当前位置:网站首页>[algorithm leetcode] interview question 04.03 Specific depth node linked list (Multilingual Implementation)
[algorithm leetcode] interview question 04.03 Specific depth node linked list (Multilingual Implementation)
2022-07-04 14:27:00 【White hat of the second leader】
List of articles
Interview questions 04.03. Specific depth node list :
Given a binary tree , Design an algorithm , Create a linked list containing all nodes at a certain depth ( such as , If the depth of a tree is D, Then create D A linked list ). Returns an array containing a linked list of all depths .
Examples 1:
Input :
[1,2,3,4,5,null,7,8]
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 7
/
8
Output :
[[1],[2,3],[4,5,7],[8]]
analysis
- Facing this algorithm problem , The second leader was lost in thought .
- If you are familiar with binary trees and linked lists , You will understand that it is actually the sequence traversal of binary tree , Each layer is combined into a linked list .
Answer key
rust
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
// Definition for singly-linked list.
// #[derive(PartialEq, Eq, Clone, Debug)]
// pub struct ListNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub next: Option<Box<ListNode>>
// }
//
// impl ListNode {
// #[inline]
// fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// ListNode {
// next: None,
// val
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn list_of_depth(tree: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<Option<Box<ListNode>>> {
let mut ans: Vec<Option<Box<ListNode>>> = Vec::new();
let mut queue = std::collections::VecDeque::new();
queue.push_back(tree);
while !queue.is_empty() {
