当前位置:网站首页>深度剖析C语言数据在内存中的存储
深度剖析C语言数据在内存中的存储
2022-07-06 08:28:00 【终为—NULL】
作者: 终是—NULL
座右铭:每天进步一点点,坚持带来大改变!
文章内容: C语言数据在内存中的存储。
前言:
经过前面一段时间的学习我们已经了解了在C语言中包含各种数据,但我们是否真正理解了类型的意义,以及不同的数据类型在内存中是如何存储的。接下来我们一一开始解剖。
目录
1.数据类型的详细介绍:
1.整形家族
char
unsigned char
signed char
short
unsigned short [int]
signed short [int]
int
unsigned int
signed int
long
unsigned long [int]
signed long [int]
2.浮点型家族
float
double
3.构造类型
> 数组类型
> 结构体类型 struct
> 枚举类型 enum
> 联合类型 union
4.指针类型
int *pi;
char *pc;
float* pf;
void* pv;
5.空类型
void
2.类型的意义
1.不同的数据类型决定了定义变量的时候我们在内存上申请多大的内存空间。
2.不同的数据类型决定了我们在向开辟好的空间存放数据的时候以什么样的形式进行存储
3.不同的数据类型在内存中的存储
1.概念引入:
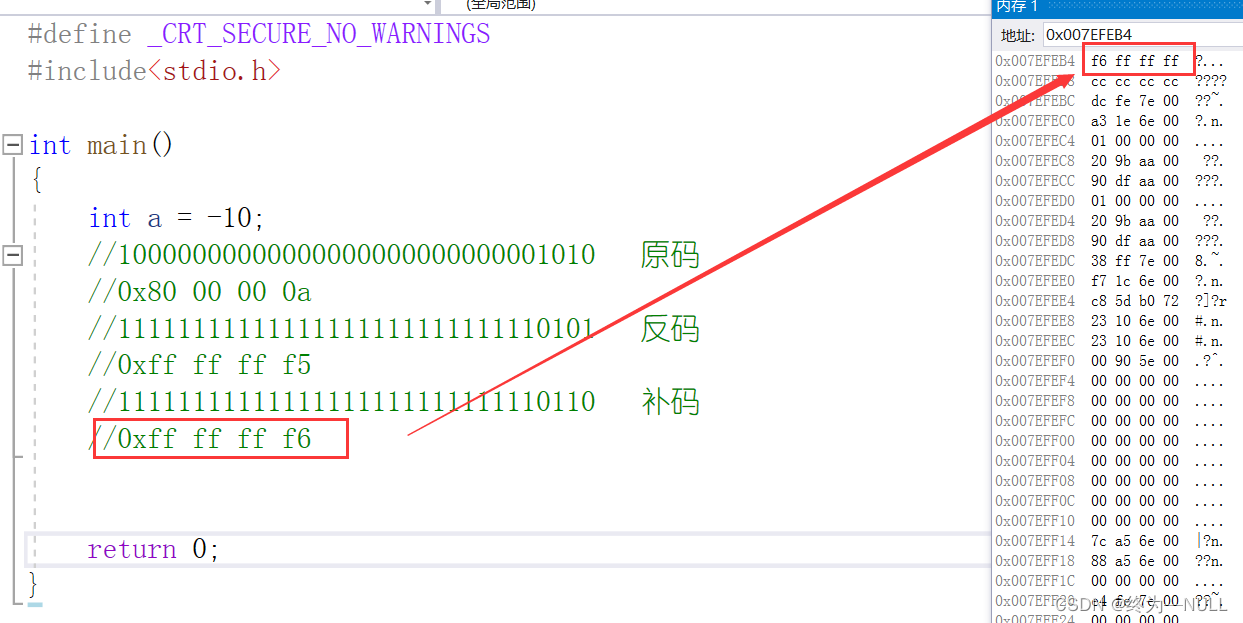
数据在计算机中是以二进制的形式进行存储:有三种表示方法,即原码,反码,补码。
