当前位置:网站首页>PyTorch nn.RNN 参数全解析
PyTorch nn.RNN 参数全解析
2022-07-02 09:42:00 【raelum】
一、简介
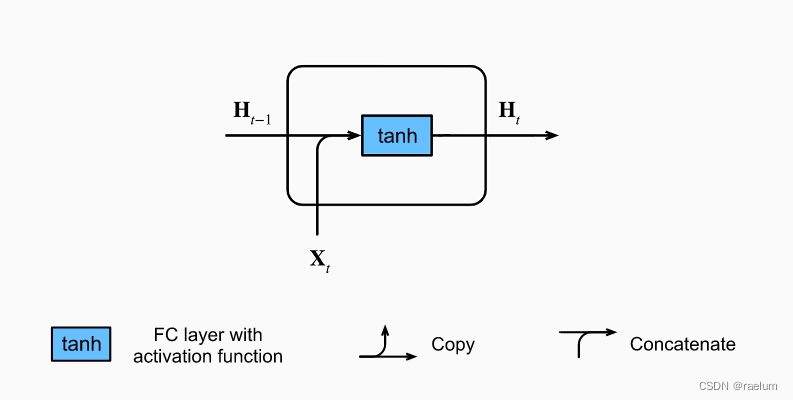
torch.nn.RNN 用于构建循环层,其中的计算规则如下:
h t = tanh ( W i h x t + b i h + W h h h t − 1 + b h h ) (1) \boldsymbol{h}_{t}=\tanh({\bf W}_{ih}\boldsymbol{x}_t+\boldsymbol{b}_{ih}+{\bf W}_{hh}\boldsymbol{h}_{t-1}+\boldsymbol{b}_{hh}) \tag{1} ht=tanh(Wihxt+bih+Whhht−1+bhh)(1)
其中 h t \boldsymbol{h}_{t} ht 是 t t t 时刻的隐层状态, x t \boldsymbol{x}_{t} xt 是 t t t 时刻的输入。下标 i i i 是 i n p u t input input 的简写,下标 h h h 是 h i d d e n hidden hidden 的简写。 W , b {\bf W},\boldsymbol{b} W,b 分别是权重和偏置。
二、前置知识
先回顾一下普通的神经网络,我们在训练它的过程中通常会投喂一小批量的数据。不妨设 batch_size = N \text{batch\_size}=N batch_size=N,则投喂的数据的形式为:
X = [ x 1 T ⋮ x N T ] N × d {\bf X}= \begin{bmatrix} \boldsymbol{x}_1^{\text T} \\ \vdots \\ \boldsymbol{x}_N^{\text T} \end{bmatrix}_{N\times d} X=⎣⎢⎡x1T⋮xNT⎦⎥⎤N×d
其中 x i = ( x i 1 , x i 2 , ⋯ , x i d ) T \boldsymbol{x}_i=(x_{i1},x_{i2},\cdots,x_{id})^{\text T} xi=(xi1,xi2,⋯,xid)T 为特征向量,维数为 d d d。
在处理序列问题中,我们会将词元转化成对应的特征向量。例如在处理一个英文句子时,我们通常会通过某种手段将每个单词转化为合适的特征向量。设序列(句子)长度为 L L L,于是在此情景下,一个句子可以表示为:
seq i = [ x i 1 T ⋮ x i L T ] L × d \text{seq}_i= \begin{bmatrix} \boldsymbol{x}_{i1}^{\text T} \\ \vdots \\ \boldsymbol{x}_{iL}^{\text T} \end{bmatrix}_{L\times d} seqi=⎣⎢⎡xi1T⋮xiLT⎦⎥⎤L×d
其中的每个 x i j , j = 1 , ⋯ , L \boldsymbol{x}_{ij},\;j=1,\cdots, L xij,j=1,⋯,L 都对应了句子 seq i \text{seq}_i seqi 中的一个单词。在上述约定下,我们在 t t t 时刻投喂给RNN的数据为:
X t = [ x 1 t T ⋮ x N t T ] N × d (2) {\bf X}_t= \begin{bmatrix} \boldsymbol{x}_{1t}^{\text T} \\ \vdots \\ \boldsymbol{x}_{Nt}^{\text T} \end{bmatrix}_{N\times d}\tag{2} Xt=⎣⎢⎡x1tT⋮xNtT⎦⎥⎤N×d(2)
从而 ( 1 ) (1) (1) 式改写为
H t = tanh ( X t W i h + b i h + H t − 1 W h h + b h h ) (3) {\bf H}_t=\tanh({\bf X}_t{\bf W}_{ih}+\boldsymbol{b}_{ih}+{\bf H}_{t-1}{\bf W}_{hh}+\boldsymbol{b}_{hh})\tag{3} Ht=tanh(XtWih+bih+Ht−1Whh+bhh)(3)
其中 H t , H t − 1 {\bf H}_t,{\bf H}_{t-1} Ht,Ht−1 的形状为 N × h N\times h N×h, W i h {\bf W}_{ih} Wih 的形状为 d × h d\times h d×h, W h h {\bf W}_{hh} Whh 的形状为 h × h h\times h h×h, b i h , b h h \boldsymbol{b}_{ih},\boldsymbol{b}_{hh} bih,bhh 的形状为 1 × h 1\times h 1×h,求和时利用广播机制。
在 nn.RNN 中,我们是一次性将所有时刻的数据全部投喂进去,数据形式为:
X = [ seq 1 , seq 2 , ⋯ , seq N ] N × L × d or X = [ X 1 , X 2 , ⋯ , X L ] L × N × d {\bf X}=[\text{seq}_1,\text{seq}_2,\cdots,\text{seq}_N]_{N\times L\times d}\quad\text{or}\quad {\bf X}=[{\bf X}_1,{\bf X}_2,\cdots,{\bf X}_L]_{L\times N\times d} X=[seq1,seq2,⋯,seqN]N×L×dorX=[X1,X2,⋯,XL]L×N×d
其中左边代表 batch_first=True 的情形,右边代表 batch_first=False 的情形。
注意: 在一个 batch 中,所有 sequence 的长度要保持相同,即 L L L 需一致。
三、解析
3.1 所有参数

