当前位置:网站首页>Golang单元测试、Mock测试以及基准测试
Golang单元测试、Mock测试以及基准测试
2022-07-03 17:10:00 【小菜鸡本菜】
之前参加字节跳动青训营而整理的笔记
Golang拥有一套单元测试和性能测试系统,仅需要添加很少的代码就可以快速测试一段需求代码。
一、单元测试

单元测试主要包括:输入、测试单元、输出、期望以及与期望的校对。
测试单元包括函数或者结合了一些函数的模块等。我们通过将输出与期望值进行校对,来验证代码的正确性。
通过单元测试,可以一方面保证质量,例如在覆盖率足够的情况下,如果在旧代码中添加了新的代码,通过单元测试可以验证新的代码是否破坏了功能正确性。
另一方面,也提升了效率,例如代码中出现了bug,通过编写单元测试,我们能够在较短的时间内定位或修复问题。
1.1、golang规则
规则1:所有测试文件以_test.go结尾。
_test.go 程序不会被普通的 Go 编译器编译,所以当放应用部署到生产环境时它们不会被部署;
只有gotest会编译所有的程序:普通程序和测试程序。
规则2:测试文件中必须导入testing包,并且函数必须写为func TestXxx(*testing.T)形式。
例如,某个函数Add的测试函数为TestAdd,如下所示:
//main.go
func Add(a, b int) int {
return a + b
}
//main_test.go
func TestAdd(t *testing.T) {
trueOutput := Add(1, 2)
expectOutput := 3
if trueOutput != expectOutput {
t.Errorf("Expected %v do not match actual %v", expectOutput, trueOutput)
}
}
规则3:测试的初始化逻辑放到TestMain中。
这是一个比较好的用法,TestMain函数具体信息如下:
func TestMain(m *testing.M){
//测试前:数据装载、配置初始化等前置工作
//...
code := m.Run()
//测试后:释放资源等收尾工作
//...
os.Exit(code)
}
例如:
func TestMain(m *testing.M) {
//测试前
fmt.Println("开始了!")
run := m.Run()
//测试后
fmt.Println("结束了!")
os.Exit(run)
}
func TestAdd(t *testing.T) {
trueOutput := Add(1, 2)
expectOutput := 3
if trueOutput != expectOutput {
t.Errorf("Expected %v do not match actual %v", expectOutput, trueOutput)
}
}
//测试结果
//开始了!
//=== RUN TestAdd
//--- PASS: TestAdd (0.00s)
//PASS
//
//结束了!
1.2、举例&第三方测试包
在该例子中,我们期望HelloTom函数返回“Tom”,如果返回的不是“Tom”则表示测试失败。
很明显,本次测试是失败的。
func HelloTom() string {
return "Jerry"
}
func TestHelloTom(t *testing.T) {
output := HelloTome()
expectOutput := "Tom"
if output != expectOutput {
t.Errorf("Expected %s do not match actual %s", expectOutput, output)
}
}
//测试结果
//=== RUN TestHelloTom
//main_test.go:28: Expected Tom do not match actual Jerry
//--- FAIL: TestHelloTom (0.00s)
在单元测试函数中,经常需要编写判断逻辑,我们可以使用一些开源的测试包来帮助简化代码。
例如使用Testift。使用go get安装:
go get github.com/stretchr/testify
将上述例子使用Testify后,代码如下:
func TestHelloTom(t *testing.T) {
output := HelloTom()
assert.Equal(t, "Tom", output)
}
1.3、覆盖率
问题:
- 如何衡量代码是否经过了足够的测试?
- 如何评价项目的测试水准?
- 如何评估项目是否达到了高水准测试等级?
我们需要评估单元测试,于是需要引入了单元测试覆盖率。
覆盖率在一定程度上反应了测试用例的覆盖度,越完备那么代码的正确性越有保证。
例子:
func JudgePassLine(score int16) bool {
if score >= 60 {
return true
}
return false
}
func TestJudgePassLine(t *testing.T) {
isPass := JudgePassLine(70)
expectOutput := true
if expectOutput != isPass {
t.Errorf("Expected %v do not match actual %v", expectOutput, isPass)
}
}
使用命令:
go test judgment_test.go judgment.go --cover
结果:
=== RUN TestJudgePassLine
--- PASS: TestJudgePassLine (0.00s)
PASS
coverage: 40.0% of statements in ./...
如果使用Goland的话,会显示出测试代码的范围。很明显,JudgePassLine函数的前两行(例子中第2、3行)已经被验证,而return false并没有被验证。
我们可以再写一个分支的单元测试,来提高覆盖率。
func TestJudgePassLine(t *testing.T) {
isPass := JudgePassLine(70)
expectOutput := true
if expectOutput != isPass {
t.Errorf("Expected %v do not match actual %v", expectOutput, isPass)
}
}
func TestJudgePassLineFail(t *testing.T) {
isPass := JudgePassLine(50)
expectOutput := false
if expectOutput != isPass {
t.Errorf("Expected %v do not match actual %v", expectOutput, isPass)
}
}
//结果
//=== RUN TestJudgePassLine
//--- PASS: TestJudgePassLine (0.00s)
//=== RUN TestJudgePassLineFail
//--- PASS: TestJudgePassLineFail (0.00s)
//PASS
//
//coverage: 60.0% of statements in ./...
从结果可以看出,目前覆盖率已经达到60%了(还有其他函数没有写单元测试)。
