当前位置:网站首页>Brush questions --- binary tree --2
Brush questions --- binary tree --2
2022-07-02 12:08:00 【The dishes are not right】
Balanced binary trees

Their thinking :
Every node of a binary tree The absolute value of the height difference between the left and right subtrees is not more than 1 . Our tips have been given in the title , We need to find the height of the left subtree first , In finding the height of the right subtree , Then look at their height difference .
int getHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int lightLeft=getHeight(root.left);
int lightRight=getHeight(root.right);
return lightLeft>lightRight?lightLeft+1:lightRight+1;
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return true;
}
int left=getHeight(root.left);
int right=getHeight(root.right);
if(Math.abs(left-right)<=1&&isBalanced(root.left)&&isBalanced(root.right)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
There is another way that we can judge whether the absolute value of the height difference between the left and right subtrees exceeds 1, If exceeded 1 Just return a negative number , So if the final result returns a negative number , Then this tree is not a balanced binary tree .
private int getHeight1(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int lightLeft=getHeight(root.left);
int lightRight=getHeight(root.right);
if(lightLeft>=0 && lightRight>=0 && Math.abs(lightLeft- lightRight)<=1){
return Math.max(lightLeft,lightRight)+1;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
public boolean isBalanced1(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return true;
}
return getHeight1(root)>=0;
}
Symmetric binary tree
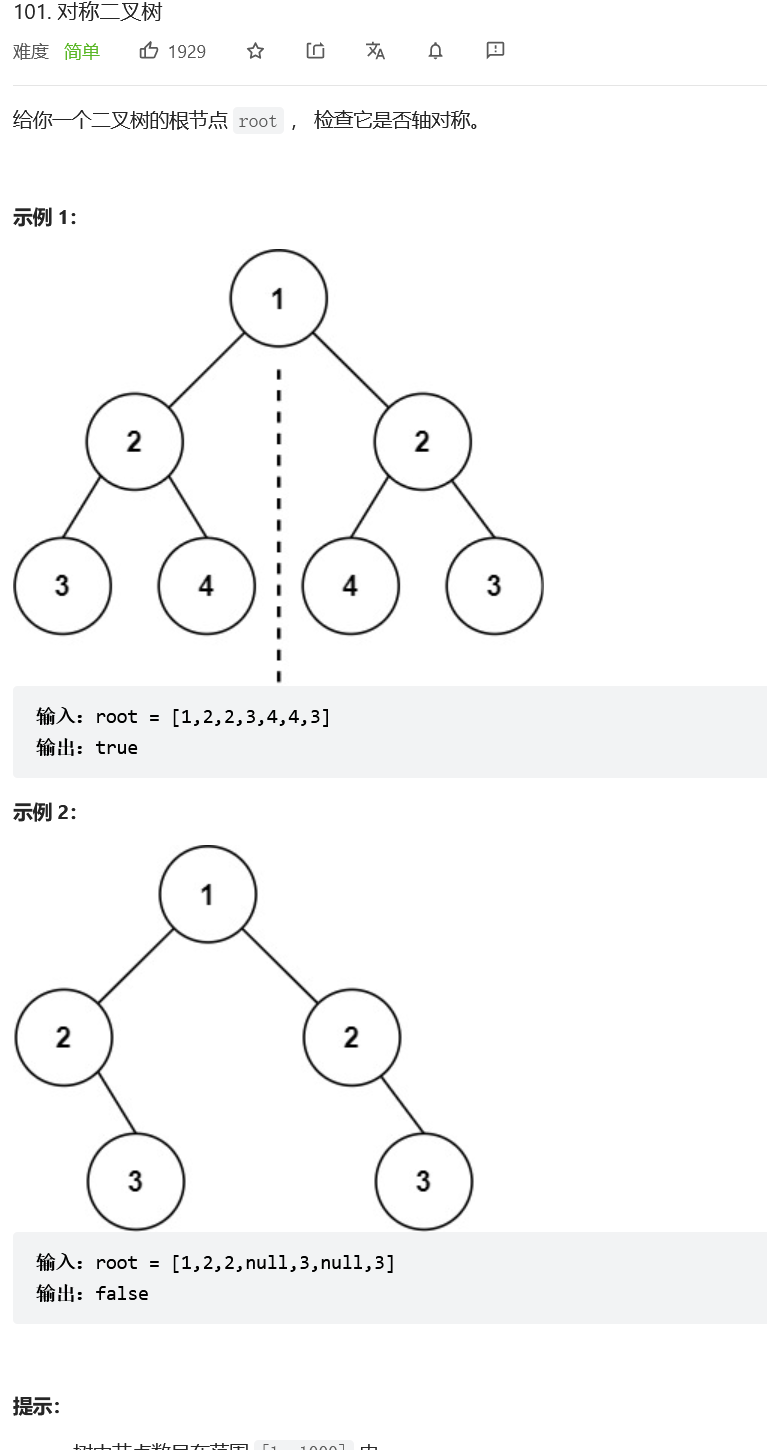 Their thinking :
Their thinking :
public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode rightTree,TreeNode leftTree){
if(leftTree==null && rightTree!=null) return false;
if(leftTree!=null && rightTree==null) return false;
if(leftTree==null && rightTree==null) return true;
if(rightTree.val!=leftTree.val){
return false;
}
return isSymmetricChild(leftTree.left,rightTree.right)&&
isSymmetricChild(leftTree.right,rightTree.left);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return true;
return isSymmetricChild(root.left,root.right);
}
Binary tree traversal
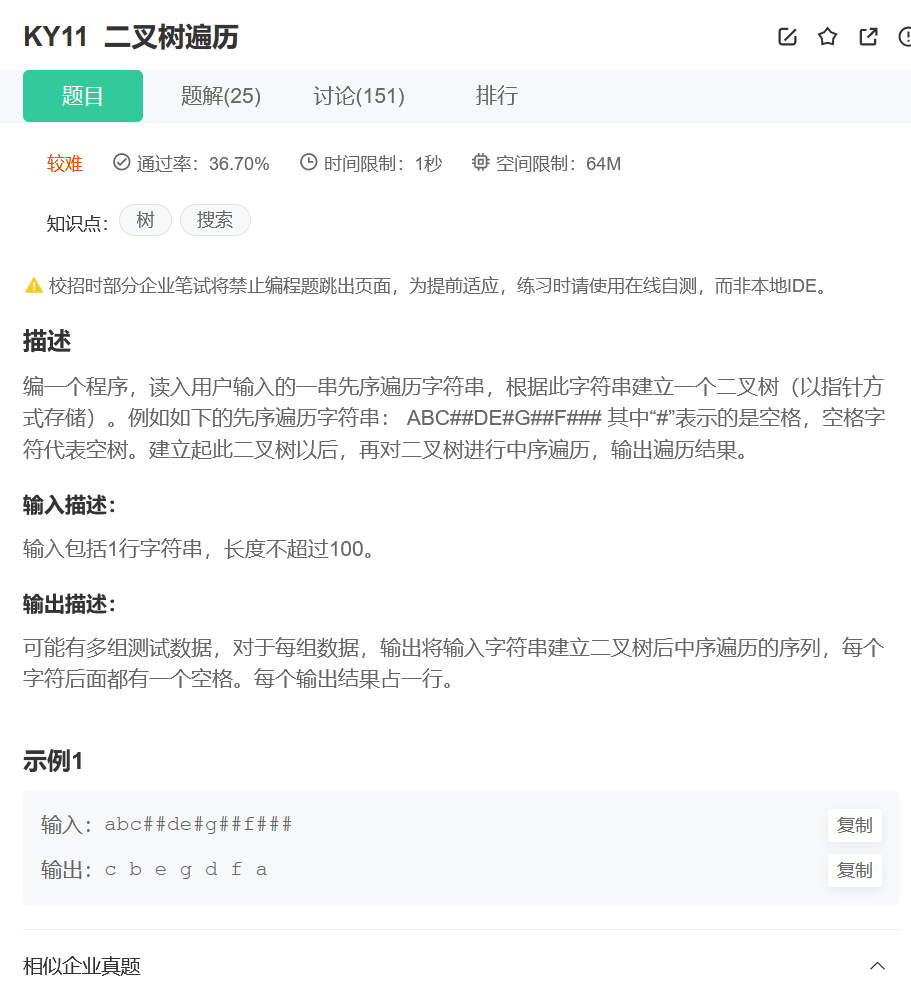 Their thinking : The title gives the result of preorder traversal , So when we build this binary tree , It also needs to be built in the way of preorder traversal .
Their thinking : The title gives the result of preorder traversal , So when we build this binary tree , It also needs to be built in the way of preorder traversal .