let mut head = Some(Box::new(ListNode::new(0)));
let mut tail = head.as_mut();
let size = queue.len();
for _ in 0..size {
let node = queue.pop_front().unwrap().unwrap();
let mut node = node.borrow_mut();
if node.left.is_some() {
queue.push_back(node.left.take());
}
if node.right.is_some() {
queue.push_back(node.right.take());
}
tail.as_mut().unwrap().next = Some(Box::new(ListNode::new(node.val)));
tail = tail.unwrap().next.as_mut();
}
ans.push(head.as_mut().unwrap().next.take());
}
ans
}
}
go
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * type ListNode struct { * Val int * Next *ListNode * } */
func listOfDepth(tree *TreeNode) []*ListNode {
var ans []*ListNode
queue := []*TreeNode{
tree}
for len(queue) > 0 {
head := &ListNode{
}
tail := head
size := len(queue)
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
node := queue[i]
if node.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Right)
}
tail.Next = &ListNode{
Val: node.Val}
tail = tail.Next
}
ans = append(ans, head.Next)
queue = queue[size:]
}
return ans
}
typescript
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * class TreeNode { * val: number * left: TreeNode | null * right: TreeNode | null * constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left) * this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right) * } * } */
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * val: number * next: ListNode | null * constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) { * this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val) * this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next) * } * } */
function listOfDepth(tree: TreeNode | null): Array<ListNode | null> {
const ans = [];
