当前位置:网站首页>Depth analysis based on synchronized lock
Depth analysis based on synchronized lock
2020-11-09 12:28:00 【AnonyStar】

1. Problem introduction
The kids have been exposed to threads , They also use threads , Today we are going to talk about thread safety , Before that, let's look at a simple code case . Code case :
/**
* @url: i-code.online
* @author: AnonyStar
* @time: 2020/10/14 15:39
*/
public class ThreadSafaty {
// Shared variables
static int count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create thread
Runnable runnable = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
count ++;
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(runnable,"Thread-"+i).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("count = "+ count);
}
}
Execution results :
Problem specification
In the above code we can see , Defines a thread runnable The public member variables are ++ operation , And cycle five times , One millisecond at a time , And then we're in the main thread main Method to create 100 threads and start , Then the main thread sleeps for five seconds to wait for all threads to finish . We expect the result to be 500 . But after the actual implementation, we found that count The value of is not fixed , Less than 500 Of , This is the problem of data security caused by multithreading !
Through the above cases, we can clearly see the problem of thread safety , So let's see if there is any way to avoid this kind of security problem ? We can imagine that the reason for this security problem is that we have access to shared data , So whether we can change the process of thread access to shared data into a serial process, then there is no such problem . Here we can think of what we said before **
lock** , We know that locking is a synchronous way to handle concurrency , At the same time, it is also mutually exclusive , stay Java Locking is achieved bysynchronizedkeyword
2. The basic knowledge of lock
2.1 Synchronized The understanding of
stay Java We know that there is a keyword of the rank of the elder synchronized , It's the key to locking , But we always think of it as a heavyweight lock , In fact as early as jdk1.6 A lot of optimization has been done on it , Make it very flexible . It's not always a heavyweight lock anymore , It's the introduction of ** Biased locking ** and ** Lightweight lock . ** We will introduce in detail .
synchronized The basic use of
synchronizedmodification Example method , Locks on the current instancesynchronizedmodification Static methods , Locks on the current class object ,synchronizedmodification Code block , Specify the lock object , Lock a given object ,
In the above case , We're going to get into being
synchronizedModify the synchronization code before , The corresponding lock must be obtained , In fact, this is also reflected in different types of modification , Represents the control granularity of the lock
