当前位置:网站首页>Shared memory for interprocess communication
Shared memory for interprocess communication
2022-07-07 06:21:00 【*insist】
1.1 The introduction of shared memory
Shared memory is the fastest form of interprocess communication , By calling the system interface (shmget) Open up a piece of physical memory by the operating system , Then map to the process address space through the page table , Thus, users can use this memory , Two processes share a shared memory, and communication can be established through data interaction .
1.2 Create a schematic diagram between virtual memory and physical memory before and after shared memory
The connection between virtual memory and physical memory before shared memory is not created
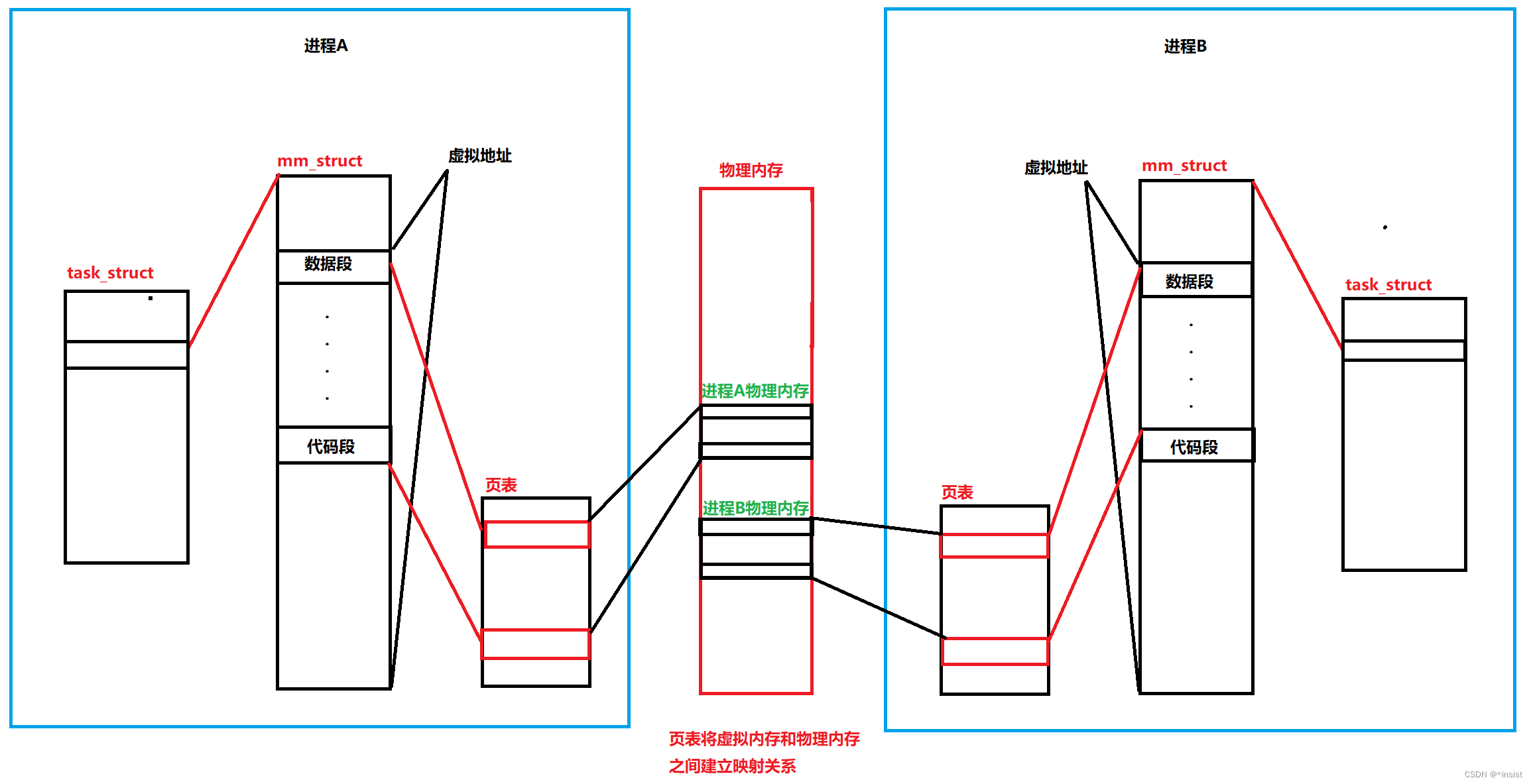
- The connection between virtual address and physical memory is established through page table , All we see are physical memory mapped to the page table Virtual memory Not real physical memory ,
- among task_struct Is the data structure of the process ( This data structure is used to describe Managing the data structure is the management of the process ) mm_struct Is the data structure of the process address space
The connection between virtual memory and physical memory after creating shared memory
![[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-x5X339Qj-1656584415666)(C:\Users\ Hua ge \AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220629224323893.png)]](/img/ae/ec1f70cf3a96bf117d12de5e5f4a97.png)
- After creating shared memory , After pointing the physical addresses of the two processes to the block of physical memory, the two processes can see the same resource , So as to realize the interaction of information , Achieve communication
2.1 The specific steps of communication through shared memory
- 1、 Request shared memory By function shmget() establish ( apply ) Out of shared memory
![[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-hdtuovKM-1656584415668)(C:\Users\ Hua ge \AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220629225840008.png)]](/img/c2/1d0b34f281e8b5609355b096512e9a.png)
- 2、 Attach shared memory to the process address space By function shmat() Hook the of the process to the shared memory ; In essence, the process opens up a new virtual address space , By modifying the page table , Cancel the mapping relationship between the original virtual memory and physical memory , Will share memory ( This physical memory ) Establish a mapping relationship with the virtual memory of the process , Enable processes to use shared memory
- 3、 Disassociate shared memory By function shmdt() Disassociate shared memory ; Modify page table , Cancel the mapping relationship between shared memory and virtual memory , Restore the mapping relationship between the original physical memory and virtual memory of the process
![[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-CiDzFixX-1656584415671)(C:\Users\ Hua ge \AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220629234723251.png)]](/img/e7/7dd03a7ac7c8a5178de83c2826f571.png)
4、 Free up shared memory By function int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf); Free up shared memory ; The life cycle of shared memory is automatically released with the kernel rather than with the end of the process ( Different from file ), If you don't release it after using it, the memory will be less and less , Memory leak , So remember to release the applied shared memory after using it
![[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-AGPCMcJS-1656584415672)(C:\Users\ Hua ge \AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220629234820210.png)]](/img/26/290e8bcd252b06f39dd3c7c6981448.png)
2.2 Instructions for viewing and deleting shared memory
2.2.1 View shared memory
// Input instruction
ipcs -m
2.2.2 Delete shared memory
// Input instruction
ipcrm -m +[shmid]//shmid It's shared memory id( user )
3.1 A simple demonstration of two processes communicating through the same shared memory
- Two processes share a shared memory , Then directly operate on the memory , It's like mallocc Use the same space that comes out , No need to call the system interface read write And so on to access this memory .

