当前位置:网站首页>Linear list --- circular linked list
Linear list --- circular linked list
2022-07-07 02:27:00 【Programming a small program】
Circular linked list : The characteristic of circular linked list is that the address of the head node can be found through the pointing of the tail node ;
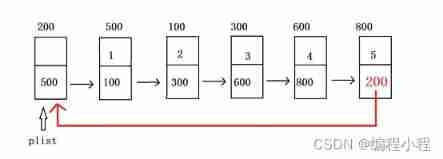
The structure design is the same as that of the single linked list :
typedef int ELEM_TYPE;
typedef struct Clist
{
ELEM_TYPE data; // Data fields
struct Clist* next; // Pointer to the domain
} Clist, * PClist;
The main functions are as follows :
1. Initialization operation
In the initialization operation of the circular list, the first node's next The domain points to its own address
void Init_clist(struct Clist* plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return;
}
plist->next = plist;
}2. Tail interpolation function
First apply for a new node pnewnode, And then take it. next The domain points to the address of the first node , Then apply for a temporary node p Point it to the address of the tail node , And then let p Of next Domain points to pnewnode The address of .
bool Insert_tail(PClist plist, ELEMTYPE val)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
//1. Buy new nodes
struct Clist *pnewnode = (struct Clist*)malloc(1 * sizeof(struct Clist));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
pnewnode->data = val;// New nodes purchased Finished processing
//2. Find the insertion location ( Through... With precursors for loop )
struct Clist *p = plist;
for(p; p->next!=plist; p=p->next);
// here for Loop execution ends p Point to the tail node
//3. Insert
pnewnode->next = p->next;
p->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}Circular linked list complete code
clist.h
// Circular linked list structure design
typedef int ELEMTYPE;
typedef struct Clist
{
ELEMTYPE data; // Data fields Storing data
struct Clist* next;// Pointer to the domain The address of the next node ( At the end next Save the address of the header node )
}Clist, *PClist;
// Circular linked list owned Executable function declaration :
// initialization
void InitClist(struct Clist* plist);
// Head insertion
bool Insert_head(PClist plist, ELEMTYPE val);
// Tail insertion
bool Insert_tail(PClist plist, ELEMTYPE val);
// Insert by position
bool Insert_pos(PClist plist, int pos, ELEMTYPE val);
// Head deletion
bool Del_head(PClist plist);
// Deletion at the end
bool Del_tail(PClist plist);
// Delete by location
bool Del_pos(PClist plist, int pos);
// Delete... By value
bool Del_val(PClist plist, ELEMTYPE val);
// lookup ( If I find , You need to return the address of the found node )
struct Clist* Search(struct Clist *plist, ELEMTYPE val);
// Sentenced to empty
bool IsEmpty(PClist plist);
// Full sentence ( Circular linked list does not need this operation )
// To obtain the length of the
int Get_length(PClist plist);
// Empty
void Clear(PClist plist);
// The destruction 1
void Destroy1(PClist plist);
// The destruction 2
void Destroy2(PClist plist);
// Print
void Show(struct Clist *plist);clist.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include "clist.h"
// There are few in the circular linked list NULL, nullptr
// initialization
void InitClist(struct Clist* plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return;
}
//plist->data; // Data fields do not handle
plist->next = plist;
}
// Head insertion
bool Insert_head(PClist plist, ELEMTYPE val)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
//1. Buy new nodes
struct Clist *pnewnode = (struct Clist*)malloc(1 * sizeof(struct Clist));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
pnewnode->data = val;// New nodes purchased Finished processing
//2. Find the insertion location ( Head insertion Don't look for )
//3. Insert
pnewnode->next = plist->next;
plist->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}
// Tail insertion
bool Insert_tail(PClist plist, ELEMTYPE val)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
//1. Buy new nodes
struct Clist *pnewnode = (struct Clist*)malloc(1 * sizeof(struct Clist));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
pnewnode->data = val;// New nodes purchased Finished processing
//2. Find the insertion location ( Through... With precursors for loop )
struct Clist *p = plist;
for(p; p->next!=plist; p=p->next);
// here for Loop execution ends p Point to the tail node
//3. Insert
pnewnode->next = p->next;
p->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}
// Insert by position
bool Insert_pos(PClist plist, int pos, ELEMTYPE val)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
assert(pos>=0 && pos<=Get_length(plist));
//1. Buy new nodes
struct Clist *pnewnode = (struct Clist*)malloc(1 * sizeof(struct Clist));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
pnewnode->data = val;// New nodes purchased Finished processing
//2. Find the insertion location ( Through... With precursors for loop )
struct Clist *p = plist;
for(int i=0; i<pos; i++)
{
p = p->next;
}
// here for Loop execution ends p Point to the appropriate location to be inserted
//3. Insert
pnewnode->next = p->next;
p->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}
// Head deletion
bool Del_head(PClist plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(IsEmpty(plist))// Not empty Then there is at least one valid value
{
return false;
}
//1. The pointer p Point to the node to be deleted
struct Clist *p = plist->next;