- Let's revise the case we wrote earlier , By using
synchronizedKeywords make it thread safe
// Create thread
Runnable runnable = () -> {
synchronized (ThreadSafaty.class){
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
count ++;
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
Just add
synchronized (ThreadSafaty.class)Modification of , Put the content of the operation into the code block , Then thread safety will be achieved
- Through the above practice, we can intuitively feel
synchronizedThe role of , This is our usual use in development , Have you ever wondered , How is this lock stored and implemented ? So we're going to explore the mystery of it
Java The realization of middle lock
- We know that locks are mutually exclusive (
Mutual Exclusion) Of , So where does it mark its existence ? - We also know that multiple threads can acquire locks , Then locks must be shared
- What we are most familiar with
synchronizedWhat's the process of getting the lock ? How is its lock stored ? - We can observe
synchronizedThe grammar of , You can see **synchronized(lock)Is based onlockTo control the lock granularity ,** It must be understood here that , When we get the lock, we are an object , So is the lock related to this object ? - So far , We point all the key information to the object , So we need to take this as a starting point , Let's first understand that the object is in
jvmThe distribution form in , Let's look at how locks are implemented .
Memory layout of objects
-
Here we only talk about objects in
HeapLayout in , It doesn't involve too many details about the object creation process , We will elaborate on these contents in a separate article , Can pay attention toi-code.onlineBlog or wx" Yunqi code " -
In our most commonly used virtual machine
hotspotThe distribution of objects in memory can be divided into three parts : Object head (Header)、 Real data (Instance Data)、 The filling (Padding)
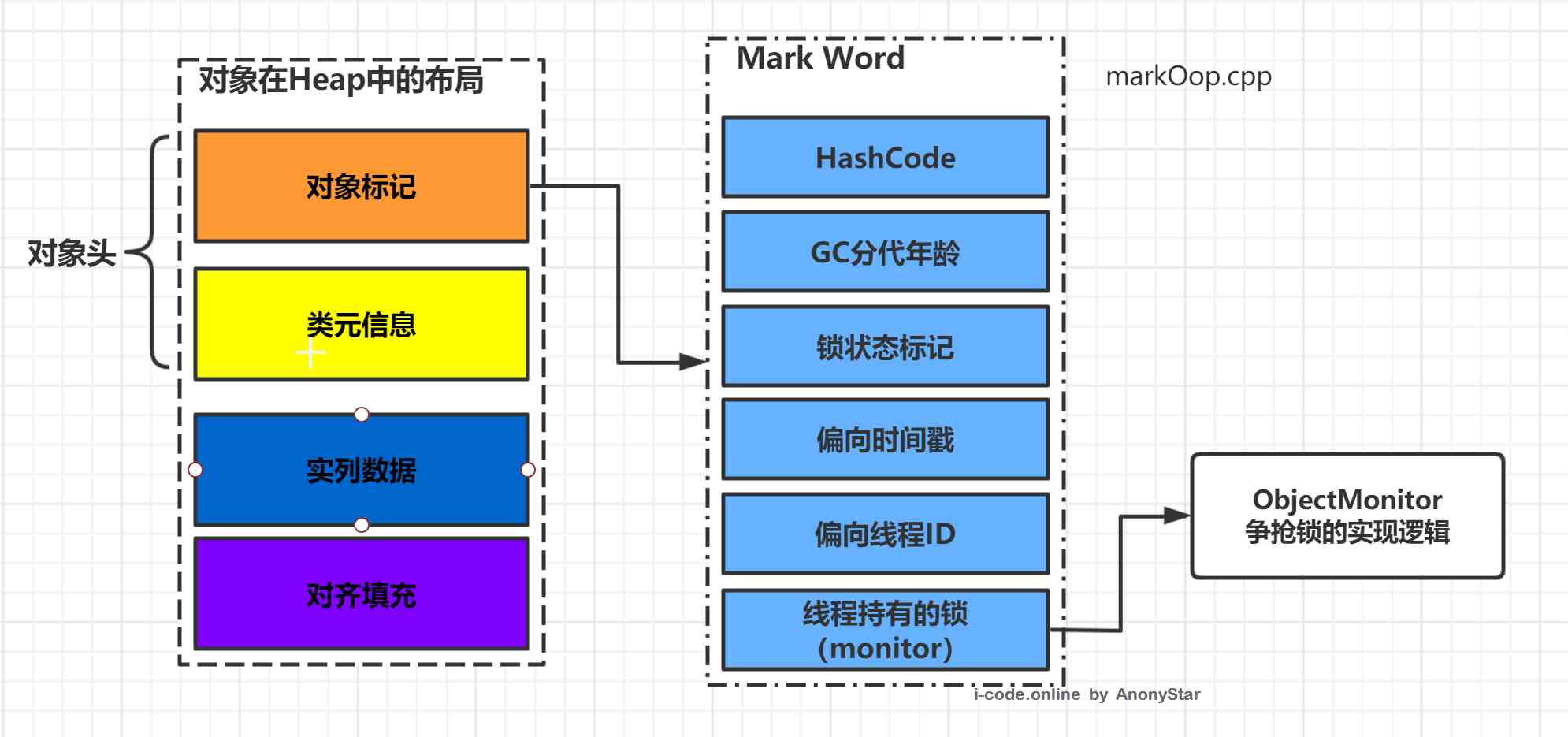
- From the above diagram, we can see that , Object in memory , It consists of three parts , The head of the object is divided into Object tags and class meta information , In the object tag, it mainly includes as shown in the figure
hashcode、GC Generational age 、 Lock flag State 、 Biased lock holding threads id、 A lock held by a thread (monitor) Wait for six things , The length of this part of data is 32 Bit and 64 The virtual machines of bit are respectively 32bit and 64bit, Officially, this part is calledMark Word. Mark WordIt's actually a data structure that can be dynamically defined , This allows a very small space to store as much data as possible , Reuse your own memory space according to the state of the object , For example 32 Bit of virtual machine , If the object is not locked by a synchronization lock ,Mark WordOf 32 In a bit memory cell ,25 To store hashcode ,4 One for storage GC Generational age ,2 Latch flag bits ,1 A fixed position 0, According to the distribution of each state, you can directly refer to the following chart