三种表示方法都有对应的符号位:最高位‘0’表示正数,最高位‘1’表示负数
三种不同表示方法规则:
原码:直接按照对应的二进制位写出来
反码:符号位不变,其它位按位取反补码:反码加一得到补码
2.数据在内存中的存放形式:
int a= - 10;
总结:通过调试发现数据在内存中是以补码的形式进行存储的。
3.数据在内存中的存放顺序:
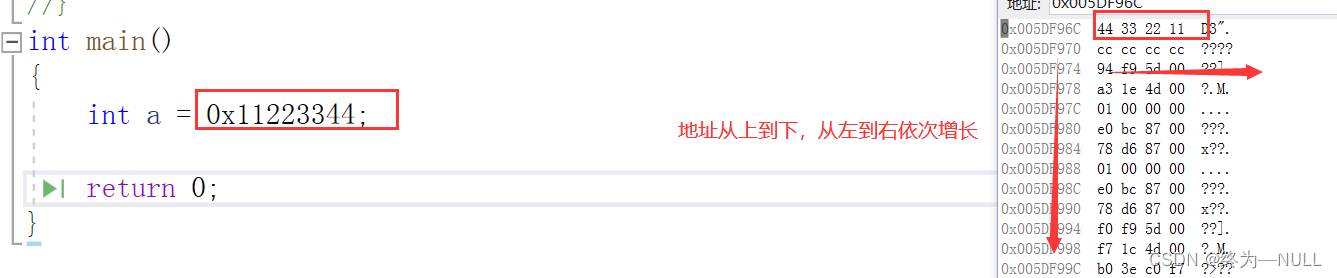
1.大小端:
现象:
为什么我们定义的数据和内存中存储的数据是相反的呢?
大端存储:低字节序(低权值位)的数据存放到高地址处,高字节序(高权值位)的数据存放到低地址处。
小端存储:低字节序(低权值位)的数据存放到低地址处,高字节序(高权值位)的数据存放到高地址处。
存放数据使用大端存储还是小端存储取决于编译器。在VS中采用小端存储。
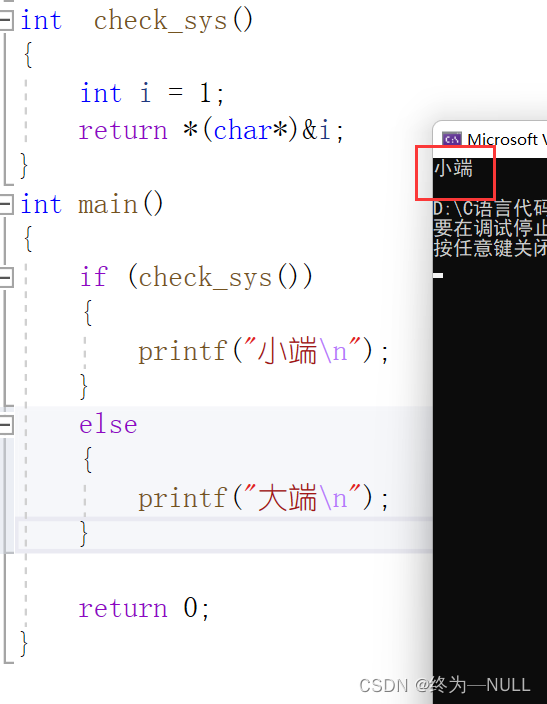
2.判断大小端:
题目描述:写一段代码,判断使用的编译器是小端存储还是大端存储。
思路:将整形数据1强转为char类型,然后进行解应用
#include<stdio.h> int check_sys() { int i = 1; return *(char*)&i; } int main() { if (check_sys()) { printf("小端\n"); } else { printf("大端\n"); } return 0; }
4.char类型的数据在内存中的存储
char
