当前位置:网站首页>Binary search tree (basic operation)
Binary search tree (basic operation)
2022-07-07 16:36:00 【Joey Liao】
List of articles
Binary search tree ( Characteristics ) It introduces BST The basic characteristics of , Binary search tree is also used 「 Middle order traversal order 」 To solve several problems , This article is to realize BST Basic operation of : Judge BST Legitimacy 、 increase 、 Delete 、 check . among 「 Delete 」 and 「 Judge legitimacy 」 Slightly complicated .
BST The basic operation of mainly depends on 「 Left small right big 」 Characteristics of , You can do operations similar to binary search in binary tree , Finding an element is very efficient . For example, this is a legal binary tree :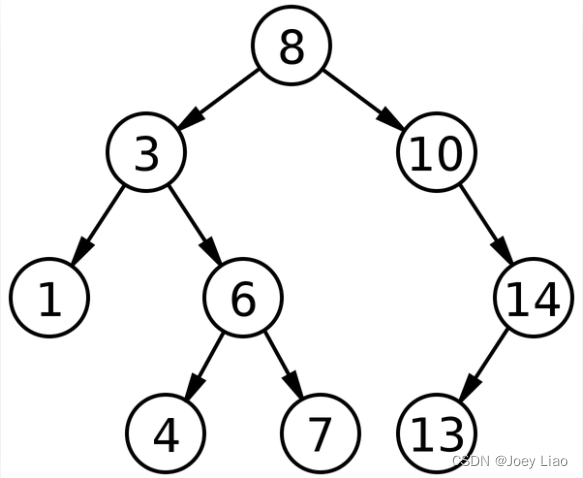
about BST Related issues , You may often see code logic like the following :
void BST(TreeNode root, int target) {
if (root.val == target)
// Find the target , Do something
if (root.val < target)
BST(root.right, target);
if (root.val > target)
BST(root.left, target);
}
One 、 Judge BST Legitimacy
Force to buckle 98 topic 「 Verify binary search tree 」 Is to let you judge the input BST Is it legal .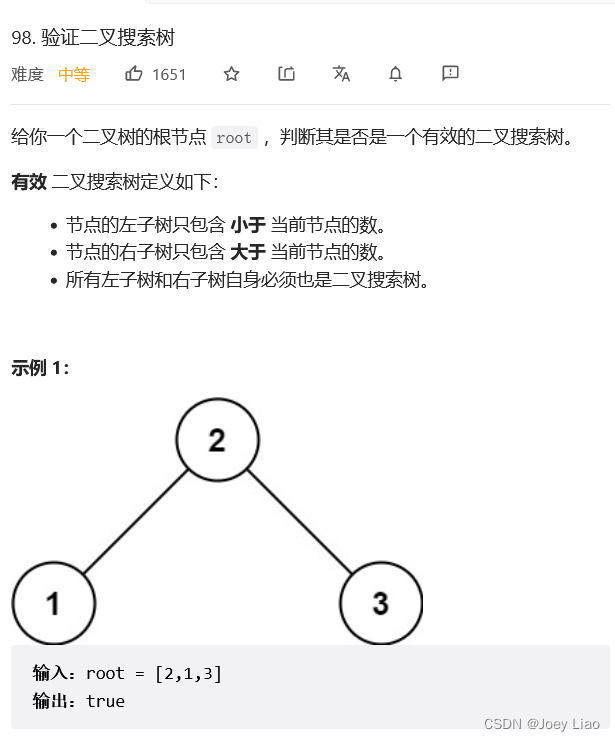 One thing to note is that you can't directly compare yourself with left and right children , But the idea is wrong ,BST Each node of the tree should be smaller than all the nodes of the subtree on the right , The correct code is as follows :
One thing to note is that you can't directly compare yourself with left and right children , But the idea is wrong ,BST Each node of the tree should be smaller than all the nodes of the subtree on the right , The correct code is as follows :
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return traverse(root,null,null);
}
public boolean traverse(TreeNode root,TreeNode minNode,TreeNode maxNode){
if(root==null) return true;
if(minNode!=null&&minNode.val>=root.val) return false;
if(maxNode!=null&&maxNode.val<=root.val) return false;
return traverse(root.left,minNode,root)&&traverse(root.right,root,maxNode);
}
}
stay BST Search elements in
Force to buckle 700 topic 「 Search in binary search tree 」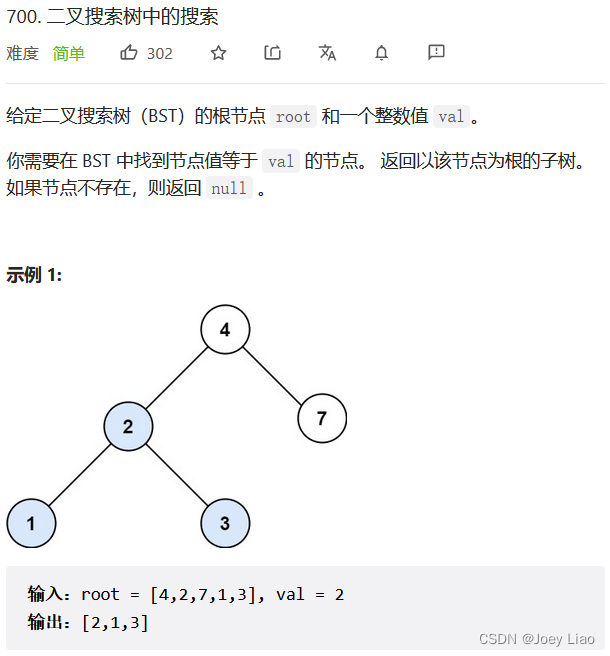 Very simple dichotomy :
Very simple dichotomy :
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root==null) return null;
if(val<root.val){
return searchBST(root.left,val);
}else if(val>root.val){
return searchBST(root.right,val);
}
return root;
}
}
stay BST Insert a number
The operation of data structure is nothing but traversal + visit , Traversal is 「 look for 」, The interview is 「 Change 」. Specific to this question , Insert a number , Is to find the insertion position first , Then insert it .
