当前位置:网站首页>JVM_ 15_ Concepts related to garbage collection
JVM_ 15_ Concepts related to garbage collection
2022-07-06 00:53:00 【shouanzh】
List of articles
- 1.System.gc() The understanding of the
- 2. Memory overflow and memory leak
- 3.Stop The World
- 4. Parallel and concurrent garbage collection
- 5. Safe points and safe areas
- 6. Quote Overview
- 7. Strong citation (Strong Reference) - No recovery
- 8. Soft citation (Soft Reference) - If there is not enough memory, it will be recycled
- 9. Weak reference (Weak Reference) - Discovery is recycling
- 10. Virtual reference (Phantom Reference) - Object recovery tracking
- 11. Terminator references
1.System.gc() The understanding of the
- By default , adopt System.gc() person Runtime.getRuntime().gc() Call to , Will explicitly trigger Full GC, At the same time, the old generation and the new generation are recycled , Trying to free memory occupied by discarded objects .
- However System.gc() The call comes with a disclaimer , Calls to the garbage collector cannot be guaranteed .( There is no guarantee of immediate effect )
- JVM The implementer can use System.gc() Call to determine JVM Of GC Behavior . And in general , Garbage collection should be automatic , No manual triggering required , Otherwise, it would be too much trouble . In some special cases , For example, we are writing a performance benchmark , We can call... Between runs System.gc().
public class SystemGCTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemGCTest();
System.gc();// remind jvm The garbage collector of gc, But it's not sure if it's going to be done right now gc
// System.gc() And Runtime.getRuntime().gc() It does the same thing .
System.runFinalization();// Force the invocation of finalize() Method
}
// GC Called before recycling finalize() Method
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
super.finalize();
System.out.println("SystemGCTest Rewrote finalize()");
}
}
The code for
/** * Set up JVM Parameters -XX:+PrintGCDetails */
public class LocalVarGC {
/** * Trigger Minor GC No recycling objects , And then trigger Full GC Store the object in old District */
public void localvarGC1() {
byte[] buffer = new byte[10 * 1024 * 1024]; // 10MB
System.gc();
}
/** * Trigger YoungGC When , It's been recycled */
public void localvarGC2() {
byte[] buffer = new byte[10 * 1024 * 1024];
buffer = null;
System.gc();
}
/** * Will not be recycled , Because it is also stored in the local variable table, the index is 1 In the groove of */
public void localvarGC3() {
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[10 * 1024 * 1024];
}
System.gc();
}
/** * Will be recycled , Because it is also stored in the local variable table, the index is 1 In the groove of , But as defined later value Replaced this slot */
public void localvarGC4() {
{
byte[] buffer = new byte[10 * 1024 * 1024];
}
int value = 10;
System.gc();
}
/** * localvarGC5 The array in has been recycled */
public void localvarGC5() {
localvarGC1();
System.gc();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalVarGC local = new LocalVarGC();
local.localvarGC1();
}
}
2. Memory overflow and memory leak
2.1 out of memory (OOM)
- Memory overflow is relative to memory leak , Although easier to understand , But again , Memory overflow is also one of the main causes of program crash .
- because GC It's been developing , So in general , Unless the memory used by the application grows very fast , Garbage collection can't keep up with the speed of memory consumption , Otherwise, it is not easy to appear OOM The situation of .
- Most of the time ,GC We're going to do garbage collection for all ages , If you can't do it, just enlarge it , Have an exclusive Full GC operation , At this time, a lot of memory will be recycled , For applications to continue to use .
- javadoc Chinese vs OutOfMemoryError The explanation is , No free memory , And the garbage collector can't provide more memory .
First of all, there is no free memory : explain Java There is not enough heap memory for the virtual machine . There are two reasons :
Java The heap memory setting of the virtual machine is not enough .
- such as : There may be a memory leak ; It is also possible that the size of the heap is set unreasonably , For example, we have to deal with a considerable amount of data , But there is no explicit specification of JVM The heap size or the specified value is too small . We can go through the parameters -Xms 、-Xmx To adjust .
A lot of large objects are created in the code , And can't be collected by garbage collector for a long time .( Existence is quoted )
- For the old version of Oracle JDK, Because the size of the permanent generation is limited , also JVM Recycling of permanent waste ( Such as , Constant pool recycling 、 Uninstall types that are no longer needed ) Very negative , So when we keep adding new types , Permanent generation appears OutOfMemoryError Very often , Especially when there are a lot of dynamic type generation at runtime ; similar intern String cache takes up too much space , It can also lead to OOM problem . Corresponding exception information , It will be marked as related to the permanent generation :“java.lang.OutOfMemoryError:PermGen space".
- With the introduction of metadata area , Method area memory is no longer so embarrassed , So corresponding OOM Some changes , appear OOM, The exception message becomes :“java.lang.OutOfMemoryError:Metaspace". Not enough direct memory , It can also lead to OOM.