32 position HotSpot Virtual machine object header Mark Word
| The lock state | 25bit | 4bit | 1bit( Is it biased lock ) | 2bit( Lock flag position ) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23bit | 2bit | ||||
| unlocked | Object's HashCode | Generational age | 0 | 01 | |
| Biased locking | Threads ID | Epoch( Bias timestamp ) | Generational age | 1 | 01 |
| Lightweight lock | Pointer to the lock record in the stack | 00 | |||
| Heavyweight lock | A pointer to a heavyweight lock | 10 | |||
| GC Mark | empty | 11 |
What is said above is 32 Bit virtual machine , We need to pay attention to . Another part of the object header is the type pointer , Let's not go into details here , The concerns you want to know
i-code.online, Will continue to update the relevant content
- The following content will refer to the source code view , Need to download the source code in advance , If you don't know how to download , You can see 《 download JDK And Hotspot Virtual machine source code 》 This article , Or attention
Yunqi code. - In our familiar virtual machine
HotspotTo realizeMark WordCode inmarkOop.cppin , We can see the following clip , This is a description of the virtual machineMarkWordStorage layout of :
- When we're in
newWhen an object , The virtual machine layer actually creates ainstanceOopDescobject , Familiar to usHotspotVirtual machine usesOOP-KlassModel to describeJavaObject instances , amongOOPIt's the familiar common object pointer , andKlassIt describes the specific types of objects , stayHotspotWe useinstanceOopDescandarrayOopDescTo describe , amongarrayOopDescUsed to describe array types , - about
instanceOopDescWe can realize it fromHotspotSource code found in . Corresponding toinstanceOop.hppIn file , And the correspondingarrayOopDescstayarrayOop.hppin , Let's take a look at the relevant content :
- We can see
instanceOopDescInheritedoopDesc, andoopDescIt is defined inoop.hppin ,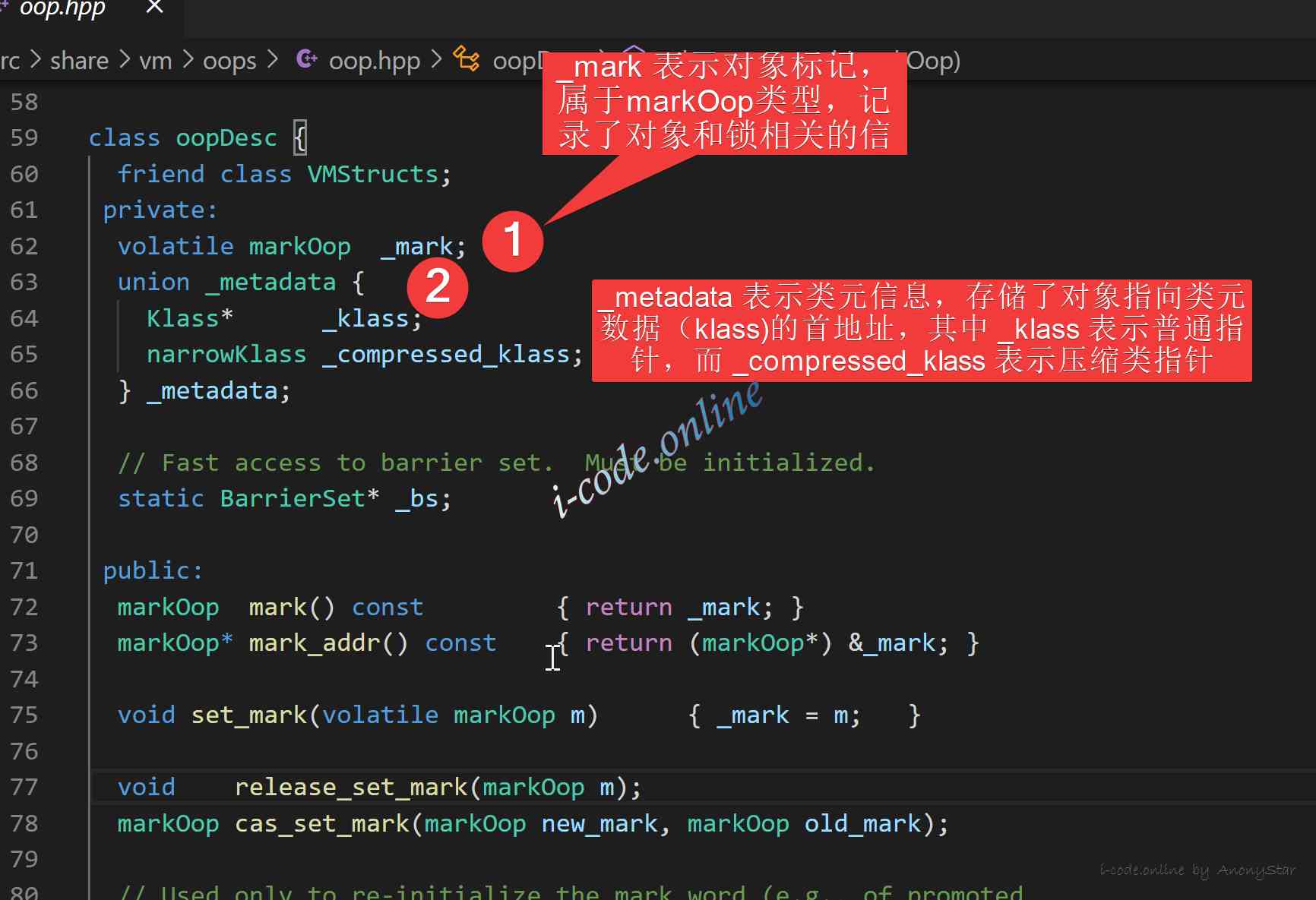
- We can see the relevant information in the above figure , The text is also annotated , So next we're going to explore
_markThe implementation of defines , as follows , We see it ismarkOopDesc
- Through code follow-up, we can find
markOopDescIn the definition ofmarkOop.hppIn file , As shown in the figure below :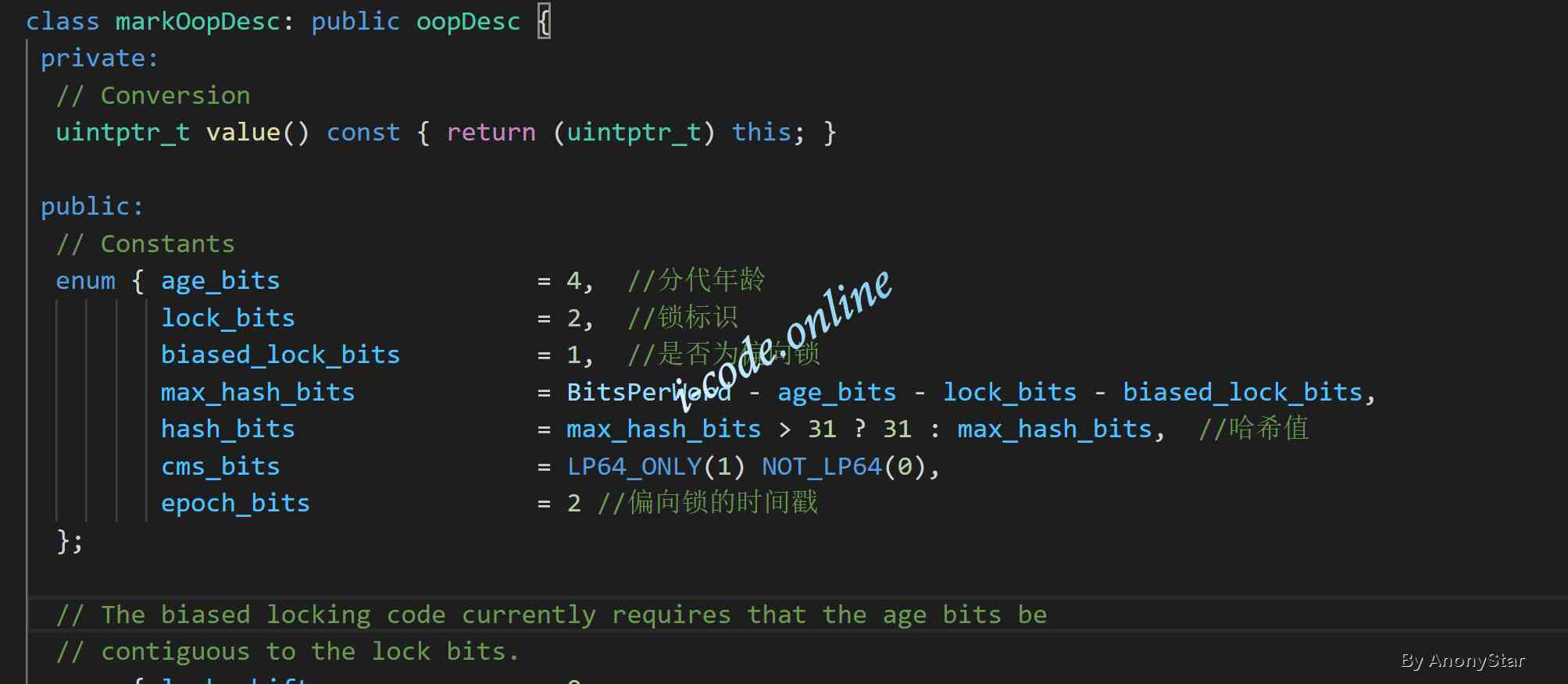
- In the above picture, we can see , There's an enumeration inside . Recorded
markOopStorage items in , So when we actually develop , WhensynchronizedWhen an object is used as a lock, then the information of the following series of locks is the same asmarkOoprelevant . As in the table abovemark wordThe distribution record shows the meaning of the specific parts - Because we're actually creating objects in jvm Layers will generate a