signed char ; //有符号的
unsigned char;//无符号的
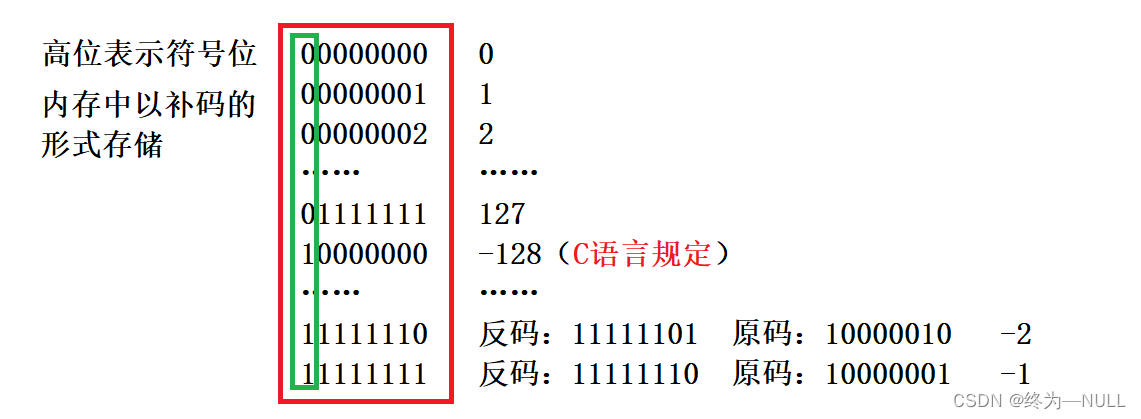
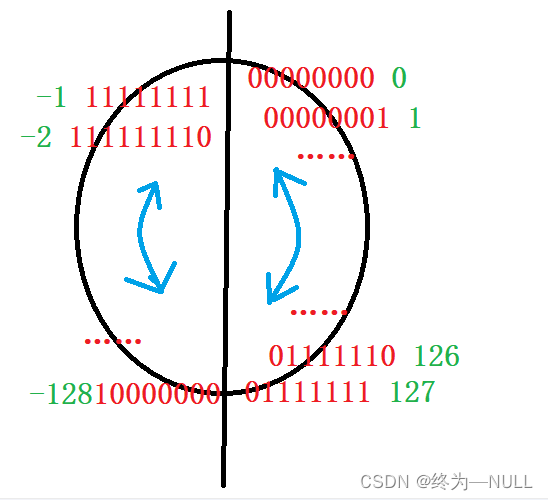
1.有符号char在内存中存储数据范围:
总结:有符号的char类型的数据存储范围为-128~127
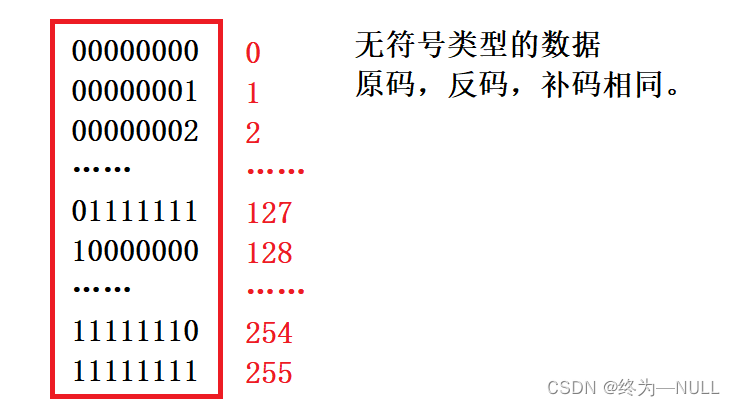
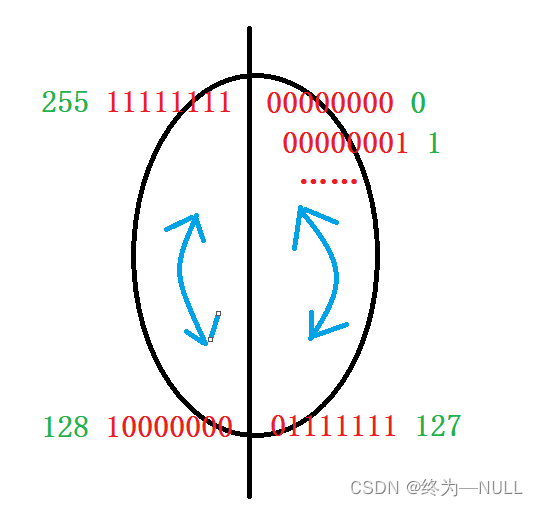
2.无符号char在内存中存储数据范围:
总结:无符号类型的数据在内存中的存储范围为0~255
5.浮点数在内存中的存储规则
1.浮点数的存储规则:
根据国际标准IEEE(电气和电子工程协会) 754,任意一个二进制浮点数V可以表示成下面的形式:
(-1)^S * M * 2^E
(-1)^S表示符号位,当S=0,V为正数;当S=1,V为负数。
M表示有效数字,大于等于1,小于2。
2^E表示指数位。
举例:
5.5
二进制形式:101.1
科学计数法:1.011*2^2
加上符号位:(-1)^0*1.011*2^2
0==S M==1.001 E==2
2.浮点数存入内存的规则
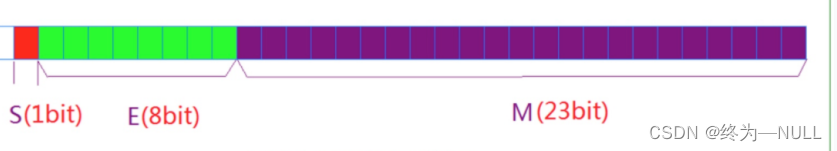
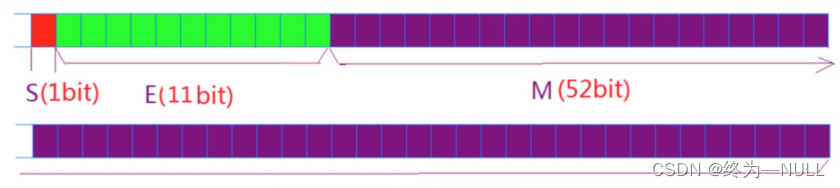
1.32位单精度浮点数:
最高位1位是符号位S,然后是8位指数E,剩下的M是23位有效数字(不包含小数点前面的1,为了提高精度)。
