当前位置:网站首页>Nanny hand-in-hand teaches you to write Gobang in C language
Nanny hand-in-hand teaches you to write Gobang in C language
2022-07-06 10:23:00 【East-sunrise】
Sanzi 、 Mine clearance ...... These games are not unfamiliar to you ? But if you can program these games by yourself , That should be a cool thing
Catalog
One 、 Sanzi game display and introduction
Two 、 Programming of Sanzi chess game
1. Game start interface and code prototype template
4. Player and computer chess design
5. Game winning and losing decision design
3、 ... and 、 The final code is rendered
Preface
C After learning functions and arrays , We can write some classic games by ourselves . This enables us to master knowledge more skillfully . Today we will pass C Language , To achieve a simple version of three chess games ! Now let's work together step by step !!
One 、 Sanzi game display and introduction
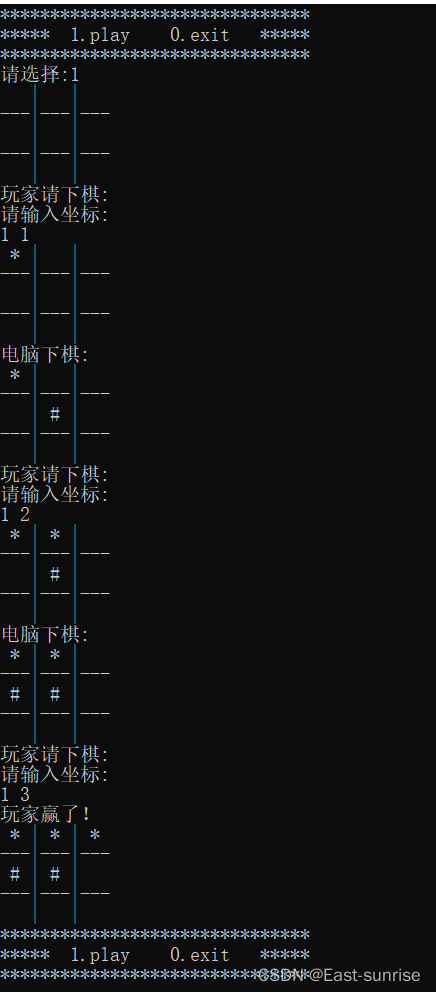
Before we start sharing today , Let's have a general understanding of the final presentation of the game and prepare the programming ideas first
- First, before the game starts , There will be a start menu for players to choose , You can choose whether to play or not
- When the player chooses to start the game, it immediately presents a chessboard that allows the player to play chess
- Then there is the process of the game , Players and computers play chess respectively for man-machine game
- As the game goes on, it will decide whether to win or lose the game and give the result
- Finally, when the game is over, the selection menu will appear again for players to choose whether to continue the game
️ When we have a general design and idea of the game we are going to realize, we can start our programming journey ~~
Two 、 Programming of Sanzi chess game
1. Game start interface and code prototype template
Before we start programming, we should have mastered the knowledge of functions , Because the code of the game is not very simple and will be divided into many parts . At this time, we need to use the encapsulation function to make our program more concise and readable .
️ Here I want to share a little experience of my own :
When we have mastered functions , When you want to start programming, you can first follow the idea to give a program prototype , When you want to realize what functions, you can first define a function , Wait until the idea is clear before implementing the function
Code display :
int main()
{
int input = 0;
do {
Menu();
printf(" Please select :");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch(input)
{
case 1:
Game();
break;
case 0:
printf(" Quit the game \n");
break;
default:
printf(" Wrong choice !\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}- The above code is the prototype template of the Sanzi game , It can also be understood as our programming idea to realize this game . According to the functions we want to realize, I also encapsulated the functions according to the idea . Such as Menu( )、Gmae( )
- And through our opening game display and ideas , We want players to be able to play games more than once ( Sanzi chess may be a little naive for primary school students , But college students are just fine ) So we should create a loop structure
- secondly , When the program is running, the start menu of the game will appear , That is to say, the menu has been printed out before judgment , It has been executed once ------> Then we should adopt do......while structure
- And when you make a choice , It should be able to perform different functions after judging according to the choices you make ------> Then we can adopt switch structure . Here is a small design that can make the code more concise , We can find out , When we choose 0 When you exit the game, you exit the cycle , When input is not 0 The choice will continue to cycle . Then we can just put our input variable input Put it in do......while Structural while Determine the position .
