当前位置:网站首页>Single source shortest path exercise (I)
Single source shortest path exercise (I)
2022-07-06 00:15:00 【rikka-l】
Single source shortest path exercise
Single source shortest path mapping method
Heat Wave
Topic link : Heat Wave
analysis : A more naked question , Directly build drawings and then set templates , I'll just use spfa The water has passed .
Code implementation :
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N=2510,M=12410;
int n,m,str,ed;
int dist[N];
int h[N],e[M],ne[M],idx=1,w[M];// Chained forward star storage graph
bool st[N];
queue<int> q;
void add(int a,int b,int c){
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],w[idx]=c,h[a]=idx++;
}
void spfa(){
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);
dist[str]=0;
q.push(str);
st[str]=1;
while(q.size()){
auto t=q.front();
q.pop();
st[t]=0;
for(int i=h[t];i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(dist[j]>dist[t]+w[i]){
dist[j]=dist[t]+w[i];
if(!st[j]) q.push(j),st[j]=1;// here st[j] It's good to remove it , But it will be less efficient
}
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m>>str>>ed;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
add(a,b,c);
add(b,a,c);
}
spfa();
cout<<dist[ed]<<endl;
return 0;
}
messenger
Topic link : messenger
analysis : For this question , We found that , For addition 1 Every point outside , The shortest time required for communication is 1 The shortest distance to this point , And the time when all points complete the communication is when all points arrive 1( except 1 Outside ) The maximum value in the shortest circuit of , So we just need to 1 To all points ( except 1 Outside ) The shortest circuit of .
Code implementation :
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m;
const int N=110;
int g[N][N];
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
memset(g,0x3f,sizeof g);
// Here we don't need to initialize g[i][i] by 0, Therefore, it will not be used when updating , It's also right to update without this status
while(m--){
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
g[a][b]=g[b][a]=min(g[a][b],c);// Prevent multiple edges
}
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++)
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
g[i][j]=min(g[i][j],g[i][k]+g[k][j]);
int res=0;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)// Attention from 2 Start , If from 1 Start , Because we didn't put g[1][1] Initialize to 0, Can cause errors
if(g[1][i]==INF) {
res=-1;
break;
}
else res=max(res,g[1][i]);
cout<<res;
return 0;
}
Sweet butter
Topic link : Sweet butter
analysis : For this question , We can enumerate every pasture to put sugar , Then find out the shortest path from this pasture to all other pastures , Then enumerate the pastures of each cow , Find these distances and choose the smallest one . If you go directly to dijkstra It may time out , Here we use spfa, The author of this question has no card spfa.
Code implementation :
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int s,n,m,tmp;
const int N=810,M=2910;
int res=INF;
int id[N],e[M],ne[M],idx=1,h[N],w[M];
bool st[N];
int dist[N];
queue<int> q;
void add(int a,int b,int c){
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],w[idx]=c,h[a]=idx++;
}
int spfa(int str){
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);
q.push(str);
st[str]=1;
dist[str]=0;
while(q.size()){
auto t=q.front();
q.pop();
st[t]=0;
for(int i=h[t];i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(dist[j]>dist[t]+w[i]){
dist[j]=dist[t]+w[i];
if(!st[j]) q.push(j),st[j]=1;
}
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=s;i++)
if(dist[id[i]]==INF) return INF;// Once two pastures are disconnected , Go straight back to INF
else ans+=dist[id[i]];
return ans;
}
int main(){
cin>>s>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=s;i++) cin>>id[i];// Record the pasture of each cow
while(m--){
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
add(a,b,c),add(b,a,c);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) res=min(res,spfa(i));
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}
Minimum cost
Topic link : Minimum cost
analysis : An interesting question , We use... Separately spfa and dijkstra Explain it once .
Let's think about it first , hypothesis A The amount of money ordered is SA, After each point, the remaining money is the original Ci times , It goes through all points to B Then there is an equation SA*C1*C2*C3......=100, We demand SA The minimum value of , Just ask that pile C The maximum value of the product of , Again because Ci Greater than 0 Less than or equal to 1, So the more multiplied, the smaller , Next we discuss two approaches .
spfa:spfa Is based on its relaxation operation , For a starting point , If we can update adjacent points through its edges ( All points are initially initialized to 0, The starting point is initialized to 1), That is the C The product of becomes smaller , Just operate and add this point to the queue , therefore spfa Find the shortest path 、 The longest way is ok .
