当前位置:网站首页>Task of gradle learning
Task of gradle learning
2022-07-03 20:13:00 【Nicholas_ hzf】
Catalog
One 、 Create tasks in many ways
1. Create task with task name
- Example :
// Create task with task name
def Task taskCreatedByName = task taskCreatedByName
// def Task taskCreatedByName = task(taskCreatedByName)
taskCreatedByName.doLast {
println " This is a task created by task name "
}
- Prototype :
Task task(String name) throws InvalidUserDataException;
2. Based on the task name and the configured Map Object creation task
- Example :
// Based on the task name and the configured Map Object creation task
def Task taskCreatedByNameAndMap = task taskCreatedByNameAndMap,group:BasePlugin.BUILD_GROUP
taskCreatedByNameAndMap.doLast {
println " This is a task configured by task name and Map Object creation task "
}
- Prototype :
Task task(Map<String, ?> args, String name) throws InvalidUserDataException;
- Map Available configurations of objects
| Configuration item | describe | The default value is |
|---|---|---|
| type | Based on an existing Task To create , Similar to inheritance | DefaultTask |
| overwrite | Whether to replace the existing Task, And type In combination with | false |
| dependsOn | Configure task dependencies | [] |
| action | One added to the task Action Or a closure | null |
| description | Configuration task description | null |
| group | Configure the grouping of tasks | null |
3. Create a task with task name and closure configuration
- adopt Map Objects can be configured with a limited number of items , So you can go through Closure In the form of More flexible and comprehensive Configuration of
- Example :
// Create a task with task name and closure configuration
task taskCreatedByNameAndClosure {
doLast {
println " This is a task created by task name and closure configuration "
}
}
- Prototype :
Task task(String name, Closure configureClosure);
4. With task name 、Map Parameters and closure configuration create tasks
- Example :
// With task name ,Map Object and closure configuration creation task
task taskCreatedByNameMapAndClosure,group:BasePlugin.BUILD_GROUP,{
doLast {
println " This is a task name ,Map Object and closure configuration creation task "
}
}
- Prototype :
Task task(Map<String, ?> args, String name, Closure configureClosure);
5. TaskContainer Object's create Method to create a task
- Use TaskContainer There are many ways to create tasks for objects , You can see Project.java File to see different creation methods , Here is only one example
- Example :
// TaskContainer Object's create Method to create a task
tasks.create('taskCreatedByTaskContainer') {
doLast {
println " This is a pass TaskContainer Object creation task "
}
}
- Prototype :
Task create(String name, Closure configureClosure) throws InvalidUserDataException;
Two 、 Multiple ways to access tasks
1. Access task with task name
The tasks we create will become Project One of the attribute , The attribute name is the task name , So you can access the operation task through the task name
task task1
task1.doLast {
println " Access task with task name "
}
2. Access tasks by accessing collection elements
The task is all through TaskContainer Object created , stay Project.java in tasks Namely TaskContainer The object of , So you can adopt tasks To get the corresponding task
In the sample code “[]” It doesn't mean tasks It's a Map, It is Groovy heavy load This operator , Follow up the source code and you will find that it is finally called findByName(String name) Realized
task task2
// TaskContainer getTasks();
tasks['task2'].doLast {
println " Access tasks by accessing collection elements "
}
3. Access through the path
There are two ways to access by path :get And find
difference :get When you can't find a task, you will Throw an exception and find When the task cannot be found return null
task task3
tasks['task3'].doLast {
println "----- Access tasks through paths -----"
println tasks.findByPath(':task2')
println tasks.getByPath(':task2')
println tasks.findByPath(':task0')
println tasks.getByPath(':task0')
}
// TaskContainer.java
@Nullable
Task findByPath(String path);
Task getByPath(String path) throws UnknownTaskException;
4. Access... By name
There are two ways to access by name :get And find
difference :get When you can't find a task, you will Throw an exception and find When the task cannot be found return null
task task4
tasks['task4'].doLast {
println "----- Access tasks by name -----"
println tasks.findByName('task2')
println tasks.getByName('task2')
println tasks.findByName('task0')
// println tasks.getByPath('task0')
}
// TaskCollection.java
// TaskContainer Inherited from TaskCollection<Task> and PolymorphicDomainObjectContainer<Task>
// getByName Method from TaskCollection
@Override
T getByName(String name) throws UnknownTaskException;
// NamedDomainObjectCollection.java
// TaskCollection Inherit NamedDomainObjectSet
// NamedDomainObjectSet Inherit NamedDomainObjectCollection
// findByName Method from NamedDomainObjectCollection
@Nullable
T findByName(String name);
5. It is worth noting that , When accessing tasks through paths , The parameter value can be path or task name , But when accessing tasks by name , The parameter value can only be the task name
3、 ... and 、 Task grouping and description
- Task grouping is to group tasks classification , Facilitate our understanding of the task Sort out
- Task description is to describe the task explain , Convenient for others Know the purpose of the task
task task5
task5.group = BasePlugin.BUILD_GROUP
task5.description = " This is a build Grouped tasks "
task5.doLast {
println "group:$group,description:$description"
}

