当前位置:网站首页>Ros2 - node (VII)
Ros2 - node (VII)
2022-07-05 06:50:00 【Me and nano】
ROS2 Robot operating system
List of articles
Preface
Robot is a synthesis of various functions , Each function is like a working cell of a robot , Many cells are connected by some mechanism , Become a robot as a whole .
stay ROS in , We give these “ cells ” Took a name , That is the node .
One 、 Communication model
A complete robot system may not be a physical whole , For example, such a robot :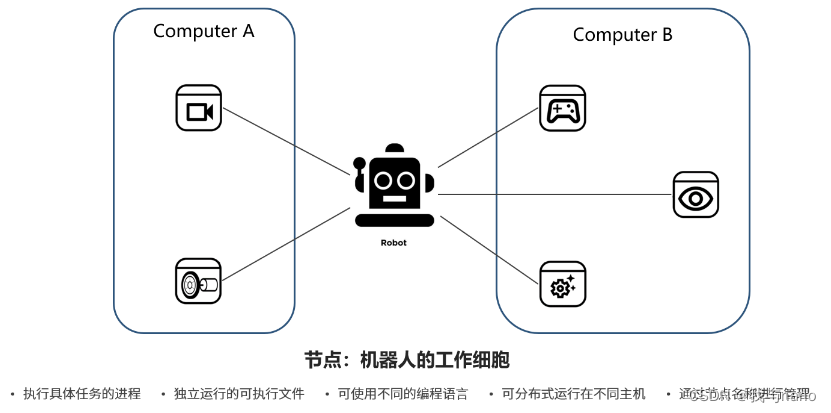
The responsibility of the node in the robot system is to perform some specific tasks , From the perspective of computer operating system , Also called process ;
Each node is an executable file that can run independently , For example, execute a python Program , Or perform C++ Compile the generated results , All of them are running a node ;
Since each node is an independent execution file , Naturally, you can think of , The programming language that gets this execution file can be different , such as C++、Python, Even Java、Ruby Wait for more language .
These nodes are cells with different functions , According to the different system design , It may be located on the computer A, It may also be located on the computer B, It may also run in the cloud , This is called distributed , That is, it can be distributed on different hardware carriers ;
Each node needs to have a unique name , When we want to find a node , Or when you want to query the status of a node , You can query by the name of the node .
Nodes can also be compared to workers one by one , Do different tasks separately , Some of them work in front-line factories , Some provide support in the logistics department , They may not know each other , But together they push the robot “ factory ”, Complete more complex tasks .
Two 、 Specific use
1.Hello World node ( Process oriented )
ROS2 Of course, the implementation of the node in the needs to write a program , We from Hello World Routine starts , First, let's implement the simplest node , The function is not complicated , It's a cycle of printing “Hello World” String to the terminal .
