当前位置:网站首页>手撕——排序
手撕——排序
2022-07-02 03:53:00 【編程SHARE】
插入排序
插入排序的前提是未插入時該序列有序。
假如是從小到大排序,插入的數為key,從右向左找小於等於key的值,如果不滿足那麼原來的向後移動一比特進行覆蓋,直到滿足或者找完進行插入。
重複上面的操作。
void InsertSort(int* a, int n)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n-1; i++)
{
int end=i;
int key = a[end + 1];
while (end>=0)
{
if (a[end] <= key)
break;
else
a[end + 1] = a[end];
end--;
}
a[end + 1] = key;
}
}
時間複雜度O(n*n)
該排序適合接近有序的情况下,在該種情况下時間複雜度接近O(n)
希爾排序
有插入排序演變過來
希爾排序有兩個步驟:
1.預排序(盡可能變得有序)
2.插入排序
例:
預排序:把待排序的一組數分為gap組,每一組進行插入排序
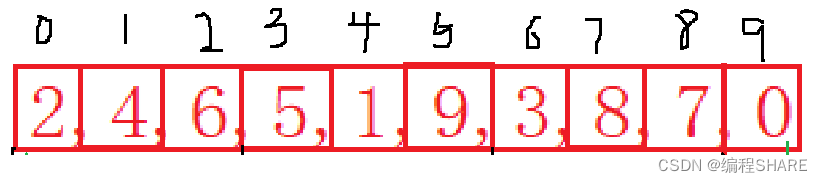
把這10組數分成3組:
第1組:2,5,3,0
第2組:4,1,8
第3組:6,9,7
經過預排之後的順序
最後全部的進行插入排序,就可以得到有序的序列。
上面例子的代碼:
void ShellSort(int* a, int n)
{
int gap = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < n-gap; i++)
{
int end=i;
int key = a[end + gap];
while (end >= 0)
{
if (a[end] <= key)
break;
else
a[end + gap] = a[end];
end -= gap;
}
a[end + gap] = key;
}
InsertSort(a, n);
}
希爾排序動態圖
void ShellSort(int* a, int n)
{
int gap = n;
while (gap>1)
{
gap = gap / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < n-gap; i++)
{
int end = i;
int key = a[end + gap];
while (end >= 0)
{
if (a[end] <= key)
break;
else
a[end + gap] = a[end];
end -= gap;
}
a[end + gap] = key;
}
}
}
選擇排序

選擇排序很簡單,每一次選出最小的反在前面,選出最大的放在後面。
void SelectSort(int* a, int n)
{
int min, max;
int begin = 0, end = n - 1;
while (begin < end)
{
min = max = begin;
for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++)
{
if (a[min] > a[i])
min = i;
if (a[max] < a[i])
max = i;
}
swap(&a[min], &a[begin]);
//注意
if (begin == max)
max = min;
swap(&a[max], &a[end]);
begin++;
end--;
}
}
時間複雜度O(N)
堆排序

void AdjustDwon(int* a, int n, int root)
{
int father = root;
int child = 2 * father + 1;
while (child <n)
{
if (child<n - 1 && a[child]<a[child + 1])
child++;
if (a[father] < a[child])
{
swap(&a[father], &a[child]);
father = child;
child = 2 * father + 1;
}
else
return;
}
}
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDwon(a, n, i);
}
for (i = n - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
swap(&a[0], &a[i]);
AdjustDwon(a, i-1, 0);
}
}
冒泡排序

void BubbleSort(int* a, int n)
{
int begin = 0;
int end = n - 1;
for (int i = begin; i < n-1; i++)
{
for (int j = begin; j < end; j++)
{
if (a[j+1] < a[j])
swap(&a[j], &a[j+1]);
}
end--;
}
}
快速排序

