当前位置:网站首页>Sqlserver functions, creation and use of stored procedures
Sqlserver functions, creation and use of stored procedures
2022-07-04 14:25:00 【Roman Sultan Mohammed】
1. function
stay SQLserer in , Functions are often used , But most of the time, only some system functions are used .
Classification of functions :
MS Divide function types into three categories
- Scalar function
- Table-valued functions
- System function
Scalar functions are interpreted as
The user-defined scalar function returns in RETURNS A single data value of the type defined in clause . For inline scalar functions , The scalar value returned is the result of a single statement . For scalar functions with multiple statistics , The body of a function can contain a series of... That return a single value Transact-SQL sentence . The return type can be divided by text、 ntext、 image、 cursor and timestamp Any data type other than .( It can be roughly understood as returning a specific value )
Table valued functions are introduced as
User defined table valued functions (TVF) return surface data type . For inline table valued functions , No function body ; A table is a single SELECT The result set of the statement ( Just return a table )
The system function is SQLServer Provided functions that can be used directly .
Custom function
Scalar function
The formula of custom scalar function is
-- Transact-SQL Scalar Function Syntax
CREATE [ OR ALTER ] FUNCTION [ schema_name. ] function_name
( [ { @parameter_name [ AS ][ type_schema_name. ] parameter_data_type
[ = default ] [ READONLY ] }
[ ,...n ]
]
)
RETURNS return_data_type
[ WITH <function_option> [ ,...n ] ]
[ AS ]
BEGIN
function_body
RETURN scalar_expression
END
[ ; ]
The definition of scalar function is relatively simple . It is mainly divided into two parts , The first part
CREATE [ OR ALTER ] FUNCTION [ schema_name. ] function_name
( [ { @parameter_name [ AS ][ type_schema_name. ] parameter_data_type
[ = default ] [ READONLY ] }
[ ,...n ]
]
) // Define function name and parameters , for example
// Create function CountRectangleSize(@len int,@wid int) // Of course, you can also set default values and readonly attribute
// return int
RETURNS return_data_type
The second part is more flexible
[ WITH <function_option> [ ,...n ] ]
// Function options ------ stay BEGIN Before the start , You can make some settings , Like starting a transaction , Here is MS The explanation of
// NATIVE COMPILATION
//| SCHEMABINDING
//| [ EXECUTE AS Clause ]
//| [ RETURNS NULL ON NULL INPUT | CALLED ON NULL INPUT ]
[ AS ]
//BEGIN and END Is the body of the function , Perform relevant operations in it ( Defining variables , assignment , Judge ....)
BEGIN
function_body
RETURN scalar_expression
END
A complete benchmarking function
CREATE FUNCTION GetReactangleSize(@len int,@wid int)
returns int
BEGIN
DECLARE @Res int;
SET @Res = ( SELECT @len * @wid )
RETURN @Res
END
perform :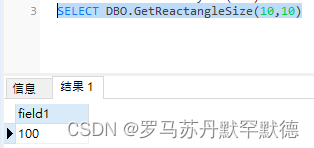
Table-valued functions
The formula of table valued function is
CREATE [ OR ALTER ] FUNCTION [ schema_name. ] function_name
( [ { @parameter_name [ AS ] [ type_schema_name. ] parameter_data_type
[ = default ] [READONLY] }
[ ,...n ]
]
)
RETURNS @return_variable TABLE <table_type_definition>
[ WITH <function_option> [ ,...n ] ]
[ AS ]
BEGIN
function_body
RETURN
END
[ ; ]
It's just different from scalar functions in declaring the return value , Because the returned table structure needs to be customized
Here is a direct example to demonstrate
Those who don't want to define their own tables can use the following export sql file
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for Student
-- ----------------------------
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM sys.all_objects WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(N'[dbo].[Student]') AND type IN ('U'))
DROP TABLE [dbo].[Student]
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Student] (
[ID] int IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[Name] varchar(200) COLLATE Chinese_Taiwan_Stroke_CI_AS NOT NULL,
[Age] int NOT NULL,