有了前置知识后,我们就能很方便的解释这些参数了。
input_size:即 d d d;hidden_size:即 h h h;num_layers:即RNN的层数。默认是 1 1 1 层。该参数大于 1 1 1 时,会形成 Stacked RNN,又称多层RNN或深度RNN;nonlinearity:即非线性激活函数。可以选择tanh或relu,默认是tanh;bias:即偏置。默认启用,可以选择关闭;batch_first:即是否选择让batch_size作为输入的形状中的第一个参数。当batch_first=True时,输入应具有 N × L × d N\times L\times d N×L×d 这样的形状,否则应具有 L × N × d L\times N\times d L×N×d 这样的形状。默认是False;dropout:即是否启用dropout。如要启用,则应设置dropout的概率,此时除最后一层外,RNN的每一层后面都会加上一个dropout层。默认是 0 0 0,即不启用;bidirectional:即是否启用双向RNN,默认关闭。
3.2 输入参数

这里我们只考虑有 batch 的情况。
当 batch_first=True 时,输入 input 应具有形状 N × L × d N\times L\times d N×L×d,否则应具有形状 L × N × d L\times N\times d L×N×d。
h_0 为初始时刻的隐状态。当RNN为单向RNN时,h_0 的形状应为 num_layers × N × h \text{num\_layers}\times N\times h num_layers×N×h;当RNN为双向RNN时,h_0 的形状应为 ( 2 ⋅ num_layers ) × N × h (2\cdot \text{num\_layers})\times N\times h (2⋅num_layers)×N×h。如不提供该参数的值,则默认为全0张量。
3.3 输出参数
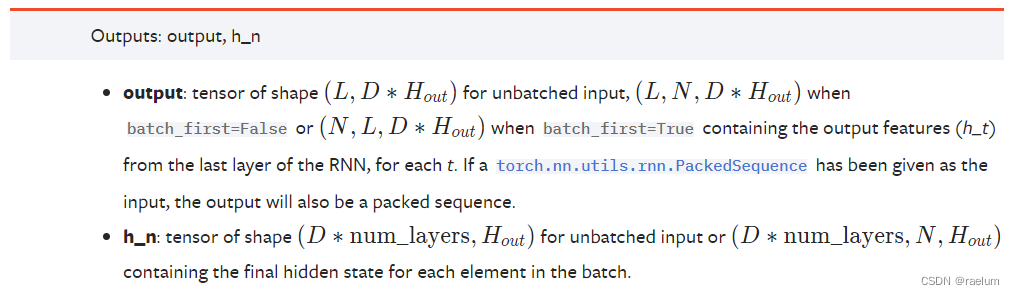
这里我们只考虑有 batch 的情况。
当RNN为单向RNN时:若 batch_first=True,输出 output 具有形状 N × L × h N\times L\times h N×L×h,否则具有形状 L × N × h L\times N\times h L×N×h。当 batch_first=False 时,output[t, :, :] 代表时刻 t t t 时,RNN最后一层(之所以用最后一层这个术语是因为有可能出现Stacked RNN情形)的输出 h t \boldsymbol{h}_t ht。h_n 代表最终的隐状态,形状为 num_layers × N × h \text{num\_layers}\times N\times h num_layers×N×h。
当RNN为双向RNN时:若 batch_first=True,输出 output 具有形状 N × L × 2 h N\times L\times 2h N×L×2h,否则具有形状 L × N × 2 h L\times N\times 2h L×N×2h。h_n 的形状为 ( 2 ⋅ num_layers ) × N × h (2\cdot \text{num\_layers})\times N\times h (2⋅num_layers)×N×h。
事实上,对于单向RNN,有
output = [ H 1 , H 2 , ⋯ , H L ] L × N × h , h_n = [ H L ] 1 × N × h \text{output}=[{\bf H}_1,{\bf H}_2,\cdots,{\bf H}_L]_{L\times N\times h},\quad \text{h\_n}=[{\bf H}_L]_{1\times N\times h} output=[H1,H2,⋯,HL]L×N×h,h_n=[HL]1×N×h
四、通过例子来进一步理解 nn.RNN
以单隐层单向RNN为例(接下来的例子都默认 batch_first=False)。
假设有一个英文句子:He ate an apple.,忽略 . 并设置词元为单词(word)时,该序列的长度为 4 4 4。简便起见,我们假设每个词元都对应了一个 6 6 6 维的特征向量,则上述的序列可写成:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
torch.manual_seed(42)
seq = torch.randn(4, 6) # 只是为了举例
print(seq)
# tensor([[ 1.9269, 1.4873, 0.9007, -2.1055, 0.6784, -1.2345],
# [-0.0431, -1.6047, 0.3559, -0.6866, -0.4934, 0.2415],
# [-1.1109, 0.0915, -2.3169, -0.2168, -0.3097, -0.3957],
# [ 0.8034, -0.6216, -0.5920, -0.0631, -0.8286, 0.3309]])
将这个句子视为一个 batch,即(注意形状为 L × N × d L\times N\times d L×N×d):
inputs = seq.unsqueeze(1)
print(inputs)
# tensor([[[ 1.9269, 1.4873, 0.9007, -2.1055, 0.6784, -1.2345]],
# [[-0.0431, -1.6047, 0.3559, -0.6866, -0.4934, 0.2415]],
# [[-1.1109, 0.0915, -2.3169, -0.2168, -0.3097, -0.3957]],
# [[ 0.8034, -0.6216, -0.5920, -0.0631, -0.8286, 0.3309]]])
print(inputs.shape)
