当前位置:网站首页>Heap (priority queue) topic
Heap (priority queue) topic
2022-07-06 09:12:00 【NP_ hard】
List of articles
problem Ⅰ
451. Sort Characters By Frequency
Given a string s, sort it in decreasing order based on the frequency of the characters. The frequency of a character is the number of times it appears in the string.
Return the sorted string. If there are multiple answers, return any of them.
Example 1:
Input: s = "tree"
Output: "eert"
Explanation: 'e' appears twice while 'r' and 't' both appear once.
So 'e' must appear before both 'r' and 't'. Therefore "eetr" is also a valid answer.
Example 2:
Input: s = "cccaaa"
Output: "aaaccc"
Explanation: Both 'c' and 'a' appear three times, so both "cccaaa" and "aaaccc" are valid answers.
Note that "cacaca" is incorrect, as the same characters must be together.
Example 3:
Input: s = "Aabb"
Output: "bbAa"
Explanation: "bbaA" is also a valid answer, but "Aabb" is incorrect.
Note that 'A' and 'a' are treated as two different characters.
solution 1 hashmap and priority queue
class Solution {
public:
string frequencySort(string s) {
priority_queue<pair<int, char>> pq;
unordered_map<char, int> maps;
string res = "";
for(auto it : s)
maps[it]++;
for(auto it : maps)
pq.push({
it.second, it.first});
while(!pq.empty()){
for(int i=0; i<pq.top().first; i++)
res.push_back(pq.top().second);
pq.pop();
}
return res;
}
};

solution 2 bucket
class Solution {
public:
string frequencySort(string s) {
unordered_map<char, int> maps;
string res = "";
for(auto it : s) maps[it]++;
vector<vector<char>> bucket(s.size()+1);
for(auto it : maps)
bucket[it.second].push_back(it.first);
for(int i=s.size(); i>=1; i--){
for(auto charc : bucket[i])
res += string(i, charc);
}
return res;
}
};
problem Ⅱ
973. K Closest Points to Origin
Given an array of points where points[i] = [xi, yi] represents a point on the X-Y plane and an integer k, return the k closest points to the origin (0, 0).
The distance between two points on the X-Y plane is the Euclidean distance (i.e., √(x1 - x2)2 + (y1 - y2)2).
You may return the answer in any order. The answer is guaranteed to be unique (except for the order that it is in).
Example 1: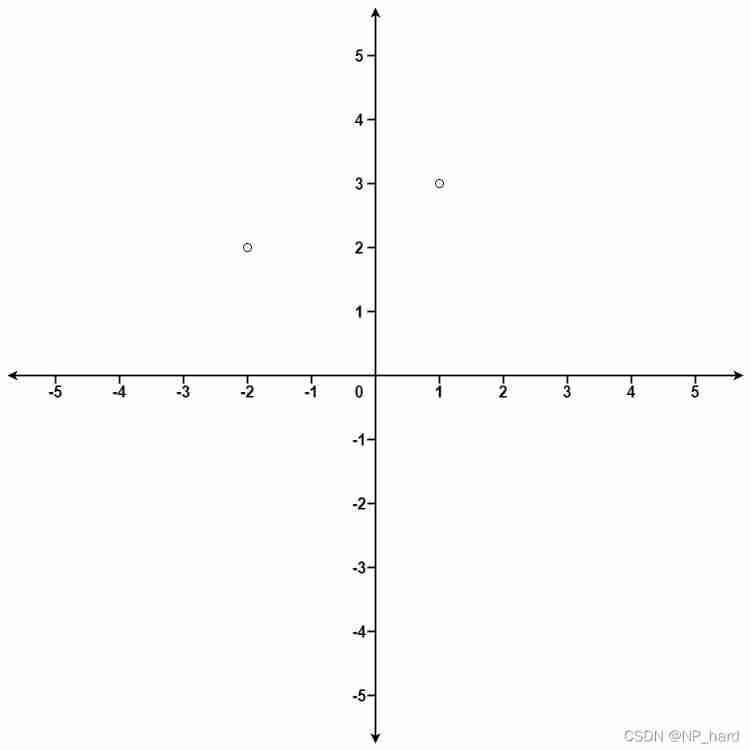
Input: points = [[1,3],[-2,2]], k = 1
Output: [[-2,2]]
Explanation:
The distance between (1, 3) and the origin is sqrt(10).
The distance between (-2, 2) and the origin is sqrt(8).
Since sqrt(8) < sqrt(10), (-2, 2) is closer to the origin.
We only want the closest k = 1 points from the origin, so the answer is just [[-2,2]].
Example 2:
Input: points = [[3,3],[5,-1],[-2,4]], k = 2
Output: [[3,3],[-2,4]]
Explanation: The answer [[-2,4],[3,3]] would also be accepted.
my solution 1 max priority queue
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> kClosest(vector<vector<int>>& points, int k) {
priority_queue<pair<int, int>> pq;
for(int i=0; i<points.size(); i++){
int ans = pow(points[i][0],2)+pow(points[i][1], 2);
pq.push({
ans, i});
while(pq.size() > k) pq.pop();
}
vector<vector<int>> res;
while(!pq.empty()){
res.push_back(points[pq.top().second]);
pq.pop();
}
return res;
}
};