- Use
gradle tasksThe command can View task information , Including task grouping and description
- stay AS in Gradle Task You can see the grouping of tasks in the list , Mouse hovering The description of a task can be seen
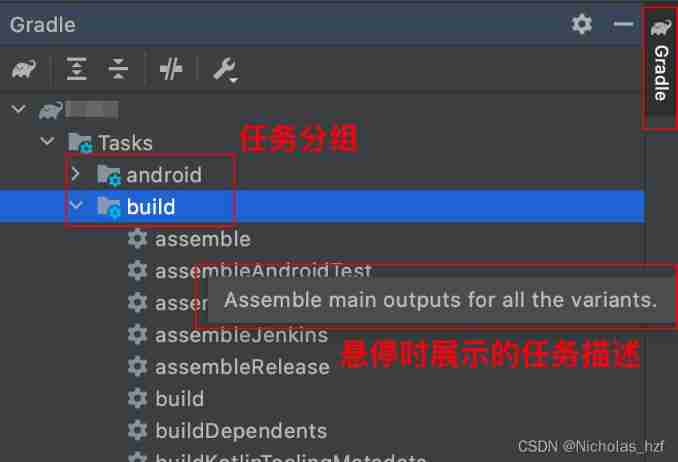
Four 、 Task execution analysis
- The execution of the task is actually A series of tasks Action Implementation
// AbstractTask.java
@Override
public List<ContextAwareTaskAction> getTaskActions() {
if (actions == null) {
actions = new ArrayList<ContextAwareTaskAction>(3);
}
return actions;
}
- See the implementation of the task through the source code ( Version number :7.0.2)
- Example
task executeTask(type: Task6)
executeTask.doFirst {
println "Task Execute before self execution doFirst"
}
executeTask.doLast {
println "Task Execute after self execution doLast"
}
class Task6 extends DefaultTask {
@TaskAction
def doSelf(){
println "Task Self execution doSelf"
}
}

- Source code analysis doSelf() Method — When creating a task ,Gradle Will resolve tasks with
@TaskActionHow to annotate , Performed as a task Action, And then throughprependParallelSafeAction(...)Method Action Add to Action In the execution list of
// AbstractTask.java
@Override
public void prependParallelSafeAction(final Action<? super Task> action) {
if (action == null) {
throw new InvalidUserDataException("Action must not be null!");
}
getTaskActions().add(0, wrap(action));
}
- Source code analysis doFirst(…) Method — Always in Action Execute the of the list first place Insert operation , a key
getTaskActions().add(0, wrap(action, actionName));
// AbstractTask.java
@Override
public Task doFirst(final Action<? super Task> action) {
return doFirst("doFirst {} action", action);
}
@Override
public Task doFirst(final String actionName, final Action<? super Task> action) {
hasCustomActions = true;
if (action == null) {
throw new InvalidUserDataException("Action must not be null!");
}
taskMutator.mutate("Task.doFirst(Action)", new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
getTaskActions().add(0, wrap(action, actionName));
}
});
return this;
}
- Source code analysis doLast(…) Method — Always in Action Execute the of the list Last Insert operation , a key
getTaskActions().add(wrap(action, actionName));
// AbstractTask.java
@Override
public Task doLast(final Action<? super Task> action) {
return doLast("doLast {} action", action);
}
@Override
public Task doLast(final String actionName, final Action<? super Task> action) {
hasCustomActions = true;
if (action == null) {
throw new InvalidUserDataException("Action must not be null!");
}
taskMutator.mutate("Task.doLast(Action)", new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
getTaskActions().add(wrap(action, actionName));
}
});
return this;
}
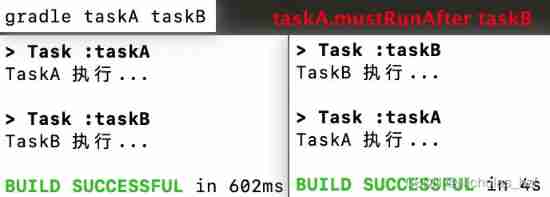
5、 ... and 、 Task sequencing
Say sort , It's not accurate , It should be Assign tasks A On mission B After execution , And according to the called api Dissimilarity , Implementation or not yes Probably and A certain The distinction between
shouldRunAftershould Execute aftermustRunAftermust Execute after
task taskA
taskA.doLast{
println "TaskA perform ..."
}
task taskB
taskB.doLast{
println "TaskB perform ..."
}
taskA.mustRunAfter taskB
6、 ... and 、 Enable and disable tasks
enabled attribute , The default is true Express Enable Mission , Set as false will Ban This task
task task7
task7.doLast{
println "Task7 perform ..."
}
task7.enabled = false