Throwing out OutOfMemoryError Before , Usually the garbage collector is triggered , Try your best to clear up the space .
- for example : In the analysis of citation mechanism , involves JVM Will try to recycle Objects pointed to by soft references, etc .
- stay java.nio.BIts.reserveMemory() In the method , We can clearly see ,System.gc() Will be called , To clear the space .
Of course , Nor is the garbage collector triggered under any circumstances .
- such as , Let's assign a super object , Like a very large array that exceeds the maximum value of the heap ,JVM You can tell that garbage collection doesn't solve the problem , So just throw it out OutOfMemoryError.
2.2 Memory leak (Memory Leak)
- Also known as “ Storage leakage ”. Strictly speaking , Only objects are no longer used by programs , however GC They can't recycle their situation , Memory leak .
- But the actual situation is that many times there are some bad practices ( Or negligence ) It can lead to a long life cycle of an object or even OOM, It can also be called in a broad sense “ Memory leak ”.
- Although a memory leak does not immediately cause a program crash , But once a memory leak occurs , The available memory in the program will be gradually eroded , Until you run out of memory , In the end OutOfMemory abnormal , Cause the program to crash .
- Be careful , Storage space here doesn't mean physical memory , It's virtual memory size , The size of the virtual memory depends on the size set by the disk swap .
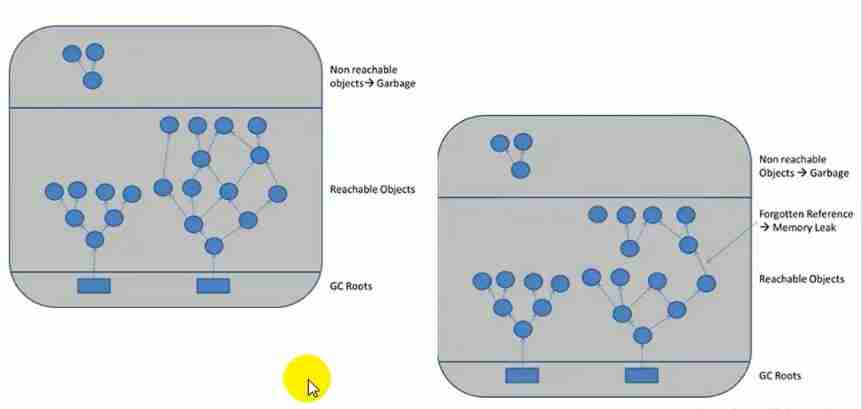
- Java Using the accessibility analysis algorithm , The top data is unreachable , It's what needs to be recycled . Later, some objects are not needed , It makes sense to disconnect references , But there are some chains that are not broken , As a result, there is no way to recycle .
give an example
- The singleton pattern
The lifecycle of the singleton is as long as the application , So in the singleton program , If you hold a reference to an external object , Then this external object cannot be recycled , It will lead to a memory leak . - Some offer close The resource of is not closed, resulting in a memory leak
Database connection (dataSourse.getConnection()), network connections (Socket) and IO The connection must be manual close, Otherwise, it can't be recycled .
3.Stop The World
- Stop-The-World, abbreviation STW, refer to GC In the course of the event , Will produce applications ( User threads ) The pause of . When a pause occurs, the entire application thread is suspended , No response , It's kind of like getting stuck , This pause is called STW.
- Enumerating root nodes in reachability analysis algorithm (GC Roots) It will lead to all Java Execution thread pause .
- The analysis must be done in a snapshot that ensures consistency
- Consistency means that the whole execution system appears to be frozen at a certain point in time during the whole analysis period
- If the object reference relationship is still changing during the analysis process , The accuracy of the analysis results can not be guaranteed
- Enumerating root nodes in reachability analysis algorithm (GC Roots) It will lead to all Java Execution thread pause .
- By STW The interrupted application thread will finish GC Then recover , Frequent interruptions can make users feel like a movie cassette caused by poor network speed , So we need to reduce STW Happen .
- STW Events and which one GC irrelevant , be-all GC It's all about this .
- Even if it is G1 It can't be completely avoided Stop-The-World It happened , It can only be said that the garbage collector is getting better and better , Recycling efficiency is getting higher and higher , Shorten the pause time as much as possible .
- STW yes JVM Automatically initiated and completed in the background . When the user is not visible , Stop all the normal working threads of the user .
- Don't use... In development System.gc(); It can lead to Stop-The-World Happen .
