当前位置:网站首页>21. [STM32] I don't understand the I2C protocol. Dig deep into the sequence diagram to help you write the underlying driver
21. [STM32] I don't understand the I2C protocol. Dig deep into the sequence diagram to help you write the underlying driver
2022-07-05 15:48:00 【According to point_ DW】
Author's brief introduction : Hello, everyone , My name is DW, Share some of my new knowledge every day , Look forward to making progress with you
Series column :STM32
Development board :STM32F103If there is anything that is not well written, you are welcome to correct
Creation time :2022 year 7 month 3 Japan
I2C(Inter-Integrated Circuit BUS) For integrated circuit bus , The bus is controlled by NXP Company design , It is mainly used for master-slave communication between master controller and slave devices .IIC and SPI Strictly speaking, interfaces are a combination of software and hardware defined by people , It is divided into physical layer and protocol layer .
SDA(Serial data) It's the data line , It is used to transmit data .
SCL(Serial clock line) It's a clock line , It controls the timing of data transmission .

I2C The three most important points are :
1. Start and end conditions
2. Reply and non reply
3. The validity of the data
below , I will introduce how to use these three important knowledge points one by one , Because of the SDA Output and input mode selection , So first configure its output and input modes .
// Mode configuration out input
void I2C_Mode(u8 addr){
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
if(addr){ //out
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = SDA;//PB0
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;// Output rate
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_PP;// Push pull output
}
else{ //Input
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = SCL;//PB1
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_IPU;// Push pull output
}
GPIO_Init(I2C_PROT,&GPIO_InitStructure);// Initialization pin
}1: The output mode
0 : The input mode
Start and end conditions
1. When SCL When it's high level ,SDA Online by Jump from high to low Is defined as Starting conditions .
2. When SCL When it's high level ,SDA Online by Jump from low to high Is defined as Stop conditions .
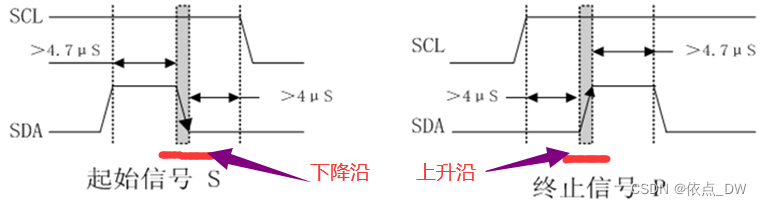
Starting conditions
It can be known from the sequence diagram ,SCL and SDA It is high level by default , At the same time, it needs to be delayed 4.7us above , I give it 5us Delay of , After the SDA Pull it down , Further delay 5us, At the same time SCL Pull it down , Then the writing of the starting condition sequence code is completed .
Pay attention here ,SDA Select output mode
// start
void I2C_Start(void){
I2C_Mode(Out);
SCL_High;
SDA_High;
delay_us(5);
SDA_Low;
delay_us(5);
SCL_Low;
}The end condition