nativeOfc++objectoop/oopdescTo map , And every object has amonitorMonitor object for , Can be inmarkOop.hppsee , In fact, in multithreading, seizing the lock is just fighting formonitorTo modify the corresponding tag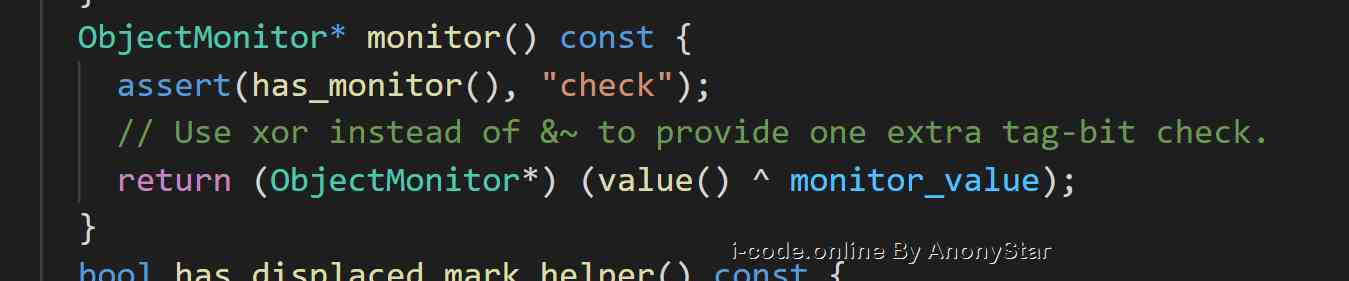
Synchronized In depth
- stay
JavainsynchronizedIs the most basic method to achieve mutual exclusion synchronization , It's a block structure (Block Structured) Synchronization syntax of , afterjavacAfter compiling, it will be formed before and after the blockmonitorrenterandmonitorexitTwo bytecode instructions , And they all need onereferenceType to indicate the lock object , The specific lock object depends onsynchronizedDecorated content , It has been said that it is not elaborated .
《 In depth understanding of Java virtual machine 》 This is described in : according to 《Java Virtual machine specification 》 The requirements of , In execution monitorenter When the command , First try to get the lock of the object . If This object is not locked , Or the current thread already has a lock on that object , Just increase the lock counter by one , And in the execution monitorexit The value of the lock counter is subtracted by one during the instruction . Once the value of the counter is zero , The lock was then released . If you get an object Lock failed , Then the current thread should be blocked and waiting , Until the object requesting the lock is released by the thread holding it
- So be
synchronizedDecorated blocks of code are reentrant to the same thread , This also avoids the possibility of deadlock caused by repeated entry of the same thread - stay
synchronizedLock the end of the code directly before releasing , It will block other threads after
Why do you say synchronized It's a heavyweight lock
- In terms of execution costs , Holding a lock is a heavyweight (
Heavy-Weight) Operation process , Because inJavaThreads in the operating system are mapped to the native kernel threads of the operating system , If you want to block and wake up a thread, you need to schedule it through the operating system , This will inevitably lead to the conversion between user mode and kernel mode , But this conversion is very processor time consuming , Especially for the program with simple business code , It may take longer than the execution of the business code itself , SosynchronizedIt's a massive operation , But in thejdk6After that, a lot of optimization has been done , Make it less heavy
Lock optimization
- stay
JDK5Upgrade toJDK6After a series of lock improvements , Optimize locks through a variety of techniques , Give WaysynchronizedNo longer as heavy as before , This involves adaptive spin (Adaptive Spinning)、 Lock elimination (Lock Elimination)、 Lock expansion (Lock Coarsening)、 Lightweight lock (LightWeight Locking)、 Biased locking (Biased Locking) etc. , These are all used to optimize and improve the competition of multi-threaded access to shared data .