Code implementation :
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int n,m,A,B;
const int N=2010,M=2e5+10;
int e[M],ne[M],idx=1,h[N];
double w[M];
double dist[N];
bool st[N];
queue<int> q;
void add(int a,int b,double c){
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],w[idx]=c,h[a]=idx++;
}
void spfa(){
dist[B]=1;
st[B]=1;
q.push(B);
while(q.size()){
auto t=q.front();
q.pop();
st[t]=0;
for(int i=h[t];i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(dist[j]<dist[t]*w[i]){
dist[j]=dist[t]*w[i];
if(!st[j]) q.push(j),st[j]=1;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int x,y,z;
cin>>x>>y>>z;
double c=(100.0-z)/100;// Translate into... In our analysis c
add(x,y,c);
add(y,x,c);
}
cin>>A>>B;
spfa();// hold B As a starting point
printf("%.8lf",100/dist[A]);
return 0;
}
dijkstra: We know ,dijkstra It is based on greed , For the shortest path problem , Let's find the shortest distance to the end , At the beginning, it is itself , Then use it to update other points , But it cannot solve the longest path problem ( I won't prove it here ,《 Introduction to algorithms 》 There should be ), And for us, the most demanding C, We find the biggest one every time C To update , At the beginning, it is also itself , Then use a similar method to update , We found that it can also AC.( Here I have a guess ,dijkstra The reason why we can't find the longest way is that the nearest one to the end is not the end itself .) Prove concretely that I really won't , I'm too fond of vegetables. , Left tears of frustration .
Code implementation :( I don't want to write anymore , Just stick it y All in all )
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2010;
int n, m, S, T;
double g[N][N];
double dist[N];
bool st[N];
void dijkstra(){
dist[S] = 1;// The starting point is initialized to 1, Other points are 0
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
int t = -1;
// Find the biggest C
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] < dist[j]))
t = j;
st[t] = true;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
dist[j] = max(dist[j], dist[t] * g[t][j]);// to update
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
while (m -- ){
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
double z = (100.0 - c) / 100;// Translate into... In our analysis C
g[a][b] = g[b][a] = max(g[a][b], z);
}
cin >> S >> T;
dijkstra();
printf("%.8lf\n", 100 / dist[T]);
return 0;
}
By the way , For this question ,dijkstra:570ms about ,spfa:242ms about .
The best ride
Topic link : The best ride
analysis : There are some skills in the construction of this problem , First , There must be many solutions to this problem ( I guess. ), Since we are the single source shortest path exercise , Let's use the single source shortest path method . For each route , The distance from the previous point to any subsequent point is set to 1, Then we find the shortest path from the beginning to the end , subtracting 1 That's the answer. ( Because once it was transferred on the same route ), But there is another special case , When the start point and the end point coincide , The shortest path is 0, subtract 1 Namely -1 了 , So we have to deal with it in a special way .
Code implementation :
// acutely , How do you feel that I wrote bfs A wave of spfa taste
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int n,m,tmp;
const int N=510,M=25010,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int e[M],ne[M],idx=1,h[N];
int stop[N];
int dist[N];
queue<int> q;
void add(int a,int b){
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++;
}
void bfs(){
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);
dist[1]=0;
q.push(1);
while(q.size()){
auto t=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=h[t];i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(dist[j]==INF){
// the reason being that bfs, The first update must be the minimum
dist[j]=dist[t]+1;
q.push(j);
}
}
}
}
int main(){
string s;
cin>>m>>n;
getline(cin,s);// Spit out \n, because cin Will not read the end \0
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
getline(cin,s);
stringstream ss(s);//se Put in ss in
int cnt=0;
while(ss>>tmp) stop[cnt++]=tmp;// Read the numbers into tmp in
for(int j=0;j<cnt;j++)
for(int k=j+1;k<cnt;k++)
add(stop[j],stop[k]);// Bordering
}
bfs();// Because the edge right is 1, direct bfs
if(dist[n]==INF) puts("NO");// unsolvable
else cout<<max(dist[n]-1,0)<<endl;
return 0;
}
Expensive betrothal gifts
Topic link : Expensive betrothal gifts
analysis : The most interesting question ! I was dizzy when I read the questions. Hurry . The most difficult thing is to consider how to build a map and compare easy. I have to say that the mapping method of this problem is really awesome ... We artificially design a virtual starting point , The distance from it to all items is the price of these items , Then connect the equivalent substitutes , The price is the gold coins needed after replacement , Then this problem becomes a shortest path problem , The starting point is a virtual starting point , The end is 1, But there is another constraint to this problem , Is the grade difference , We enumerate all possible level ranges , Then only update the points that meet the grade requirements while finding the shortest path , thus , This problem is perfectly solved !