ros2 run learning_node node_helloworld
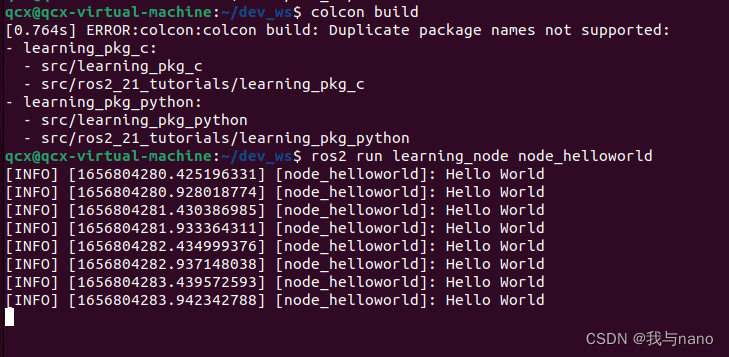
Code parsing :
import rclpy # ROS2 Python Interface library
from rclpy.node import Node # ROS2 Node class
import time
def main(args=None): # ROS2 Node main entrance main function
rclpy.init(args=args) # ROS2 Python Interface initialization ** Fixed programming **
node = Node("node_helloworld") # establish ROS2 Node object and initialize ** You need to create a class as an object to use **
while rclpy.ok(): # ROS2 Whether the system operates normally
node.get_logger().info("Hello World") # ROS2 Log output similar print
time.sleep(0.5) # Sleep control cycle time
node.destroy_node() # Destroy the node object
rclpy.shutdown() # close ROS2 Python Interface
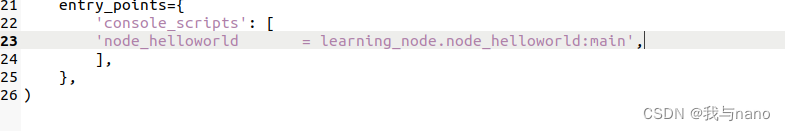
After writing the code, you need to set the compilation options of the function package , Let the system know Python Program entry , To open a feature pack setup.py file , Add the following entry point configuration :
entry_points={
'console_scripts': [
'node_helloworld = learning_node.node_helloworld:main', node . Code file name .main
],
Create node process
Programming interface initialization
Create nodes and initialize
Realize node functions
Destroy the node and close the interface
2.Hello World node ( object-oriented )
So in ROS2 The development of , We recommend that you use object-oriented programming , For example, the code just now can be changed to this , Although it looks a little complicated , But the code will be more readable and portable , Debugging will also be more convenient .
ros2 run learning_node node_helloworld_class
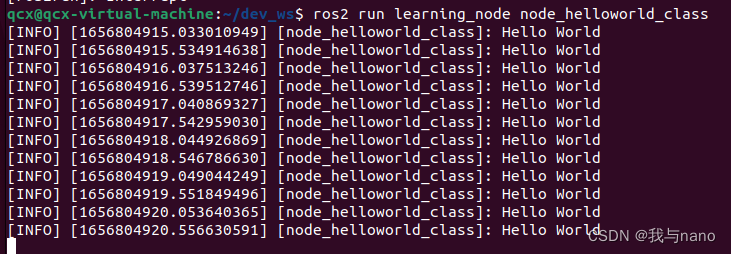
Code parsing :
import rclpy # ROS2 Python Interface library
from rclpy.node import Node # ROS2 Node class
import time
"""
Create a HelloWorld node , Output during initialization “hello world” journal
"""
class HelloWorldNode(Node):
def __init__(self, name):
super().__init__(name) # ROS2 Node parent class initialization
while rclpy.ok(): # ROS2 Whether the system operates normally
self.get_logger().info("Hello World") # ROS2 Log output
time.sleep(0.5) # Sleep control cycle time
def main(args=None): # ROS2 Node main entrance main function
rclpy.init(args=args) # ROS2 Python Interface initialization
node = HelloWorldNode("node_helloworld_class") # establish ROS2 Node object and initialize
rclpy.spin(node) # Loop waiting for ROS2 sign out
node.destroy_node() # Destroy the node object
rclpy.shutdown() # close ROS2 Python Interface
After writing the code, you need to set the compilation options of the function package , Let the system know Python Program entry , To open a feature pack setup.py file , Add the following entry point configuration :
entry_points={
'console_scripts': [
'node_helloworld = learning_node.node_helloworld:main',
'node_helloworld_class = learning_node.node_helloworld_class:main',
],
Compile a piece of code before you run it , After compilation, the code will be copied to install In the folder , Each run ros run It's all about install Documents in , If you don't compile, you will run the old code .
Programming interface initialization
Create nodes and initialize
Realize node functions
Destroy the node and close the interface
3. Object recognition node
you 're right , Next, let's take the task of machine vision as an example , Simulate the implementation process of nodes in the actual robot .
We first find a picture of apple on the Internet , By writing a node to identify the apple in the picture .