[Birth] datetime NOT NULL
)
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[Student] SET (LOCK_ESCALATION = TABLE)
GO
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of Student
-- ----------------------------
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[Student] ON
GO
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Student] ([ID], [Name], [Age], [Birth]) VALUES (N'1', N'? Jianxiong ', N'22', N'1999-07-22 00:00:00.000')
GO
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Student] ([ID], [Name], [Age], [Birth]) VALUES (N'2', N' Ten thousand days ', N'22', N'2022-06-21 00:00:00.000')
GO
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Student] ([ID], [Name], [Age], [Birth]) VALUES (N'3', N' Li Cheng ?', N'19', N'2022-07-01 16:01:48.880')
GO
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Student] ([ID], [Name], [Age], [Birth]) VALUES (N'4', N' Jinwu ', N'18', N'2022-07-01 16:02:23.850')
GO
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [dbo].[Student] OFF
GO
-- ----------------------------
-- Auto increment value for Student
-- ----------------------------
DBCC CHECKIDENT ('[dbo].[Student]', RESEED, 4)
GO
-- ----------------------------
-- Triggers structure for table Student
-- ----------------------------
CREATE TRIGGER [dbo].[T1]
ON [dbo].[Student]
WITH EXECUTE AS CALLER
FOR INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
AS
BEGIN
SELECT * FROM Student
END
GO
-- ----------------------------
-- Primary Key structure for table Student
-- ----------------------------
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[Student] ADD CONSTRAINT [PK_Student_ID] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ([ID])
WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON)
ON [PRIMARY]
GO
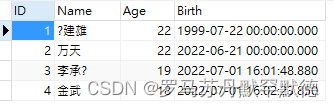
Create Function WhoAgeIsBelow(@limit int)
returns @tb TABLE(
Name varchar(20),
Birth datetime
) // Table valued functions need to customize the returned table structure , Of course, there is a simplified way to wait
AS
BEGIN
// Then insert the table structure of the query @tb that will do
insert @tb SELECT Name,Birth from Student where Age < @limit
// there return Is constant , But there must be no subsequent value
return
END
test , Input 20, Get the following 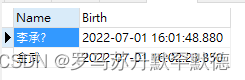
Of course , If the return table you need is very simple , Then you can also use a simplified method .
This simplified method is called Inline table valued functions
// Inline table valued functions do not need to define the return table structure , Use it directly return Return the queried table
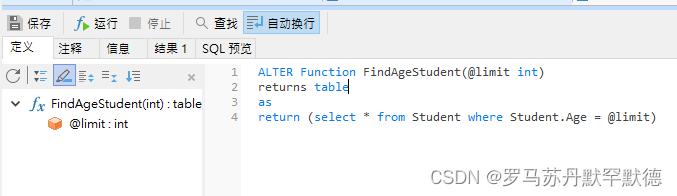
Create Function FindAgeStudent(@limit int)
returns table
as
return (select * from Student where Student.Age = @limit)
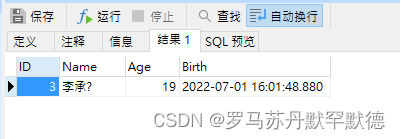
Add :
In a custom function , You cannot modify the records of the table , You can't use insert,update,delete sentence .
Again , You can't execute stored procedures in custom functions .
example :
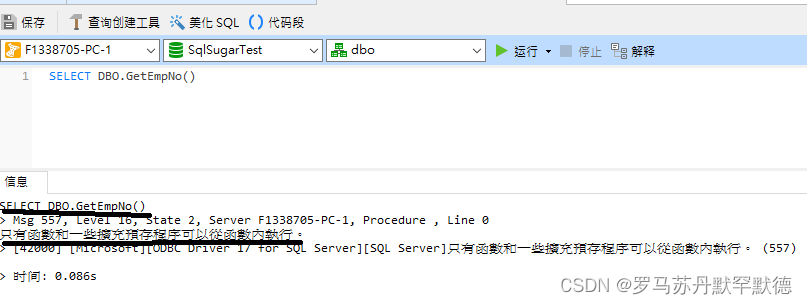
ALTER FUNCTION GetEmpNo()
returns int
BEGIN
DECLARE @wdnmd int,@result varchar(20);
set @wdnmd = (SELECT COUNT(*) FROM t_role_permission)
EXEC @result = plusplus // Defining and executing a stored procedure in a function will not report an error , But an error will be reported when using the function
return @wdnmd
END
2. stored procedure
Compared to function , Stored procedures are more flexible . It is defined in Microsoft documentation as follows
- Accept input parameters and return multiple values to the calling procedure or batch in the form of output parameters .
- Contains information for performing operations in the database ( Including calling other procedures ) Programming statements for .
- Returns the status value to the calling procedure or batch , To indicate success or failure ( And the reasons for the failure ).
Compared to function , It can be said to be a superset of scalar functions , Can realize the function function function , Can also complete programming , Operations such as modifying records .