Code implementation :
We found that , As long as we can build maps , Write casually in the back !
This is the heap optimization I wrote dijkstra:117ms, Maybe because there are many sides
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N=110,M=1e4+10,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int e[M],ne[M],idx,h[N],w[M],level[N];
int m,n,res=INF;
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a,int b,int c){
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],w[idx]=c,h[a]=idx++;
}
int dijkstra(int left){
priority_queue<PII,vector<PII>,greater<PII>> heap;
memset(st,0,sizeof st);
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);
dist[0]=0;
heap.push({
0,0});
// This sentence was added at the beginning st[0]=1, As a result, it was adjusted for a long time , I'm so angry
while(heap.size()){
auto t=heap.top();
heap.pop();
int tmp=t.second;
if(st[tmp])continue;
st[tmp]=1;
for(int i=h[tmp];~i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(dist[j]>dist[tmp]+w[i]&&level[j]>=left&&level[j]<=left+m){
// The grade can only be updated if it meets the requirements
dist[j]=dist[tmp]+w[i];
heap.push({
dist[j],j});
}
}
}
return dist[1];
}
int main(){
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
cin>>m>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int p,x;
cin>>p>>level[i]>>x;
add(0,i,p);
while(x--){
int t,v;
cin>>t>>v;
add(t,i,v);
}
}
for(int i=level[1]-m;i<=level[1];i++)// Enumerate the left boundary of the level interval , The right boundary is the left boundary +m, Here, because the grade difference between the two sides of indirect transactions cannot exceed m, Therefore, the length of the grade interval is m
res=min(res,dijkstra(i));
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}
This is a y Overall simplicity dijkstra:72ms
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m;
int w[N][N], level[N];
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
int dijkstra(int down, int up){
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
dist[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i ++ ){
int t = -1;
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j ++ )
if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j]))
t = j;
st[t] = true;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ )
if (level[j] >= down && level[j] <= up)
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + w[t][j]);
}
return dist[1];
}
int main(){
cin >> m >> n;
memset(w, 0x3f, sizeof w);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) w[i][i] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
int price, cnt;
cin >> price >> level[i] >> cnt;
w[0][i] = min(price, w[0][i]);
while (cnt -- ){
int id, cost;
cin >> id >> cost;
w[id][i] = min(w[id][i], cost);
}
}
int res = INF;
for (int i = level[1] - m; i <= level[1]; i ++ ) res = min(res, dijkstra(i, i + m));
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- Single merchant v4.4 has the same original intention and strength!
- Key structure of ffmpeg - avformatcontext
- NSSA area where OSPF is configured for Huawei equipment
- Global and Chinese markets for pressure and temperature sensors 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- 硬件及接口学习总结
- 【GYM 102832H】【模板】Combination Lock(二分图博弈)
- What is information security? What is included? What is the difference with network security?