First install opencv
sudo apt install python3-opencv
The probability of using this instruction cannot be used , I followed Gu Yue Jude's course , Then stepped on many pits , You can use the following two lines of code to install .
pip3 install numpy
pip3 install opencv-python
Then you can run the routine :
ros2 run learning_node node_object # Pay attention to recompile after modifying the image path
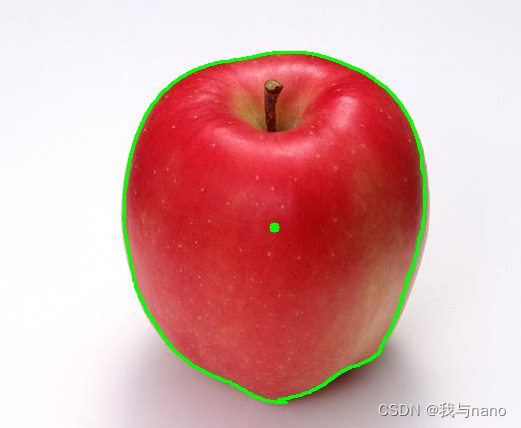

Before operation, you need to learning_node/node_object.py The image path in the code , Change to actual path , Recompile and run after modification :
image = cv2.imread('/home/qcx/dev_ws/src/ros2_21_tutorials/learning_node/learning_node/apple.jpg')
After the routine runs successfully , A visualization window will pop up , You can see that Apple has been successfully recognized , A green box will outline the apple , The green dot in the middle indicates the central point .
Code parsing :
import rclpy # ROS2 Python Interface library
from rclpy.node import Node # ROS2 Node class
import cv2 # OpenCV Image processing library
import numpy as np # Python Numerical calculation library
lower_red = np.array([0, 90, 128]) # Red HSV Lower threshold
upper_red = np.array([180, 255, 255]) # Red HSV Upper threshold
def object_detect(image):
hsv_img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV) # Images from BGR The color model is converted to HSV Model
mask_red = cv2.inRange(hsv_img, lower_red, upper_red) # Image binarization
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(mask_red, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) # Contour detection in image
for cnt in contours: # Remove some noise with too small contour area
if cnt.shape[0] < 150:
continue
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) # Get the upper left corner of the outline of the apple xy Pixel coordinates and the width and height of the contour range
cv2.drawContours(image, [cnt], -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)# Outline the apple
cv2.circle(image, (int(x+w/2), int(y+h/2)), 5, (0, 255, 0), -1)# Draw the center point of the apple image
cv2.imshow("object", image) # Use OpenCV Display the processed image effect
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def main(args=None): # ROS2 Node main entrance main function
rclpy.init(args=args) # ROS2 Python Interface initialization
node = Node("node_object") # establish ROS2 Node object and initialize
node.get_logger().info("ROS2 Node example : Detect the apple in the picture ")
image = cv2.imread('/home/qcx/dev_ws/src/ros2_21_tutorials/learning_node/learning_node/apple.jpg') # Read images
object_detect(image) # Apple detection
rclpy.spin(node) # Loop waiting for ROS2 sign out
node.destroy_node() # Destroy the node object
rclpy.shutdown() # close ROS2 Python Interface
After writing the code, you need to set the compilation options of the function package , Let the system know Python Program entry , To open a feature pack setup.py file , Add the following entry point configuration :
entry_points={
'console_scripts': [
'node_helloworld = learning_node.node_helloworld:main',
'node_helloworld_class = learning_node.node_helloworld_class:main',
'node_object = learning_node.node_object:main',
],
Call camera recognition
ros2 run learning_node node_object_webcam
If you are operating in a virtual machine , The following settings are required : 1. Set the virtual machine to be compatible USB3.1; 2. Connect the camera to the virtual machine on the mobile device .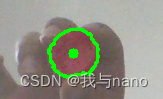
I am calling the camera of the computer , The effect is OK
Compared with the previous procedure , The biggest change here is to modify the source of the image , Use OpenCV Medium VideoCapture() To drive the camera , And cycle read Camera information , And identify .