Specific code :
// The header file Include with ftok() Created key Required parameters Pathname and proj_id
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/ipc.h>
#include<sys/shm.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#define pathname "/home/zh/nodeput/lesson23"
#define proj_id 0x36
#define SIZE 4096
-------------------------------------------
//client.c
#include"serve.h"
int main()
{
key_t key=ftok(pathname,proj_id);
if(key<0)
{
perror("ftok");
}
int shmid=shmget(key,SIZE,IPC_CREAT);// establish
char* mem=(char*)shmat(shmid,NULL,0);// Hook up
// Start communicating
int i=0;
while(1)
{
mem[i] = 'A'+ i;// Here is the direct use of the developed shared memory Assign a value to it Then another process can print it out
i++;
mem[i]='\0';
sleep(1);
}
shmdt(mem);// To relate
shmctl(shmid,IPC_RMID,NULL);// Release
return 0;
}
-------------------------
//serve.c
#include"serve.h"
int main()
{
key_t key=ftok(pathname,proj_id);// Generate key
if(key<0)
{
perror("ftok");
return 1;
}
int shmid= shmget(key,SIZE,IPC_CREAT|IPC_EXCL|0644);// adopt key Create shared memory
if(shmid<0)
{
perror("shmget");
return 2;
}
char* mem=(char*)shmat(shmid,NULL,0);// Attach shared memory
// Start communicating
while(1)
{
printf("client sent: %s\n",mem);
sleep(1);
}
shmdt(mem);// Disassociate shared memory
shmctl(shmid,IPC_RMID,NULL);// Free up shared memory
return 0;
}
3.1.1 A few points to be noted :
- 1、*key_t ftok(const char pathname,int proj_id)** The first parameter of the function is a path that must exist , It can be a file or a directory
- 2、 The path must exist ,ftok Just according to the documents inode Uniqueness in the system to take a value , It has nothing to do with the permissions of the file
- 3、proj_id Yes, according to your own agreement , Set at will . This number , Some call it project ID stay UNIX On the system , It's going to be theta 1 To 255,8 A bit ,2 Bytes
3.1.2 Introduction to the parameter return value of several functions
1. Create shared memory function
int shmget(key_t key,size_t size,int shmflg)
The first parameter :key key It's through ftok() Functions are based on pathname and proj_id A value created with a unique mapping relationship , Help the operating system to identify a piece of shared memory
The second parameter :size size Is the size of the shared memory we want to create , The memory we see is actually virtual memory , Physical memory is mapped out through the page table , Always mention mapping , But how does the computer map the virtual address space to the real physical memory ? So that's the point Memory segmentation and paging mode 了 This conversion process has operating system and CPU Joint completion . The operating system is CPU Set the page table CPU adopt MMU The unit performs address translation To put it simply , It is to divide the linear address space into one by one 4k Of ( Almost all PC All operations on use 4KB The size of the page ) Logical page , Divide the memory pages into fixed size physical pages in the same way 4kb,4096 byte , In order to make better use of memory size Alignment is best 4096 That is to say, it is better to set it to 4096 Integer multiple
The third parameter :shmflg It is mainly related to some signs , Include IPC_CEREAT and IPC_EXCL, These two are with open() Of O_CREAT and O_EXCL similar .
- Instructions :
- 1、 If it is IPC_CREAT Used alone is if the function corresponds to key If the shared memory of does not exist, create and return the shared memory of this block shmid If the shared memory of this block already exists, it will directly return its corresponding shmid IPC_CREAT Use alone shmget() The function call is bound to succeed , Or return the shared memory that already exists shmid Or return the newly created shared memory shmid
- 2、 If it is IPC_CREAT and IPC_EXCL Use together is to create and return the corresponding God when and only when the block shared memory does not exist shmid, Otherwise it will return -1
- 3、IPC_EXCL It doesn't make much sense to use the logo alone Only and IPC_CREAT Only when used together can it play its role , It can ensure that the successfully created shared memory must be newly created , Instead of existing .
