当前位置:网站首页>Go learning notes - multithreading
Go learning notes - multithreading
2022-07-02 12:13:00 【Ostrich5yw】
Multithreaded programming
A process can contain multiple threads , These threads must be running the same program ( process == Program ), And are passed by threads that already exist in the current process system call Created in a way . Process is the basic unit of resource allocation , Thread is the basic unit of scheduling , Threads cannot exist independently of processes .
All threads have their own thread stack , To store your private data ( Included in the virtual memory address of the process ). Many resources in a process will also be shared by threads , Including the code segment stored in the virtual memory address of the current process 、 Data segment 、 Pile up 、 Signal processing functions 、 File descriptor ( Non-negative integer ). Because of this , Creating a thread does not consume as much resources as creating a process , Because most of its resources are shared without being copied .
( One ) Thread Introduction
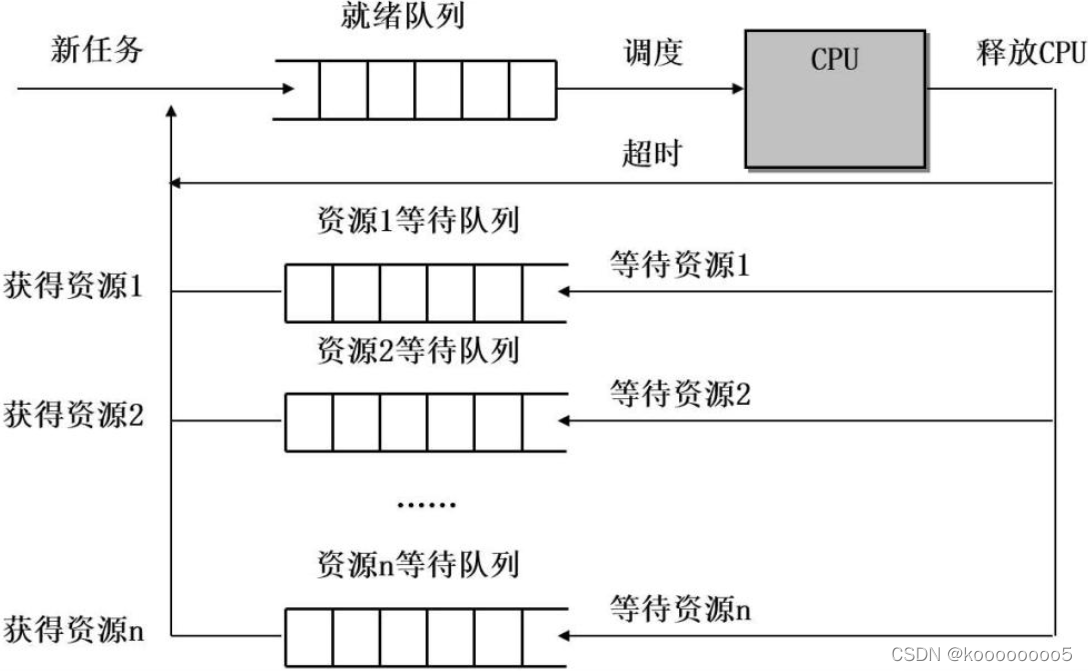
One 、 Thread state
Unlike the family tree structure of processes , The relationship between threads is equal . They can perform the following four operations on each other .
| operation | effect |
|---|---|
| pthread_create | Create thread —— except The main thread Create with the process , Other threads pass in code snippets and parameters to create , And will return TID. |
| pthread_cancel(TID) | Thread termination —— Cancel given TID Represents the thread , The target thread will always accept the request and respond to it at some cancellation point . |
| pthread_join(TID) | Connection terminated thread —— Wait until it's time TID The thread represented terminates , And inform the calling thread of its return value . |
| pthread_detach(TID) | Detaching threads —— Make the target thread unconnectable . The kernel will automatically clean up and destroy when it terminates . |