import java.util.*;
class TreeNode{
public char val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(char val){
this.val=val;
}
}
public class Main{
public static int i = 0 ;
public static TreeNode createTree(String str) {
TreeNode root = null;
if(str.charAt(i) != '#') {
root = new TreeNode(str.charAt(i));
i++;
root.left = createTree(str);
root.right = createTree(str);
}else {
// encounter # It's an empty tree
i++;
}
return root;
}
public static void inorder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
inorder(root.right);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
// Be careful hasNext and hasNextLine The difference between
while (in.hasNextLine()) {
// Note multiple inputs
String str = in.nextLine();
TreeNode root = createTree(str);
inorder(root);
}
}
}
The nearest common ancestor of a binary tree
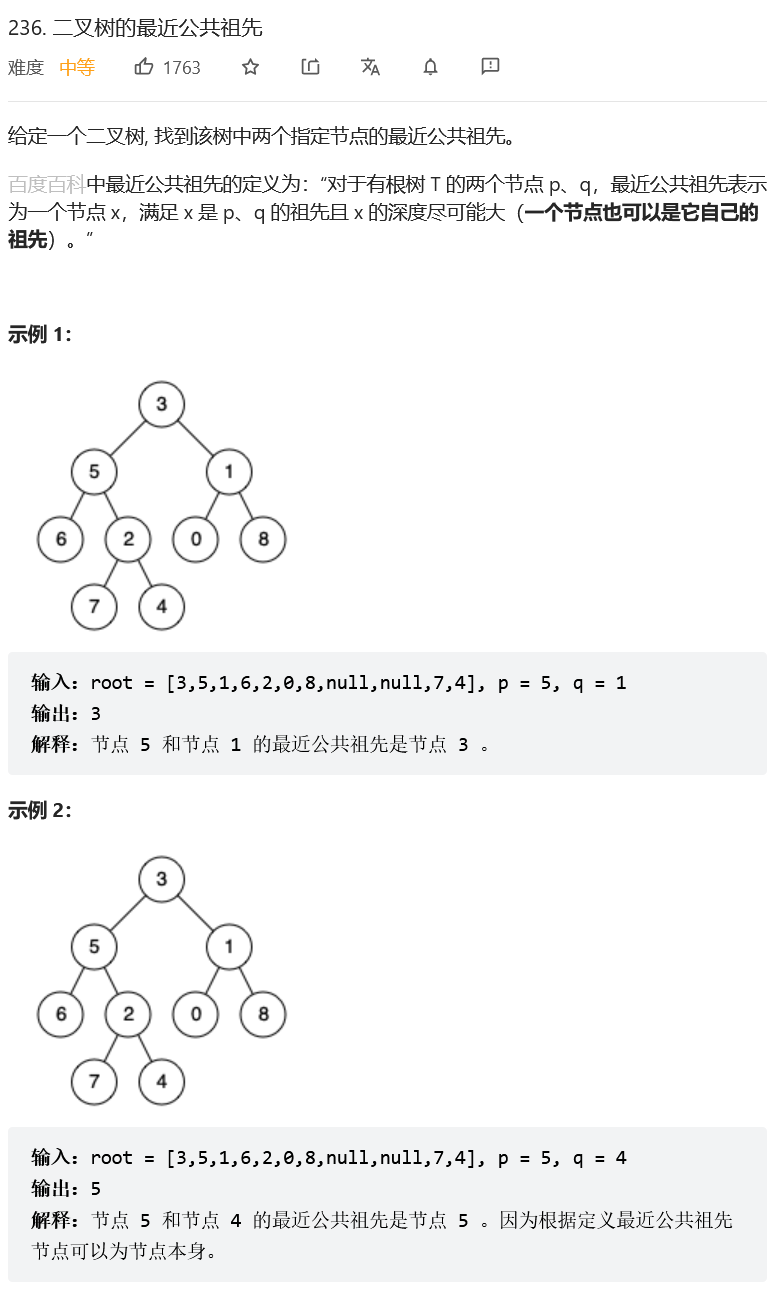
Their thinking :
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null) return null;
if(p==root || q==root){
return root;
}