The code for
/** * PrintThread The thread prints every second * WorkThread Every thread created 10000 An array GC once */
public class StopTheWorldDemo {
public static class WorkThread extends Thread {
List<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<byte[]>();
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
list.add(buffer);
}
if (list.size() > 10000) {
list.clear();
System.gc(); // Will trigger full gc, And then there will be STW event
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static class PrintThread extends Thread {
public final long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
// Print time information per second
long t = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
System.out.println(t / 1000 + "." + t % 1000);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
WorkThread w = new WorkThread();
PrintThread p = new PrintThread();
w.start();
p.start();
}
}
You can see that the results of the program are not printed on time every second , This is because GC In the process STW, The user thread will get stuck for a certain time 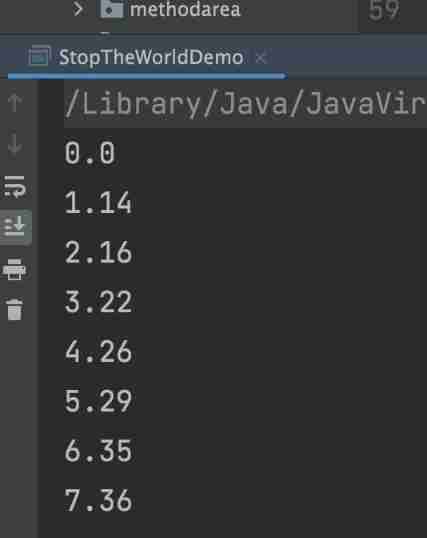
4. Parallel and concurrent garbage collection
4.1 Parallelism and concurrency in programs
4.1.1 Concurrent (Concurrent)
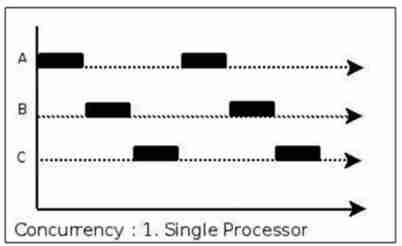
- In the operating system , It means that several programs in a period of time are between the start and the completion of running , And these programs are all running on the same processor .
- Concurrency is not really “ At the same time ”, It's just CPU Divide a time period into several time segments ( Time interval ), And then switch back and forth between these time intervals , because CPU The processing speed is very fast , As long as the time interval is handled properly , It makes users feel that multiple applications are running at the same time .
- Over a period of time , There are multiple tasks in progress . From a single time segment , There is only one task in progress .
4.1.2 parallel (Parallel)
- When the system has more than one CPU when , When one CPU When executing a process , the other one CPU Another process can be executed , The two processes do not preempt each other CPU resources , You can do it at the same time , We call it parallel (Parallel).
- In fact, the determinant of parallelism is not CPU The number of , It is CPU The number of cores , For example, a CPU Multiple cores can also be parallel .
- Suitable for scientific calculation , Background processing and other weak interaction scenes

4.1.3 Concurrent vs parallel
- Concurrent , It refers to multiple things , It happened at the same time .
- parallel , It refers to multiple things , At the same time .
- Multiple concurrent tasks preempt each other's resources .
- Parallel tasks do not preempt each other's resources .
- Only in many CPU Or a CPU In the case of multicore , It's going to happen in parallel .
- otherwise , What seems to happen at the same time , In fact, they are all executed concurrently .
4.2 Concurrency and parallelism of garbage collection
Concurrency and parallelism , In the context of talking about garbage collectors , They can be explained as follows :
- parallel (Parallel): Multiple garbage collection threads working in parallel , But the user thread is still waiting .
- Such as ParNew、Parallel Scavenge、Parallel Old;
- Serial (Serial)
- Compared to the concept of parallelism , Single thread execution .
- If there's not enough memory , Then the program is suspended , start-up JVM Garbage collector for garbage collection . After recycling , Restart the thread of the program .
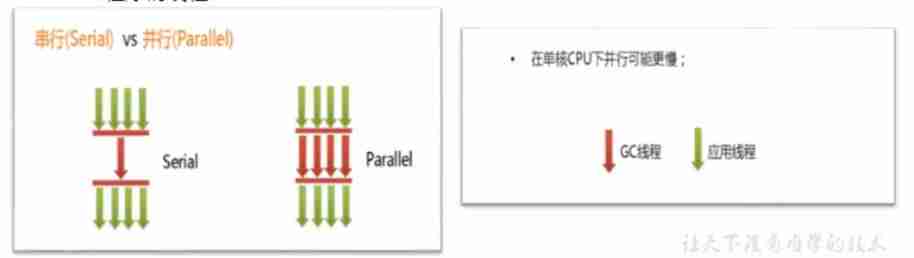
- Concurrent (Concurrent): It refers to the simultaneous execution of user thread and garbage collection thread ( But not necessarily in parallel , May alternate ), The garbage collection thread does not stop the running of the user program during execution .
- The user program is running , The garbage collector thread runs in another CPU On
- Such as :CMS、G1

5. Safe points and safe areas
5.1 safer
- Program execution does not stop at all places to start GC, It's only in a certain position that you can stop and start GC, These locations are called “ safer (SafePoint)”.