# torch.Size([4, 1, 6])
有了 inputs,我们还需要初始化隐状态 h_0,不妨设 h = 3 h=3 h=3:
h_0 = torch.randn(1, 1, 3)
print(h_0)
# tensor([[[ 1.3525, 0.6863, -0.3278]]])
接下来创建RNN层,事实上只需要输入 input_size 和 hidden_size 即可:
rnn = nn.RNN(6, 3)
观察输出:
outputs, h_n = rnn(inputs, h_0)
print(outputs)
# tensor([[[-0.5428, 0.9207, 0.7060]],
# [[-0.2245, 0.2461, -0.4578]],
# [[ 0.5950, -0.3390, -0.4598]],
# [[ 0.9281, -0.7660, 0.5954]]], grad_fn=<StackBackward0>)
print(h_n)
# tensor([[[ 0.9281, -0.7660, 0.5954]]], grad_fn=<StackBackward0>)
五、从零开始手写一个单隐层单向RNN
首先写好框架:
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size):
super().__init__()
pass
def forward(self, inputs, h_0):
pass
我们的计算遵循 ( 3 ) (3) (3) 式,即:
H t = tanh ( X t W i h + b i h + H t − 1 W h h + b h h ) {\bf H}_t=\tanh({\bf X}_t{\bf W}_{ih}+\boldsymbol{b}_{ih}+{\bf H}_{t-1}{\bf W}_{hh}+\boldsymbol{b}_{hh}) Ht=tanh(XtWih+bih+Ht−1Whh+bhh)
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size):
super().__init__()
self.W_ih = torch.randn(input_size, hidden_size)
self.W_hh = torch.randn(hidden_size, hidden_size)
self.b_ih = torch.randn(1, hidden_size)
self.b_hh = torch.randn(1, hidden_size)
def forward(self, inputs, h_0):
L, N, d = inputs.shape # 分别对应序列长度、批量大小和特征维度
H = h_0[0] # 因为h_0的形状为(1,N,h),我们需要使用(N,h)去计算
outputs = [] # 用来存储h_1,h_2,...,h_L
for t in range(L):
X_t = inputs[t]
H = torch.tanh(X_t @ self.W_ih + self.b_ih + H @ self.W_hh + self.b_hh)
outputs.append(H)
h_n = outputs[-1].unsqueeze(0) # h_n实际上就是h_L,但此时的形状为(N,h)
outputs = torch.cat(outputs, 0).unsqueeze(1)
return outputs, h_n
为了检验我们的RNN是正确的,我们需要使用相同的输入来验证我们的输出是否与之前的一致。
torch.manual_seed(42)
seq = torch.randn(4, 6)
inputs = seq.unsqueeze(1)
h_0 = torch.randn(1, 1, 3)
# 保持RNN内部参数:权重和偏置一致
rnn = nn.RNN(6, 3)
params = [param.data.T for param in rnn.parameters()]
my_rnn = RNN(6, 3)
my_rnn.W_ih = params[0]
my_rnn.W_hh = params[1]
my_rnn.b_ih[0] = params[2]
my_rnn.b_hh[0] = params[3]
outputs, h_n = my_rnn(inputs, h_0)
print(outputs)
# tensor([[[-0.5428, 0.9207, 0.7060]],
# [[-0.2245, 0.2461, -0.4578]],
# [[ 0.5950, -0.3390, -0.4598]],
# [[ 0.9281, -0.7660, 0.5954]]])
print(h_n)
# tensor([[[ 0.9281, -0.7660, 0.5954]]])
可以看出结果与之前的一致,这说明我们构造的RNN是正确的。
最后
博主才疏学浅,如有错误请在评论区指出,感谢!
边栏推荐
- Summary of flutter problems
- C#基于当前时间,获取唯一识别号(ID)的方法
- 通讯录的实现(文件版本)
- pgsql 字符串转数组关联其他表,匹配 拼接后原顺序展示
- C # method of obtaining a unique identification number (ID) based on the current time
- Precautions for scalable contract solution based on openzeppelin
- How to Visualize Missing Data in R using a Heatmap
- GGHIGHLIGHT: EASY WAY TO HIGHLIGHT A GGPLOT IN R
- to_bytes与from_bytes简单示例
- HOW TO CREATE AN INTERACTIVE CORRELATION MATRIX HEATMAP IN R
猜你喜欢