Its syntax is as follows
-- Transact-SQL Syntax for Stored Procedures in SQL Server and Azure SQL Database
CREATE [ OR ALTER ] { PROC | PROCEDURE }
[schema_name.] procedure_name [ ; number ]
[ { @parameter_name [ type_schema_name. ] data_type }
[ VARYING ] [ = default ] [ OUT | OUTPUT | [READONLY]
] [ ,...n ]
[ WITH <procedure_option> [ ,...n ] ]
[ FOR REPLICATION ]
AS { [ BEGIN ] sql_statement [;] [ ...n ] [ END ] }
[;]
<procedure_option> ::=
[ ENCRYPTION ]
[ RECOMPILE ]
[ EXECUTE AS Clause ]
Stored procedures can also have return values , The return value must be int,
Of course, you can set OUT/OUTPUT Implement multiple return values
create proc SetStuAge(@age int)
AS
BEGIN
Update Student set Age = @age
SELECT * from Student
END
perform :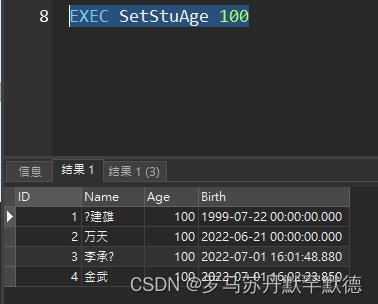
Process control of stored procedures
Process control can also be used in user-defined functions , But because it is impossible to change records in user-defined functions , So I don't use much . In the stored procedure, it is often used .
1. Judge
grammar :
IF search_condition
BEGIN
statement_list
END
ELSE
BEGIN
statement_list
END
The structure of judgment is relatively simple , Only need IF/ELSE Use the following BEGIN and END Declare the area
example
CREATE PROC panduan(@sign varchar(5))
AS
BEGIN
IF @sign = 'A'
BEGIN
SELECT * from Student
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SELECT 8*8
END
END
EXEC panduan 'A'
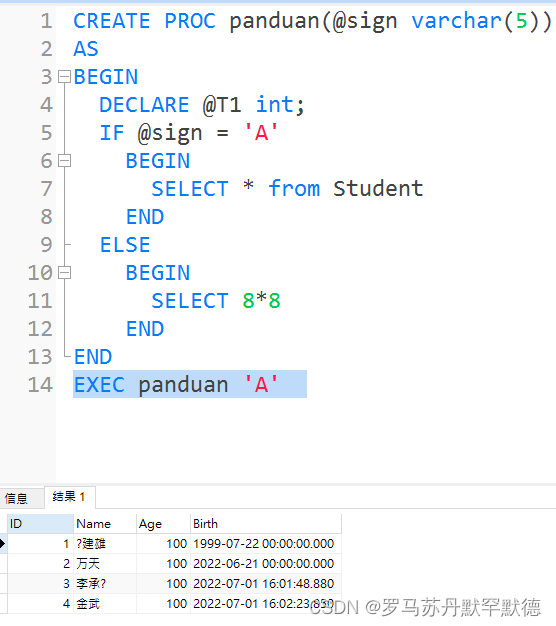
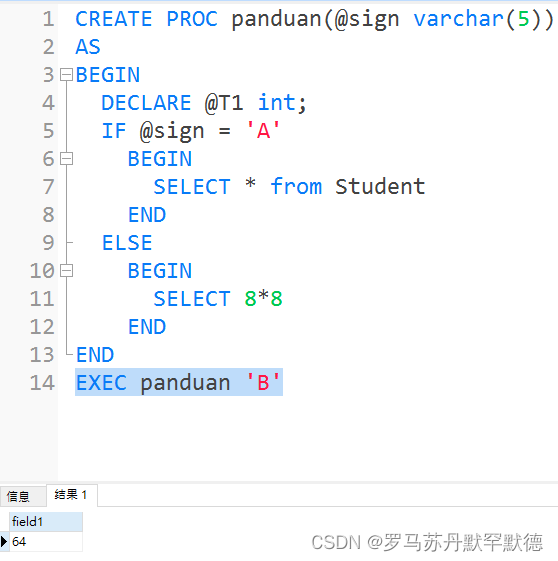
2. loop
The loop control of stored procedures is more complex
Generally speaking ,SqlServer Loops are also used in the same way as programming languages While keyword
WHILE loop_condition BEGIN
statement_list
END
WHILE The usage of keyword alone is relatively simple , however It's usually with Cursor Use with cursor
Create proc WhileDemo
AS
BEGIN
While (select Age from Student where ID = 1) <= 200
BEGIN
PRINT 'while Cycle test '
update Student set Age = Age + 10 where ID = 1
END
END
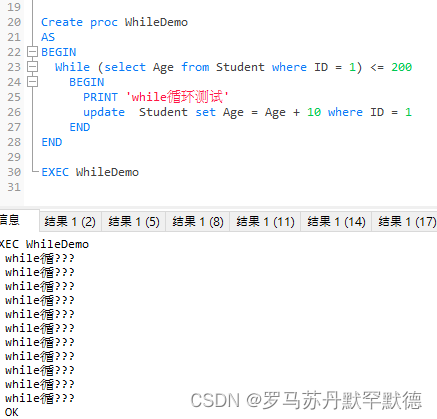
CURSOR Cursor loop
cursor Is the cursor type of the stored procedure , Used to traverse the queried records , Similar to... In programming languages foreach loop
cursor The method of using is very flexible , The syntax is roughly as follows
-- declare cursor
ISO Syntax
DECLARE cursor_name [ INSENSITIVE ] [ SCROLL ] CURSOR
FOR select_statement
[ FOR { READ ONLY | UPDATE [ OF column_name [ ,...n ] ] } ]
[;]
Transact-SQL Extended Syntax
DECLARE cursor_name CURSOR [ LOCAL | GLOBAL ]
[ FORWARD_ONLY | SCROLL ]
[ STATIC | KEYSET | DYNAMIC | FAST_FORWARD ]
[ READ_ONLY | SCROLL_LOCKS | OPTIMISTIC ]
[ TYPE_WARNING ]