When the program prototype and ideas have been preliminarily formed , Then the concrete realization of the game began .
First of all Menu() Implementation of function , Is to print out the game start menu . This function is relatively simple , I'll just go over it here .
void menu() {
printf("*******************************\n");
printf("***** 1.play 0.exit *****\n");
printf("*******************************\n");
}Then there is right Game( ) Implementation of function . This is the highlight of today ️......
2. Build a chessboard
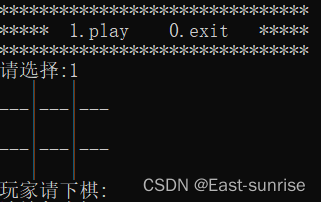
- When we choose to start the game, we will first present an initial chessboard , This chessboard looks simple, but it's not
- We should think of , This is a board for us to play chess next , Instead of simply using printf Function can print out a few lines and columns . And we and every piece under the computer will be saved on the chessboard until the end of this round of game . That means the chessboard must have the function of storing elements -------> Array
- you 're right , It's an array. . So building a chessboard is equivalent to initializing an array , And the array elements are initialized to spaces . So we can Game() Function, and then encapsulate a function to initialize the chessboard InitBoard().
- After initializing the chessboard, the chessboard presentation should be printed , Here we can encapsulate a function that renders a chessboard DisplayBoard(). Initializing the chessboard and printing the chessboard are also operations on the array , So for these two functions, we should pass in the array and the number of rows and columns of the chessboard
- And when printing the chessboard, we also need to print the division line of each chessboard , This is also the problem we should consider
Code display :
void InitBoard(char board[3][3], int 3, int 3)
{
for(int i = 0;i<3;i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
board[i][j] = ' ';
}
}
void DispalyBoard(char board[3][3], int 3, int 3)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
printf(" %c | %c | %c \n", board[i][0], board[i][1], board[i][2]);
// Print split lines
if (i < row - 1)// Building this judgment can make the last line of the chessboard have no split lines
printf("---|---|---\n");
}
}After reading the above code, do you have any findings or ideas ?
If one day , Want to pursue higher difficulty , Not limited to three chess . Want to become Gobang ? Cross chess ? Don't you want to put everything in the code “3” Change everything ? And there will also be errors in the division of the chessboard, which needs to be rewritten .
So the above program was written by us “ die ” 了 , That is, the coupling degree of the code is too high , Poor expansion . Then we need to do “ Decoupling ” So as to improve the expansion of our program
We can define macros at the beginning of the program #define, Define the number of lines of the chessboard ROW And number of columns COL, And optimize the function of printing chessboard .
Optimized version code display :
#define ROW 3
#define COL 3
void InitBoard(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col)
{
for(int i = 0;i<row;i++)
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
board[i][j] = ' ';
}
}
void DisplayBoard(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col)
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
// Print data
//printf(" %c | %c | %c \n", board[i][0], board[i][1], board[i][2]);
// Print each line of the chessboard and think about what you can think of as the same group
// Then carry out a conditional cycle
// At this time you will find , Space + data + Space + | It's a group.
// There is no delimiter in the last one , Then print several groups of columns
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf(" %c ", board[i][j]);
if (j < col - 1)
printf("|");
}
printf("\n");
// Print split lines --- Don't forget to add a judgment so that the last line has no split line
//printf("---|---|---\n");
if (i < row - 1)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf("---");
if (j < col - 1)
printf("|");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}notes : The above is for initializing the checkerboard function IntialBoard() and Render checkerboard function DisplayBoard() The definition of . When printing the separator of the chessboard, I want to improve the expansion of the program , So it's a little difficult . I present the relevant thoughts through comments in the code .
