当前位置:网站首页>Why can't strings be directly compared with equals; Why can't some integers be directly compared with the equal sign
Why can't strings be directly compared with equals; Why can't some integers be directly compared with the equal sign
2022-07-03 15:52:00 【Zhangjian Tianya 2.0】
Basic data type :
Basic data types can be regarded as keywords
Integer type :byte(1) short(2) int(4) long(8) Numbers represent byte sizes One byte has eight binary numbers
floating-point :float(4) double(8) Floating point numbers can be accurate to six decimal places at most
Character :char unocode
Boolean type :boolean true/false(1)
Where defined variables store values
Reference data type : class , Interface ; Array
Where the variable stores the address of the data heap memory
Heap memory and stack memory
Stack memory generally stores variables defined by keywords
Heap memory storage class ; Interface ; Variables such as arrays Generally, the storage form is to use a variable to store the code of the segment value , This code points to a section of memory in the heap memory , The memory stores data
Constant pool ( A special area contained in heap memory )
character string :
String str ="ABC"; First look for this value in the constant pool :
1 If yes, return the address in the constant pool
2 Create the content of this segment of data and store it in the constant pool , Returns the address in the constant pool
String strc = new String("ABC");
1 Now look in the constant pool , No, just create one in the constant pool
2 Then create an object in the heap memory ; Finally, the address in the heap memory is returned
Numbers :
example :
int c = 10,d=10;// This kind of data is relatively insensitive
System.out.println(c==d);
Integer a1=10,b1=10;// It is also the return address, but it is the same address ; All in the constant pool
Integer a2=128,b2=128;// When creating objects like this ( The data is too large )
System.out.println(a2.equals(b2));
System.out.println(a2==b2);
System.out.println(a1==b1);In turn true reason : The first comparison is binary coding
true equals The method is directly correct after comparison
false When the scope of comparison exceeds -128 To 127 The object is not stored in the constant pool ; New objects will be formed in heap memory , The address is no longer in the constant pool memory
true :a1,b1 The returned values are all addresses in the constant pool
String instances :
public class Charcompare {
static String str;// front static The role of
// Heap memory and stack memory ; Stack memory generally stores the types defined by keywords , local variable , Global variables, etc
// When using reference types to store values, they are usually stored in heap memory ; Constant pool in heap memory ( Convenient comparison ); Create objects like keywords ( Stored in the constant pool ; Return constant pool address )
public static void main(String[] args) {
String stra = "ABCD";// Create directly in the constant pool ; What is returned is the code in the constant pool
String strb ="ABCD";
String strc =new String("ABCD");// First create in the constant pool ; Then go back to the heap to create ; The last value returned is the code in the heap
String strd = new String("ABCD");
System.out.println(stra==strb);// The first one is right because ; Because this creation method returns the addresses in the constant pool
System.out.println(stra.equals(strc));// Look for the equals Source code
System.out.println(strc==strd);// Incorrect because the data created with the reference data type , It will first open up an address in the heap memory ; The string variable name stores the number of the address
// The returned value is finally the code of heap memory ; This kind of creation is to reopen the space memory in the heap memory ; So the codes are different
equals Explanation of source code analysis :
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
if (anObject instanceof String) {
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}such as a.equals(b)
1 first if Judge a and b Is it an object (this Is it possible to point directly to a)
2 Judge anObject Is it right? String Example : Not so False
3 Judge a,b Whether the string length is equal ( among value refer to a This string to the left of the dot )
String anotherString =(String)anobject Will instance anobject Strong to string type
4 Judge whether individual characters are equal in turn
5 If both are satisfied, the final return value is true
Be careful boolean The returned value is a Boolean value
边栏推荐
- Salary 3000, monthly income 40000 by "video editing": people who can make money never rely on hard work!
- Subclass hides the function with the same name of the parent class
- Halcon and WinForm study section 1
- Visual upper system design and development (Halcon WinForm) -2 Global variable design
- Visual upper system design and development (Halcon WinForm) -1 Process node design
- nifi从入门到实战(保姆级教程)——flow
- Jvm-06-execution engine
- 首发!!lancet饿了么官方文档
- 驱动与应用程序通信
- App移动端测试【5】文件的写入、读取
猜你喜欢
UnityShader——MaterialCapture材质捕捉效果 (翡翠斧头)