- SafePoint The choice of is very important , If too little, it may lead to GC The waiting time is too long , If it is too frequent, it may cause performance problems at runtime . The execution time of most instructions is very short , Usually based on “ Whether the program has the characteristics of long execution ” As the standard . such as : Select some instructions that take longer to execute as Safe Point, Such as method call 、 Loop jump and abnormal jump, etc .
- How to be in GC occurs , Check that all threads run to the nearest safe point and stop ?
- Preemptive interrupt :( At present, no virtual machine adopts )
- First interrupt all threads . If there are threads that are not safe , Just restore the thread , Run to the safe point of the thread .
- Active interrupt :
- Set an interrupt flag , Each thread runs to Safe Point When polling this flag actively , If the interrupt flag is true , Then suspend your own interrupt .( There is a polling mechanism )
- Preemptive interrupt :( At present, no virtual machine adopts )
5.2 The safety area
- SafePoint The mechanism ensures that when the program is executed , In not too long time will meet the access GC Of SafePoint. however , Program “ Don't execute ” When? ? For example, the thread is in Sleep State or Blocked state , At this point the thread cannot respond JVM Interrupt request for ,“ go ” Go to a safe place to suspend ,JVM It's also less likely to wait for the thread to wake up . In this case , You need a safe area (Safe Region) To solve .
- Security zone means in a piece of code , The referential relationship of the object does not change , Start anywhere in this area GC It's all safe . We can also put Safe Region See it as being expanded SafePoint.
Actual execution :
- When the thread runs to Safe Region When the code , First of all, the logo has entered Safe Region, If it happens in this period of time GC,JVM Will ignore the label as Safe Region Thread in state ;
- When the thread is about to leave Safe Region when , Will check the JVM Has it been completed GC, If it's done , Then continue to run , Otherwise, the thread must wait until it is received and can leave safely Safe Region Signal stop ;
6. Quote Overview
- We want to be able to describe such an object : When there is enough memory , It can be kept in memory ; If memory space is tight after garbage collection , Then you can discard these objects .
Strong citation 、 Soft citation 、 Weak reference 、 What's the difference between virtual references ? What is the specific use scenario ?
- stay JDK 1.2 After version ,Java The concept of reference is extended , Divide references into :
- Strong citation (Strong Reference)
- Soft citation (Soft Reference)
- Weak reference (Weak Reference)
- Virtual reference (Phantom Reference)
this 4 In turn, the quoting strength decreased . In addition to strong references , other 3 All references can be found in java.lang.ref They were found in the bag . Here's the picture , Shows this 3 The class corresponding to each reference type , Developers can use them directly in their applications .
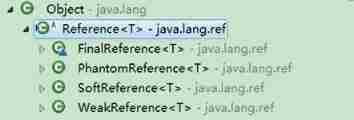
Reference Only terminator references in subclasses are visible within the package , other 3 All the reference types are public, You can use... Directly in your application .
- Strong citation (StrongReference): Most traditional “ quote ” The definition of , It refers to the common reference assignment in the program code , It's like "Object obj = new Object() " This quoting relationship . In any case , As long as the strong quoting relationship still exists , The garbage collector will never recycle the referenced objects .
- Soft citation (SoftReference): Before the system is about to run out of memory , These objects will be included in the scope of recycling for the second time . If there is not enough memory after this recycle , An out-of-memory exception is thrown .
- Weak reference (WeakReference): Objects associated with weak references can only survive until the next garbage collection . When the garbage collector is working , Whether there is enough memory space , Objects associated with weak references will be recycled .
- Virtual reference (PhantomReference): Whether an object has a virtual reference , It doesn't affect their survival time at all , You can't get an instance of an object through a virtual reference . The only purpose of setting a virtual reference association for an object is to receive a system notification when the object is collected by the collector .
7. Strong citation (Strong Reference) - No recovery
- stay Java In the program , The most common type of reference is strong reference ( General system 99% All of the above are strong references ), That's our most common common common object reference , It's also the default reference type .
- When in Java Used in language new Operator to create a new object , And assign it to a variable , This variable becomes a strong reference to the object .
- Strongly referenced objects are touchable , The garbage collector will never recycle the referenced objects .
- For a normal object , If there are no other reference relationships , As long as the scope of the reference is exceeded or will be explicitly corresponding ( strong ) The reference is assigned to null, It can be collected as garbage , Of course, the specific recycling time depends on the garbage collection strategy .
- Relative , Soft citation 、 Objects with weak and virtual references are soft reachable 、 Weakly palpable and unreasonably palpable , under certain conditions , It's all recyclable . therefore , Strong citation is the cause of Java One of the main causes of memory leaks .