It can be known from the sequence diagram ,SCL The default state is high ,SDA The default state is low , At the same time, it needs to be delayed 4.7us above , I give it 5us Delay of , hold SDA pull up , Further delay 5us, Then the completion of the end condition timing code .
Pay attention here ,SDA Select output mode
towards SDA Bus write : The output mode
towards SDA Bus read : The input mode
// end
void I2C_Stop(void){
I2C_Mode(Out);
SDA_Low;
delay_us(5);
SCL_High;
delay_us(5);
SDA_High;
}Response and non response
Every time the master sends a byte of data to the slave , The master always needs to wait for a reply from the slave , To confirm whether the slave has successfully received the data , The clock needed by the slave to answer the host is still provided by the host , The response appears every time the host completes 8 The clock period immediately following the data bit transmission , Low level 0 To answer ,1 It means no response .
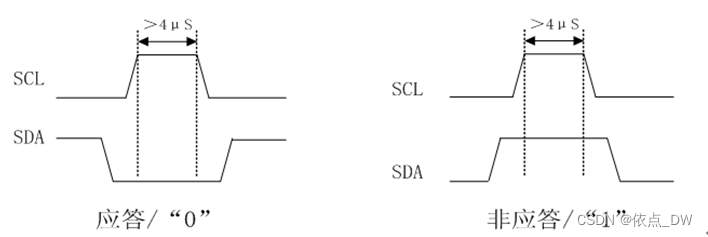
It can be known from the sequence diagram , No matter in the answer state , Or in the non response state ,SCL It's all high level , Well, first put SCL pull up , Then delay 4us, To determine SDA The state of ;
Define a Time Variable , If you don't answer , Both read SDA Data bits for 1, Just send a stop signal , Indicates that the device does not exist , Prevent the program from stopping stuck in this position , Then a non reply signal is returned 1;
If you read SDA Data bits for 0, To answer , Then put SCL Pull it down , Time delay 4us, Finally back to 0, It completes an operation of answering .
// Answer non answer judgment
u8 I2C_Write_Ack(void){
u8 Time;
I2C_Mode(Input);
SCL_High;
delay_us(4);
while(GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(I2C_PROT,SDA)){
if(++Time>250){
I2C_Stop();
return 1;//1 Non response
}
}
SDA_Low;//0 The reply
delay_us(4);
return 0;
}The validity of the data
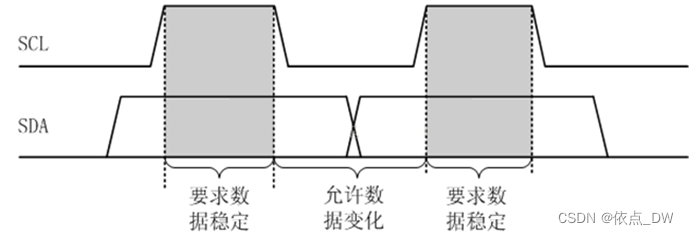
stay Writing data when , When SCL Low power level , Allow data to change , At this time, you can write data . that , How to operate ? First of all, we need to put SCL Pull it down , And then keep 4us; Then select the output mode , Then start from the high position bit One bit Writing data .
Be careful :I2C Write data from the high order .
// Write Bytes
void I2C_Write_Byte(u8 data){
SCL_Low;
delay_us(4);
for(u8 i=0;i<8;i++){
I2C_Mode(Out);
if((data<<i)&0x80) SDA_High;
else
SDA_Low;
SCL_High;
delay_us(4);
SCL_Low;
delay_us(4);
}
}
stay Reading data when , Select input mode , We need to SCL Bus up , Because at this time, the data is stable and effective , After reading the SDA The data of , If SDA High level ,data Or on the 0x01, After reading the data , take SCL Pull it down , Finally back to data.
data<<=1;// Read data from the low order , Keep moving left , Low will become high .
// Reading data
u8 I2C_Read_Data(void){
u8 data;
for(u8 i=0;i<8;i++){
I2C_Mode(Input);
SCL_High;
delay_us(4);
data<<=1;
if(GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(I2C_PROT,SDA) == SET){
data |= 0x01;
}
SCL_Low;
delay_us(4);
}
return data;
}
Since then , All the three parts of the code have been written , After we understand the principle and usage of these three sequences , Next, I will tell you how to drive on this basis I2C Interface OLED.
OLED brief introduction