2.64位双进度浮点数:
最高位1位是符号位S,然后是11位指数E,剩下的M是52位有效数字(不包含小数点前面的1,为了提高精度)。
指数E的存储规则:
E是一个无符号数,所以E为8位,范围为0~255,如果E为11位,范围为0~2047.
但是因为浮点数是存在负数的,所以在存储的时候单精度浮点数加上127,双精度浮点数加上1023
3.浮点数从内存中取出的规则
1.E不全为0或不全为1:
指数E的值减去127(1023),在有效数字前面加上1.
2.E全为0:
浮点数的E等于1-127或者(1-1023)即为真实值。
有效数字前面不在加上1,而是还原为0.xxxxx的小数,这样是为了表示正负0,以及接近0的很小的数字。
3.E全为1:
这时,如果有效数字M全为0,表示±无穷大(正负取决于符号位s);
4.举例:
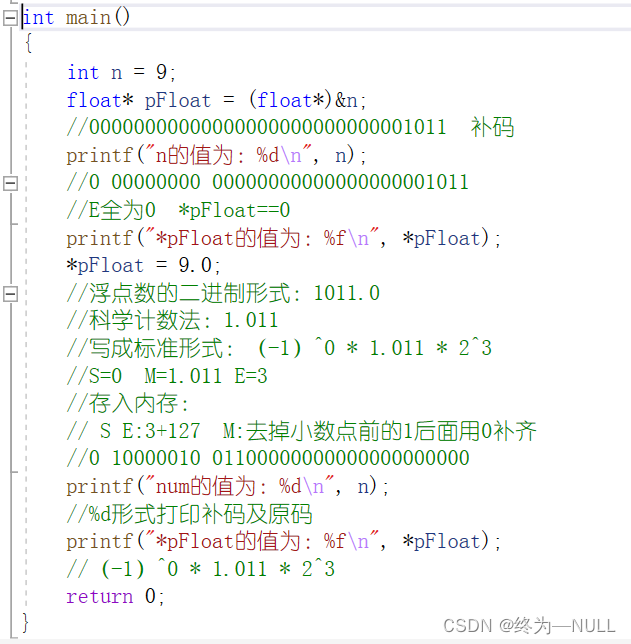
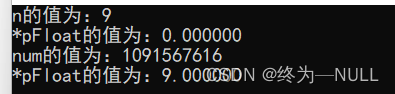
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int n = 9; float *pFloat = (float *)&n; printf("n的值为:%d\n",n); printf("*pFloat的值为:%f\n",*pFloat); *pFloat = 9.0; printf("num的值为:%d\n",n); printf("*pFloat的值为:%f\n",*pFloat); return 0; }代码解释:
6.总结
以上就是关于整形数据和浮点数在内存中的存储规则。希望能对你有所帮助,如果中间内容有错误和不足的地方欢迎留言评论。
边栏推荐
- ESP series pin description diagram summary
- Tidb backup and recovery introduction
- All the ArrayList knowledge you want to know is here
- sublime text的编写程序时的Tab和空格缩进问题
- 电脑F1-F12用途
- [research materials] 2022 enterprise wechat Ecosystem Research Report - Download attached
- Leetcode question brushing (5.31) string
- LDAP application (4) Jenkins access
- What is CSRF (Cross Site Request Forgery)?
- 从 CSV 文件迁移数据到 TiDB
猜你喜欢
![[research materials] 2022 enterprise wechat Ecosystem Research Report - Download attached](/img/35/898a8086bc35462b0fcb9e6b58b86b.jpg)
[research materials] 2022 enterprise wechat Ecosystem Research Report - Download attached
指针进阶---指针数组,数组指针
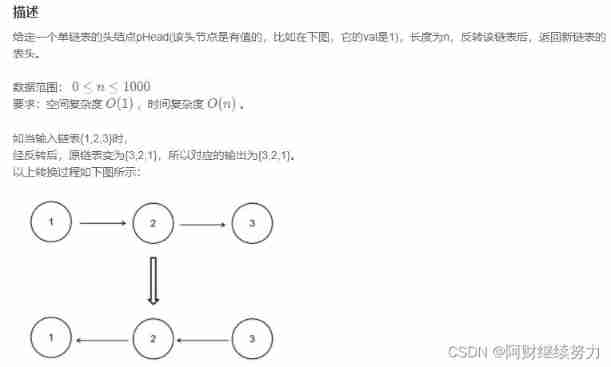
2022.02.13 - NC001. Reverse linked list
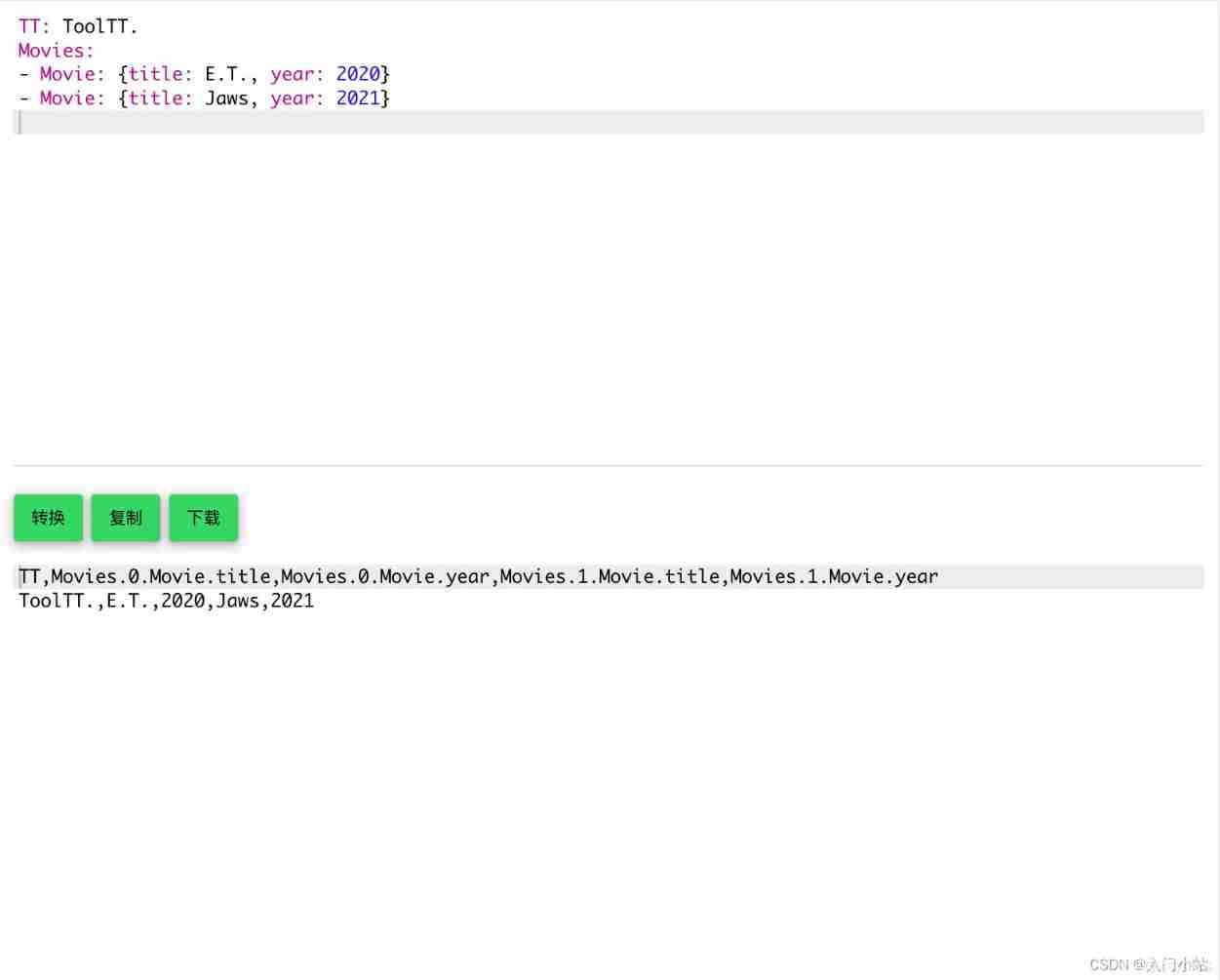
Online yaml to CSV tool
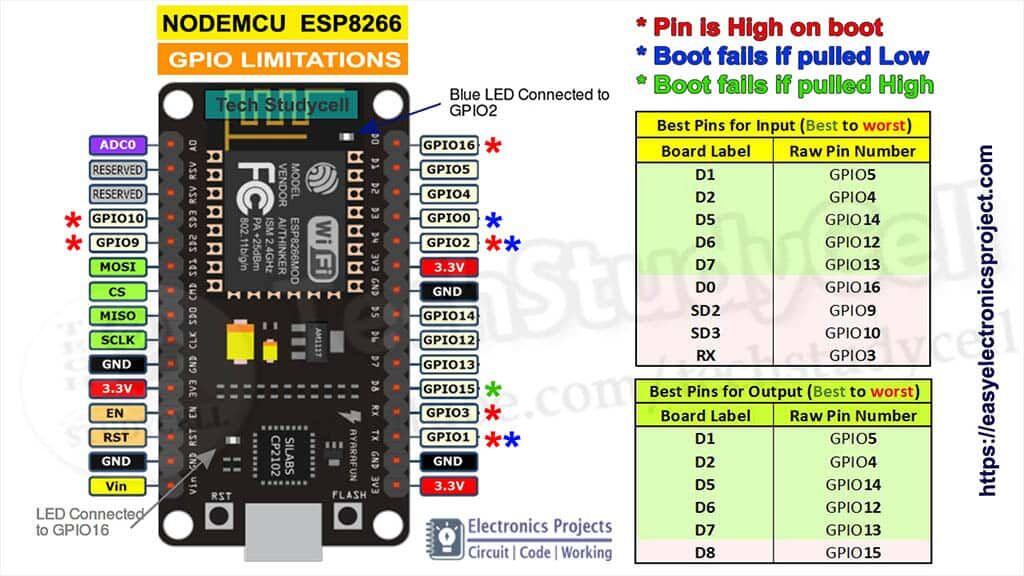
ESP系列引脚說明圖匯總
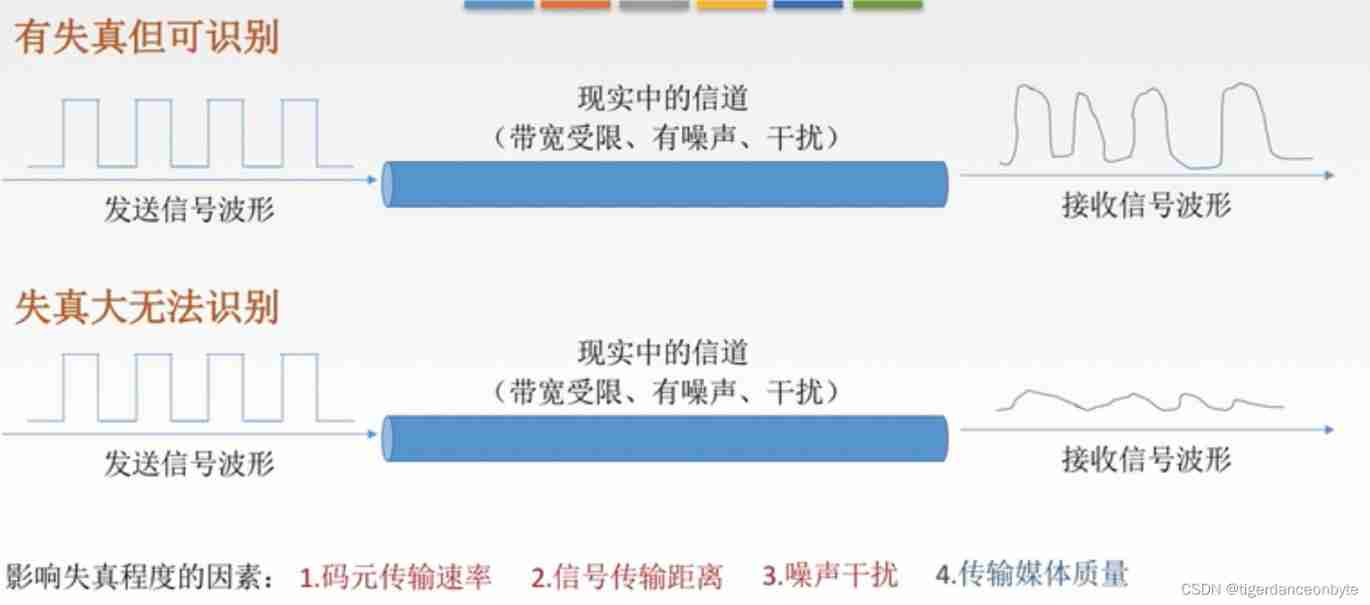
Bottom up - physical layer
JVM performance tuning and practical basic theory - Part 1

ESP系列引脚说明图汇总
Circular reference of ES6 module
egg. JS project deployment online server
随机推荐
Modify the video name from the name mapping relationship in the table
【刷题】牛客网面试必刷TOP101
Zhong Xuegao, who cannot be melted, cannot escape the life cycle of online celebrity products
游戏解包的危害及资源加密的重要性
Pointer advanced --- pointer array, array pointer
IOT -- interpreting the four tier architecture of the Internet of things
2. File operation - write
On the day of resignation, jd.com deleted the database and ran away, and the programmer was sentenced
Configuring OSPF load sharing for Huawei devices
VMware 虚拟化集群
Function coritization
查看局域网中电脑设备
[research materials] 2021 China online high growth white paper - Download attached
MySQL learning record 10getting started with JDBC
Research Report on Market Research and investment strategy of microcrystalline graphite materials in China (2022 Edition)
leetcode刷题 (5.31) 字符串
JVM 快速入门
egg. JS directory structure
vulnhub hackme: 1
tree树的精准查询