7、 ... and 、 Mission onlyIf Assertion
- What is? onlyIf Assertion : It's just one. Conditional expression .Task There is one in the class
onlyIfMethod , This method receives a Closure parameters , According to the return value true/false To decide whether the task is performed or skipped - Example :
task task8
task8.onlyIf{
println "Task8 perform ..."
false
}
task task9
task9.onlyIf{
println "Task9 perform ..."
true
}

8、 ... and 、 Task rules
- adopt The second section Learning from , We know many ways to access tasks , When we access tasks by task name , If The corresponding task does not exist , Then it will call us Added rules To deal with this situation
// DefaultNamedDomainObjectCollection.java
@Override
public T findByName(String name) {
T value = findByNameWithoutRules(name);
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
ProviderInternal<? extends T> provider = index.getPending(name);
if (provider != null) {
// TODO - this isn't correct, assumes that a side effect is to add the element
provider.getOrNull();
// Use the index here so we can apply any filters to the realized element
return index.get(name);
}
if (!applyRules(name)) {
return null;
}
return findByNameWithoutRules(name);
}
- Example :
tasks.addRule " This is the description of the task rule ",{
String taskName ->
task(taskName).doLast{
println "$taskName non-existent , Unable to execute ..."
}
}
- If the task is not found when the rule is not added Compile failed

- The task not found after adding rules will Follow the rules ( An example is printing information )

Sort out and learn from the ruthless boss of Feixue 《Android Gradle Authoritative guide 》 And Internet materials
边栏推荐
- [raid] [simple DP] mine excavation
- Blue Bridge Cup: the fourth preliminary - "simulated intelligent irrigation system"
- Machine learning support vector machine SVM
- What is the difference between a kill process and a close process- What are the differences between kill process and close process?
- Popularize the basics of IP routing
- 1.5 learn to find mistakes first
- JMeter plug-in installation
- PR notes:
- FPGA learning notes: vivado 2019.1 project creation
- Basic command of IP address configuration ---ip V4
猜你喜欢
![2022 - 06 - 30 networker Advanced (XIV) Routing Policy Matching Tool [ACL, IP prefix list] and policy tool [Filter Policy]](/img/b6/5d6b946d8001e2d73c2cadbdce72fc.png)
2022 - 06 - 30 networker Advanced (XIV) Routing Policy Matching Tool [ACL, IP prefix list] and policy tool [Filter Policy]
FPGA 学习笔记:Vivado 2019.1 工程创建
2022-06-27 advanced network engineering (XII) IS-IS overhead type, overhead calculation, LSP processing mechanism, route revocation, route penetration
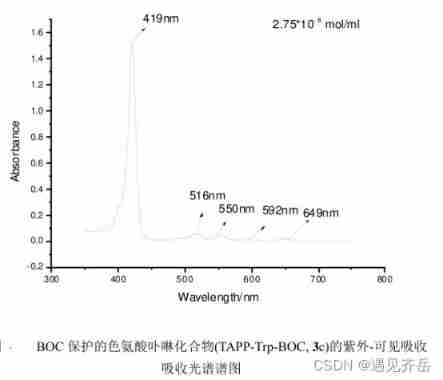
BOC protected tryptophan porphyrin compound (TAPP Trp BOC) Pink Solid 162.8mg supply - Qiyue supply
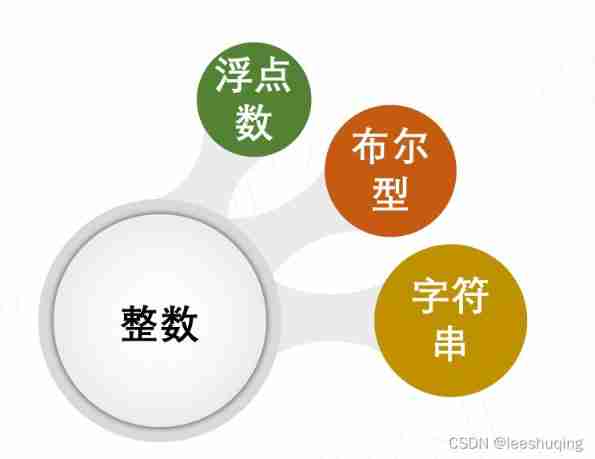
2.4 conversion of different data types
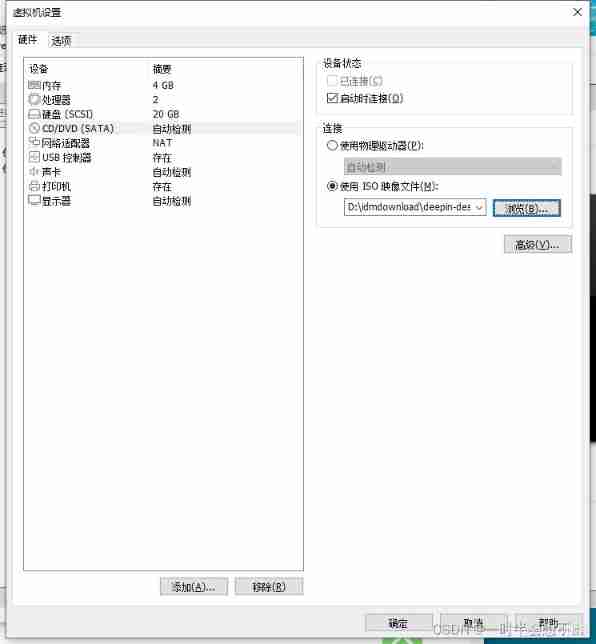
Virtual machine installation deepin system