Be careful :
(1) The thread is a connectable thread by default . If it is not connected at its termination , Will become a zombie thread , When other processes connect to the zombie process , It will be recycled .
(2) The separation operation is irreversible .
(3) To create a new city, you need to call the system call and give the execution function and parameters , Threads can have return values .
(4)return、 system call exit Will terminate the current 、 All threads . Display call pthread_exit It will also terminate the thread . The difference between the two is that calling the former by the main thread will terminate all threads in the process , The latter will only terminate the main thread .
Two 、 Thread scheduling
Thread execution always tends to CPU Limited or IO be limited to . And the scheduler will be IO Restricted threads provide higher dynamic priority . The scheduler will try to make a thread in a specific CPU Up operation , This can improve cache Hit rate and efficient use of memory , When one CPU When you're too busy , The scheduler also migrates threads to idle CPU function .
| name | explain | effect |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic priority | It can be adjusted in real time by the scheduler ( Based on the static priority, we get ) | Determine the running order of threads |
| Static priority | It can only be specified by the application , The default is 0 | decision CPU The size of the time slice |
Threads will be arranged in the active priority array according to the size of the dynamic priority . When a thread has occupied a long CPU Time (T<= Time slice size ), Then the thread will be placed in the expired priority array , The subsequent thread will be placed in CPU Up operation . When the active array has no waiting threads , The active array will be exchanged with the expired array , Continue running the thread on the newly activated array .
Threads will join the corresponding waiting queue because they wait for an event or condition to occur , And then go to sleep . When the event occurs , The kernel will notify all threads in the corresponding waiting queue , These threads will be awakened and transferred to the appropriate run queue .
| Status name | describe |
|---|---|
| An interruptible sleep state | Sleep until a condition becomes true , If a hardware interrupt is generated 、 Release the waiting system resources or send a signal . |
| Uninterrupted sleep | It can only be interrupted by hardware 、 The waiting system resources are released and awakened , Does not respond to signals passed by other processes . |
3、 ... and 、 Thread implementation model
- User level threading model
Threads are fully managed by the user level thread library . These threads are stored in the user space of the process , The kernel is not aware of . Thread creation 、 End 、 Switching is completed in user mode . However, because threads cannot be scheduled by the kernel , Therefore, the process is regarded as an indivisible unit by the scheduler , Multithreading concurrency and CPU Load balancing . What it implements is actually a multi-user thread corresponding to a kernel scheduling entity (M:1).
- Kernel level threading model ——Linux
Threads are managed by the kernel . Application to thread creation 、 End 、 Synchronization must be completed through system calls provided by the kernel , Therefore, the operating system does not need to manage threads at the online library level . However, the kernel creates a large number of scheduling entities corresponding to threads , More kernel resources will be used , At the same time, the cost of thread management in the kernel is much higher than that of user level thread management , Thread creation 、 Switch 、 Synchronization also takes more time , It puts a huge burden on the kernel scheduler . What it realizes is that each user level thread corresponds to a kernel scheduling entity (1:1).
- Two level threading model ——Go
Threads are managed by the kernel and thread library . A process can be associated with multiple kernel scheduling entities , The threads in the process do not correspond to them one by one , These threads can be mapped to the same associated kernel scheduling entity . That is, first create multiple kernel level threads through the operating system kernel , These kernel level threads are used to schedule user level threads . It actually implements multiple user level threads corresponding to multiple kernel scheduling entities (M:N).Go User level threads are called goroutine.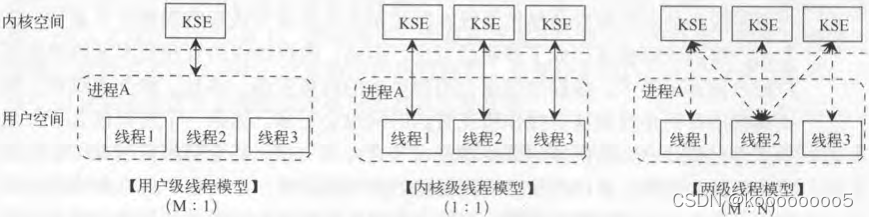
Four 、 Thread synchronization
Because a considerable part of the virtual memory address owned by a process can be shared by all threads in the process , To ensure the consistency of shared data , The concept of critical region is introduced . That is, a certain resource or code segment that can only be accessed or executed serially . By using mutex 、 Synchronization tools such as atomic operation ensure that the critical region is effective .
- The mutex
At the same time , A constraint that allows only one thread to be in a critical region is called mutex . Before each thread enters the critical zone , Must lock an object first , Only the thread that successfully locks the object can enter the critical zone , Otherwise blocking . This object is called The mutex .
Mutexes are divided into initialization —( Unlocked state )— lock —( Locked state )— Unlock —( Unlocked state ). The critical area of each mutex protection should be within a reasonable range and as large as possible , However, if multiple threads frequently enter and exit large critical areas and conflict occurs , It should be considered to segment the critical area and protect it with different mutexes . Note that the critical area protected by different mutexes should not contain the same kind of resources ( Different ) operation . This will cause multiple processes to enter the same critical region through different mutexes .
The only problem caused by the emergence of mutexes is deadlock . Usually by “ Try locking - Back off ” perhaps “ Fixed sequence lock ” solve . The former fails to lock multiple locks , Will unlock the previous mutex , And try locking again ; The latter specifies the order in which all threads are locked , Always locked 1 Can be locked 2.
- Condition variables,
Condition variables are used in combination with mutexes . When the corresponding shared data state changes , Notify other blocked processes .
| operation | effect |
|---|---|
| Wait for a notice (wait) | Block the current thread , Until the notification from the condition variable is received |
| Single notice (signal) | This condition variable sends a notification to at least one thread waiting for its notification |
| Broadcast notice (broadcast) | This condition variable sends a notification to all threads waiting for it to notify |
Be careful :(1) Wait for the notification operation to be carried out in the critical area , That is, after the thread obtains the mutex , It is found that the value of the critical zone does not meet the conditions , So unlock the mutex and block the thread .
(2) Wait for a notice ( Unlock mutex , Block the current thread ) It's an atomic operation . After blocking, the thread will wait for the condition variable notification , And try to lock again .
5、 ... and 、 Thread safety
Thread safety : A code block , It can be executed concurrently by multiple threads , And always achieve the desired results , Thread safety .
Reentrant function : A function , If multiple threads call the result concurrently , The result is always the same as when they are called in any order , It is considered to be a reentrant function . If a function takes the shared data as the result it returns or includes it in the result it returns , It must not be a reentrant function .
Program performance index : Response time and throughput .
Correctness and scalability of the program : The latter refers to increase CPU In the case of the number of cores , Its running speed will not be adversely affected ( In a multiple CPU Under the condition of parallelism , Realize serial operations such as mutexes , Kernel required 、CPU Jointly coordinate ,CPU The more cores , The more complex the coordination work is ). How to balance the relationship between the two ?
- Control the purity of critical zone : The critical area code only contains the code that operates the shared data
- Control the granularity of critical zone : Too fine granularity will increase the number of underlying coordination work , So merge the critical areas of several operations with the same shared data .
- Reduce code execution time in critical areas : For a critical area that contains operations on different shared data , It should be divided into several critical zones ; At the same time, improve the algorithm .
- Avoid holding mutexes for a long time : In the critical area, the code will wait for some shared data , The conditional variable is introduced to unlock and lock the mutex in time .
- Atomic operations are preferred over mutexes
边栏推荐
- 输入一个三位的数字,输出它的个位数,十位数、百位数。
- mysql索引和事务
- SCM power supply
- CDA data analysis -- Introduction and use of aarrr growth model
- Leetcode739 每日温度
- 【C语言】杨辉三角,自定义三角的行数
- Multiply LCA (nearest common ancestor)
- 初始JDBC 编程
- Lekao: contents of the provisions on the responsibility of units for fire safety in the fire protection law
- 自然语言处理系列(二)——使用RNN搭建字符级语言模型
猜你喜欢