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left!=null && right!=null){
return root;
}else if(left==null && right!=null){
return right;
}else if(left!=null && right==null){
return left;
}
return null;
}
There's a second way :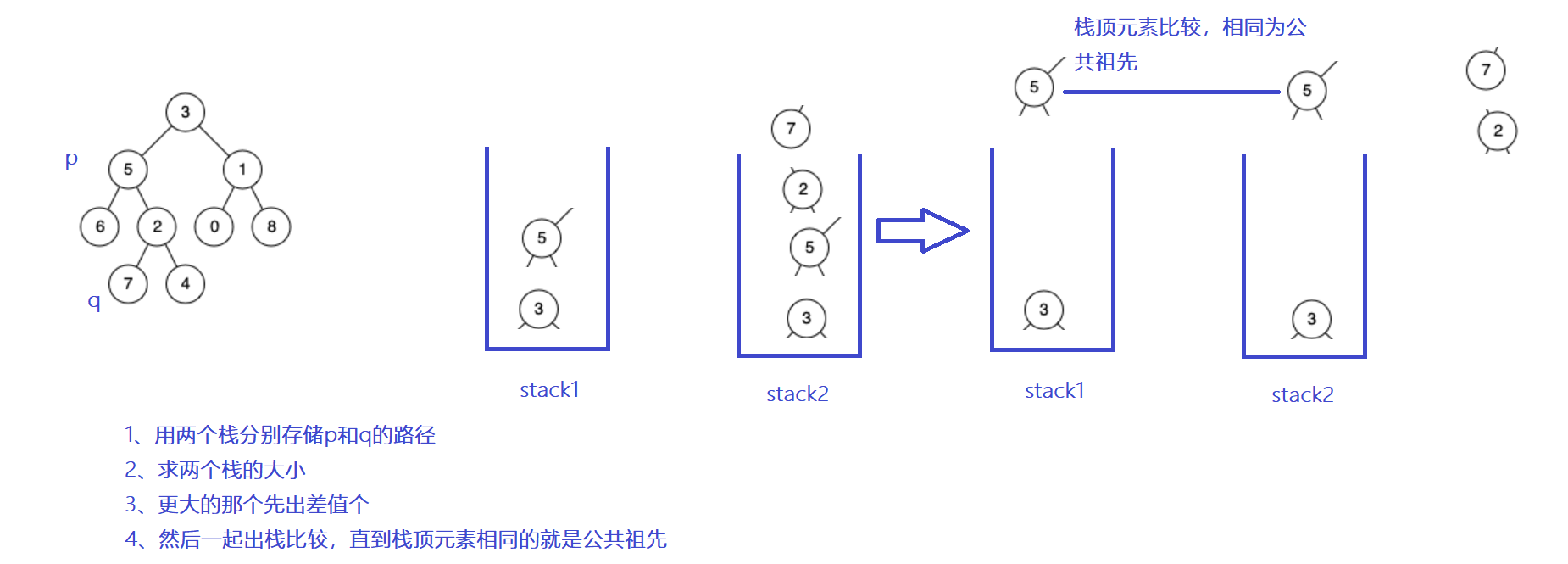
public boolean getPath(TreeNode root,TreeNode node,Stack<TreeNode> stack){
if(root==null || node==null) return false;
stack.push(root);
if(root==node) return true;
boolean flg=getPath(root.left,node,stack);
if(flg){
return true;
}
boolean flg1=getPath(root.right,node,stack);
if(flg1){
return true;
}
stack.pop();
return false;
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null) return null;
Stack<TreeNode> stack1=new Stack<>();
getPath(root,p,stack1);
Stack<TreeNode> stack2=new Stack<>();
getPath(root,q,stack2);
int size1=stack1.size();
int size2=stack2.size();
if(size1-size2>0){
int size=size1-size2;
while(size!=0){
stack1.pop();
size--;
}
while(!stack1.isEmpty() && !stack2.isEmpty()){
if(stack1.peek()==stack2.peek()){
return stack1.pop();
}else{
stack1.pop();
stack2.pop();
}