2. communication interface : 3-wire SPI, 4-wire SPI, I2C
3. Screen type : OLED
4. Control chip : SSD1306
5. The resolution of the : 128*64(Pixel)
6. Dimensions : 128*64(Pixel)
7. Display color : Yellow blue ( Two color block screen )
8. working temperature : -20°C ~ 70°C
9. Storage temperature : -30°C ~ 80°C
10. visual angle : >160
matters needing attention :OLED The display is different from LCD,OLED Power on is unresponsive , You need a driver to display !
Wiring way :
SDA --- PC0
SCL --- PC1
VCC --- 5V
GND --- The earth
OLED Communication address and register address

be-all I2C Devices will have hardware addresses , That is, the address of the chip , You can know from the manual ,b7~b2 Is fixed ,b1(SA0) General choice 0,bo(R/W) Used to determine the I2C Operation mode of general interface ,R/w # = 1, It is in read mode .R/w # = 0, It is in write mode . Generally only to OLED Writing data , Therefore, its address is :0111 1000(0x78) , So we define OLED The device address is
#define OLED 0X78
0x78: Write device address
Bus sequence diagram
We can know from the bus sequence diagram , The process of sending data or commands is as follows :

According to the above steps , The code we write is as follows :
void OLED_Write_Cmd_Data(u8 cmd,u8 data){
I2C_Start();
I2C_Write_Byte(OLED);
I2C_Write_Ack();
if(!cmd){
I2C_Write_Byte(0X00);
I2C_Write_Ack();
I2C_Write_Byte(data);
}
else{
I2C_Write_Byte(0X40);
I2C_Write_Ack();
I2C_Write_Byte(data);
}
I2C_Write_Ack();
I2C_Stop();
}0: Write orders
1: Writing data
thus , The most important part of the code has been written , Other things about OLED The description of has been detailed and clear in the ninth article :
9.[STM32]0.96 " OLED Hard to understand ? Take a look at this . Well, let's see the effect !

In order to facilitate the next search , Remember to pay a little attention .
This chapter ends , I'll see you in the next chapter
Reference material :
1.STM32 Firmware library manual
2. The punctual atoms STM32 Incomplete manual _ Library function version
3. Reference video Reference article 9.[STM32]0.96 " OLED Hard to understand ? Take a look at this
Data uploaded , You need to take it yourself
边栏推荐
- Install PHP extension spoole
- Transfer the idea of "Zhongtai" to the code
- D-snow halo solution
- Au - delà du PARM! La maîtrise de l'Université de Pékin propose diverse pour actualiser complètement le classement du raisonnement du NLP
- lv_font_conv离线转换
- 18.[STM32]读取DS18B20温度传感器的ROM并实现多点测量温度
- Bubble sort, insert sort
- Bugku easy_ nbt
- Value series solution report
- 如何将 DevSecOps 引入企业?
猜你喜欢
OSI 七层模型

Analytic hierarchy process of mathematical modeling (including Matlab code)
Common redis data types and application scenarios
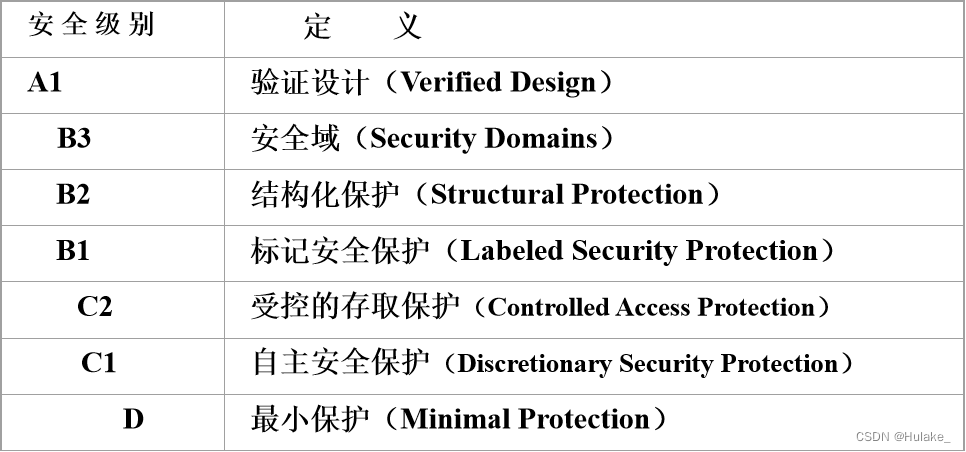
Database learning - Database Security
Detailed explanation of C language branch statements

