Preface
Assertions are an integral part of a complete test case , Use cases only add assertions , Compare the actual results with the expected results , To judge whether it passes .
unittest The framework provides its own assertion method , Such as :assertEqual、assertTrue、assertIn etc. ,pytest It also has its own way of asserting , That is to use assert To assert that .
assert
pytest Use in python Source Ecology assert Field assertion .
Common assertions
pytest Common assertions are as follows :
- Judge whether it is equal ,assert Actual( The actual result ) == Expected( Expected results )
- Judge whether it is not equal ,assert Actual != Expected, Other such as >、<、>=、<= Can be used directly .
- Judge xx Is it true ,assert xx
- Judge xx Is it not true ,assert not xx
- Judge b Does it include a,assert a in b
- Judge b It doesn't contain a,assert a not in b
assert The asserted object can be a string 、int、float、list、dict、tuple Any type .
Examples of use
Customize an interface to query all user information , The format of the return parameter is as follows :
{
"code": 1000,
"data": [
{"id": 1, "username": " Lau Andy ", "sex": 0, "telephone": "12306", "address": " Kowloon, Hong Kong "},
{"id": 2, "username": " Anita Mui ", "sex": 1, "telephone": "95511", "address": " Huangpu District, Shanghai "},
{"id": 3, "username": " Danny chan ", "sex": 0, "telephone": "10086", "address": " Haidian District, Beijing "},
]
}
The use case assertions are as follows :
def test_get_all_users():
''' Query all user information '''
url = "http://127.0.0.1:5000/users"
res = requests.get(url=url).text
res = json.loads(res)
# Whether the assertion is equal
assert res['code'] == 1000
# Assertion returns results data Is it True( This is actually to judge whether it is empty )
assert res['data']
Andy = {"id": 1, "username": " Lau Andy ", "sex": 0, "telephone": "12306", "address": " Kowloon, Hong Kong "}
# Assertion returns results data Whether it contains Andy Lau's information
assert Andy in res['data']
Assertion passed :

Let's modify the script to make the assertion fail , as follows :
def test_get_all_users():
''' Query all user information '''
url = "http://127.0.0.1:5000/users"
res = requests.get(url=url).text
res = json.loads(res)
# Whether the assertion is equal
assert res['code'] == 1001
# Assertion returns results data Is it True( This is actually to judge whether it is empty )
assert not res['data']
Andy = {"id": 1, "username": " Lau Andy ", "sex": 0, "telephone": "12306", "address": " Kowloon, Hong Kong "}
# Assertion returns results data Whether it contains Andy Lau's information
assert Andy not in res['data']
The operation results are as follows :
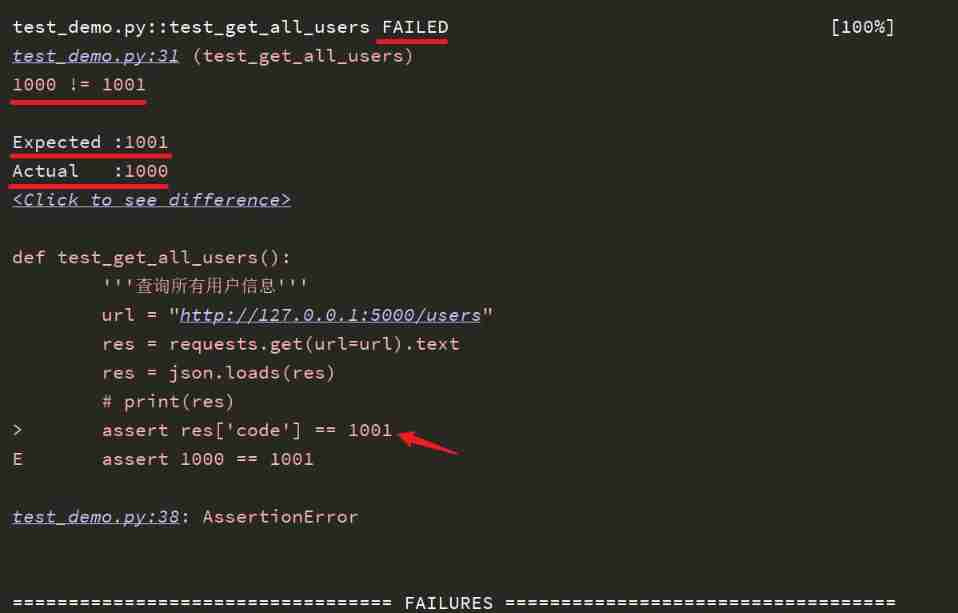
You can see ,code Of Actual by 1000, and Excepted by 1001, So the assertion directly reports an error , Do not continue to execute the following code .