Last question , We summarized BST Traversal framework in , Namely 「 look for 」 The problem of . Direct framing , add 「 Change 」 The operation of . When it comes to 「 Change 」, It is similar to the construction of binary tree , Function to return TreeNode type , And receive the return value of recursive call .
TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
// Find an empty location to insert a new node
if (root == null) return new TreeNode(val);
// if (root.val == val)
// BST In general, existing elements are not inserted into
if (root.val < val)
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
if (root.val > val)
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
return root;
}
stay BST Delete a number from
This is a little more complicated , It's similar to the insert operation , First 「 look for 」 Again 「 Change 」, Write the frame first
TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root.val == key) {
// I found it , To delete
} else if (root.val > key) {
// Go to the left sub tree to find
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
} else if (root.val < key) {
// Go to the right subtree to find it
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
}
return root;
}
We found the target node , Like nodes A, How to delete this node , This is the difficulty . Because you can't destroy a node when you delete it BST The nature of . There are three situations , Use pictures to illustrate .
situation 1: A It happens to be the end node , Both child nodes are empty , Then it can die on the spot .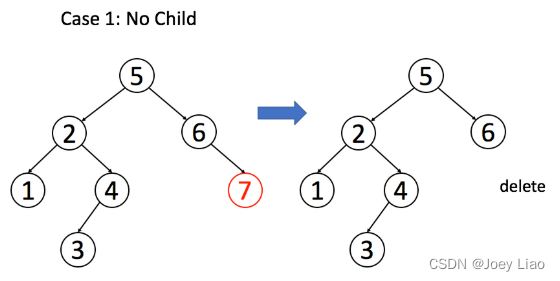
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return null;
situation 2:A There is only one non empty child node , So it wants the child to take over his place .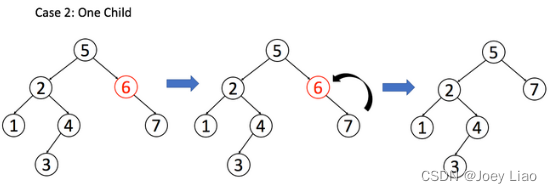
if(root.left==null) return root.right;
if(root.right==null) return root.left;
situation 3:A There are two child nodes , Sorry for the inconvenience , In order not to destroy BST The nature of ,A We have to find the largest node in the left subtree , Or the smallest node in the right subtree to replace itself . Let's talk about... In the second way .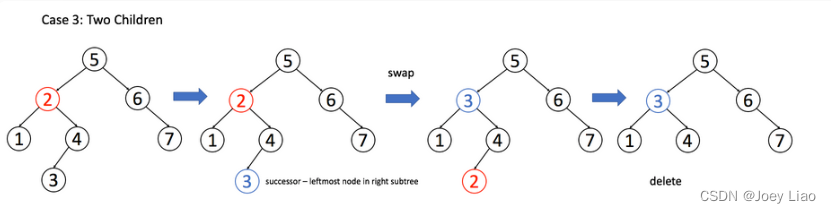
if(root.left!=null&&root.right!=null){
TreeNode minNode=getMin(root.right);
root.val=minNode.val;
root.right=deleteNode(root.right,minNode.val);
}
The analysis of the three situations is finished , Fill in the frame , Simplify the code
TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (root.val == key) {
// these two items. if Take the situation into consideration 1 and 2 It's all handled correctly
if (root.left == null) return root.right;
if (root.right == null) return root.left;
// Deal with the situation 3
// Get the smallest node of the right subtree
TreeNode minNode = getMin(root.right);
// Delete the smallest node of the right subtree
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minNode.val);