}
}else{
int size=size2-size1;
while(size!=0){
stack2.pop();
size--;
}
while(!stack1.isEmpty() && !stack2.isEmpty()){
if(stack1.peek()==stack2.peek()){
return stack1.pop();
}else{
stack1.pop();
stack2.pop();
}
}
}
return null;
}
Binary search tree and double linked list
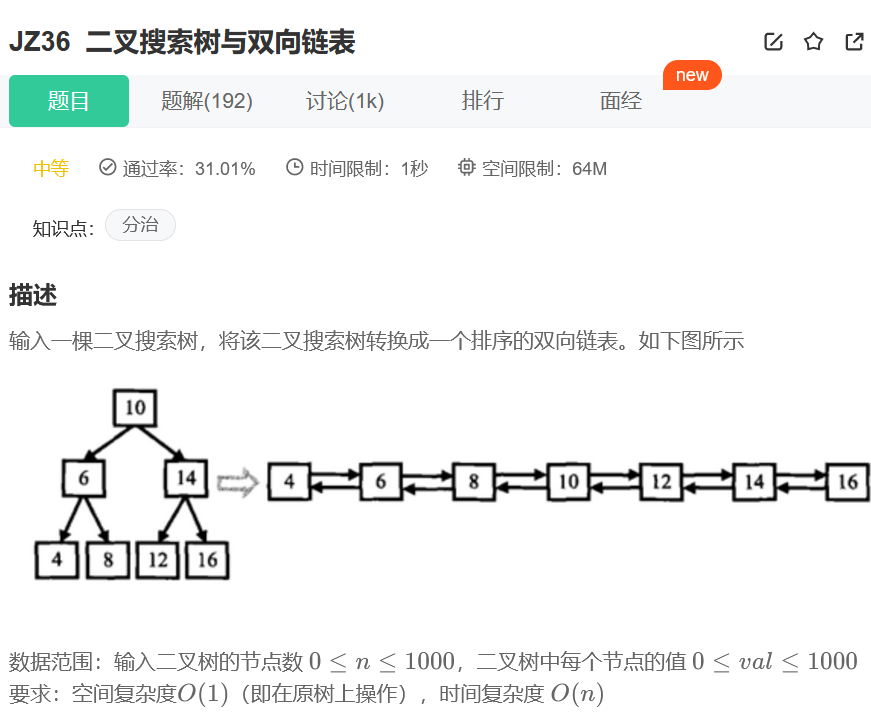 Their thinking :
Their thinking :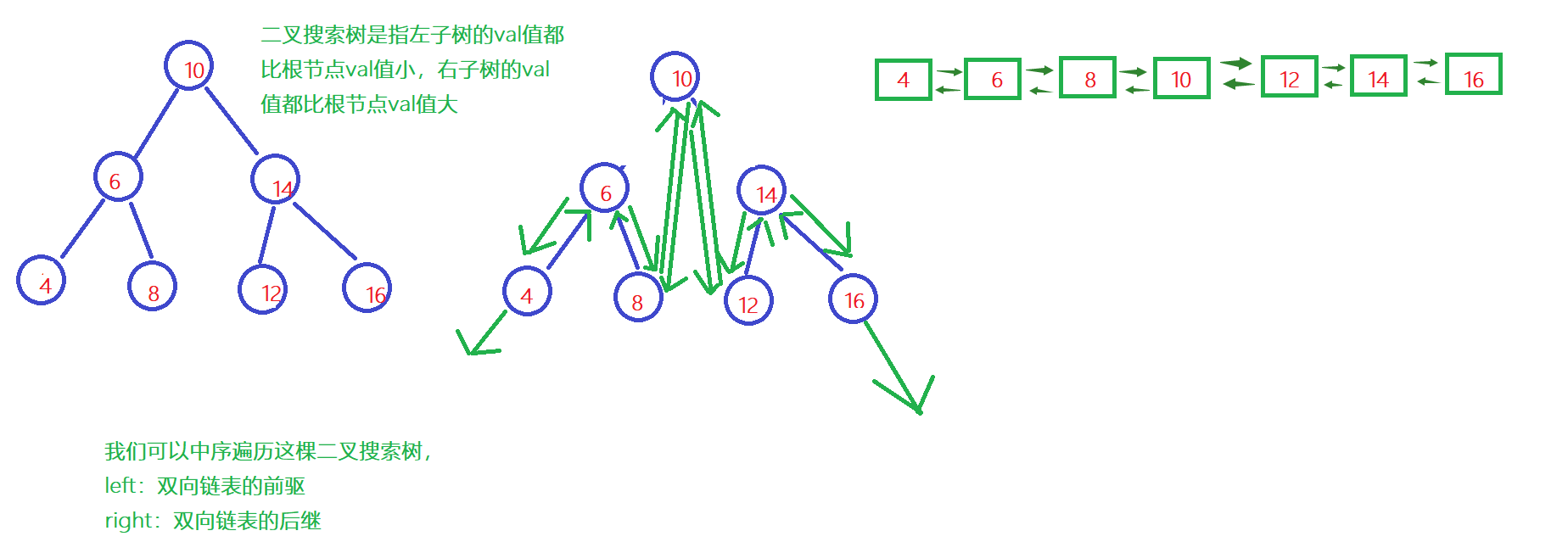
TreeNode pre=null;
public void inorder (TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return;
inorder(root.left);
root.left=pre;
if(pre!=null){
pre.right=root;
}
pre=root;
inorder(root.right);
}
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree==null) return null;
inorder(pRootOfTree);
TreeNode head=pRootOfTree;
while(head.left!=null){
head=head.left;
}
return head;
}
Construction of binary trees from traversal sequences of preorder and middle order

Their thinking :
public int index=0;
public TreeNode createTreeByPandI(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend){
if(inbegin>inend) return null;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[index]);