- 4、 Specify for the user's read and write permissions SHM_R and SHM_W(SHM_R>3) and (SHM_W>3) Is a set of read and write permissions ,(SHM_R>6) and (SHM_W>6) Is the global read and write permission
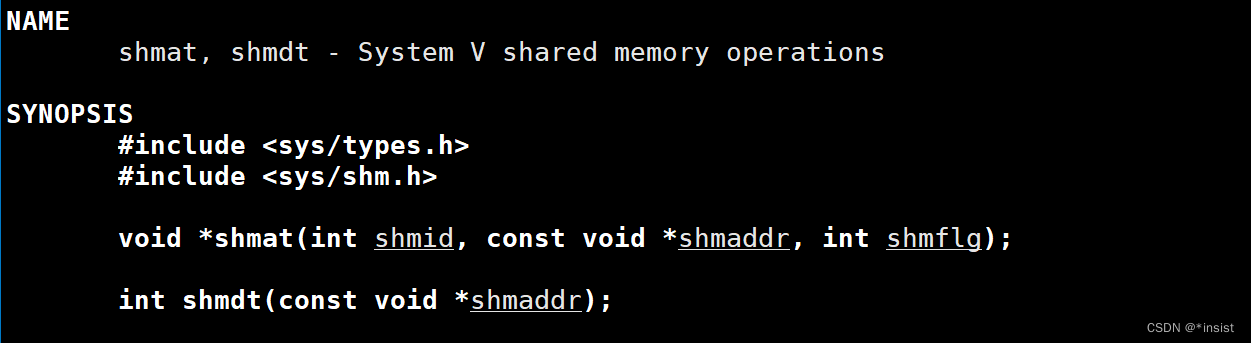
2. Attach shared memory function
**void shmat(int shmid, const void shmaddr, int shmflg);
- The first parameter :shmid Namely shmget Create a good shared memory shmid( An integer identifier ), You can release the corresponding shared memory through this identifier
- The second parameter :shmaddr Is the designated address , If NULL Then the operating system automatically selects an appropriate address ; If it is not empty and is not specified SHM_RND, Then this paragraph links to shmaddr On the specified address , If shmaddr Not empty and specifies SHM_RND Then this segment is connected to shmaddr -(shmaddr mod SHMLAB) On the address indicated .SHM_RND Command means rounding ,SHMLAB It means multiple of low boundary address , It's always 2 Power of . The expression is to take the address down to the nearest SHMLAB Multiple . Unless you plan to run the application on only one hardware ( This is unlikely nowadays ), Otherwise, do not specify the address to which the shared segment is connected . Therefore, it is generally necessary to specify shmaddr by 0, So that the kernel can choose the address
- The third parameter :shmflg If it is 0 It's read-write mode ,SHM_RD0NLY It's read-only mode
3. To associate shared memory functions
**void shmat(int shmid, const void shmaddr, int shmflg)
- The first parameter :shmid Namely shmget Create a good shared memory shmid( An integer identifier ), You can release the corresponding shared memory through this identifier
- The second and third parameters are the same as the above shmat() identical
4. Free shared memory function
*int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds buf)
- The first parameter : Identifier of shared memory
- The second parameter : Operation command Yes IPC_STAT、IPC_SET、IPC_RMID
- IPC_STAT Is to check the status of shared memory , Put the shared memory shmid_ds The structure is copied to buf in
- IPC_SET Is to change the state of shared memory , hold buf Referred to shmid_ds The structure of the uid、gid、mode Copy to shared memory shmid Within the structure
- IPC_RMID Is to free this shared memory
- The third parameter :buf Management structure of shared memory , Type of structure
- Return value : success 0 error -1
4.1 Comparison between shared memory communication and pipeline communication
1. Shared memory communication copies data less times , Fast
Shared memory can be used directly after it is created , It's like malloc Open up the same space , There is no need to call another function to access this memory
When communicating with the pipeline, you need to call the system interface after creating the pipeline read() and write() To access the pipeline file , In this way, there is data copy operation between buffers , Thus, the efficiency becomes low
![[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-bdMBg9KY-1656584415675)(1.1 The introduction of shared memory /image-20220630181015039.png)]](/img/d9/82e87aec47645eb3c5e971b4a1442e.png)
2. The pipeline has its own synchronization and mutual exclusion mechanism , Shared memory does not
Having studied pipelines, we know that pipelines have their own synchronization and mutual exclusion mechanisms , Reading and writing cannot be done at the same time . But shared memory does not have this mechanism , This makes it possible to read and write data at the same time , To achieve a mechanism similar to synchronization and mutual exclusion, locks or semaphores are needed
边栏推荐
- JVM命令之 jstack:打印JVM中线程快照
- Crudini 配置文件编辑工具
- 基于FPGA的VGA协议实现
- 雷特智能家居龙海祁:从专业调光到全宅智能,20年专注成就专业
- JVM命令之 jinfo:实时查看和修改JVM配置参数
- 谷歌 Chrome 浏览器发布 103.0.5060.114 补丁修复 0-day 漏洞
- [FPGA tutorial case 14] design and implementation of FIR filter based on vivado core
- When we talk about immutable infrastructure, what are we talking about
- CloudCompare-点对选取
- 3428. 放苹果
猜你喜欢
How to set up in touch designer 2022 to solve the problem that leap motion is not recognized?

