud to terrain_point_crop_ in , After voxel filtering, we get terrain_point_crop_.
void GraphPlanner::terrainCallback( const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2::ConstPtr &terrain_msg) { terrain_point_->clear(); terrain_point_crop_->clear(); pcl::fromROSMsg(*terrain_msg, *terrain_point_); pcl::PointXYZI point; int terrainCloudSize = terrain_point_->points.size(); for (int i = 0; i < terrainCloudSize; i++) { point = terrain_point_->points[i]; float pointX = point.x; float pointY = point.y; float pointZ = point.z; // kObstacleHeightThres : 0.20 # the obstacle height that will be considered when filtering the terrain cloud // kOverheadObstacleHeightThres : 1.20 # the overhead obstacle height that will be considered when filtering the terrain cloud // higher than 0.2 lower than 1.2 The obstacle point cloud of is judged to cause obstacles to robot action if (point.intensity > kObstacleHeightThres && point.intensity < kOverheadObstacleHeightThres) { point.x = pointX; point.y = pointY; point.z = pointZ; terrain_point_crop_->push_back(point); } } pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointXYZI> point_ds; point_ds.setLeafSize(kDownsampleSize, kDownsampleSize, kDownsampleSize); point_ds.setInputCloud(terrain_point_crop_); point_ds.filter(*terrain_point_crop_); }
3. Then subscribe /local_graph as well as /graph_planner_command, And execute the callback function . Don't look here for the moment
2. execute()
This part of the function and exeploration.cpp() Function related
边栏推荐
- 怎样写一个增广矩阵到txt文件中
- 应用实践 | 数仓体系效率全面提升!同程数科基于 Apache Doris 的数据仓库建设
- How to turn on win11 game mode? How to turn on game mode in win11
- Application practice | the efficiency of the data warehouse system has been comprehensively improved! Data warehouse construction based on Apache Doris in Tongcheng digital Department
- Reinforcement learning - learning notes 9 | multi step TD target
- Ternary expressions, generative expressions, anonymous functions
- Win11时间怎么显示星期几?Win11怎么显示今天周几?
- npm uninstall和rm直接删除的区别
- Embedded development: how to choose the right RTOS for the project?
- DBSync新增对MongoDB、ES的支持
猜你喜欢
How does win11 unblock the keyboard? Method of unlocking keyboard in win11
Implementation method of data platform landing

Customer case | China law network, through observing the cloud, greatly shortens the time of fault location
![Jerry's manual matching method [chapter]](/img/92/74281c29565581ecb761230fbfd0f3.png)
Jerry's manual matching method [chapter]

IP网络主动测评系统——X-Vision
Time standard library
Crawler (17) - Interview (2) | crawler interview question bank
Win11时间怎么显示星期几?Win11怎么显示今天周几?
Why can't win11 display seconds? How to solve the problem that win11 time does not display seconds?
Anti climbing killer
随机推荐
海外代理推荐
Revit secondary development - Hide occlusion elements
How to close eslint related rules
Relationship between URL and URI
C # Development -- pit encountered in JS intermodulation
. Net automapper use
Get the week start time and week end time of the current date
双塔模型的最强出装,谷歌又开始玩起“老古董”了?
Add get disabled for RC form
[advanced MySQL] index details (I): index data page structure
Latest Android advanced interview questions summary, Android interview questions and answers
如何选择合适的自动化测试工具?
Blender exchange group, welcome to the water group ~
MIT6.S081-Lab9 FS [2021Fall]
三元表达式、各生成式、匿名函数
OpenGL configure assimp
[azure microservice service fabric] start the performance monitor in the SF node and set the method of capturing the process
ByteDance senior engineer interview, easy to get started, fluent
How does win11 time display the day of the week? How does win11 display the day of the week today?
Record a garbled code during servlet learning