Strong reference examples
/** * Strongly referenced tests */
public class StrongReferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer("Hello word");
StringBuffer str1 = str;
str = null;
System.gc(); // Call garbage collection
try {
Thread.sleep(3000); // Set up 3 Second delay guarantee GC Garbage collection can be achieved
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(str1); // Hello word
}
}
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer("hello word");
- local variable str Point to StringBuffer The heap space of the instance , adopt str You can manipulate this instance , that str Namely StringBuffer Strong references to instances
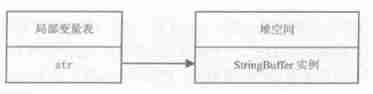
- here , If you run another assignment statement
StringBuffer str1 = str;
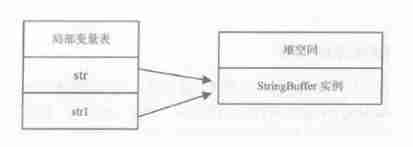
- So we're going to str = null; Then the objects in the original heap will not be recycled , Because there are other objects pointing to this area
The two references in this example , Are all strong references , Strong references have the following characteristics :
- Strong references can directly access the target object .
- The object that the strong reference points to will not be recycled by the system at any time , The virtual machine would rather throw OOM abnormal , It doesn't recycle the object that a strong reference points to .
- Strong references can cause memory leaks .
8. Soft citation (Soft Reference) - If there is not enough memory, it will be recycled
- Soft references are used to describe some useful , But not the necessary object . Only objects associated with soft references , Before the system is about to run out of memory , These objects will be listed in the recycling scope for a second recycling , If there is not enough memory for this collection , An out-of-memory exception is thrown .
- Be careful , The first recycle here is an unreachable object
- Soft references are often used to implement memory sensitive caching . such as : Caching is useful for soft references . If you have free memory , You can keep the cache temporarily , Clean up when memory is low , This ensures that the cache is used at the same time , Does not run out of memory .
- When the garbage collector decides to recycle soft reachable objects at some point , Will clean up soft references , And optionally put the reference in a reference queue (Reference Queue).
- Similar to weak references , It's just Java Virtual Opportunities try to make soft references live longer , Forced to clean up .
- One sentence summary : When there is enough memory , Reachable objects with soft references are not recycled ; When there is not enough memory , Will reclaim the reachable object of soft reference .
stay JDK 1.2 After the edition, there is java.lang.ref.SoftReference Class to implement soft references
// Declare strong references
Object obj = new Object();
// Create a soft reference
SoftReference<Object> sf = new SoftReference<>(obj);
obj = null; // Destroy strong references , This operation is necessary , Otherwise, there will be strong references and soft references
The code for
/** * Soft reference testing : If there is not enough memory, it will be recycled * -Xms10m -Xmx10m */
public class SoftReferenceTest {
public static class User {
public User(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int id;
public String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "] ";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create objects , Create soft references
// SoftReference<User> userSoftRef = new SoftReference<User>(new User(1, "hello"));
// The line above , Equivalent to the following three lines of code
User u1 = new User(1, "hello");
SoftReference<User> userSoftRef = new SoftReference<>(u1);
u1 = null;// Cancel strong reference
// Retrieving strong reference objects from soft references
System.out.println(userSoftRef.get()); //[id=1, name=hello]
System.gc();
System.out.println("After GC:");
// Get objects in soft references after garbage collection
System.out.println(userSoftRef.get()); //[id=1, name=hello] Because the heap has enough memory , All reachable objects that do not recycle soft references .
try {
// Let the system think that memory resources are insufficient
// byte[] b = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 7]; // Will be submitted to the OOM, The soft quote is null
// Let the system think that memory resources are tight
byte[] b = new byte[1024 * 7168 - 350 * 1024]; // Not to report OOM, The soft quote is null
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// Get the data from the soft reference again
System.out.println(userSoftRef.get());// In the newspaper OOM Before , The garbage collector will recycle reachable objects of soft references .