2.7 format output of values
2022 Xinjiang latest road transportation safety officer simulation examination questions and answers

Gym welcomes the first complete environmental document, which makes it easier to get started with intensive learning!
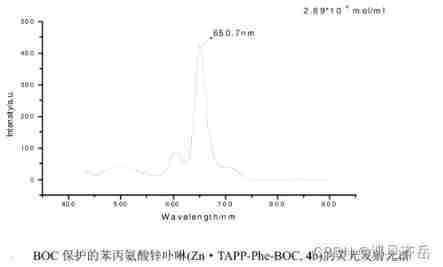
BOC protected phenylalanine zinc porphyrin (Zn · TAPP Phe BOC) / iron porphyrin (Fe · TAPP Phe BOC) / nickel porphyrin (Ni · TAPP Phe BOC) / manganese porphyrin (Mn · TAPP Phe BOC) Qiyue Keke
随机推荐
【c】 Digital bomb
Global and Chinese market of full authority digital engine control (FADEC) 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Global and Chinese market of electrolyte analyzers 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Global and Chinese markets for medical temperature sensors 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
App compliance
kubernetes集群搭建efk日志收集平台
7. Data broker presentation
Test changes in Devops mode -- learning and thinking
IP address is such an important knowledge that it's useless to listen to a younger student?
BOC protected phenylalanine zinc porphyrin (Zn · TAPP Phe BOC) / iron porphyrin (Fe · TAPP Phe BOC) / nickel porphyrin (Ni · TAPP Phe BOC) / manganese porphyrin (Mn · TAPP Phe BOC) Qiyue Keke
Typora charges, WTF? Still need support
BOC protected alanine zinc porphyrin Zn · TAPP ala BOC / alanine zinc porphyrin Zn · TAPP ala BOC / alanine zinc porphyrin Zn · TAPP ala BOC / alanine zinc porphyrin Zn · TAPP ala BOC supplied by Qiyu
Chapter 1: find the algebraic sum of odd factors, find the same decimal sum s (D, n), simplify the same code decimal sum s (D, n), expand the same code decimal sum s (D, n)
2022 Xinjiang latest road transportation safety officer simulation examination questions and answers
Print linked list from end to end
5. MVVM model
Global and Chinese market of speed limiter 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Pat grade B 1009 is ironic (20 points)
10 smart contract developer tools that miss and lose
Parental delegation mechanism