当前位置:网站首页>Force buckle 5_ 876. Intermediate node of linked list
Force buckle 5_ 876. Intermediate node of linked list
2022-07-08 02:15:00 【Don't sleep in class】
Given a header node as head The non empty single chain table of , Returns the middle node of the linked list .
If there are two intermediate nodes , Then return to the second intermediate node .
Example 1:
Input :[1,2,3,4,5]
Output : Nodes in this list 3 ( Serialization form :[3,4,5])
The returned node value is 3 . ( The evaluation system expresses the serialization of this node as follows [3,4,5]).
Be careful , We returned one ListNode Object of type ans, such :
ans.val = 3, ans.next.val = 4, ans.next.next.val = 5, as well as ans.next.next.next = NULL.
Example 2:
Input :[1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output : Nodes in this list 4 ( Serialization form :[4,5,6])
Because the list has two intermediate nodes , Values, respectively 3 and 4, Let's go back to the second node .
Tips :
The number of nodes in a given list is between 1 and 100 Between .
source : Power button (LeetCode)
Java solution 1
A similar is used here C Double pointer method in language , Quick pointer Each move Two grid , Slow pointer Each move One grid Finally, when the fast pointer is finished, the slow pointer is half finished .
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
Java solution 2
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode[] A = new ListNode[100];
int t = 0;
while (head != null) {
A[t++] = head;
head = head.next;
}
return A[t / 2];
}
}
Python solution
there Python The traditional method is adopted , First save the linked list into the list , Get the intermediate elements of the list through the index .
class Solution:
def middleNode(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
A = [head]
while A[-1].next:
A.append(A[-1].next)
return A[len(A) // 2]
边栏推荐
- 微信小程序uniapp页面无法跳转:“navigateTo:fail can not navigateTo a tabbar page“
- leetcode 869. Reordered Power of 2 | 869. Reorder to a power of 2 (state compression)
- Where to think
- For friends who are not fat at all, nature tells you the reason: it is a genetic mutation
- 分布式定时任务之XXL-JOB
- JVM memory and garbage collection -4-string
- 【每日一题】648. 单词替换
- In the digital transformation of the financial industry, the integration of business and technology needs to go through three stages
- 企业培训解决方案——企业培训考试小程序
- 发现值守设备被攻击后分析思路
猜你喜欢
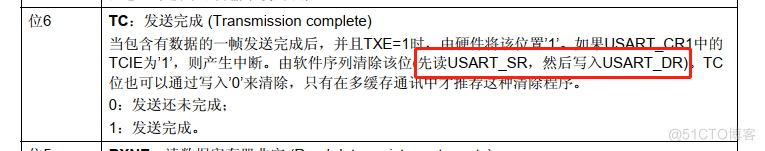
关于TXE和TC标志位的小知识
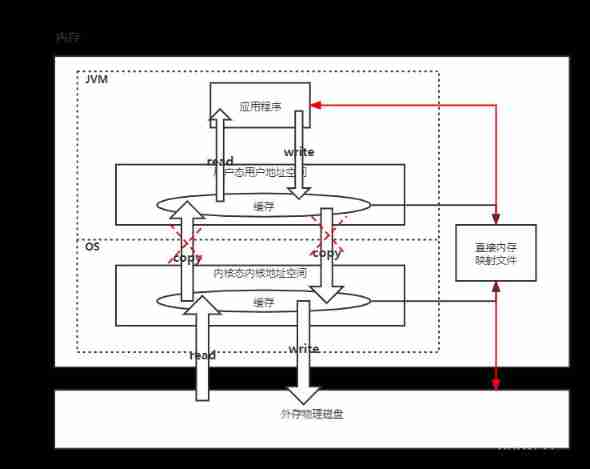
JVM memory and garbage collection-3-direct memory

《ClickHouse原理解析与应用实践》读书笔记(7)
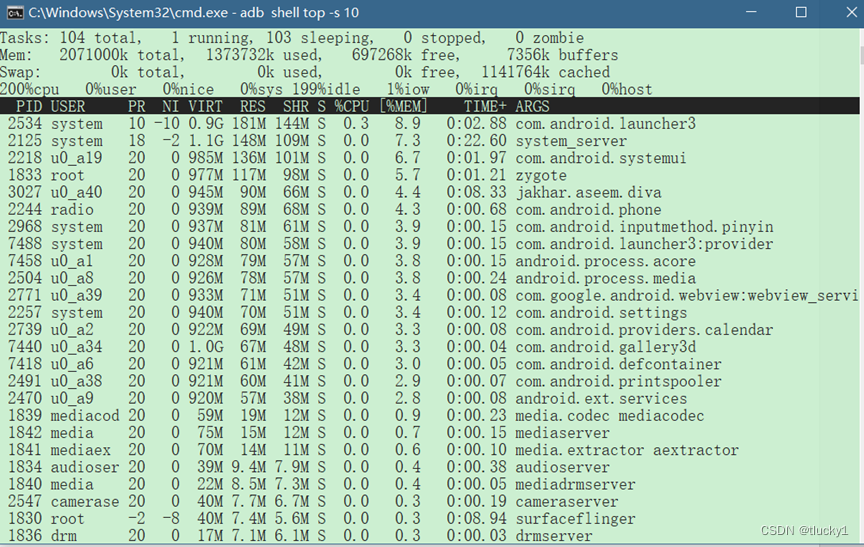
adb工具介绍

leetcode 866. Prime Palindrome | 866. prime palindromes

What are the types of system tests? Let me introduce them to you
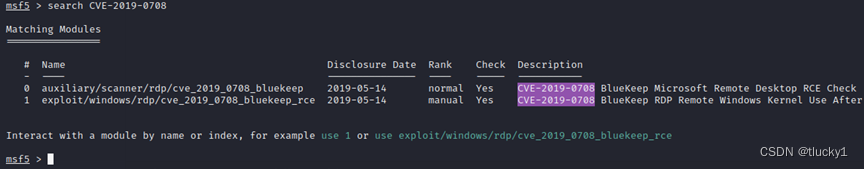
metasploit

Talk about the cloud deployment of local projects created by SAP IRPA studio

leetcode 866. Prime Palindrome | 866. 回文素数
Leetcode featured 200 channels -- array article
随机推荐
Cross modal semantic association alignment retrieval - image text matching
Applet running under the framework of fluent 3.0
Height of life
Redismission source code analysis
力扣4_412. Fizz Buzz
leetcode 865. Smallest Subtree with all the Deepest Nodes | 865.具有所有最深节点的最小子树(树的BFS,parent反向索引map)
BizDevOps与DevOps的关系
OpenGL/WebGL着色器开发入门指南
[reinforcement learning medical] deep reinforcement learning for clinical decision support: a brief overview
MySQL查询为什么没走索引?这篇文章带你全面解析
Redission源码解析
leetcode 866. Prime Palindrome | 866. 回文素数
"Hands on learning in depth" Chapter 2 - preparatory knowledge_ 2.1 data operation_ Learning thinking and exercise answers
Relationship between bizdevops and Devops
Random walk reasoning and learning in large-scale knowledge base
XXL job of distributed timed tasks
Redisson distributed lock unlocking exception
阿南的判断
发现值守设备被攻击后分析思路
CorelDRAW2022下载安装电脑系统要求技术规格