// Find the position of the root node traversed in the middle order
int rootindex=findIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[index]);
if(rootindex==-1){
return null;
}
index++;
// Create left subtree and right subtree
root.left=createTreeByPandI(preorder,inorder,inbegin,rootindex-1);
root.right=createTreeByPandI(preorder,inorder,rootindex+1,inend);
return root;
}
public int findIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key){
for(int i=inbegin;i<=inend;i++){
if(key==inorder[i]){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
if(inorder==null ||preorder==null) return null;
return createTreeByPandI(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
Construct binary tree from middle order and post order traversal sequence
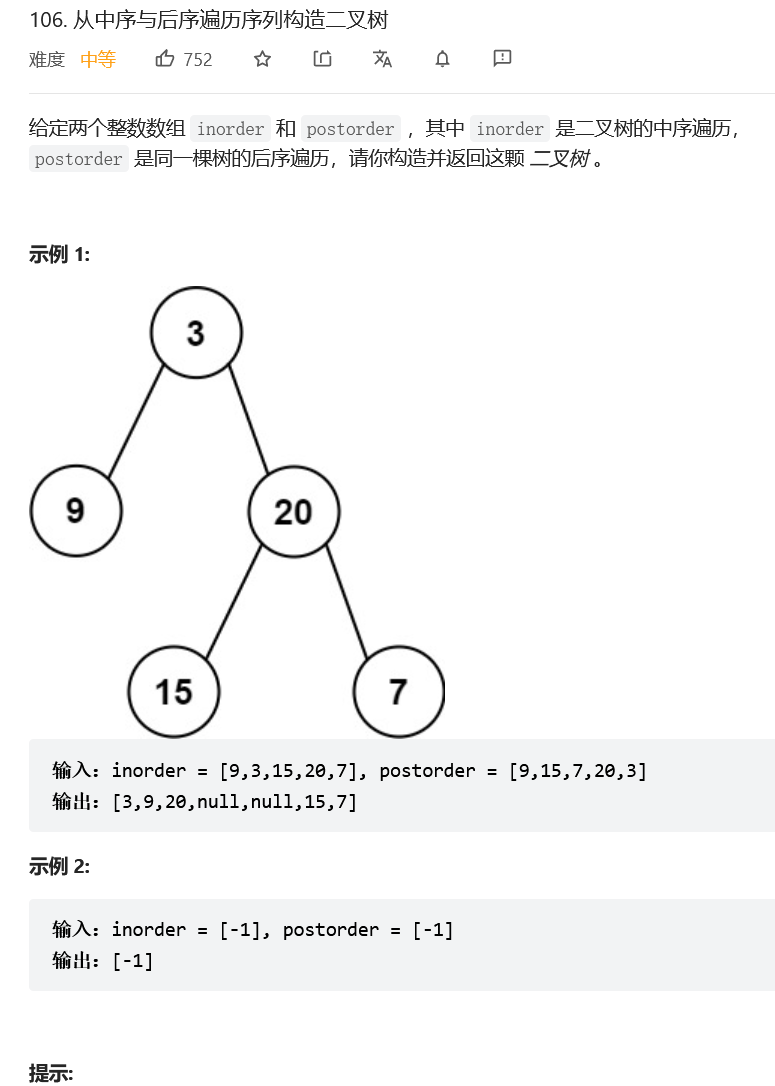 Their thinking :
Their thinking :
The implementation method is roughly the same as the above question , But pay attention to the order in which the left and right subtrees are created .