NOTE :time complexity : O ( n l o g k ) O(nlogk) O(nlogk)space complexity : O ( k ) O(k) O(k)
solution 2 sort
class Solution {
public:
int dis(vector<int>& point) {
return point[0] * point[0] + point[1] * point[1];
}
vector<vector<int>> kClosest(vector<vector<int>>& points, int k) {
sort(points.begin(), points.end(), [&](vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b) {
return dis(a) < dis(b);
});
return vector<vector<int>>(points.begin(), points.begin() + k);
}
};
NOTE :time complexity : O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn)space complexity : O ( l o g n ) t o O ( n ) O(logn)\ to\ O(n) O(logn) to O(n)
great solution 1 binary search
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> kClosest(vector<vector<int>>& points, int k) {
// Precompute the Euclidean distance for each point,
// define the initial binary search range,
// and create a reference list of point indices
vector<double> distances;
vector<int> remaining;
double low = 0, high = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
distances.push_back(euclideanDistance(points[i]));
high = max(high, distances[i]);
remaining.push_back(i);
}
// Perform a binary search of the distances
// to find the k closest points
vector<int> closest;
while (k) {
double mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
vector<vector<int>> result = splitDistances(remaining, distances, mid);
vector<int>& closer = result[0];
vector<int>& farther = result[1];
if (closer.size() > k) {
// If more than k points are in the closer distances
// then discard the farther points and continue
remaining.swap(closer);
high = mid;
} else {
// Add the closer points to the answer array and keep
// searching the farther distances for the remaining points
k -= closer.size();
closest.insert(closest.end(), closer.begin(), closer.end());
remaining.swap(farther);
low = mid;
}
}
// Return the k closest points using the reference indices
vector<vector<int>> answer;
for (int index : closest) {
answer.push_back(points[index]);
}
return answer;
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> splitDistances(vector<int>& remaining, vector<double>& distances,
double mid) {
// Split the distances around the midpoint
// and return them in separate vectors
vector<vector<int>> result(2);
vector<int> &closer = result[0], &farther = result[1];
for (int index : remaining) {
if (distances[index] <= mid) {
closer.push_back(index);
} else {
farther.push_back(index);
}
}
return result;
}
double euclideanDistance(vector<int>& point) {
// Calculate and return the squared Euclidean distance
return point[0] * point[0] + point[1] * point[1];
}
};
NOTE :time complexity : O ( n ) O(n) O(n)space complexity : O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
great solution 2 quick select
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> kClosest(vector<vector<int>>& points, int k) {
return quickSelect(points, k);
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> quickSelect(vector<vector<int>>& points, int k) {
int left = 0, right = points.size() - 1;
int pivotIndex = points.size();
while (pivotIndex != k) {
// Repeatedly partition the vector
// while narrowing in on the kth element
pivotIndex = partition(points, left, right);
if (pivotIndex < k) {
left = pivotIndex;
} else {
right = pivotIndex - 1;
}
}
// Return the first k elements of the partially sorted vector
return vector<vector<int>>(points.begin(), points.begin() + k);
};
int partition(vector<vector<int>>& points, int left, int right) {
vector<int>& pivot = choosePivot(points, left, right);
int pivotDist = squaredDistance(pivot);
while (left < right) {
// Iterate through the range and swap elements to make sure
// that all points closer than the pivot are to the left
if (squaredDistance(points[left]) >= pivotDist) {
points[left].swap(points[right]);
right--;
} else {
left++;
}
}
// Ensure the left pointer is just past the end of
// the left range then return it as the new pivotIndex
if (squaredDistance(points[left]) < pivotDist)
left++;
return left;
};
vector<int>& choosePivot(vector<vector<int>>& points, int left, int right) {
// Choose a pivot element of the vector
return points[left + (right - left) / 2];
}
int squaredDistance(vector<int>& point) {
// Calculate and return the squared Euclidean distance
return point[0] * point[0] + point[1] * point[1];
}
};
NOTE :time complexity : O ( n ) O(n) O(n)space complexity : O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1)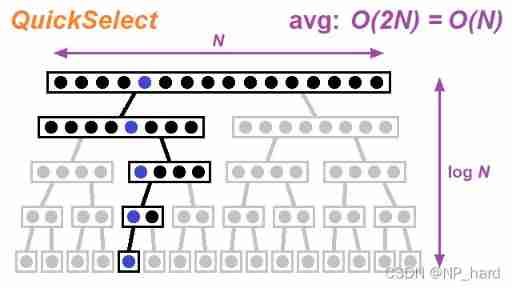
边栏推荐
- 使用标签模板解决用户恶意输入的问题
- Selenium+pytest automated test framework practice
- [OC-Foundation框架]-<字符串And日期与时间>
- 项目连接数据库遇到的问题及解决
- Detailed explanation of dynamic planning
- Leetcode: Sword finger offer 42 Maximum sum of continuous subarrays
- Selenium+Pytest自动化测试框架实战(下)
- BN folding and its quantification
- Redis之哨兵模式
- LeetCode:39. 组合总和
猜你喜欢
UML图记忆技巧
![[MySQL] limit implements paging](/img/94/2e84a3878e10636460aa0fe0adef67.jpg)
[MySQL] limit implements paging
![[today in history] February 13: the father of transistors was born The 20th anniversary of net; Agile software development manifesto was born](/img/70/d275009134fcbf9ae984c0f278659e.jpg)
[today in history] February 13: the father of transistors was born The 20th anniversary of net; Agile software development manifesto was born