博士申请 | 上海交通大学自然科学研究院洪亮教授招收深度学习方向博士生
uniapp开发小程序如何使用微信云托管或云函数进行云开发
JMeter function assistant - random value, random string, fixed value random extraction
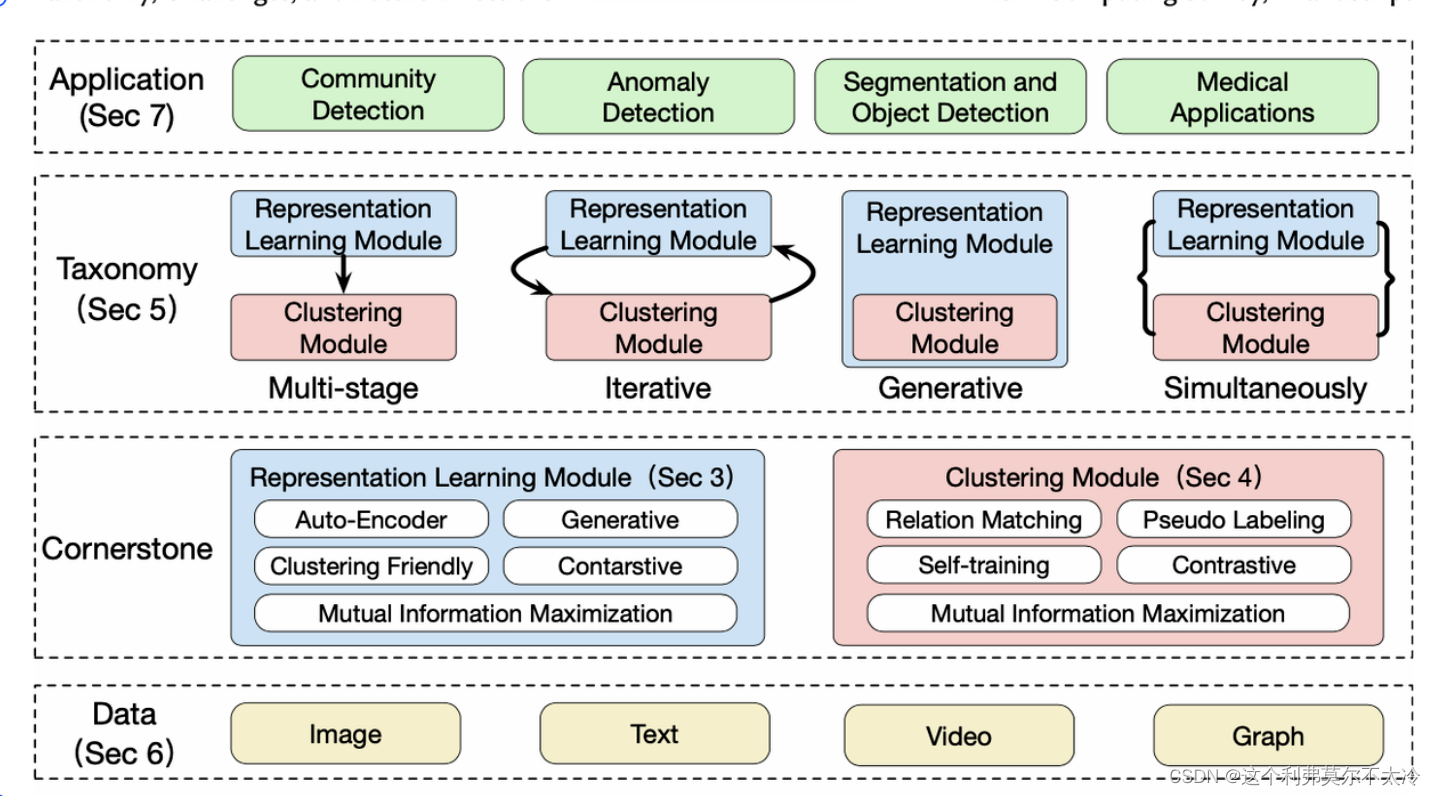
深度聚类:将深度表示学习和聚类联合优化
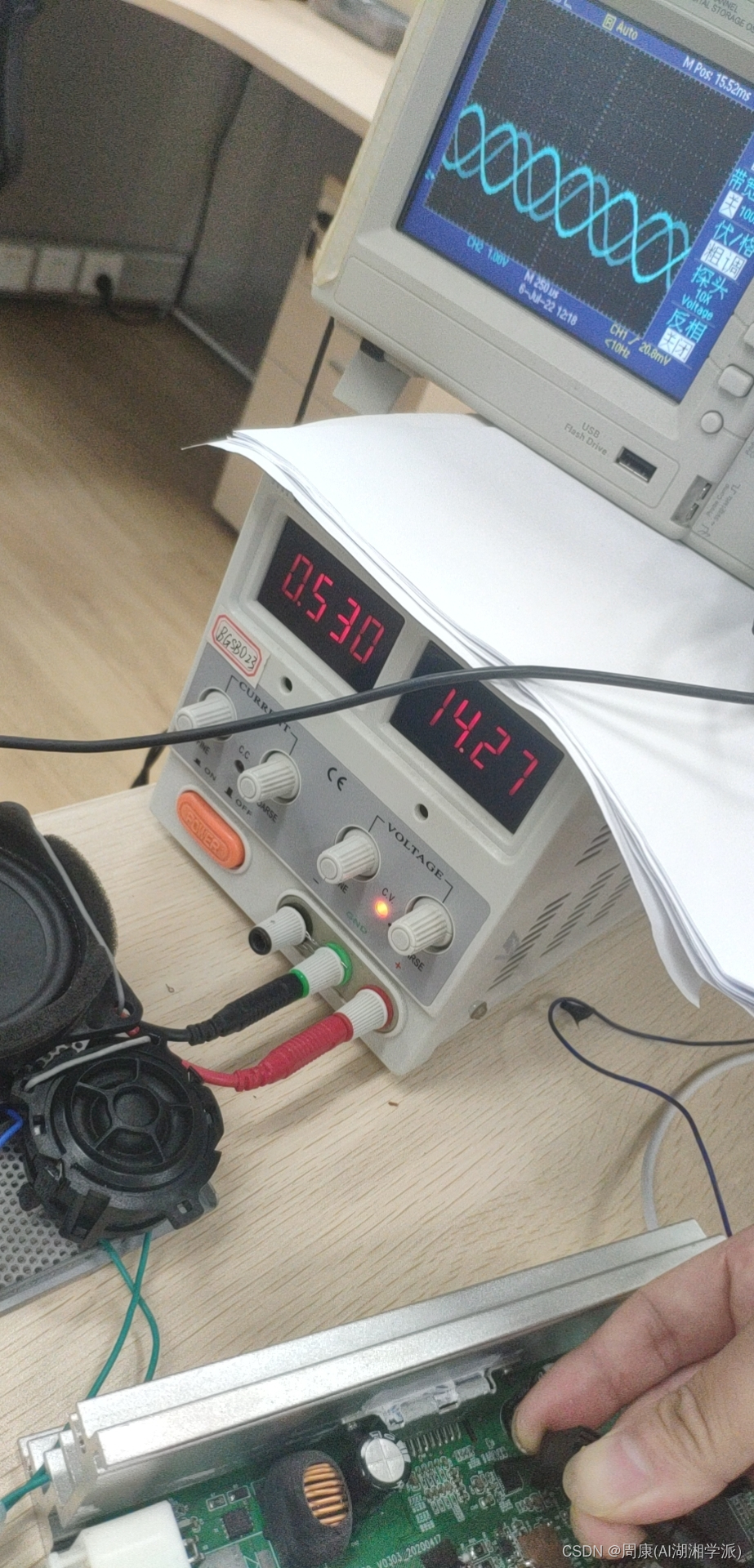

基于ADAU1452的DSP及DAC音频失真分析
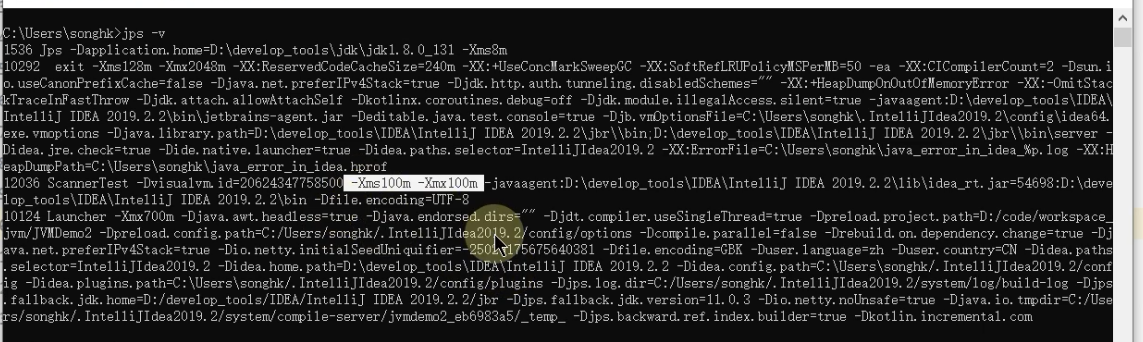