Jvm-05-object, direct memory, string constant pool

Unityshader - materialcapture material capture effect (Emerald axe)

Jvm-02-class loading subsystem

The markdown file obtains the pictures of the network and stores them locally and modifies the URL
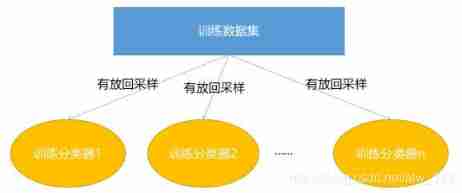
Popular understanding of random forest
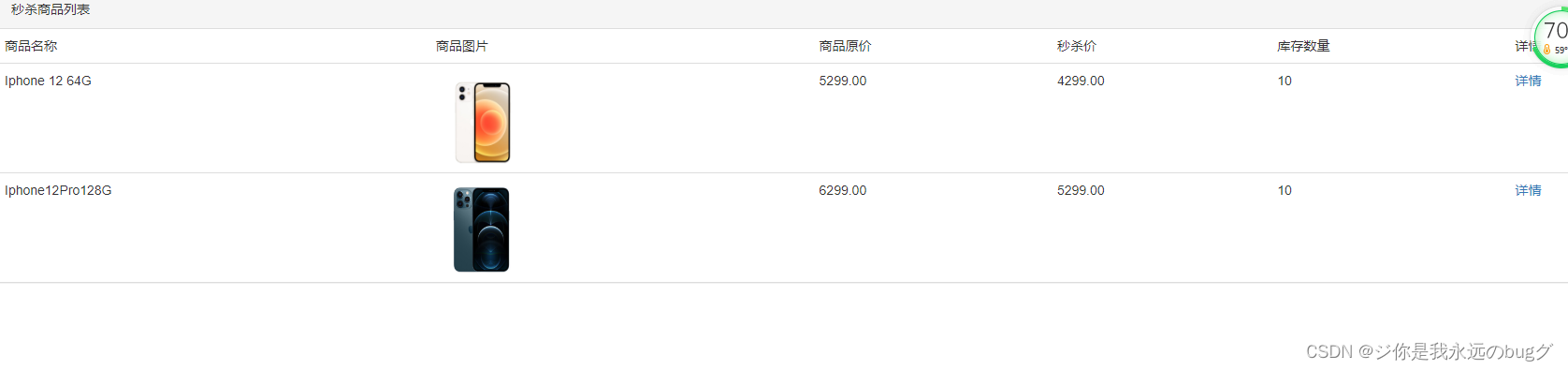
Seckill system 3- product list and product details

Creation and destruction of function stack frames

How are integer and floating-point types stored in memory

详解指针进阶1
随机推荐
Jvm-03-runtime data area PC, stack, local method stack
Concurrency-01-create thread, sleep, yield, wait, join, interrupt, thread state, synchronized, park, reentrantlock
Microservices - load balancing ribbon
秒杀系统2-Redis解决分布式Session问题
自定义注解
CString在多线程中的问题
Redis在Windows以及Linux系统下的安装
Principles of several common IO models
Jvm-05-object, direct memory, string constant pool
[系统安全] 四十三.Powershell恶意代码检测系列 (5)抽象语法树自动提取万字详解
Visual upper system design and development (Halcon WinForm) -2 Global variable design
Seckill system 2 redis solves the problem of distributed session
坚持输出需要不断学习
首发!!lancet饿了么官方文档
Function introduction of JMeter thread group
从 flask 服务端代码自动生成客户端代码 -- flask-native-stubs 库介绍
Unity function - unity offline document download and use
Concurrency-02-visibility, atomicity, orderliness, volatile, CAS, atomic class, unsafe
子类隐藏父类的同名函数
Baidu AI Cloud helps Shizuishan upgrade the smart health care model of "Internet + elderly care services"