当然,在实际项目中,要达到100%的覆盖率是一个可望不可及的目标,一般来说,覆盖率在50%~60%能够认为在一些主流的情况下是没有问题的,但是可能还有有一些异常分支没有覆盖到,对一些例如”提现“等资金类的操作,对覆盖率会要求更高,一般会要求达到覆盖率80%以上。
为了能够提高覆盖率,有一些好的实践:
- 测试分支相互独立、全面覆盖。
- 测试单元粒度足够小,因此要求函数单一职责。
二、Mock测试
2.1、项目中的依赖
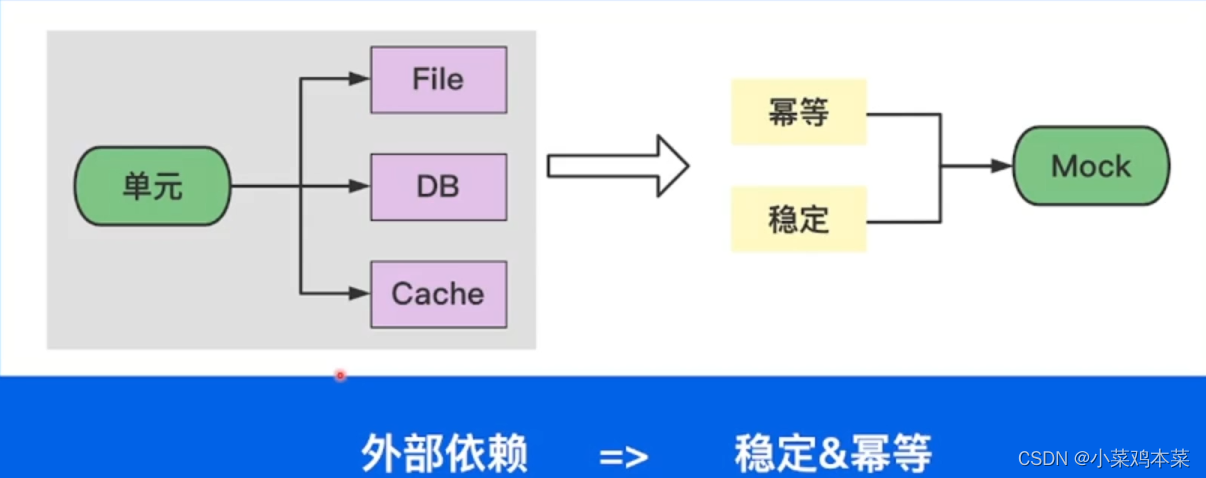
在一些复杂项目中,会依赖一些数据库、文件或缓存等,这些属于项目的一个强依赖。
单元测试的主要目标有2个:
- 幂等。幂等指重复运行一个测试的结果与之前是一致的。
- 稳定。指单元测试是能够相互隔离的,单元测试中的函数能在任何时间任何地点独立运行。
如果单元测试中直接调用数据库等外部依赖,那测试是不稳定的,例如:
func ReadFirstLine() string {
open, err := os.Open("log")
defer open.Close()
if err != nil {
return ""
}
scanner := bufio.NewScanner(open)
for scanner.Scan() {
return scanner.Text()
}
return ""
}
func ProcessFirstLine() string {
line := ReadFirstLine()
destLine := strings.ReplaceAll(line, "11", "00")
return destLine
}
//Test
func TestProcessFirstLine(t *testing.T) {
firstLine := ProcessFirstLine()
expectOutput := "line00"
if firstLine != expectOutput {
t.Errorf("Expected %s do not match actual %s", expectOutput, firstLine)
}
}
从这个例子中可以看出,测试依赖于外部文件,假如外部文件被删除或篡改了,那么这个测试就不可运行了。
因此就需要引入mock机制。
2.2、Mock
常用的开源Mock包monkey:https://github.com/bouk/monkey
该包提供了快速Mock函数:
- 为一个函数打桩
- 为一个方法打桩
打桩可以理解为用一个函数A去替换一个函数B,B就是原函数,A就是打桩函数。
例子:
将上述读取文件单元测试代码修改,对ReadFirstLine打桩测试,使测试不再依赖本地文件。
func TestProcessFirstLine(t *testing.T) {
//mock打桩
monkey.Patch(ReadFirstLine, func() string {
return "line00"
})
defer monkey.Unpatch(ReadFirstLine)
//
firstLine := ProcessFirstLine()
expectOutput := "line00"
if firstLine != expectOutput {
t.Errorf("Expected %s do not match actual %s", expectOutput, firstLine)
}
}
mock在运行时实现,基于go的unsafe包,将内存中函数的地址替换成运行时函数地址。
三、基准测试
go提供了基准测试框架,基准测试是指测试一段程序运行时的性能。
在基准测试中,函数会被调用 N 次(N 是非常大的数,如 N = 1000000),并展示 N 的值和函数执行的平均时间,单位为 ns(纳秒,ns/op)。
- 使用基准测试能够优化代码,当然,这需要对当前代码分析。
例子:
负载均衡例子,随机选择执行服务器
var ServerIndex [10]int
func InitServerIndex() {
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
ServerIndex[1] = i + 100
}
}
func Select() int {
return ServerIndex[rand.Intn(10)]
}
//测试
//串行的基准测试
func BenchmarkSelect(b *testing.B) {
InitServerIndex()
b.ResetTimer()
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
Select()
}
}
//并行的基准测试
func BenchmarkSelectParallel(b *testing.B) {
InitServerIndex()
b.ResetTimer()
b.RunParallel(func(pb *testing.PB) {
for pb.Next() {
Select()
}
})
}
测试结果:
BenchmarkSelect-16 180309266(N) 6.596 ns/op(函数执行的平均时间)
BenchmarkSelectParallel-16 29328594 42.33 ns/op
可以看到在并行状态下,性能较为低下,因为Select利用了rand函数,而rand函数为了保证随机性和并发安全,持有一把全局锁,这样就降低了并发性能。
为了提升这个函数的性能,可以用fastrand。
func BenchmarkFastSelectParallel(b *testing.B) {
InitServerIndex()
b.ResetTimer()
b.RunParallel(func(pb *testing.PB) {
for pb.Next() {
FastSelect()
}
})
}
结果:
BenchmarkFastSelectParallel-16 1000000000 0.5274 ns/op
四、总结
- Golang提供了简单而强大的测试工具,而且根据Golang的规则,也使得开发人员能够一眼就明白某个单元测试对应于哪个函数。
- 使用第三方单元测试工具包能够简化我们的代码。
- 在需要使用到外部依赖的情况下,我们可以利用Mock测试来模拟外部依赖,避免发生不必要的错误。
- 基准测试能够得出一段程序的运行性能,便于开发者进行优化,例如上文给出的“随机选择执行服务器”例子。
边栏推荐
- 远程办公之如何推进跨部门项目协作 | 社区征文
- Depth first search of graph
- 一位普通程序员一天工作清单
- [RT thread] construction and use of --hwtimer of NXP rt10xx device driver framework
- SWM32系列教程4-端口映射及串口应用
- Atom QT 16_ audiorecorder
- visual studio “通常每个套接字地址(协议/网络地址/端口)只允许使用一次“
- UCORE overview
- ANOVA example
- [combinatorics] recursive equation (definition of general solution | structure theorem of general solution of recursive equation without multiple roots)
猜你喜欢
One brush 145 force deduction hot question-2 sum of two numbers (m)