3. transition
According to the first part of the game show and its ideas , We have completed the game start menu and game functions Game() Part of the function of ( Initialize chessboard 、 Present chessboard ) What will be achieved next is the focus of the game ------ Man machine game function . Similarly, we can first present our general thinking framework by defining functions .
We are going to design players to play chess before computers , And after each side finishes playing chess, a new chessboard appears . At the same time, it should also have the function of judging whether to win or lose . So I probably built the following framework
void game() { char board[ROW][COL] = { ' ' }; InitialBoard(board, ROW, COL); DisplayBoard(board, ROW, COL); while (1) { PlayerMove();// The player is down DisplayBoard(board, ROW, COL); IsWin() // Determine the winning or losing mechanism ComputerMove();// Computer move later DisplayBoard(board, ROW, COL); IsWin() // Determine the winning or losing mechanism } }In this framework, I define the player's chess function PlayerMove( ), Computer chess function ComputerMove( ), There is also a win or lose judgment function IsWin( ). Next, we will implement them one by one .
4. Player and computer chess design
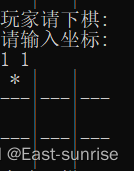
- From the display of the game, we can know , When we want players to play chess, we just need to enter the coordinates of the chess grid to play chess . The row and column coordinates of the array are from 0 At the beginning , But maybe players don't know this, right ? So this is the problem we should solve next .
- secondly , What else can we consider ? Play chess , Is it possible to go to the wrong position , Not on the chessboard ? It may also be that there are chessmen in the lower position ? So we should judge the legitimacy of playing chess coordinates
Code display :
void PlayerMove(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col)
{
int x, y;
printf(" Players please play chess :\n");
while (1)
{
printf(" Please enter the coordinates :\n");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
// Legal judgment of coordinate range
if (x >= 1 && x <= row && y >= 1 && y <= col)
{
if (board[x - 1][y - 1] == ' ')
{
board[x - 1][y - 1] = '*';
break;
}
else
{
printf(" This position has been lowered , You can't play chess , Please choose another location \n");
}
}
else
{
printf(" Illegal coordinates , Please re-enter \n");
}
}
}
When players play chess, they play chess by computer . And our simple version of Sanzi game is designed for computer chess , There is no strategy , Randomly find a space to play chess . So this random , You need to call our function to generate random numbers .
To reference a header file #include<stdlib.h> 、 #include<time.h>
Then set the random number in the main function srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
The specific principle is not much more detailed here
Code display :
void ComputerMove(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col)
{
printf(" The computer plays chess :\n");
int x, y;
// Determine whether the coordinates are occupied
while (1)
{
x = rand() % row;// The range is 0~row
y = rand() % col;
if (board[x][y] == ' ')
{
board[x][y] = '#';
break;
}
}
}5. Game winning and losing decision design
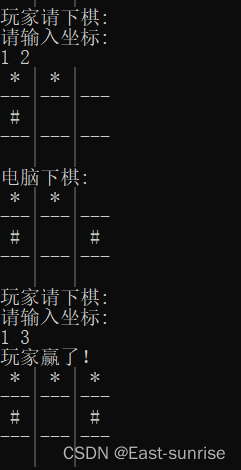
- You must know the rules of sanziqi , So the function of judging whether we win or lose is actually a process of traversing the array , See if there are three identical elements connected
- And the judgment of winning or losing should be executed every time you play chess , If there is a result, end the game , Return results
- Then at this time, we should think about a problem : How many results are there after judgment ?-------1. Game player wins 2. Computers win 3. It ends in a draw ( The chessboard is full ) 4. We haven't decided yet , The game goes on
- At the end of the day , Winning or losing judgment should return different results , And make different responses according to different results . Then we can design when players win , return ‘ * ’, Return when the computer wins ‘ # ’, Return when the game is tied ‘ Q ’, Return before deciding the outcome ‘ C ’️
Code display :
char IsWin(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col)
{
// Judge first
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
if (board[i][0] == board[i][1] && board[i][1] == board[i][2] && board[i][1] != ' ')
{
return board[i][1];
}
}
// Column
for (int i = 0; i < col; i++)
{
if (board[0][i] == board[1][i] && board[1][i] == board[2][i] && board[1][i] != ' ')
{
return board[1][i];
}
}
// Diagonals
if (board[0][0] == board[1][1] && board[1][1] == board[2][2] && board[1][1] != ' ')
{
return board[1][1];
}
if (board[0][2] == board[1][1] && board[1][1] == board[2][0] && board[0][2] != ' ')
{
return board[1][1];
}
// Coming here means no one wins , It could be a draw
if (IsFull(board,row,col))
{
return 'Q';
}
// If no one wins, it's not a draw , The game goes on
return 'c';
}In the process of designing the winning or losing judgment function , Because the chessboard is full, the result of the draw will be returned , So let's package another IsFull() Function to judge whether the chessboard is full ️
int IsFull(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col)
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
if (board[i][j] == ' ')
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}After completing the implementation of the chess function and the win or lose judgment function , Our code is also coming to an end . The rest is design Game( ) The function makes different reactions according to the different results of the win or lose judgment function .