// Replace with the smallest node of the right subtree root node
minNode.left = root.left;
minNode.right = root.right;
root = minNode;
} else if (root.val > key) {
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
} else if (root.val < key) {
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
}
return root;
}
TreeNode getMin(TreeNode node) {
// BST The one on the far left is the smallest
while (node.left != null) node = node.left;
return node;
}
such , The delete operation is complete . Pay attention to the , The above code is in processing 3 Exchange through a series of slightly complex linked list operations root and minNode Two nodes :
// Deal with the situation 3
// Get the smallest node of the right subtree
TreeNode minNode = getMin(root.right);
// Delete the smallest node of the right subtree
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, minNode.val);
// Replace with the smallest node of the right subtree root node
minNode.left = root.left;
minNode.right = root.right;
root = minNode;
Some readers may wonder , Replace root Why are nodes so troublesome , Change directly val Field is not enough ? It looks more concise and easy to understand :
It is only possible for this algorithm problem , But this operation is not perfect , We usually don't exchange nodes by modifying the value inside the node . Because in practice ,BST The data field inside the node is user-defined , It can be very complicated , and BST As a data structure ( A tool man ), Its operation should be decoupled from the data field stored internally , So we prefer to use pointer operation to exchange nodes , There's no need to care about internal data .
Finally, let's sum up , Through this article , We have summarized the following techniques :
- If the current node has an overall impact on the following child nodes , You can increase the parameter list through auxiliary functions , Passing information by means of parameters .
- On top of the binary tree recursive framework , Expand a set of BST The code framework :
void BST(TreeNode root, int target) {
if (root.val == target)
// Find the target , Do something
if (root.val < target)
BST(root.right, target);
if (root.val > target)
BST(root.left, target);
}
- According to the code framework BST Add, delete, check and modify .
边栏推荐
- 1亿单身男女“在线相亲”,撑起130亿IPO
- Markdown formula editing tutorial
- php 自带过滤和转义函数
- Geoserver2.18 series (5): connect to SQLSERVER database
- Bidding announcement: Fujian Rural Credit Union database audit system procurement project (re bidding)
- 无法将“pip”项识别为 cmdlet、函数、脚本文件或可运行程序的名称
- 95. (cesium chapter) cesium dynamic monomer-3d building (building)
- ThinkPHP URL 路由简介
- Cesium (4): the reason why gltf model is very dark after loading
- What are compiled languages and interpreted languages?