JVM命令之 jinfo:实时查看和修改JVM配置参数
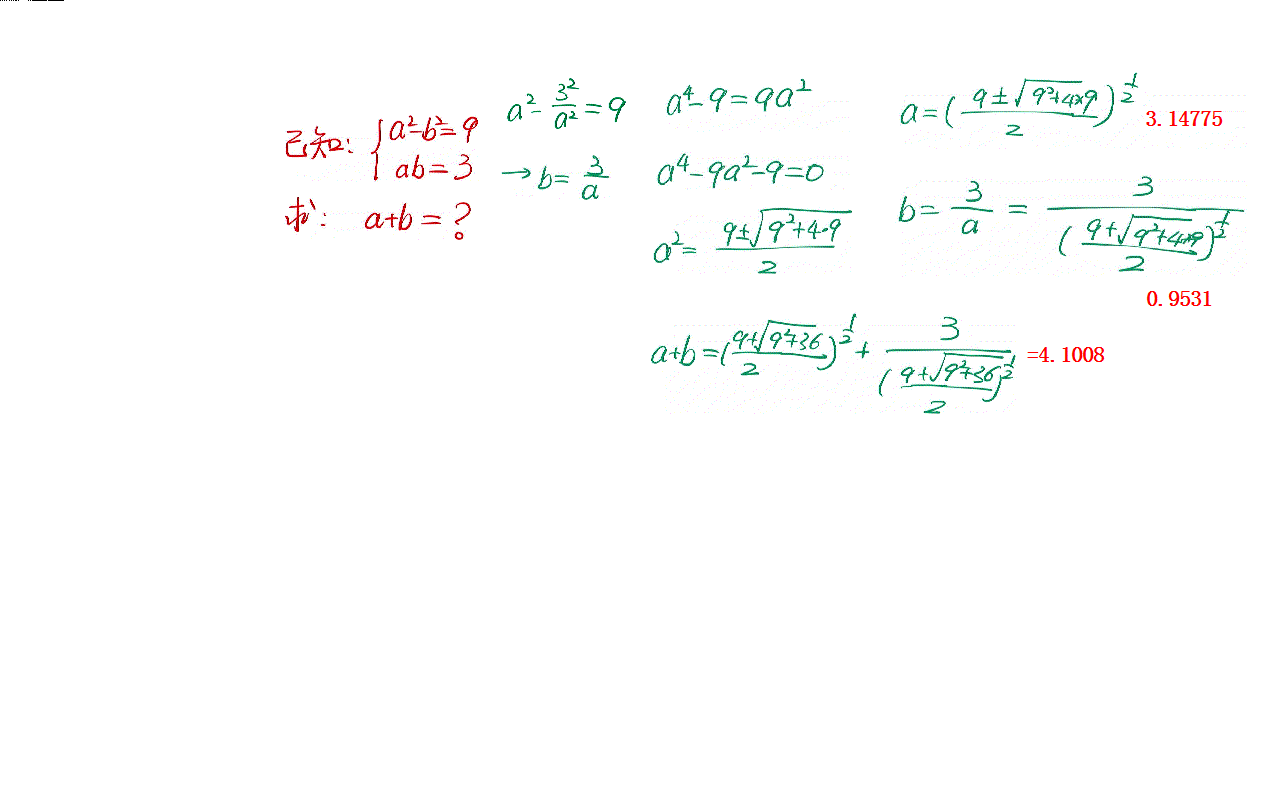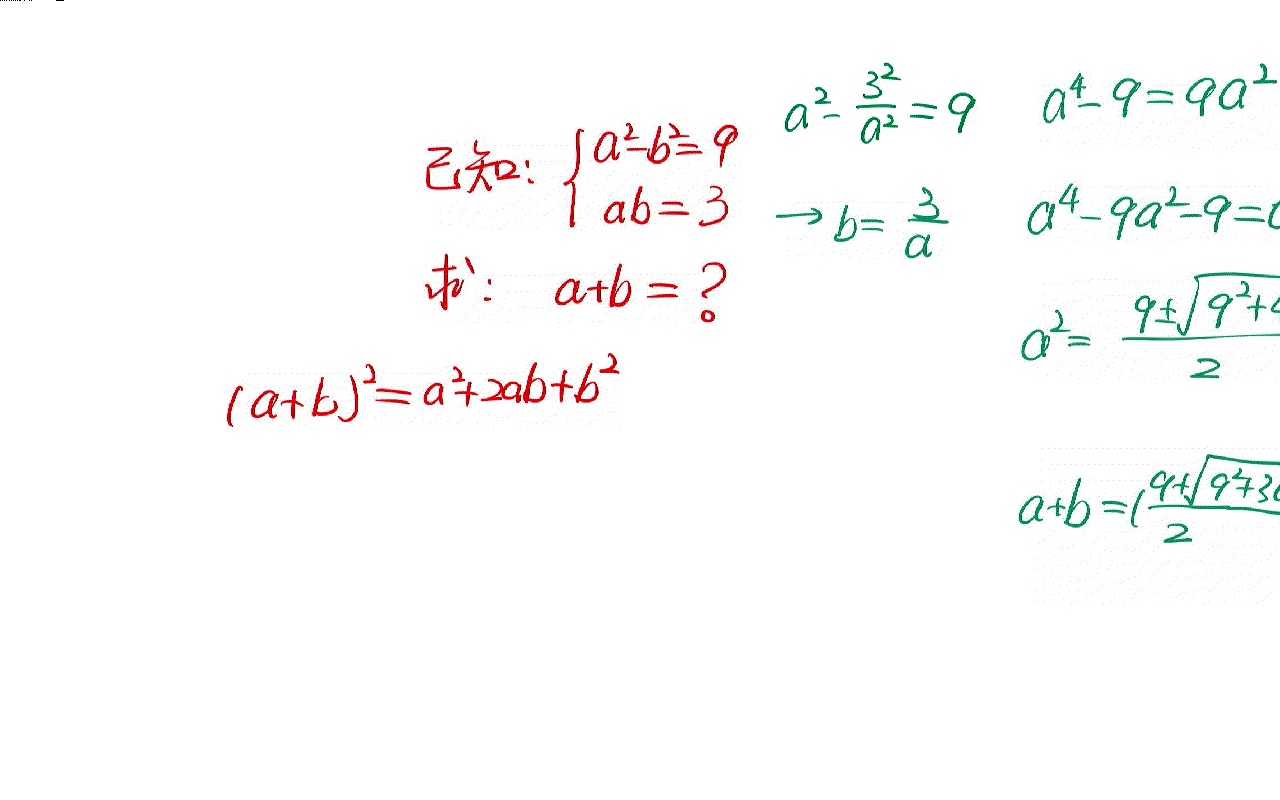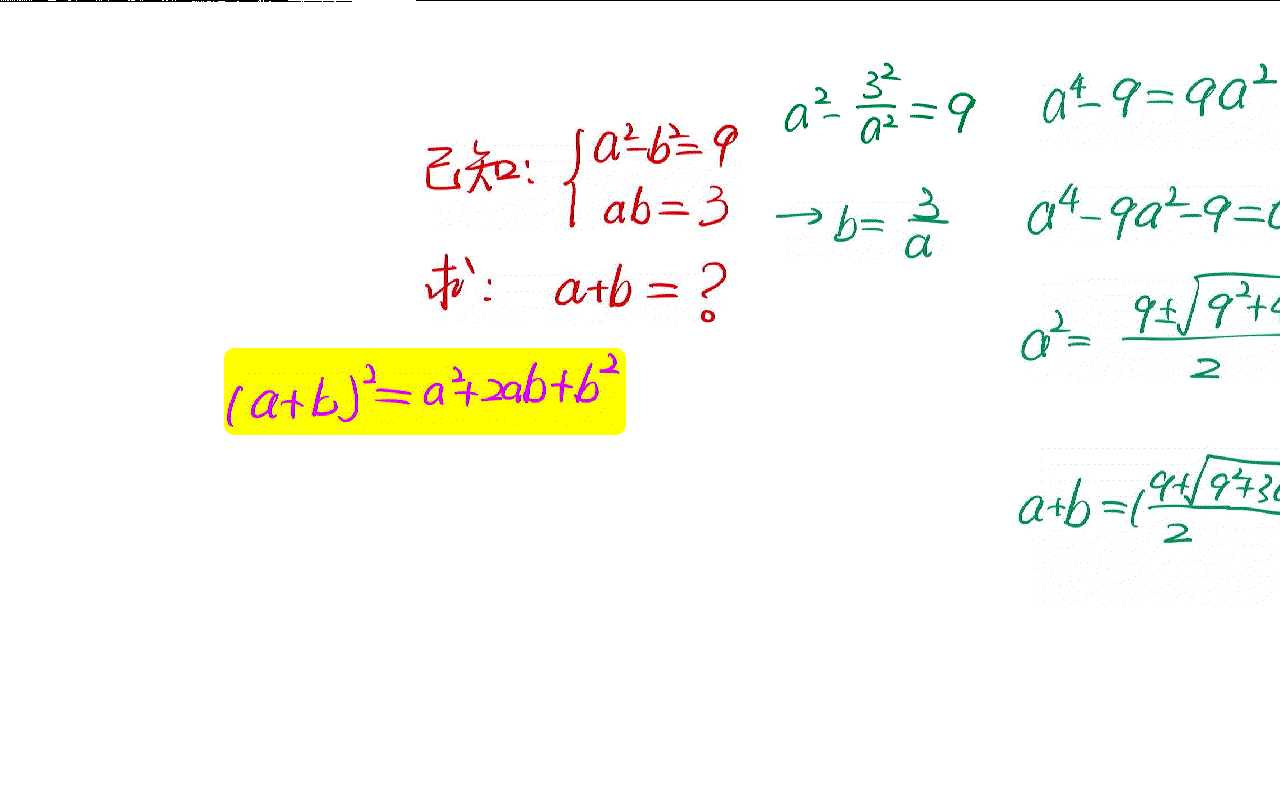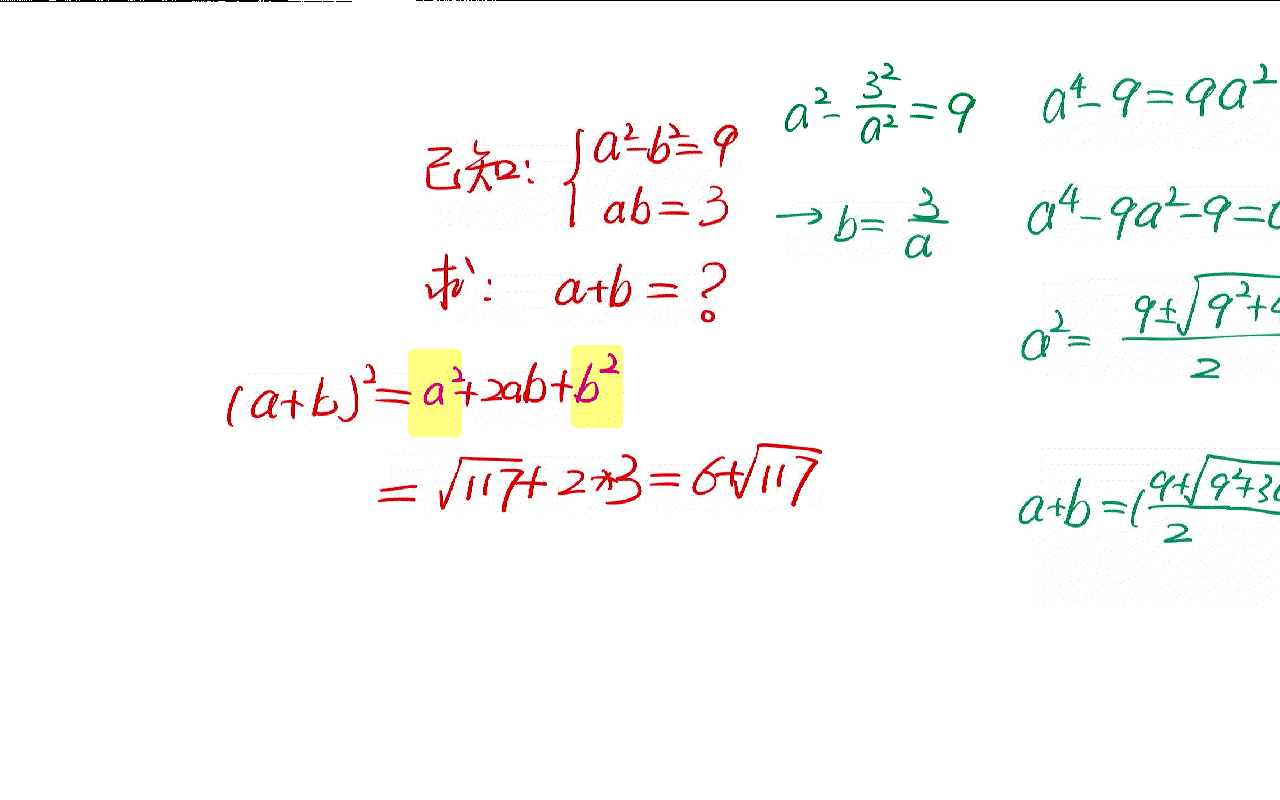
The solution of a simple algebraic problem
Peripheral driver library development notes 43: GPIO simulation SPI driver
测试开发基础,教你做一个完整功能的Web平台之环境准备