- Yunna | what are the main operating processes of the fixed assets management system
- Gavin teacher's perception of transformer live class - rasa project actual combat e-commerce retail customer service intelligent business dialogue robot system behavior analysis and project summary (4
- LeetCode 8. String conversion integer (ATOI)
猜你喜欢
Detailed explanation of APP functions of door-to-door appointment service

AtCoder Beginner Contest 254【VP记录】
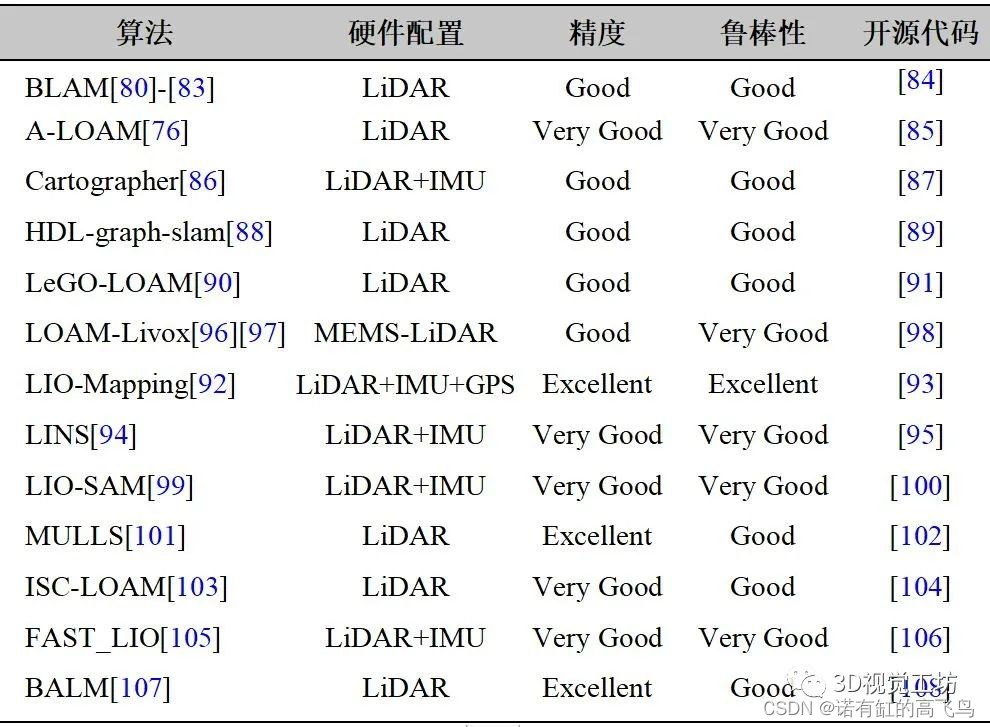
Laser slam learning record

18.(arcgis api for js篇)arcgis api for js点采集(SketchViewModel)
![Atcoder beginer contest 258 [competition record]](/img/e4/1d34410f79851a7a81dd8f4a0b54bf.gif)
Atcoder beginer contest 258 [competition record]

wx. Getlocation (object object) application method, latest version
![[noi simulation] Anaid's tree (Mobius inversion, exponential generating function, Ehrlich sieve, virtual tree)](/img/d6/c3128e26d7e629b7f128c551cd03a7.png)
[noi simulation] Anaid's tree (Mobius inversion, exponential generating function, Ehrlich sieve, virtual tree)
MySQL functions
Room cannot create an SQLite connection to verify the queries
![[designmode] composite mode](/img/9a/25c7628595c6516ac34ba06121e8fa.png)
[designmode] composite mode
随机推荐
Asynchronous task Whenall timeout - Async task WhenAll with timeout
关于slmgr命令的那些事
[Luogu cf487e] tours (square tree) (tree chain dissection) (line segment tree)
跟着CTF-wiki学pwn——ret2libc1
PHP determines whether an array contains the value of another array
JS 这次真的可以禁止常量修改了!
SQLServer连接数据库读取中文乱码问题解决
【luogu CF487E】Tourists(圆方树)(树链剖分)(线段树)
LeetCode 6006. Take out the least number of magic beans
AtCoder Beginner Contest 258【比赛记录】
[noi simulation] Anaid's tree (Mobius inversion, exponential generating function, Ehrlich sieve, virtual tree)
从底层结构开始学习FPGA----FIFO IP核及其关键参数介绍
shardingsphere源码解析
Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)【比赛记录】
【DesignMode】组合模式(composite mode)
The difference of time zone and the time library of go language
7.5 simulation summary
Mathematical model Lotka Volterra
MySQL global lock and table lock
MySql——CRUD