Dynamic debugging of multi file program x32dbg

From scratch, develop a web office suite (3): mouse events

ES集群中节点与分片的区别

使用Sqoop把ADS层数据导出到MySQL

CDH6之Sqoop添加数据库驱动
kubenetes中port、targetPort、nodePort、containerPort的区别与联系

Applet link generation

SVO2系列之深度濾波DepthFilter
Jenkins user rights management
CDA data analysis -- Introduction and use of aarrr growth model
随机推荐
子线程获取Request
SSH automatically disconnects (pretends to be dead) after a period of no operation
Leetcode122 the best time to buy and sell stocks II
Lombok common annotations
Log4j2
Jenkins voucher management
[C language] convert decimal numbers to binary numbers
单指令多数据SIMD的SSE/AVX指令集和API
Le tutoriel F - String le plus facile à comprendre de l'histoire.
Jenkins用户权限管理
YYGH-BUG-05
mysql索引和事务
使用Sqoop把ADS层数据导出到MySQL
[old horse of industrial control] detailed explanation of Siemens PLC TCP protocol
The most understandable f-string tutorial in history, collecting this one is enough
[C language] Yang Hui triangle, customize the number of lines of the triangle
Log4j2
kubeadm join时出现错误:[ERROR Port-10250]: Port 10250 is in use [ERROR FileAvailable--etc-kubernetes-pki
字符串回文hash 模板题 O(1)判字符串是否回文
(C语言)输入一行字符,分别统计出其中英文字母、空格、数字和其它字符的个数。