public int index = 0;
public TreeNode createTreeByPandI(int[] postorder, int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend){
if(inbegin>inend) return null;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[index]);
// Find the position of the root node traversed in the middle order
int rootindex=findIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,postorder[index]);
if(rootindex==-1){
return null;
}
index--;
// Create left subtree and right subtree
root.right=createTreeByPandI(postorder,inorder,rootindex+1,inend);
root.left=createTreeByPandI(postorder,inorder,inbegin,rootindex-1);
return root;
}
public int findIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int key){
for(int i=inbegin;i<=inend;i++){
if(key==inorder[i]){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
if(inorder==null ||postorder==null) return null;
index=postorder.length-1;
return createTreeByPandI(postorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
Create a string from a binary tree
 Their thinking : Here we use StringBuilder Store string , It will be more convenient and simple . Look at examples to find rules , When to add "(“, When to add ”)“, When to add ”()", It depends on whether the left subtree and the right subtree are empty .
Their thinking : Here we use StringBuilder Store string , It will be more convenient and simple . Look at examples to find rules , When to add "(“, When to add ”)“, When to add ”()", It depends on whether the left subtree and the right subtree are empty .
public void treeToString(TreeNode root,StringBuilder sb){
if(root==null) return;
sb.append(root.val);
if(root.left!=null){
sb.append("(");
treeToString(root.left,sb);
sb.append(")");
}else{
if(root.right!=null){
sb.append("()");
}else{
return;
}
}
if(root.right==null){
return;
}else{
sb.append("(");
treeToString(root.right,sb);
sb.append(")");
}
}
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return null;
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
treeToString(root,sb);
return sb.toString();
}
Preorder traversal of two tree 、 In the sequence traversal 、 Subsequent traversal ( Non recursive implementation )
Their thinking : The former sequence traversal : Traverse from root , First traverse the left subtree , Put the traversal result on the stack , After traversing the left subtree , Pop up top element , If the element at the top of the stack has a right subtree, continue to traverse , Do not continue to pop up the next element . So circular , Until you walk through the whole tree . Middle order ergodic isomorphism . Post order traversal requires a little processing , Because if you don't deal with , Will repeat traversal .
// The former sequence traversal
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
List<Integer> ret=new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
while(cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
ret.add(cur.val);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.pop();
cur=top.right;
}
return ret;
}
// In the sequence traversal
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
List<Integer> ret=new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
while(cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.pop();
ret.add(top.val);
cur=top.right;
}
return ret;
}
// Subsequent traversal