Lock elimination
- Lock elimination is that the virtual machine requires synchronization of some code when the compiler is running , However, it is detected that there is no lock for shared data competition , The main criterion is based on escape analysis technology , I don't want to expand on this , The following related articles are introduced . Here we simply understand it as , If a piece of code , Data on the heap will not escape and be accessed by other threads , Then you can treat them as data on the stack , Think they're all thread private , Thus, there is no need to synchronize locking ,
- About whether variables in the code escape , For virtual machines, complex analysis is needed to get , But it's relatively intuitive for us developers , Some people may wonder why they need extra lock synchronization since developers can understand it ?, Actually , A lot of synchronization measures on the program are not what we developers join in , It is
javaThere's a lot of stuff inside , For example, the following typical example , Here is the addition of strings
private String concatString(String s1,String s2,String s3){
return s1 + s2 + s3;
}
- We know
StringClass isfinalDecorated immutable class , So the addition of strings is done by generating newStringLet's try the first one , So the compiler optimizes this operation , stayJDK5It will be converted toStringBufferObject'sappend()operation , And in theJDK5And then it turns intoStringBuilderObject to operate . So the above code is injdk5It could become something like this :
private String concatString(String s1,String s2,String s3){
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append(s1);
sb.append(s2);
sb.append(s3);
return sb.toString();
}
- Now , You can see that , about
StringBuffer.append()Method is a synchronous method , With synchronization fast , The lock object issb, At this time, the virtual machine through the analysis found thatsbThe scope of is restricted to methods , It is impossible to escape from the method and let other threads access it , So this is after instant compilation by the server-side compiler , All synchronization actions of this code will fail and will be executed directly .
The above code is chosen for the convenience of demonstration String, Actually, it's in jdk5 And then it's all converted to Stringbuilder , There is no such problem , But in jdk There are a lot of them .
Lock coarsening
- The vulgar language about lock is actually very simple to understand , We always recommend that synchronized code blocks be as small as possible during development , Try to synchronize only in the actual scope of the shared data , The goal is to minimize synchronization operations , Let other threads get the lock faster
- This is most of the time , But there are always special circumstances , For example, in a series of continuous operations are to lock and unlock the same object repeatedly , Then this can lead to unnecessary performance loss
- It's like the above
StringThe case of , In successionappendOperations are fragmented synchronization blocks , And it's all the same lock object , This will extend the scope of the lock , To the outside of the entire sequence of operations , That's the first oneappendFrom before to lastappendAfter the operation , Put them all in a synchronous lock , This avoids multiple lock acquisition and release .
spinlocks
- Through previous understanding , We know that suspending thread and recovering thread involve the conversion between user mode and kernel state , And these are very time-consuming , This will directly affect the concurrent performance of the virtual machine .
- In our normal development , If shared data is locked for a short period of time , It is a waste of resources to suspend the blocking thread for this short time . Especially now computers are basically multi-core processors , So on this premise , Whether we can let another thread that requests the lock object not to suspend , But wait a little bit , This wait will not give up
CPUExecution time of . Wait to see if the thread holding the lock can release the lock quickly , In fact, this waiting is like an empty cycle , This technique is called a spin lock - Spin locked in
JDK6Medium and is already enabled by default , stayjdk4The introduction of . Spin lock is not blocking, it can't replace blocking . - Spinlocks require a certain number of processors , At the same time, it will occupy
CPUThe time of the , Although it avoids the overhead of thread switching , But there is a balance between them , If the lock is occupied for a short time, then spin is very valuable , It will save a lot of time , But on the contrary , If the lock takes a long time , The spinning thread will consume processor resources in vain , It's a waste of performance . - So there has to be a limit to spinlocks , That's how many times it spins , Set a spin number , If this number is exceeded, the thread is suspended in the traditional way instead of self rotation ,
- The number of spins is ten by default . But we can also go through
-XX: PreBlockSpinParameters come from defining settings
Adaptive spinlock
- We know that we can customize the number of spins , But it's hard to have a reasonable value for this , After all, there are all kinds of situations in the program , We can't set a global . So in
JDK6After that, an adaptive spin lock is introduced , That is to optimize the original spin lock - The time of spin is no longer fixed , It is determined by the previous spin time on the same lock and the state of the lock owner , If it's on the same lock object , Spin wait has just successfully acquired a lock , And support locked threads running , Then the virtual machine will be tasked, and this spin will get the lock again , That would allow the spin to last longer
- Corresponding , If for a lock , The number of times spin gains lock is very small , Then when you want to acquire the lock, you will directly ignore the spinning process, and then directly block the thread to avoid wasting processor resources
Lightweight lock
- Lightweight locks are also
JDK6A new locking mechanism is added when the , It's lightweight compared to traditional locks implemented by operating system mutexes , Lightweight locks are also an optimization , Instead of replacing heavyweight locks , The original intention of lightweight lock is to reduce the performance consumption of traditional heavyweight locks using operating system Mutex without multithreading competition . - To understand lightweight locks, we have to have objects in
HeapWe know the distribution in , That is to say, the content mentioned above .