Different data-driven code executes the same test scenario

BMINF的后训练量化实现

Export IEEE document format using latex

【文本生成】论文合集推荐丨 斯坦福研究者引入时间控制方法 长文本生成更流畅
![[OC foundation framework] - string and date and time >](/img/75/e20064fd0066810135771a01f54360.png)
[OC foundation framework] - string and date and time >

IJCAI2022论文合集(持续更新中)
Mathematical modeling 2004b question (transmission problem)
随机推荐
Intel Distiller工具包-量化实现2
QDialog
BMINF的後訓練量化實現
Notes 01
Improved deep embedded clustering with local structure preservation (Idec)
xargs命令的基本用法
数学建模2004B题(输电问题)
如何正确截取字符串(例:应用报错信息截取入库操作)
Redis之五大基础数据结构深入、应用场景
【每日一题】搬运工 (DFS / DP)
Advanced Computer Network Review(3)——BBR
Parameterization of postman
LeetCode:214. Shortest palindrome string
CUDA realizes focal_ loss
[oc]- < getting started with UI> -- common controls - prompt dialog box and wait for the prompt (circle)
[three storage methods of graph] just use adjacency matrix to go out
MongoDB 的安装和基本操作
Ijcai2022 collection of papers (continuously updated)
[Hacker News Weekly] data visualization artifact; Top 10 Web hacker technologies; Postman supports grpc
Cesium draw points, lines, and faces