}
}
}
Running results 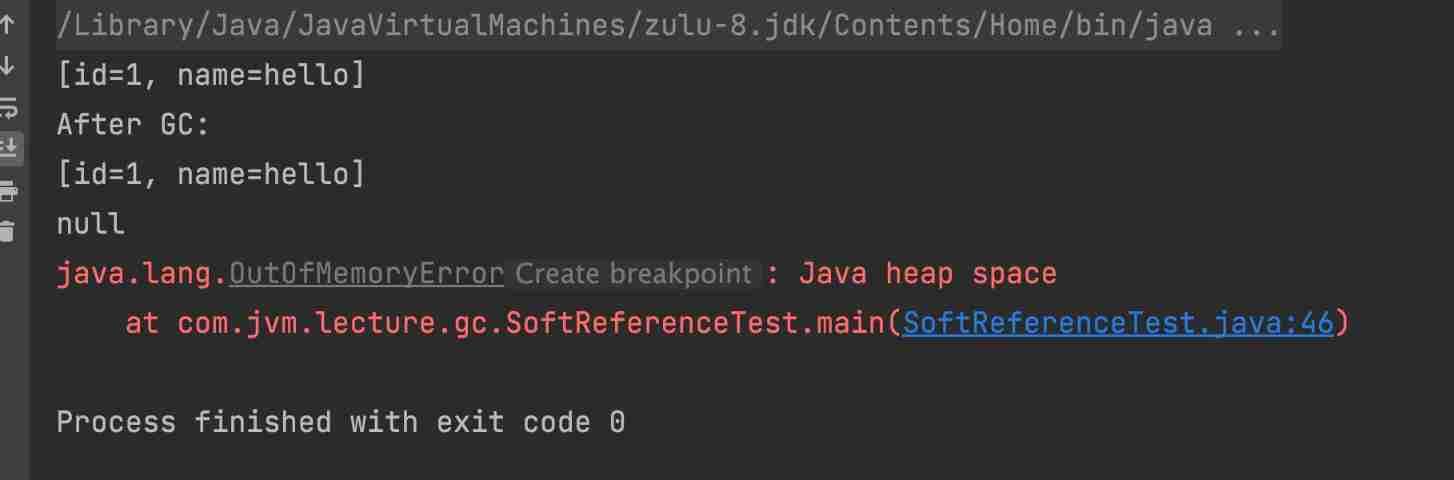
9. Weak reference (Weak Reference) - Discovery is recycling
- Weak references are also used to describe unnecessary objects , Objects that are only weakly referenced can only survive until the next garbage collection . In system GC when , Just find weak quotes , Whether or not the system heap space is used enough , All objects associated with weak references will be recycled .
- however , Because the threads of the garbage collector are usually of low priority , therefore , It's not always easy to find objects that hold weak references . under these circumstances , Weakly referenced objects can exist for a long time .
- Weak references are the same as soft references , When constructing weak references , You can also specify a reference queue , When a weakly referenced object is recycled , Will join the specified reference queue , Through this queue, you can track the recycling of objects .
- Soft citation 、 Weak references are very suitable for storing the cache data that is not available . If you do , When the system is low on memory , These cached data will be recycled , Does not cause memory overflow . And when there's enough memory , These cached data can exist for quite a long time , So as to accelerate the system .
The code for
/** * Weak reference tests */
public class WeakReferenceTest {
public static class User {
public User(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int id;
public String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "] ";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Weak references are constructed
WeakReference<User> userWeakRef = new WeakReference<User>(new User(1, "hello"));
// Retrieve objects from weak references
System.out.println(userWeakRef.get()); // [id=1, name=hello]
System.gc();
// Whether the current memory space is enough or not , Will reclaim its memory
System.out.println("After GC:");
// Try again to get the object from the weak reference
System.out.println(userWeakRef.get()); //null
}
}
The difference between soft quotation and weak quotation
The biggest difference between weakly referenced objects and soft referenced objects is , When GC When recycling , The algorithm is needed to check whether the soft reference object is recycled , For weakly referenced objects ,GC Always recycle . Weak reference objects are easier to 、 Faster to be GC Recycling .
Interview questions : Have you ever used WeakHashMap Do you ?
WeakHashMap Used to store picture information , When memory is low , Timely recovery , Avoided OOM.
10. Virtual reference (Phantom Reference) - Object recovery tracking
- Virtual reference Also known as “ Ghost quotes ” perhaps “ Phantom reference ”, Is the weakest of all reference types .
- Whether an object has a virtual reference , It doesn't determine the life cycle of an object at all . If an object only holds virtual references , So it's almost the same as no citation , It can be collected by the garbage collector at any time
- It can't be used alone , You can't use virtual references to get referenced objects . When trying to pass through virtual references get() Method to get the object , Always null.
- The only purpose of setting virtual reference associations for an object is to track the garbage collection process . such as : Can receive a system notification when this object is recycled by the collector .
- Virtual references must be used with reference queues . A virtual reference must be created with a reference queue as a parameter . When the garbage collector is ready to recycle an object , If it's found to have virtual references , After the object is recycled , Add this virtual reference to the reference queue , To inform the application of the recycling of objects .
- Since virtual references can track the collection time of an object , therefore , Some resource release operations can also be executed and recorded in virtual references .
stay JDK1.2 After the edition, there is PhantomReference Class to implement virtual references .