Pools de Threads: les composants les plus courants et les plus sujets aux erreurs du Code d'affaires

建立自己的网站(23)
ucore概述

Thread pool: the most common and error prone component of business code
![Luogu: p1155 [noip2008 improvement group] double stack sorting (bipartite graph, simulation)](/img/be/4ef38f711e7319a2cc83db2bee3a07.jpg)
Luogu: p1155 [noip2008 improvement group] double stack sorting (bipartite graph, simulation)
kubernetes资源对象介绍及常用命令(五)-(NFS&PV&PVC)

Test your trained model

【RT-Thread】nxp rt10xx 设备驱动框架之--Audio搭建和使用
大变局!全国房价,跌破万元大关
随机推荐
visual studio “通常每个套接字地址(协议/网络地址/端口)只允许使用一次“
Recommendation of good books on learning QT programming
Luogu: p2685 [tjoi2012] Bridge
图之深度优先搜索
在iptables防火墙下开启vsftpd的端口
C language string inversion
网络安全web渗透技术
One brush 146 force buckle hot question-3 longest substring without repeated characters (m)
网络硬盘NFS的安装与配置
Svn full backup svnadmin hotcopy
Luogu: p1155 [noip2008 improvement group] double stack sorting (bipartite graph, simulation)
Vs code plug-in korofileheader
The most complete postman interface test tutorial in the whole network, API interface test
[combinatorics] recursive equation (general solution structure of recursive equation with multiple roots | linear independent solution | general solution with multiple roots | solution example of recu
C language modifies files by line
聊聊接口优化的几个方法
HP 阵列卡排障一例
One brush 145 force deduction hot question-2 sum of two numbers (m)
Unity notes unityxr simple to use
Atom QT 16_ audiorecorder