Code display :
void game()
{
char ret = 0;
char board[ROW][COL] = { 0 };
InitBoard(board, ROW, COL);
DisplayBoard(board, ROW, COL);
// Start playing chess
while (1)
{
PlayerMove(board, ROW, COL);
// Judgement of winning or losing
ret = IsWin(board,ROW,COL);
if (ret != 'c')
{
break;
}
DisplayBoard(board, ROW, COL);
ComputerMove(board, ROW, COL);
// Judgement of winning or losing
ret = IsWin(board,ROW,COL);
if (ret != 'c')
{
break;
}
DisplayBoard(board, ROW, COL);
}
if (ret == '*')
{
printf(" The player won !\n");
}
else if (ret == '#')
{
printf(" The computer won !\n");
}
else
{
printf(" It ends in a draw !\n");
}
DisplayBoard(board, ROW, COL);
}
3、 ... and 、 The final code is rendered
Because there are many functions in this code , We can start another one with .h Place function declarations specifically for suffix header files , Start another one with .c Define functions for the source files of suffixes , In this way, the source file of our game test is relatively simple and easy to read
1.test.c file
#include"game.h"
void menu() {
printf("*******************************\n");
printf("***** 1.play 0.exit *****\n");
printf("*******************************\n");
}
void game()
{
char ret = 0;
char board[ROW][COL] = { 0 };
InitBoard(board, ROW, COL);
DisplayBoard(board, ROW, COL);
// Start playing chess
while (1)
{
PlayerMove(board, ROW, COL);
ret = IsWin(board,ROW,COL); // Judgement of winning or losing
if (ret != 'c')
{
break;
}
DisplayBoard(board, ROW, COL);
ComputerMove(board, ROW, COL);
ret = IsWin(board,ROW,COL); // Judgement of winning or losing
if (ret != 'c')
{
break;
}
DisplayBoard(board, ROW, COL);
}
if (ret == '*')
{
printf(" The player won !\n");
}
else if (ret == '#')
{
printf(" The computer won !\n");
}
else
{
printf(" It ends in a draw !\n");
}
DisplayBoard(board, ROW, COL);
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
int input = 0;
do {
menu();// Print menu
printf(" Please select :");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch(input)
{
case 1:
game(); // Start the game
break;
case 0:
printf(" Quit the game \n");
break;
default:
printf(" Wrong choice !\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}2.game.h file
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#define ROW 3
#define COL 3
// Initialize chessboard
void InitBoard(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col);
// Print chessboard
void DisplayBoard(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col);
// Players play chess
void PlayerMove(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col);
// The computer plays chess
void ComputerMove(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col);
// Win or lose judgment
char IsWin(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col);3.game.c file
#include"game.h"
void InitBoard(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col)
{
for(int i = 0;i<row;i++)
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
board[i][j] = ' ';
}
}
void DisplayBoard(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col)
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf(" %c ", board[i][j]);
if (j < col - 1)
printf("|");
}
printf("\n");
if (i < row - 1)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
printf("---");
if (j < col - 1)
printf("|");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
// Players play chess
void PlayerMove(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col)
{
int x, y;
printf(" Players please play chess :\n");
while (1)
{