FOR select_statement
[ FOR UPDATE [ OF column_name [ ,...n ] ] ]
[;]
-- Open cursor
OPEN { { [ GLOBAL ] cursor_name } | cursor_variable_name }
-- Read cursor
FETCH
[ [ NEXT | PRIOR | FIRST | LAST
| ABSOLUTE { n | @nvar }
| RELATIVE { n | @nvar }
]
FROM
]
{ { [ GLOBAL ] cursor_name } | @cursor_variable_name }
[ INTO @variable_name [ ,...n ] ]
-- Close cursor
CLOSE { { [ GLOBAL ] cursor_name } | cursor_variable_name }
-- Delete cursor
DEALLOCATE { { [ GLOBAL ] cursor_name } | @cursor_variable_name }
It is recommended to check the documents of Microsoft
Microsoft documents
Here is also an article recommended
SQL Cursor details
example :
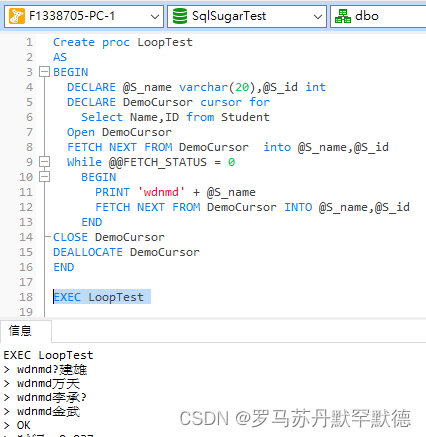
Create proc LoopTest
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @S_name varchar(20),@S_id int
-- Define cursors
DECLARE DemoCursor cursor for
Select Name,ID from Student
-- Open cursor
Open DemoCursor
-- Read cursor
FETCH NEXT FROM DemoCursor into @S_name,@S_id
While @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
PRINT 'wdnmd' + @S_name
FETCH NEXT FROM DemoCursor INTO @S_name,@S_id
END
-- Close cursor
CLOSE DemoCursor
-- Delete cursor
DEALLOCATE DemoCursor
END
边栏推荐
- Gorm read / write separation (rotation)
- MySQL stored procedure exercise
- Why should Base64 encoding be used for image transmission
- 一种架构来完成所有任务—Transformer架构正在以一己之力统一AI江湖
- ML之shap:基于boston波士顿房价回归预测数据集利用Shap值对LiR线性回归模型实现可解释性案例
- Compile oglpg-9th-edition source code with clion
- Migration from go vendor project to mod project
- 实时数据仓库
- Excel quickly merges multiple rows of data
- Digi重启XBee-Pro S2C生产,有些差别需要注意
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
The failure rate is as high as 80%. What are the challenges on the way of enterprise digital transformation?
ViewModel 初体验
【MySQL从入门到精通】【高级篇】(五)MySQL的SQL语句执行流程
LiveData
GCC【6】- 编译的4个阶段
nowcoder重排链表
2022游戏出海实用发行策略
What is the real meaning and purpose of doing things, and what do you really want
Blob, text geometry or JSON column'xxx'can't have a default value query question
R语言ggplot2可视化:gganimate包创建动画图(gif)、使用anim_save函数保存gif可视化动图
R language dplyr package summary_ If function calculates the mean and median of all numerical data columns in dataframe data, and summarizes all numerical variables based on conditions
DDD application and practice of domestic hotel transactions -- Code
PyTorch的自动求导机制详细解析,PyTorch的核心魔法
Common content type correspondence table
Leetcode t49: grouping of alphabetic words
Opencv3.2 and opencv2.4 installation
ARouter的使用
Supprimer les lettres dupliquées [avidité + pile monotone (maintenir la séquence monotone avec un tableau + Len)]
数据埋点的一些问题和想法
Incremental ternary subsequence [greedy training]