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
List<Integer> ret=new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
TreeNode prev=null;
while(cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.peek();
// When the top element of the stack is traversed or printed eject
if(top.right==null || top.right==prev){
stack.pop();
ret.add(top.val);
prev=top;// Record the most recently printed nodes
}else{
cur=top.right;
}
}
return ret;
}
The completeness test of binary tree
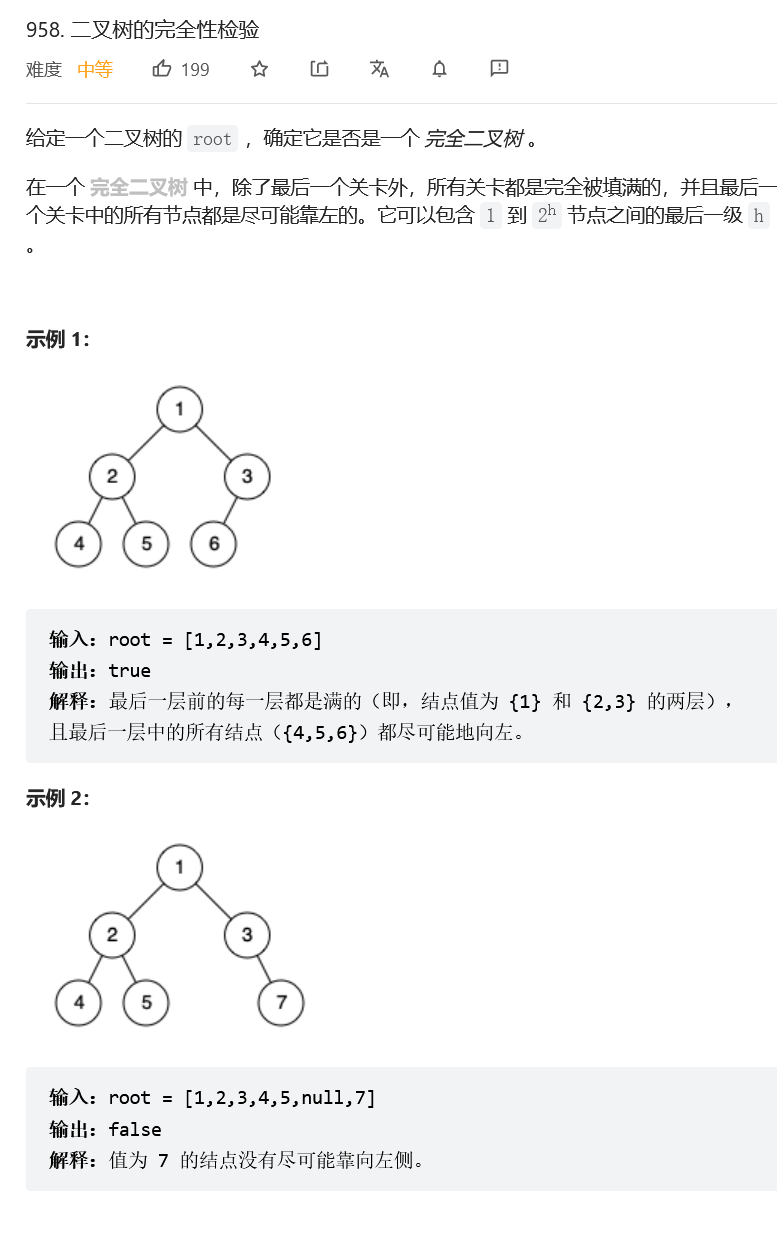
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return true;
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
boolean flg=false;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode tmp=queue.poll();
if(flg){
if(tmp.left!=null || tmp.right!=null){
return false;
}
}
if(tmp.left!=null && tmp.right!=null){
// Both the left and right children have
queue.offer(tmp.left);
queue.offer(tmp.right);
}else if(tmp.right!=null){
// Only the right child
return false;
}else if(tmp.left!=null){
// Only the left child
queue.offer(tmp.left);
flg=true;
}else{
// There are no children left or right
flg=true;;
}
}
return true;
}
Summary
That's what we have today , If you have any questions, you can leave a message in the comment area 
边栏推荐
- CONDA common command summary
- Experiment of connecting mobile phone hotspot based on Arduino and esp8266 (successful)
- mysql索引和事务
- How to Create a Beautiful Plots in R with Summary Statistics Labels
- Differences between nodes and sharding in ES cluster
- HOW TO EASILY CREATE BARPLOTS WITH ERROR BARS IN R
- Depth filter of SvO2 series
- 【C语言】十进制数转换成二进制数
- Repeat, tile and repeat in pytorch_ The difference between interleave
- 堆(优先级队列)
猜你喜欢

MSI announced that its motherboard products will cancel all paper accessories

Experiment of connecting mobile phone hotspot based on Arduino and esp8266 (successful)

Applet link generation
自然语言处理系列(一)——RNN基础
HOW TO EASILY CREATE BARPLOTS WITH ERROR BARS IN R

Filtre de profondeur de la série svo2

PgSQL string is converted to array and associated with other tables, which are displayed in the original order after matching and splicing

mysql索引和事务
倍增 LCA(最近公共祖先)
Larvel modify table fields
随机推荐
Applet link generation
(C language) input a line of characters and count the number of English letters, spaces, numbers and other characters.
BEAUTIFUL GGPLOT VENN DIAGRAM WITH R
Maximum profit of jz63 shares
Leetcode739 daily temperature
Small guide for rapid formation of manipulator (VII): description method of position and posture of manipulator
Thesis translation: 2022_ PACDNN: A phase-aware composite deep neural network for speech enhancement
Leetcode14 longest public prefix
SSH automatically disconnects (pretends to be dead) after a period of no operation
From scratch, develop a web office suite (3): mouse events
CDA数据分析——AARRR增长模型的介绍、使用
HOW TO ADD P-VALUES ONTO A GROUPED GGPLOT USING THE GGPUBR R PACKAGE
Yygh-10-wechat payment
[C language] convert decimal numbers to binary numbers
Deep understanding of NN in pytorch Embedding
HOW TO CREATE A BEAUTIFUL INTERACTIVE HEATMAP IN R
Le tutoriel F - String le plus facile à comprendre de l'histoire.
PyTorch搭建LSTM实现服装分类(FashionMNIST)
How to Add P-Values onto Horizontal GGPLOTS
基于Arduino和ESP8266的连接手机热点实验(成功)