Add exception information to the assertion result
We can assert exceptions , Output some hints , After such an assertion reports an error , It is convenient for us to check the reason .
The customized user information interface can query the information of a user , Write a test script for it as follows :
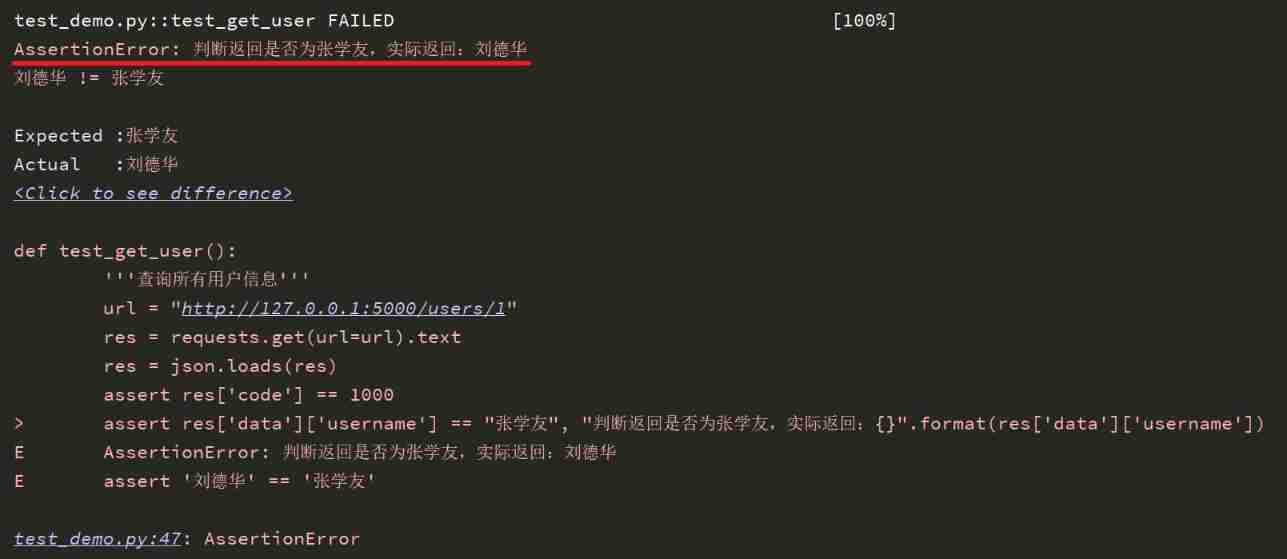
def test_get_user():
''' Query all user information '''
url = "http://127.0.0.1:5000/users/1"
res = requests.get(url=url).text
res = json.loads(res)
assert res['code'] == 1000
assert res['data']['username'] == " Jacky Cheung ", " Judge whether the return is Jacky Cheung , Actual return :{}".format(res['data']['username'])
The operation results are as follows :
summary
pytest It can also be used for Exception And Warnning To assert that , But these situations are rarely used in our tests , So don't elaborate too much .

![[uc/os-iii] chapter 1.2.3.4 understanding RTOS](/img/33/1d94583a834060cc31cab36db09d6e.jpg)
![[source code attached] Intelligent Recommendation System Based on knowledge map -sylvie rabbit](/img/3e/ab14f3a0ddf31c7176629d891e44b4.png)