printf(" Please enter the coordinates :\n");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
// Legal judgment of coordinate range
if (x >= 1 && x <= row && y >= 1 && y <= col)
{
if (board[x - 1][y - 1] == ' ')
{
board[x - 1][y - 1] = '*';
break;
}
else
{
printf(" This position has been lowered , You can't play chess , Please choose another location \n");
}
}
else
{
printf(" Illegal coordinates , Please re-enter \n");
}
}
}
// The computer plays chess
void ComputerMove(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col)
{
printf(" The computer plays chess :\n");
int x, y;
// Determine whether the coordinates are occupied
while (1)
{
x = rand() % row;// The range is 0~row
y = rand() % col;
if (board[x][y] == ' ')
{
board[x][y] = '#';
break;
}
}
}
int IsFull(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col)
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
if (board[i][j] == ' ')
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
// Judgement of winning or losing
char IsWin(char board[ROW][COL], int row, int col)
{
// Judge first
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
if (board[i][0] == board[i][1] && board[i][1] == board[i][2] && board[i][1] != ' ')
{
return board[i][1];
}
}
// Column
for (int i = 0; i < col; i++)
{
if (board[0][i] == board[1][i] && board[1][i] == board[2][i] && board[1][i] != ' ')
{
return board[1][i];
}
}
// Diagonals
if (board[0][0] == board[1][1] && board[1][1] == board[2][2] && board[1][1] != ' ')
{
return board[1][1];
}
if (board[0][2] == board[1][1] && board[1][1] == board[2][0] && board[0][2] != ' ')
{
return board[1][1];
}
if (IsFull(board,row,col))
{
return 'Q';
}
// If no one wins, it's not a draw , The game goes on
return 'c';
}Four 、 Experience
This code can be regarded as the most difficult one I have learned to write so far , Learning also benefits a lot . In fact, it does not use much knowledge , It mainly uses arrays 、 Knowledge of functions . What we gain more is a programming experience of optimizing and expanding step by step along the idea , Although sometimes I feel difficult to move forward , But after solving one level after another, the sudden openness and sense of achievement are intoxicating and enjoyable .
That's all for today's sharing , Welcome to discuss and make suggestions !️️ Praise and pay attention to a wave ~~~
边栏推荐
- The appearance is popular. Two JSON visualization tools are recommended for use with swagger. It's really fragrant
- Preliminary introduction to C miscellaneous lecture document
- AI的路线和资源
- South China Technology stack cnn+bilstm+attention
- 好博客好资料记录链接
- Chrome浏览器端跨域不能访问问题处理办法
- [after reading the series of must know] one of how to realize app automation without programming (preparation)
- MySQL real battle optimization expert 08 production experience: how to observe the machine performance 360 degrees without dead angle in the process of database pressure test?
- Pointer learning
- Routes and resources of AI
猜你喜欢
![[after reading the series of must know] one of how to realize app automation without programming (preparation)](/img/eb/e789d88f10787c302f9457ca7ca2cc.jpg)
[after reading the series of must know] one of how to realize app automation without programming (preparation)
UnicodeDecodeError: ‘utf-8‘ codec can‘t decode byte 0xd0 in position 0成功解决
History of object recognition
Const decorated member function problem
Contest3145 - the 37th game of 2021 freshman individual training match_ C: Tour guide
Pytorch LSTM实现流程(可视化版本)
What should the redis cluster solution do? What are the plans?