Lightweight lock plus lock
- When code is executed to a synchronized block of code , If the synchronization object is not locked, the lock flag bit is
01state , Then the virtual machine will first create a record named lock in the stack frame of the current threadLock RecordSpace - This lock record space is used to store the current
Mark WordA copy of the , The official added aDisplacedThe prefix of , namelyDisplaced Mark Word, As shown in the figure below , This isCASState of stack and object before operation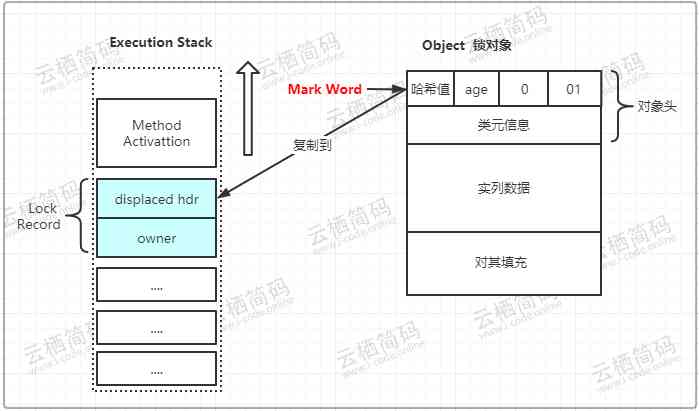
- When replication ends, the virtual opportunity passes through
CASThe operation attempts to put the object'sMark WordUpdate to pointLock RecordThe pointer to , If the update is successful, it means that the thread owns the lock of the object , And willMark WordThe lock flag bit ( The last two bits ) Turn into “00”, This means that the object is in a lightweight locked state , The state of the stack and object header is as follows :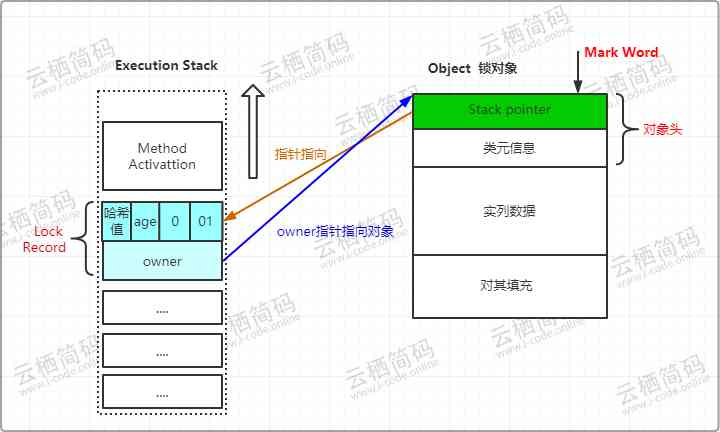
- If the above operation fails , That means that at least one thread competes with the current thread for the lock on the object , The virtual opportunity first checks the object's
Mark WordWhether to point to the current thread's stack frame , If it is , Indicates that the current thread already has a lock on this object , Then directly enter the synchronous code block to execute . Otherwise, the object has been preempted by other threads . - If there are more than two threads competing for the same lock , Then lightweight locks are no longer valid , Must inflate to a heavyweight lock , The tag bit of the lock becomes “10”, here
Mark WordStored in is a pointer to a heavyweight lock , The waiting thread must also be blocked
Unlocking of lightweight locks
- Lightweight locks are also unlocked by
CASoperations - If the object's
Mark WordStill point to the thread's lock record , Then useCASThe operation sets the object's currentMark WordAnd copied in threadsDisplaced Mark WordReplace it with - If the replacement is successful, the whole synchronization process ends , If it fails, it indicates that another thread is trying to acquire the lock , That's when you release the lock , Wakes up the suspended thread
Lightweight locks are suitable for most of the locks in the whole synchronization cycle without competition , Because if there's no competition , Lightweight locks can be passed through
CASSuccessful operation avoids the cost of using mutex , But if there is lock competition , In addition to the cost of the mutex itself, it has to happenCASThe cost of the operation , In this case, it's slower than a heavyweight lock
- The following is a complete flow chart to directly watch the lightweight lock locking and expanding process
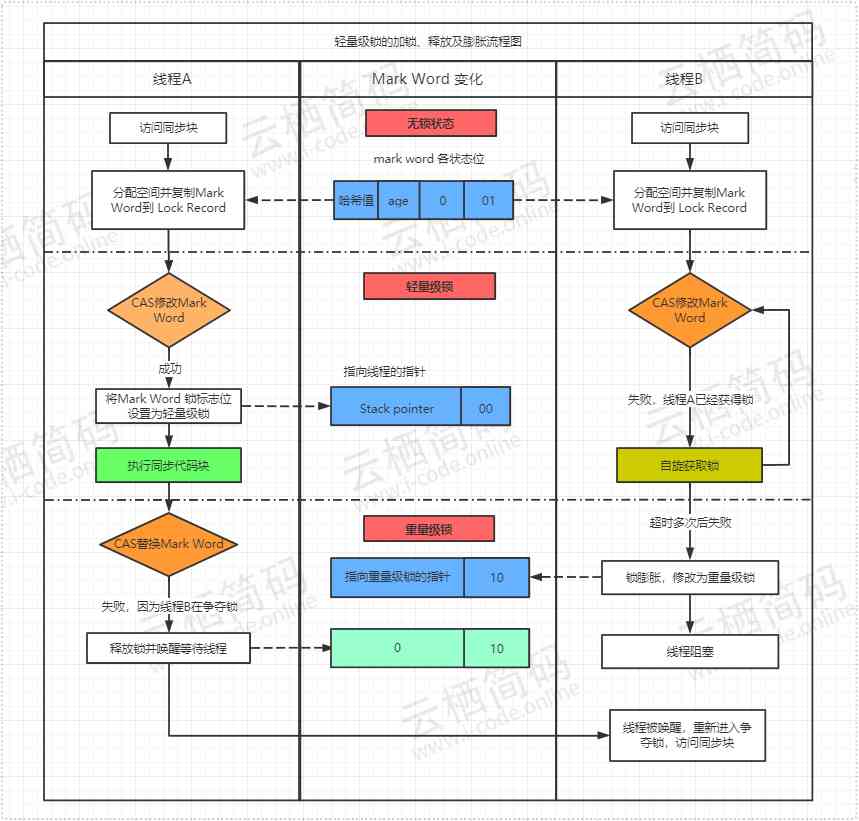
Biased locking
- Biased lock is also
JDK6A lock optimization technique is introduced , If the lightweight lock is passed without competitionCASThe operation eliminates the mutex used by synchronization , Then biased locking eliminates the entire synchronization without competition , evenCASThe operation is no longer done , As you can see, it's lighter than lightweight locks - From the distribution of object heads , There is no hash value in the biased lock, but there are more threads ID And
EpochTwo content - Biased locking means that the lock is biased toward the first thread that gets it , If the lock has not been acquired by other threads during the next execution , Then only lock biased threads will never need to synchronize again
Biased lock acquisition and revocation
- When code is executed to a synchronized block of code , The first time it is executed by a thread , The lock object is first acquired by thread , At this point, the virtual machine changes the lock flag in the object head to “01”, At the same time, change the bias lock flag bit to “1”, Indicates that the current lock object is in biased lock mode .