快速排序的基本思路就是:選出一個基值,一般是選取最左邊的為基值,然後從右邊開始進行遍曆,假設是按從小到大的順序,那麼從右邊找小的,找到小的之後,在從左邊開始找最大的,找到之後兩者進行交換。然後繼續重複上面的過程,直到左邊大於等於右邊的時候停止,然後和基數進行交換。
這是一輪
int PartSort1(int* a, int left, int right)
{
int keyi = left;
while (left < right)
{
while (left < right && a[keyi] <= a[right])
right--;
while (left < right && a[left] <= a[keyi])
left++;
swap(&a[left], &a[right]);
}
swap(&a[keyi], &a[right]);
keyi = left;
return keyi;
}
坑比特法:把基數作為坑比特,從右邊開始找小(比基數小)的,找到之後填入坑比特,該比特置變成坑比特,然後從左邊開始找大,然後再填入坑比特,直到找完(左邊大於等於右邊),把基數填入坑比特。
int PartSort2(int* a, int left, int right)
{
int keyi= left;
int temp = a[left];
while (left < right)
{
while (left<right&&a[right] >= temp)
{
right--;
}
a[keyi] = a[right];
keyi = right;
while (left < right && a[left] <= temp)
{
left++;
}
a[keyi] = a[left];
keyi = left;
}
a[keyi] = temp;
return keyi;
}
前後指針法:
前指針從基數前一個比特置開始,後指針從基數比特置開始。前指針找小,當找到小的時候,後指針加一,然後前後指針指向的數值進行交換,然後前指針繼續找小,直到查找完。
int PartSort3(int* a, int left, int right)
{
int keyi = left;
int front = keyi + 1;
int back = keyi;
while (front <= right)
{
if (a[front] <= a[keyi])
{
back++;
swap(&a[front], &a[back]);
}
front++;
}
swap(&a[back], &a[keyi]);
keyi = back;
return keyi;
}
上面描述的是一輪排序,每一輪排好之後,都可以確定好排好序之後基數的比特置,基數左邊是比它小的,右邊是比它大的,左邊繼續排序,右邊在繼續排序。當還剩一個需要排序的時候就停止排序了。
void QuickSort(int* a, int left, int right)
{
if (left >= right)
return;
int keyi = left;
//keyi = PartSort1(a, left, right);
//keyi = PartSort2(a, left, right);
keyi = PartSort3(a, left, right);
QuickSort(a, left, keyi - 1);
QuickSort(a, keyi + 1, right);
}
上面這種排序還不可以,因為他的最壞的時間複雜度為O(N*N),我們取的基數最好是該組有序數的中間值,但是這個值也不容易在無序中找到,此時我們用3數取中法,把最邊的值,最右邊的值,還有中間的值,3者進行比較,次大的為基數。為了保證還是上面的方法,我們把基數和最左邊的數進行交換。
int ThreeIn(int* a, int left, int right)
{
int middle = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (a[middle] < a[left])
{
if (a[left] < a[right])
return left;
else if (a[middle] < a[right])
return right;
else
return middle;
}
else
{
if (a[middle] < a[right])
return middle;
else if (a[left] < a[right])
return right;
else
return left;
}
}
void QuickSort(int* a, int left, int right)
{
if (left >= right)
return;
int keyi = left;
int x = ThreeIn(a, left, right);
swap(&a[keyi], &a[x]);
//keyi = PartSort1(a, left, right);
//keyi = PartSort2(a, left, right);
keyi = PartSort3(a, left, right);
QuickSort(a, left, keyi - 1);
QuickSort(a, keyi + 1, right);
}
時間複雜度O(N*logN)
以最左邊為基數,為什麼從先右邊開始呢?
在L與R交換的過程中沒有什麼可以討論的,最主要的是相遇的時候和基數進行交換的情况:
1.R遇見L,此時L為最小的或者是基數,交換之後,左小右大。
2.L遇見R:
(1)L與R沒有交換
R所處的比特置為小,R右邊都是大,左邊都是小,可以與基值進行交換。
(2)L與R交換
交換過後R還是會繼續移動到小的地方,然後和(1)一樣。
我們再討論選左邊為基值,還是討論相遇的情况
1.L遇見R
(1)沒有發生交換就相遇了,無法判斷相遇時與基值的大小。
(2)L與R交換過後再相遇,此時相遇的為大,不能和基值進行交換。
2.R遇見L
R遇見L說明R與L交換過,此時基值是小的,可以交換。
綜上所述:從左邊開始並不能完全保證相遇的地方為小的。
非遞歸形式的快速排序
1.用棧進行實現
用棧儲存一組數的上下界,如果從左開始選基數的話,根據棧的特性,我們先儲存左邊界,再儲存右邊界。每次排序都從棧中拿出2個數據。當向棧中儲存邊界的時候要主要邊界直接有沒有元素。
void QuickSortNonR1(int* a, int left, int right)
{
Stack p;
InitStack(&p);
StackPush(&p, left);
StackPush(&p, right);
while (!StackEmpty(&p))
{
right = StackTop(&p);
StackPop(&p);
left = StackTop(&p);
StackPop(&p);
int keyi = PartSort3(a, left, right);
if (keyi + 1 < right)
{
StackPush(&p, keyi+1);
StackPush(&p, right);
}
if (keyi - 1 > left)
{
StackPush(&p, left);
StackPush(&p, keyi-1);
}
}
StackDestroy(&p);
}
2.用隊列實現
根據隊列的性質,先儲存右邊界,再儲存左邊界。後面的過程和棧類似
void QuickSortNonR2(int* a, int left, int right)
{
Queue p;
QueueInit(&p);
QueuePush(&p, right);
QueuePush(&p, left);
while (!QueueEmpty(&p))
{
right = QueueFront(&p);
QueuePop(&p);
left= QueueFront(&p);
QueuePop(&p);
int keyi = PartSort3(a, left, right);
if (keyi - 1 > left)
{
QueuePush(&p, keyi - 1);
QueuePush(&p, left);
}
if (keyi + 1 < right)
{
QueuePush(&p, right);
QueuePush(&p, keyi + 1);
}
}
QueueDestroy(&p);
}
歸並排序
边栏推荐
- 蓝桥杯单片机省赛第十一届第二场
- Basic syntax of unity script (7) - member variables and instantiation
- Basic syntax of unity script (8) - collaborative program and destruction method
- 蓝桥杯单片机省赛第八届
- [punch in] flip the string (simple)
- Basic syntax of unity script (6) - specific folder
- Jetpack's livedata extension mediatorlivedata
- Demonstration description of integrated base scheme
- Recently, the weather has been extremely hot, so collect the weather data of Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou and Shenzhen last year, and make a visual map
- Kotlin basic learning 15
猜你喜欢