const queue = [tree];
while (queue.length > 0) {
const head = new ListNode();
let tail = head;
const size = queue.length;
for (let i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
const {
val, left, right } = queue.shift();
left && queue.push(left);
right && queue.push(right);
tail.next = new ListNode(val);
tail = tail.next;
}
ans.push(head.next);
}
return ans;
};
python
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def listOfDepth(self, tree: TreeNode) -> List[ListNode]:
ans = []
q = collections.deque()
q.append(tree)
while len(q) > 0:
head = ListNode()
tail = head
size = len(q)
for _ in range(size):
node = q.popleft()
node.left and q.append(node.left)
node.right and q.append(node.right)
tail.next = ListNode(node.val)
tail = tail.next
ans.append(head.next)
return ans
c
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * }; */
int getDepth(struct TreeNode* tree) {
if (!tree) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = getDepth(tree->left);
int rightDepth = getDepth(tree->right);
return fmax(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
/** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */
struct ListNode** listOfDepth(struct TreeNode* tree, int* returnSize){
int depth = getDepth(tree);
struct ListNode **ans = malloc(depth * sizeof(struct ListNode *));
*returnSize = 0;
struct TreeNode *queue[(int) pow(2, depth) - 1];
queue[0] = tree;
int start = 0;
int end = 1;
while (start < end) {
struct ListNode head = {
};
struct ListNode *tail = &head;
int curEnd = end;
while (start < curEnd) {
struct TreeNode *node = queue[start++];
if (node->left) {
queue[end++] = node->left;
}
if (node->right) {
queue[end++] = node->right;
}