Export virtual machines from esxi 6.7 using OVF tool
![[after reading the series] how to realize app automation without programming (automatically start Kwai APP)](/img/e1/bad9cfa70d3c533cfaddeee40b96f1.jpg)
[after reading the series] how to realize app automation without programming (automatically start Kwai APP)
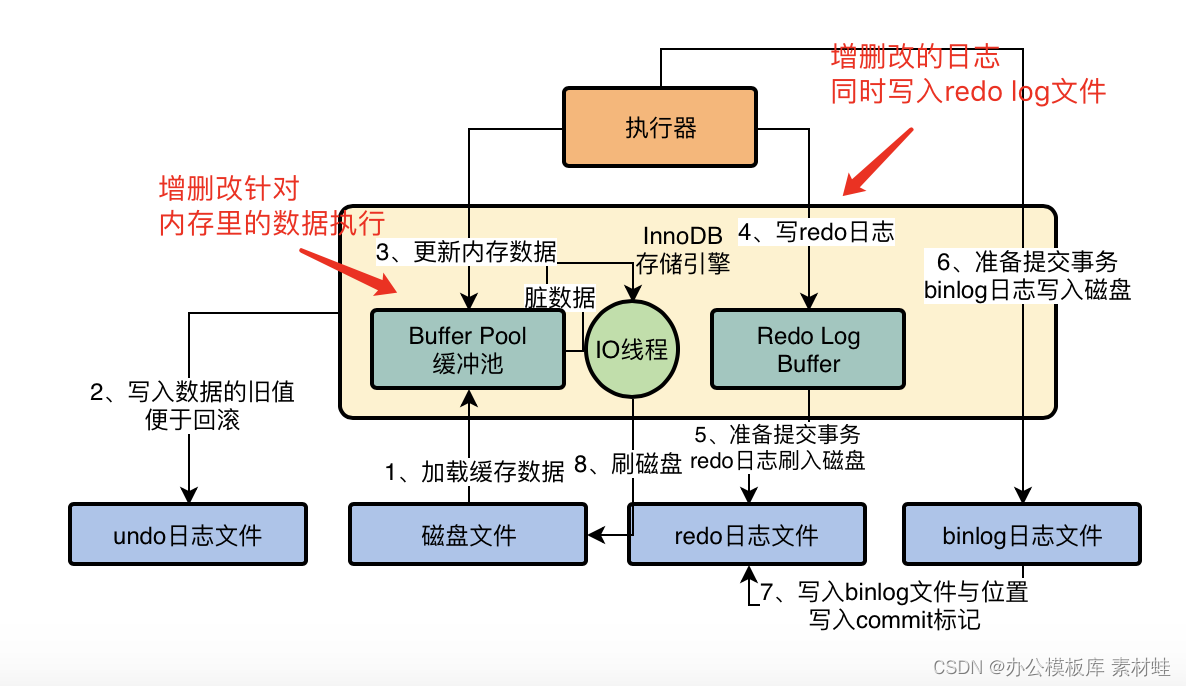
MySQL实战优化高手11 从数据的增删改开始讲起,回顾一下Buffer Pool在数据库里的地位
随机推荐
In fact, the implementation of current limiting is not complicated
MySQL combat optimization expert 06 production experience: how does the production environment database of Internet companies conduct performance testing?
The 32-year-old fitness coach turned to a programmer and got an offer of 760000 a year. The experience of this older coder caused heated discussion
Installation de la pagode et déploiement du projet flask
Good blog good material record link
Inject common SQL statement collation
解决在window中远程连接Linux下的MySQL
Contest3145 - the 37th game of 2021 freshman individual training match_ B: Password
百度百科数据爬取及内容分类识别
颜值爆表,推荐两款JSON可视化工具,配合Swagger使用真香
C杂讲 文件 初讲
Simple solution to phpjm encryption problem free phpjm decryption tool
使用OVF Tool工具从Esxi 6.7中导出虚拟机
MySQL实战优化高手05 生产经验:真实生产环境下的数据库机器配置如何规划?
The governor of New Jersey signed seven bills to improve gun safety
软件测试工程师必备之软技能:结构化思维
Use xtrabackup for MySQL database physical backup
Anaconda3 安装cv2
Time in TCP state_ The role of wait?
14 医疗挂号系统_【阿里云OSS、用户认证与就诊人】