import rclpy # ROS2 Python Interface library
from rclpy.node import Node # ROS2 Node class
import cv2 # OpenCV Image processing library
import numpy as np # Python Numerical calculation library
lower_red = np.array([0, 90, 128]) # Red HSV Lower threshold
upper_red = np.array([180, 255, 255]) # Red HSV Upper threshold
def object_detect(image):
hsv_img = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV) # Images from BGR The color model is converted to HSV Model
mask_red = cv2.inRange(hsv_img, lower_red, upper_red) # Image binarization
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(mask_red, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) # Contour detection in image
for cnt in contours: # Remove some noise with too small contour area
if cnt.shape[0] < 150:
continue
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) # Get the upper left corner of the outline of the apple xy Pixel coordinates and the width and height of the contour range
cv2.drawContours(image, [cnt], -1, (0, 255, 0), 2) # Outline the apple
cv2.circle(image, (int(x+w/2), int(y+h/2)), 5, (0, 255, 0), -1) # Draw the center point of the apple image
cv2.imshow("object", image) # Use OpenCV Display the processed image effect
cv2.waitKey(50)
def main(args=None): # ROS2 Node main entrance main function
rclpy.init(args=args) # ROS2 Python Interface initialization
node = Node("node_object_webcam") # establish ROS2 Node object and initialize
node.get_logger().info("ROS2 Node example : Detect the apple in the picture ")
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while rclpy.ok():
ret, image = cap.read() # Read a frame of image
if ret == True:
object_detect(image) # Apple detection
node.destroy_node() # Destroy the node object
rclpy.shutdown() # close ROS2 Python Interface
3、 ... and 、 Instruction Introduction
ls /dev/video* # Check the model of the camera
ros2 node list # View the list of nodes
ros2 node info <node_name> # View node information
summary
In a ROS In the robot system , Nodes are not isolated , There are many mechanisms between them to keep in touch , The connection between them will be introduced below .
边栏推荐
- Time is fast, please do more meaningful things
- CGroup CPU group source code analysis
- ROS2——Service服务(九)
- H5 module suspension drag effect
- LSA Type Explanation - lsa-1 [type 1 LSA - router LSA] detailed explanation
- Huawei bracelet, how to add medicine reminder?
- 7. Oracle table structure
- NVM Downloading npm version 6.7.0... Error
- Orin installs CUDA environment
- 乐鑫面试流程
猜你喜欢

2. Addition and management of Oracle data files
将webApp或者H5页面打包成App
PHY驱动调试之 --- MDIO/MDC接口22号和45号条款(一)
The “mode“ argument must be integer. Received an instance of Object
Orin 安装CUDA环境
Page type
Configuration method and configuration file of SolidWorks GB profile library
SD_CMD_SEND_SHIFT_REGISTER
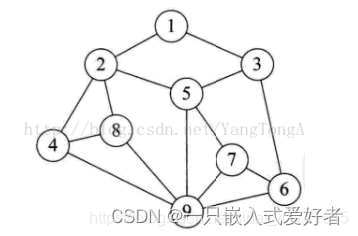
逻辑结构与物理结构

Knapsack problem acwing 9 Group knapsack problem
随机推荐
A brief introduction to heading/pitch/roll and omega/phi/kappa
Error: "mountvolume.setup failed for volume PVC fault handling
ethtool 原理介绍和解决网卡丢包排查思路(附ethtool源码下载)
. Net core stepping on the pit practice
Vscode configures the typera editor for MD
6-3 find the table length of the linked table
Cookie、Session、JWT、token四者间的区别与联系
mingling
6-4 search by serial number of linked list
The differences and connections among cookies, sessions, JWT, and tokens
Using handler in a new thread
Skywalking全部
Edge calculation data sorting
Xavier CPU & GPU 高负载功耗测试
Volcano resource reservation feature
Orin installs CUDA environment
微信小程序路由再次跳轉不觸發onload
ROS2——初识ROS2(一)
【MySQL8.0不支持表名大写-对应方案】
SolidWorks template and design library are convenient for designers to call