随机推荐
Check Point:企业部署零信任网络(ZTNA)的核心要素
蚂蚁庄园安全头盔 7.8蚂蚁庄园答案
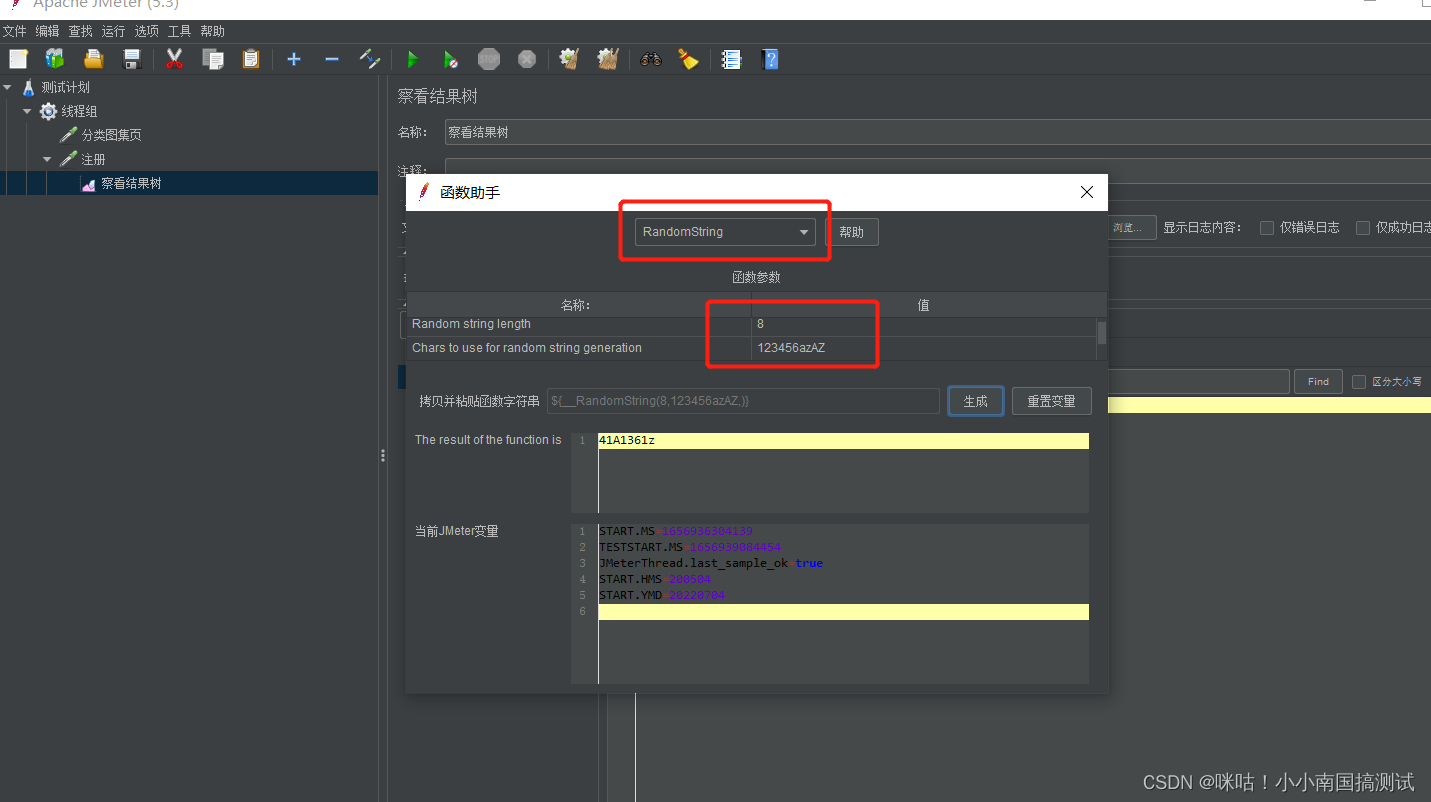
jmeter 函数助手 — — 随机值、随机字符串、 固定值随机提取
On the discrimination of "fake death" state of STC single chip microcomputer
postgresql 数据库 timescaledb 函数time_bucket_gapfill()报错解决及更换 license
CloudCompare-点对选取
JVM命令之- jmap:导出内存映像文件&内存使用情况
A freshman's summary of an ordinary student [I don't know whether we are stupid or crazy, but I know to run forward all the way]
【OpenCV】形态学滤波(2):开运算、形态学梯度、顶帽、黑帽
Bypass open_ basedir
matlab / ENVI 主成分分析实现及结果分析
Sequential storage of stacks
Solve pod install error: FFI is an incompatible architecture
雷特智能家居龙海祁:从专业调光到全宅智能,20年专注成就专业
jvm命令之 jcmd:多功能命令行
QT console output in GUI applications- Console output in a Qt GUI app?
Rk3399 platform development series explanation (interruption) 13.10, workqueue work queue
Value range of various datetimes in SQL Server 2008
JVM命令之 jstat:查看JVM统计信息
[FPGA tutorial case 13] design and implementation of CIC filter based on vivado core