猜你喜欢
TiDB For PostgreSQL和YugabyteDB在Sysbench上的性能对比
Vs2019 configuration matrix library eigen
Logback日志框架第三方jar包 免费获取
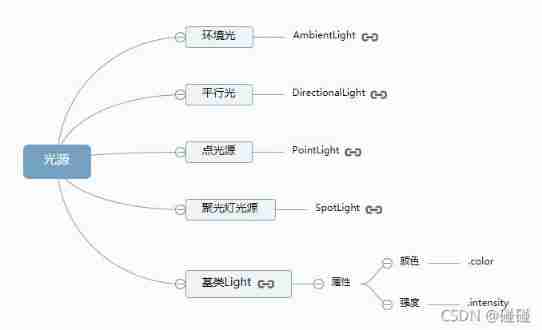
Three. JS series (1): API structure diagram-1
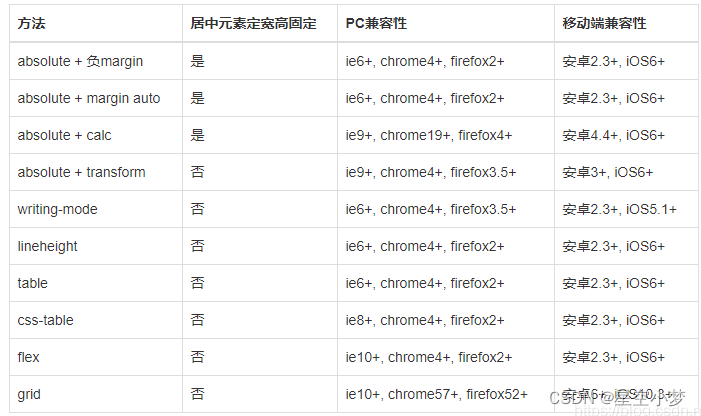
水平垂直居中 方法 和兼容

Sysom case analysis: where is the missing memory| Dragon lizard Technology

The team of East China Normal University proposed the systematic molecular implementation of convolutional neural network with DNA regulation circuit
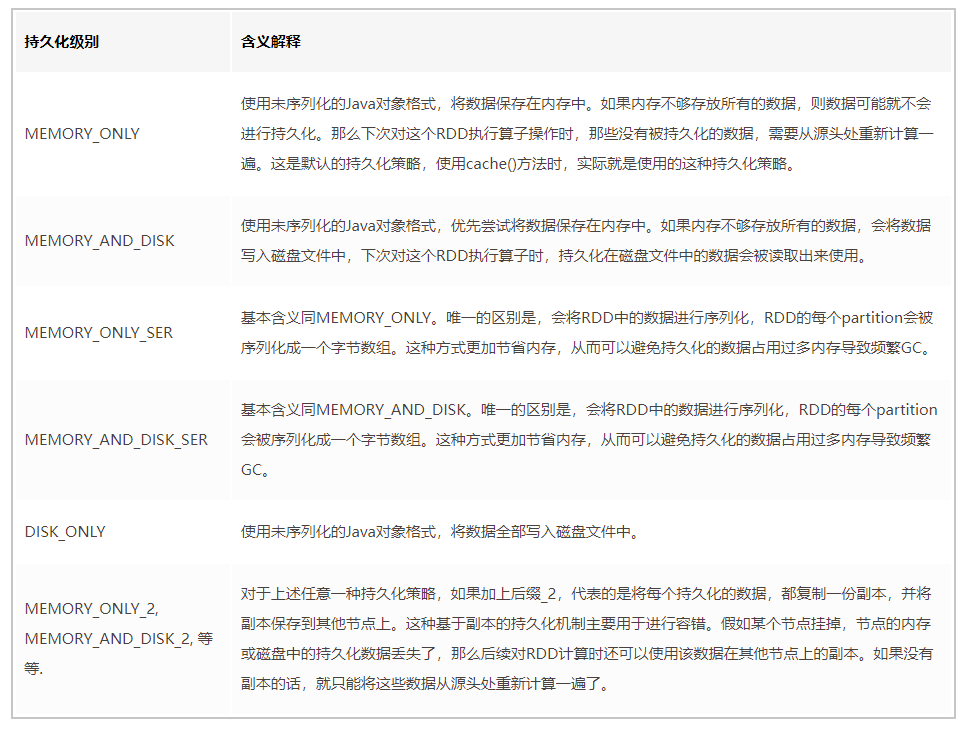
Spark Tuning (III): persistence reduces secondary queries

AutoLISP series (2): function function 2
谈谈 SAP iRPA Studio 创建的本地项目的云端部署问题
随机推荐
Tragedy caused by deleting the console statement
【MySql进阶】索引详解(一):索引数据页结构
URL和URI的关系
three. JS create cool snow effect
PHP实现微信小程序人脸识别刷脸登录功能
Personal notes of graphics (2)
torch.numel作用
删除 console 语句引发的惨案
How to query the data of a certain day, a certain month, and a certain year in MySQL
Sysom case analysis: where is the missing memory| Dragon lizard Technology
Communication mode between application program and MATLAB
二叉搜索树(特性篇)
Personal notes of graphics (4)
预测——灰色预测
Opencv configuration 2019vs
Continuous creation depends on it!
C语言进阶——函数指针
Cesium(3):ThirdParty/zip. js
[vulnhub range] thales:1
Description of vs common shortcut keys