tail->next = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
tail->next->val = node->val;
tail->next->next = NULL;
tail = tail->next;
}
ans[(*returnSize)++] = head.next;
}
return ans;
}
c++
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */
class Solution {
public:
vector<ListNode*> listOfDepth(TreeNode* tree) {
vector<ListNode *> ans;
queue<TreeNode *> q;
q.push(tree);
while (q.size() > 0) {
ListNode head = ListNode(0);
ListNode *tail = &head;
int size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
TreeNode *node = q.front();
q.pop();
if (node->left != NULL) {
q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right != NULL) {
q.push(node->right);
}
tail->next = new ListNode(node->val);
tail = tail->next;
}
ans.emplace_back(head.next);
}
return ans;
}
};
java
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */
class Solution {
public ListNode[] listOfDepth(TreeNode tree) {
List<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(tree);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ListNode head = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = head;
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
tail.next = new ListNode(node.val);
tail = tail.next;
}
list.add(head.next);
}
ListNode[] ans = new ListNode[list.size()];
list.toArray(ans);
return ans;
}
}
Original title transmission gate :https://leetcode.cn/problems/list-of-depth-lcci/submissions/
Thank you very much for reading this article ~
welcome 【 give the thumbs-up 】【 Collection 】【 Comment on 】~
It's not hard to give up , But persistence must be cool ~
I hope all of us can make a little progress every day ~
This paper is written by The white hat of the second leader :https://le-yi.blog.csdn.net/ Original blog ~