- Next, the thread passes through
CASOperation to put the frame of the thread ID Record to object header , IfCASsucceed . Then the thread holding the lock object enters the synchronization code and does not perform any synchronization operation ( Such as obtaining lock and unlocking ). Each time, it determines the current thread and the thread recorded in the lock object id Is it consistent . - If Aforementioned
CASOperation failed , That means there must be another thread getting the lock , And it was successful . In this case, there is lock competition , Then the biased pattern ends immediately , Partial lock revocation , Need to wait for global security ( There is no bytecode executing at this point in time ). It first pauses the thread that owns the biased lock , According to whether the lock object is in the locked state, whether or not to cancel the bias is determined, that is, to change the biased lock flag bit to “0”, If you undo it, it becomes unlocked (“01”) Or lightweight locks (“00”) - If the lock object is not locked , Then remove the biased lock ( Set the bias lock flag bit to “0”), At this time, the lock is not locked and cannot be biased , Because it has a hash value , It turns into a lightweight lock
- If the lock object is still locked, it will enter the lightweight lock state directly
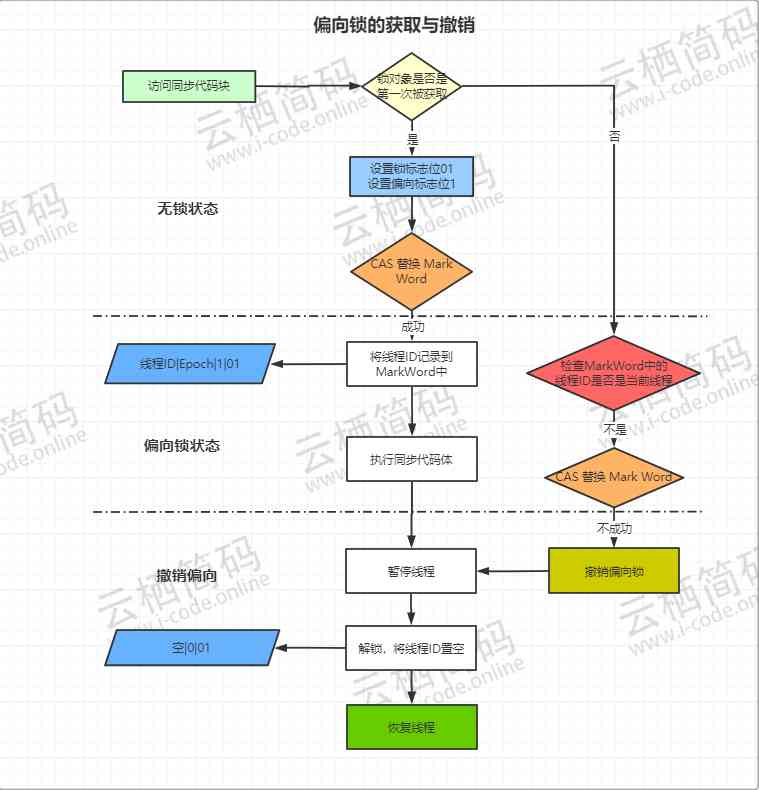
Bias lock switch
- Bias locked in
JDK6And then it's enabled by default . Due to biased locking, it is suitable for the scenario of lock free competition , If all the locks in our application are normally competitive , Can pass JVM Parameters Close the deflection lock :-XX:-UseBiasedLocking=false, Then the program will enter the lightweight lock state by default . - If you want to open the bias lock, you can use :
-XX:+UseBiasedLocking -XX:BiasedLockingStartupDelay=0
Heavyweight lock
- Heavyweight locks, that is, after the above optimizations are invalid , Inflate to a heavyweight lock , To achieve by mutex , Let's first look at the following code
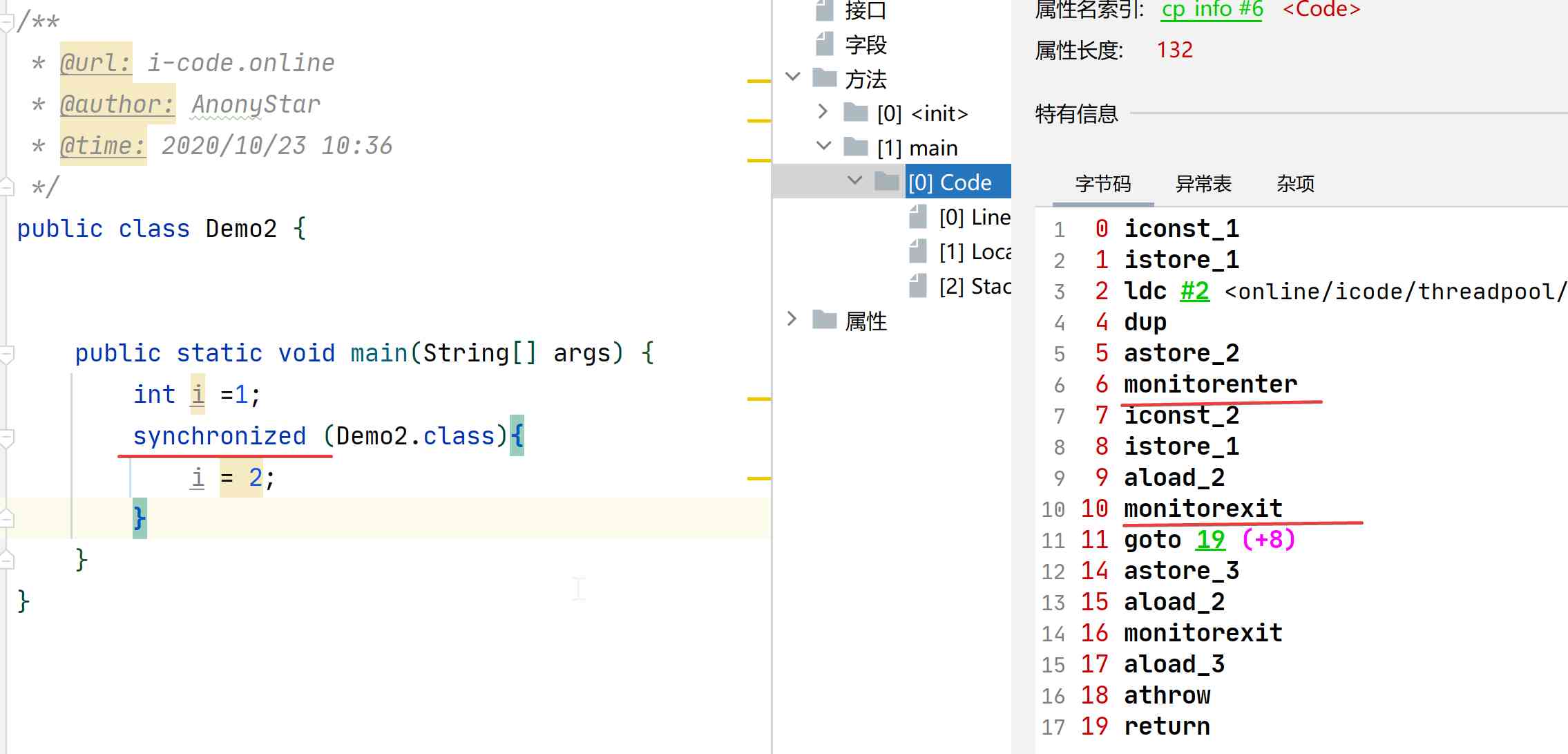
- The above code is a simple to use
synchronizedCode for , We can see the right window through bytecode tool . We found that , Before and after the synchronization code block formedmonitorenterandmonitorexitTwo instructions - stay Java There will be one in the present
monitorThe monitor , theremonitorenterThe instruction is to get the monitor of an object . And the correspondingmonitorexitTo release the monitormonitorThe ownership of the , Allow access by other threads monitorIt's system dependentMutexLock( The mutex ) To achieve , When a thread is blocked, it enters the kernel state , It will cause the system to switch between user mode and kernel mode , Which in turn affects performance
summary
- The above is about