What do you know about stock selling skills and principles
Account management of MySQL
![[ibdfe] matlab simulation of frequency domain equalization based on ibdfe](/img/a1/441f400668e736b70cb36443f2267a.png)
[ibdfe] matlab simulation of frequency domain equalization based on ibdfe

Lost a few hairs, and finally learned - graph traversal -dfs and BFS

MySQL index, transaction and storage engine
![[designmode] Prototype Pattern](/img/ee/c4e48c2ce8ff66f50f0bf13e5a0418.png)
[designmode] Prototype Pattern
Blue Bridge Cup single chip microcomputer sixth temperature recorder

蓝桥杯单片机省赛第八届

【DesignMode】建造者模式(Builder model)
go 包的使用
随机推荐
高性能 低功耗Cortex-A53核心板 | i.MX8M Mini
C language: examples of logical operation and judgment selection structure
5G时代全面到来,浅谈移动通信的前世今生
初识string+简单用法(二)
What kind of interview is more effective?
regular expression
Imageai installation
PR zero foundation introductory guide note 2
Failed to upgrade schema, error: “file does not exist
一文彻底理解评分卡开发中——Y的确定(Vintage分析、滚动率分析等)
The 7th Blue Bridge Cup single chip microcomputer provincial competition
高性能 低功耗Cortex-A53核心板 | i.MX8M Mini
[personal notes] PHP common functions - custom functions
树莓派GPIO引脚控制红绿灯与轰鸣器
软件测试人的第一个实战项目:web端(视频教程+文档+用例库)
JVM知识点
How should the team choose the feature branch development mode or trunk development mode?
蓝桥杯单片机省赛第七届
Unity脚本的基础语法(6)-特定文件夹
BiShe cinema ticket purchasing system based on SSM