lvgl 显示图片示例
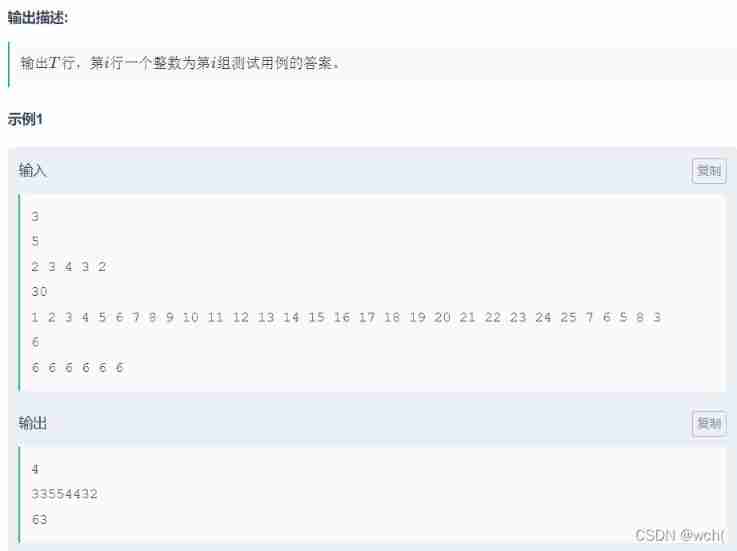
Value series solution report
Bugku telnet

Bugku's Ah Da
lv_font_conv离线转换
随机推荐
21.[STM32]I2C协议弄不懂,深挖时序图带你编写底层驱动
Garbage collection mechanism of PHP (theoretical questions of PHP interview)
Vulnhub-Moneybox
Data communication foundation - route republication
No one consults when doing research and does not communicate with students. UNC assistant professor has a two-year history of teaching struggle
First PR notes
Data communication foundation - Ethernet port mirroring and link aggregation
Data communication foundation OSPF Foundation
lv_ font_ Conv offline conversion
Explanation report of the explosion
P1451 calculate the number of cells / 1329: [example 8.2] cells
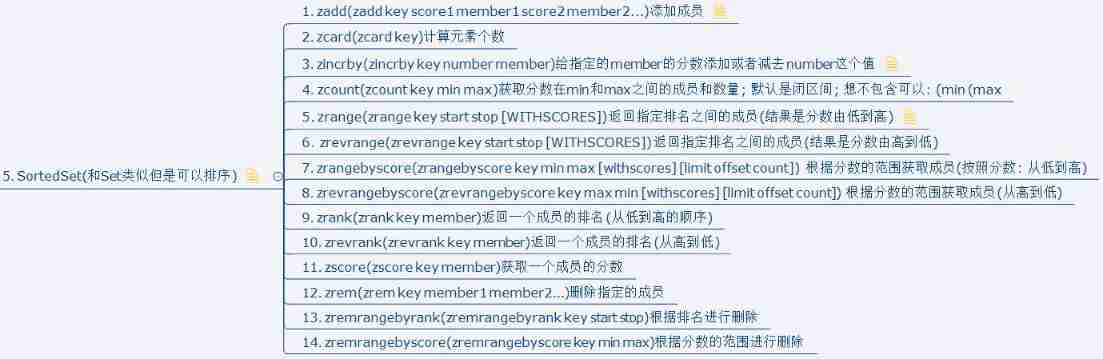
Common redis data types and application scenarios
wxml2canvas
SQL injection sqllabs (basic challenges) 1-10
力扣今日题-729. 我的日程安排表 I
定义严苛标准,英特尔Evo 3.0正在加速PC产业升级
基于OpenHarmony的智能金属探测器
episodic和batch的定义
sql server学习笔记
D-snow halo solution