synchronizedSome optimization and conversion of locks , When we turn on the bias lock and spin , The transformation of the lock is unlocked -> Biased locking -> Lightweight lock -> Heavyweight lock , - Spin lock is actually a kind of lock competition mechanism , Not a state . Spin is used in both biased and lightweight locks
- Biased locking is suitable for the scenario of lock free competition , Lightweight locks are suitable for scenarios without multiple thread contention
- Both biased and lightweight locks depend on
CASoperation , But in biased locks, only the first timeCASoperation - When an object has been computed a consistent hash , Then the object can no longer enter the biased lock state , If the object is in a lock biased state , And receive a request to calculate the hash value , Then his biased lock state will be revoked immediately , And it will inflate into a heavyweight lock . If that's why it's locked
MarkWordThere is no hash value in
This paper is written by AnonyStar Release , It can be reproduced, but the source of the original text should be stated . Welcome to the wechat public account : Yunqi code Get more quality articles More articles focus on the author's blog : Yunqi code i-code.online
版权声明
本文为[AnonyStar]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- 接口测试如何在post请求中传递文件
- Android Studio Avd「真·小白食用方法」
- 嗯,查询滑动窗口最大值的这4种方法不错....
- Suning's practice of large scale alarm convergence and root cause location based on Knowledge Map
- Kubernetes业务日志收集与监控
- EFF 认为 RIAA 正在“滥用 DMCA”来关闭 YouTube-DL
- Interface tests how to pass files in post requests
- Understanding data structures starts with this article~
- Is SEO right or wrong?
- 外贸自建网站域名的选择— Namesilo 域名购买
猜你喜欢
Handwritten digital image recognition convolution neural network
A simple ability determines whether you will learn!

真正拖垮你的,是沉没成本

Kubernetes business log collection and monitoring

Android rights
微信视频号播主排行榜2020年10月

SQL Chapter 2 Chapter 3

Adobe Experience Design /Xd 2020软件安装包(附安装教程)

inet_pton()和inet_ntop()函数详解

New features of Fedora 33 workstation
随机推荐
Detailed explanation of [golang] GC
Mapstructure detoxifies object mapping
Safety (miscellany)
Android Development - service application, timer implementation (thread + service)
What really drags you down is sunk costs
How to use function framework to develop large web application
Four steps of Android integrated payment
JVM学习(四)-垃圾回收器和内存分配
嗯,查询滑动窗口最大值的这4种方法不错...
EFF 认为 RIAA 正在“滥用 DMCA”来关闭 YouTube-DL
真正拖垮你的,是沉没成本
JVM learning (5) - execution subsystem
Go语言初始化单例变量的几种方法
Android check box and echo
【分布式】分布式锁都有哪些实现方案?
Using stream to read and write files to process large files
Clock service Android implementation of alarm clock
Fedora 33 Workstation 的新功能
Pay attention to the request forwarding problem of. Net core
移动安全加固助力 App 实现全面、有效的安全防护