Object obj = new Object(); // Declare strong references
ReferenceQueue phantomQueue = new ReferenceQueue();
PhantomReference<Object> sf = new PhantomReference<>(obj, phantomQueue);
obj = null;
The code for
/** * Virtual reference test */
public class PhantomReferenceTest {
public static PhantomReferenceTest obj; // Declaration of the current class object
static ReferenceQueue<PhantomReferenceTest> phantomQueue = null; // Reference queue
/** * When the garbage collector is ready to recycle an object , If it's found to have virtual references , After the object is recycled , * Add this virtual reference to the reference queue , To inform the application of the recycling of objects . * This thread is to operate the reference queue */
public static class CheckRefQueue extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
// The first 2 Time GC Will be obj Object recycled , At this point, there will be virtual references in the reference queue
if (phantomQueue != null) {
PhantomReference<PhantomReferenceTest> objt = null;
try {
// Take the virtual reference from the reference queue
objt = (PhantomReference<PhantomReferenceTest>) phantomQueue.remove();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (objt != null) {
System.out.println(" Tracking the garbage collection process :PhantomReferenceTest Examples are GC 了 ");
}
}
}
}
}
/** * Before garbage collection, we will call finalize() * * @throws Throwable */
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
//finalize() Method can only be called once !
super.finalize();
System.out.println(" Call the... Of the current class finalize() Method ");
obj = this; // Let the current object be referenced again
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new CheckRefQueue();
t.setDaemon(true); // Set to daemons : When there are no non daemons in the program , The execution of the daemons ends .
t.start();
phantomQueue = new ReferenceQueue<PhantomReferenceTest>(); // Instantiate reference queue
obj = new PhantomReferenceTest(); // Instantiate the current class object
// constructed PhantomReferenceTest Virtual references to objects , And specify the reference queue
PhantomReference<PhantomReferenceTest> phantomRef = new PhantomReference<PhantomReferenceTest>(obj, phantomQueue);
try {
// Cannot get object in virtual reference
System.out.println(phantomRef.get()); //null
// Remove strong references
obj = null;
// First time GC, Because objects can be resurrected ,GC Unable to recycle the object
System.gc();
Thread.sleep(1000);
if (obj == null) {
System.out.println("obj yes null");
} else {
System.out.println("obj You can use "); // Finally execute this sentence
}
System.out.println(" The first 2 Time gc");
obj = null;
System.gc(); // Once the obj Object to recycle , The virtual reference is placed in the reference queue .
Thread.sleep(1000);
if (obj == null) {
System.out.println("obj yes null"); // Finally execute this sentence
} else {
System.out.println("obj You can use ");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Running results 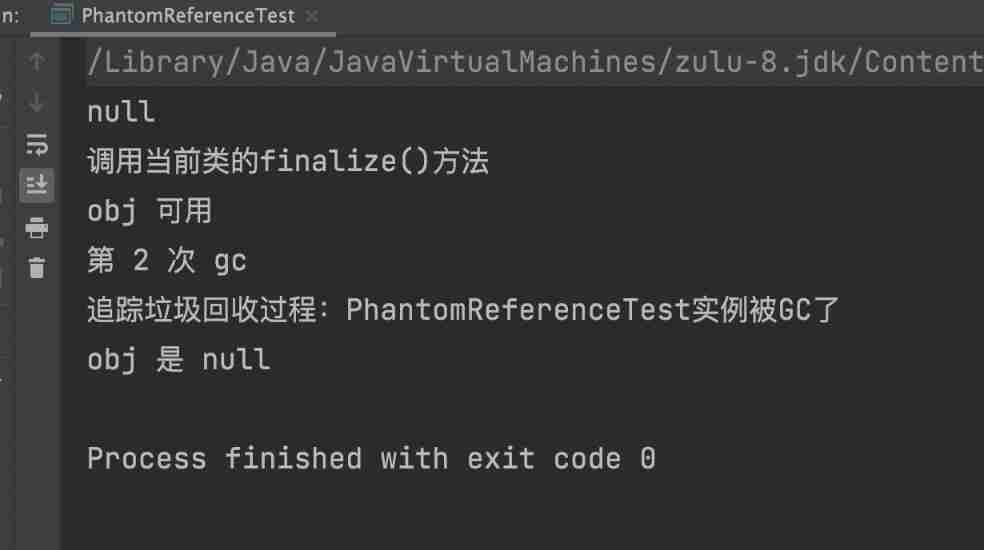
- From the above operation results, we know that , First attempt to get the value of the virtual reference , Find something you can't get , This is because a virtual reference cannot get the value of an object directly , Then for the first time GC, Because it calls finalize() Method , Resurrected the object , So the object is not recycled , But call the second time GC During operation , because finalize() Method can only be executed once , So it triggered GC operation , Recycled objects , At the same time, the second operation will be triggered, which is to store the recycled value in the reference queue .
11. Terminator references
- It's used to implement finalize() Method , Also called a terminator reference .
- No need to code manually , It is used internally with reference queues .
- stay GC when , Terminator references are queued . from Finalizer The thread finds the referenced object through the terminator reference and calls its finalize() Method , The second time GC The referenced object is recycled only when the .