Beautiful and intelligent, Haval H6 supreme+ makes Yuanxiao travel safer

What is the relationship between digital transformation of manufacturing industry and lean production
Power Spectral Density Estimates Using FFT---MATLAB
自然语言处理系列(二)——使用RNN搭建字符级语言模型
ESP32音频框架 ESP-ADF 添加按键外设流程代码跟踪

Esp32 audio frame esp-adf add key peripheral process code tracking
自然语言处理系列(三)——LSTM
Cluster Analysis in R Simplified and Enhanced

R HISTOGRAM EXAMPLE QUICK REFERENCE

SVO2系列之深度滤波DepthFilter
随机推荐
Homer forecast motif
easyExcel和lombok注解以及swagger常用注解
K-Means Clustering Visualization in R: Step By Step Guide
Fabric.js 3个api设置画布宽高
Thesis translation: 2022_ PACDNN: A phase-aware composite deep neural network for speech enhancement
ORB-SLAM2不同线程间的数据共享与传递
Amazon cloud technology community builder application window opens
HOW TO ADD P-VALUES TO GGPLOT FACETS
From scratch, develop a web office suite (3): mouse events
GGHIGHLIGHT: EASY WAY TO HIGHLIGHT A GGPLOT IN R
The selected cells in Excel form have the selection effect of cross shading
MySql存储过程游标遍历结果集
【2022 ACTF-wp】
Cmake cross compilation
qt 仪表自定义控件
K-Means Clustering Visualization in R: Step By Step Guide
H5,为页面添加遮罩层,实现类似于点击右上角在浏览器中打开
Summary of flutter problems
Beautiful and intelligent, Haval H6 supreme+ makes Yuanxiao travel safer
R HISTOGRAM EXAMPLE QUICK REFERENCE