边栏推荐
- Digi XBee 3 rf: 4 protocols, 3 packages, 10 major functions
- R语言使用lattice包中的bwplot函数可视化箱图(box plot)、par.settings参数自定义主题模式
- (1)性能调优的标准和做好调优的正确姿势-有性能问题,上HeapDump性能社区!
- 迅为IMX6Q开发板QT系统移植tinyplay
- Redis daily notes
- Excel quickly merges multiple rows of data
- 为什么图片传输要使用base64编码
- 基于51单片机的超声波测距仪
- 数据中台概念
- 關於miui12.5 紅米k20pro用au或者povo2出現問題的解决辦法
猜你喜欢

一文概览2D人体姿态估计
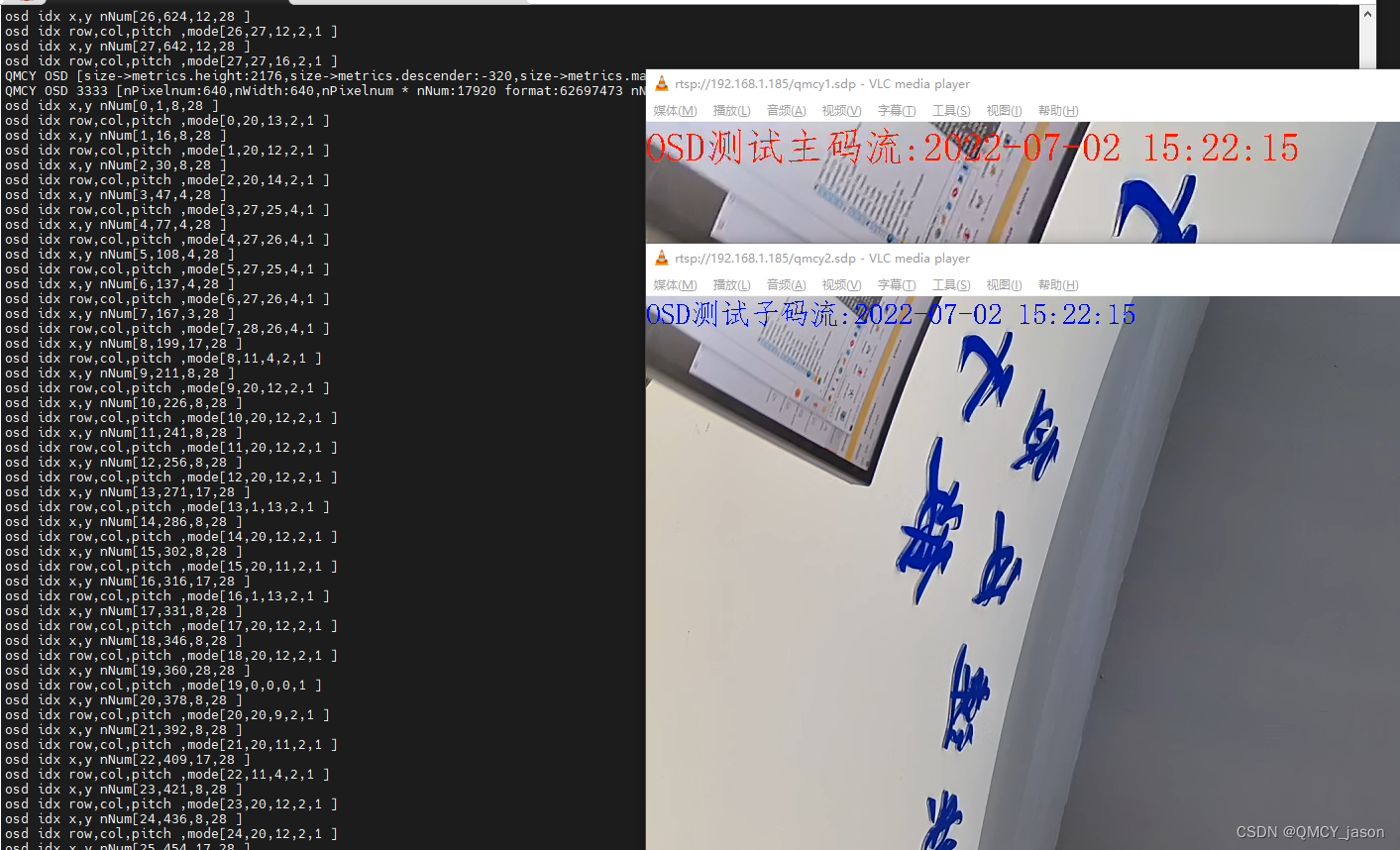
The implementation of OSD on rk1126 platform supports color translucency and multi-channel support for Chinese

codeforce:C. Sum of Substrings【边界处理 + 贡献思维 + 灵光一现】
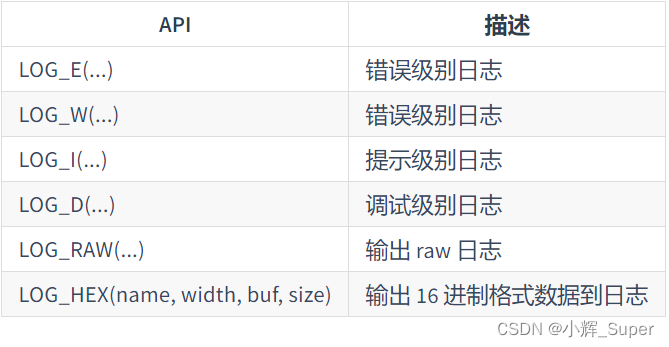
潘多拉 IOT 开发板学习(RT-Thread)—— 实验3 按键实验(学习笔记)
![递增的三元子序列[贪心训练]](/img/92/7efd1883c21c0e804ffccfb2231602.png)
递增的三元子序列[贪心训练]
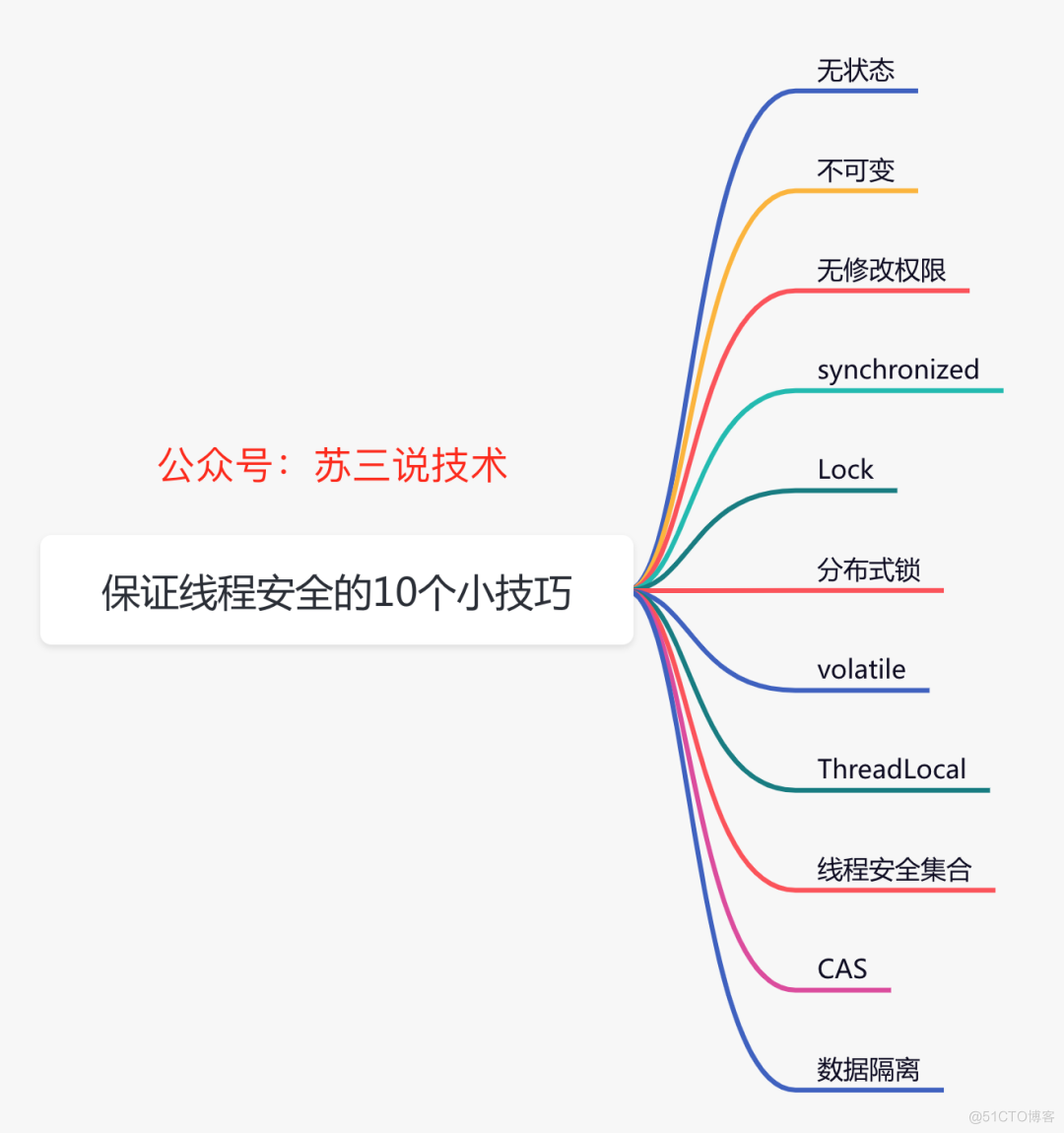
聊聊保证线程安全的 10 个小技巧
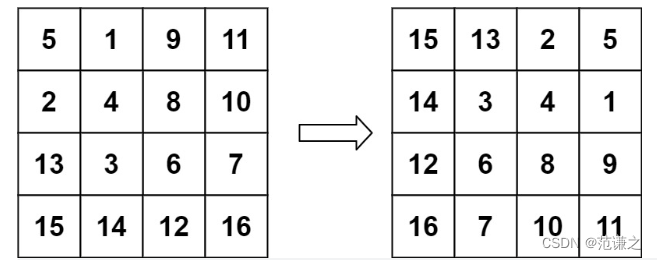
Leetcode T48:旋转图像
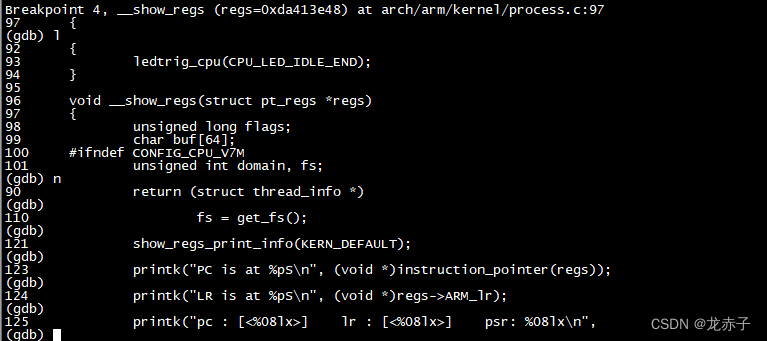
学内核之三:使用GDB跟踪内核调用链
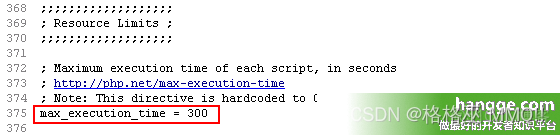
统计php程序运行时间及设置PHP最长运行时间
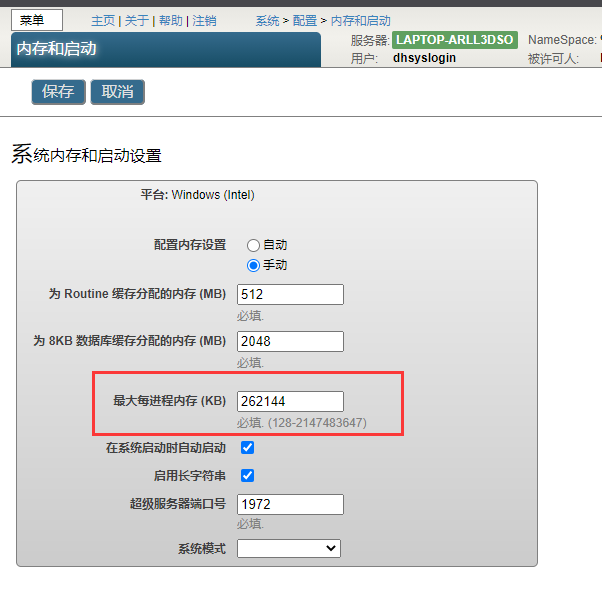
Chapter 17 process memory
随机推荐
Leetcode T48:旋转图像
leetcode:6109. 知道秘密的人数【dp的定义】
R语言使用lattice包中的bwplot函数可视化箱图(box plot)、par.settings参数自定义主题模式
【算法leetcode】面试题 04.03. 特定深度节点链表(多语言实现)
Test process arrangement (2)
架构方面的进步
R语言使用dplyr包的mutate函数对指定数据列进行标准化处理(使用mean函数和sd函数)并基于分组变量计算标准化后的目标变量的分组均值
MySQL stored procedure exercise
Digi重启XBee-Pro S2C生产,有些差别需要注意
海外游戏代投需要注意的
按照功能对Boost库进行分类
Count the running time of PHP program and set the maximum running time of PHP
Progress in architecture
商業智能BI財務分析,狹義的財務分析和廣義的財務分析有何不同?
数据中台概念
DDD application and practice of domestic hotel transactions -- Code
【云原生】我怎么会和这个数据库杠上了?
产业互联网则具备更大的发展潜能,具备更多的行业场景
第十六章 字符串本地化和消息字典(二)
MySQL triggers