边栏推荐
- curlpost-php
- Folding and sinking sand -- weekly record of ETF
- Mobilenet series (5): use pytorch to build mobilenetv3 and learn and train based on migration
- 免费的聊天机器人API
- Common API classes and exception systems
- 测试/开发程序员的成长路线,全局思考问题的问题......
- NLP basic task word segmentation third party Library: ICTCLAS [the third party library with the highest accuracy of Chinese word segmentation] [Chinese Academy of Sciences] [charge]
- 【线上小工具】开发过程中会用到的线上小工具合集
- Data analysis thinking analysis methods and business knowledge - analysis methods (III)
- Analysis of the combination of small program technology advantages and industrial Internet
猜你喜欢
可恢复保险丝特性测试

cf:C. The Third Problem【关于排列这件事】
Idea remotely submits spark tasks to the yarn cluster
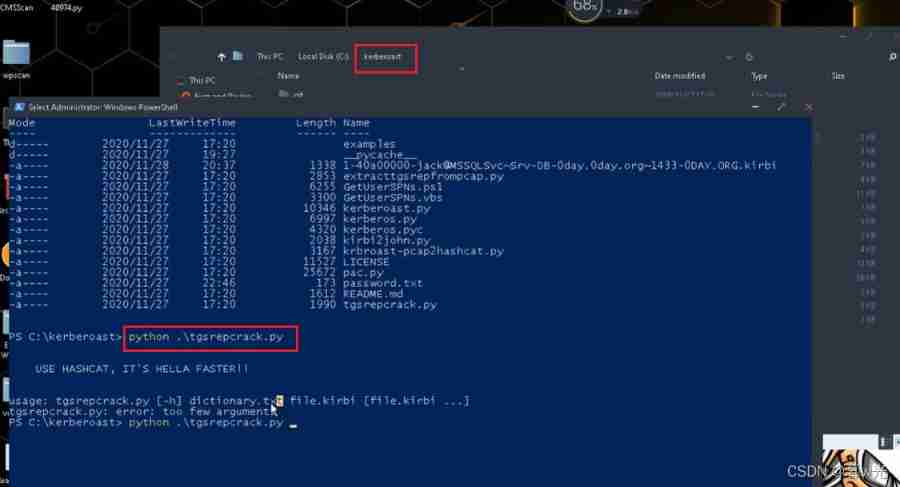
Intranet Security Learning (V) -- domain horizontal: SPN & RDP & Cobalt strike
![[groovy] compile time meta programming (AST syntax tree conversion with annotations | define annotations and use groovyasttransformationclass to indicate ast conversion interface | ast conversion inte](/img/61/73becfc3b46669d31b0cf334aa54f2.jpg)
[groovy] compile time meta programming (AST syntax tree conversion with annotations | define annotations and use groovyasttransformationclass to indicate ast conversion interface | ast conversion inte

Exciting, 2022 open atom global open source summit registration is hot

cf:H. Maximal AND【位运算练习 + k次操作 + 最大And】

关于#数据库#的问题:(5)查询库存表中每本书的条码、位置和借阅的读者编号
Common API classes and exception systems
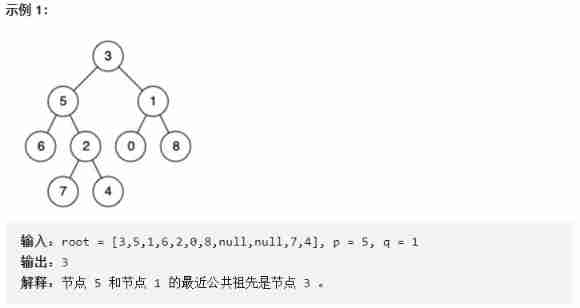
Finding the nearest common ancestor of binary tree by recursion
随机推荐
Programmer growth Chapter 9: precautions in real projects
MIT博士论文 | 使用神经符号学习的鲁棒可靠智能系统
After 95, the CV engineer posted the payroll and made up this. It's really fragrant
Interview must brush algorithm top101 backtracking article top34
C language programming (Chapter 6 functions)
Set data real-time update during MDK debug
毕设-基于SSM高校学生社团管理系统
BiShe - College Student Association Management System Based on SSM
Spark DF增加一列
[groovy] XML serialization (use markupbuilder to generate XML data | create sub tags under tag closures | use markupbuilderhelper to add XML comments)
免费的聊天机器人API
XML Configuration File
看抖音直播Beyond演唱会有感
Mobilenet series (5): use pytorch to build mobilenetv3 and learn and train based on migration
Novice entry depth learning | 3-6: optimizer optimizers
Ubantu check cudnn and CUDA versions
《强化学习周刊》第52期:Depth-CUPRL、DistSPECTRL & Double Deep Q-Network
MYSQL GROUP_ The concat function realizes the content merging of the same ID
2022-02-13 work record -- PHP parsing rich text
Cannot resolve symbol error