//2. The pointer q Point to the node before the node to be deleted
//q Namely Head node There will be no additional processing here
//3. Crossing direction
plist->next = p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
// Deletion at the end
bool Del_tail(PClist plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(IsEmpty(plist))// Not empty Then there is at least one valid value
{
return false;
}
//1. The pointer p Point to the node to be deleted ( If the tail is deleted , This points to the tail node )
struct Clist *p = plist;
for(p; p->next!=plist; p=p->next);
// here for Point to the end Represents the p Point to the tail node
//2. The pointer q Point to the penultimate node
struct Clist *q = plist;
for(q; q->next!=p; q=q->next);
// here for Point to the end Represents the q Point to p The previous node of
//3. Crossing direction
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
// Delete by location
bool Del_pos(PClist plist, int pos)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
assert(pos>=0 && pos<Get_length(plist));
if(IsEmpty(plist))
{
return false;
}
//1. The pointer p Point to the node to be deleted
//2. The pointer q Point to the previous node of the node to be deleted
// Here we use the second scheme to find pq, Look for the q Look again p
struct Clist *q = plist;
for(int i=0; i<pos; i++)
{
q = q->next;
}
struct Clist *p = q->next;
//3. Crossing direction
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
// Delete... By value
bool Del_val(PClist plist, ELEMTYPE val)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
struct Clist* p = Search(plist, val);
if(p == NULL)
{
return false;
}
struct Clist *q = plist;
for(q; q->next!=p; q=q->next);
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
// lookup ( If I find , You need to return the address of the found node )
struct Clist* Search(struct Clist *plist, ELEMTYPE val)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
for(struct Clist *p=plist->next; p!=plist; p=p->next)
{
if(p->data == val)
{
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
// Sentenced to empty
bool IsEmpty(PClist plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
return plist->next == plist;
}
// Full sentence ( Circular linked list does not need this operation )
// To obtain the length of the
/* The pointer p Run backward from the next node of the head node , If p Encountered the header node again ,
prove p I walked around and came back , This is a valid node. The traversal must have ended */
int Get_length(PClist plist)
{
// Without precursors for loop Just run once
int count = 0;
for(struct Clist *p=plist->next; p!=plist; p=p->next)
{
count++;
}
return count;
}
// Empty
void Clear(PClist plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
Destroy1(plist);
}
// The destruction 1( Infinite header deletion )
void Destroy1(PClist plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
while(plist->next != plist)
{
struct Clist *p = plist->next;
plist->next = p->next;
free(p);
}
plist->next = plist;
}
// The destruction 2( You need two pointer variables )
void Destroy2(PClist plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
struct Clist *p = plist->next;
struct Clist *q = NULL;
plist->next = plist;
while (p!=plist)
{
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
}
// Print
void Show(struct Clist *plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return false;
}
for(struct Clist *p=plist->next; p!=plist; p=p->next)
{
printf("%d ", p->data);
}
printf("\n");
}
边栏推荐
- Increase 900w+ playback in 1 month! Summarize 2 new trends of top flow qiafan in station B
- 激光雷达:Ouster OS产品介绍及使用方法
- [C # notes] reading and writing of the contents of text files
- STM32项目 -- 选题分享(部分)
- Stm32f4 --- PWM output
- Tips for web development: skillfully use ThreadLocal to avoid layer by layer value transmission
- Lumion 11.0软件安装包下载及安装教程
- Zhang Ping'an: accelerate cloud digital innovation and jointly build an industrial smart ecosystem
- Time synchronization of livox lidar hardware -- PPS method
- Sensor: introduction of soil moisture sensor (xh-m214) and STM32 drive code
猜你喜欢
3D laser slam: time synchronization of livox lidar hardware
阿里云中间件开源往事
Blackfly s usb3 industrial camera: buffer processing
postgresql之整體查詢大致過程
Tiflash source code reading (IV) design and implementation analysis of tiflash DDL module

3D激光SLAM:Livox激光雷达硬件时间同步
postgresql之integerset

本周 火火火火 的开源项目!
云原生混部最后一道防线:节点水位线设计
Data connection mode in low code platform (Part 1)
随机推荐
leetcode:5. Longest palindrome substring [DP + holding the tail of timeout]
Halcon实例转OpenCvSharp(C# OpenCV)实现--瓶口缺陷检测(附源码)
[paper reading | deep reading] anrl: attributed network representation learning via deep neural networks
大咖云集|NextArch基金会云开发Meetup来啦!
传感器:DS1302时钟芯片及驱动代码
Detailed explanation of line segment tree (including tested code implementation)
postgresql 之 数据目录内部结构 简介
[unity notes] screen coordinates to ugui coordinates
C#/VB. Net to delete watermarks in word documents
Introduction to the internal structure of the data directory of PostgreSQL
人脸识别应用解析
leetcode:736. Lisp 语法解析【花里胡哨 + 栈 + 状态enumaotu + slots】
3--新唐nuc980 kernel支持jffs2, Jffs2文件系统制作, 内核挂载jffs2, uboot网口设置,uboot支持tftp
【服务器数据恢复】raid损坏导致戴尔某型号服务器崩溃的数据恢复案例
A new path for enterprise mid Platform Construction -- low code platform
How do I dump SoapClient requests for debugging- How to dump SoapClient request for debug?
阿里云易立:云原生如何破解企业降本提效难题?
真实项目,用微信小程序开门编码实现(完结)
go swagger使用
leetcode:5. 最长回文子串【dp + 抓着超时的尾巴】