当前位置:网站首页>Polymorphism, final, etc
Polymorphism, final, etc
2022-07-07 12:36:00 【Xiaobai shelter】
1 Final
1.1 What is it?
final It's a modifier , Indicates final , Unalterable
1.2 What can be done
final Modified class , uninheritable
final Modifies the member method , Can't be overwritten
final The modified variable cannot be assigned twice , No default , Assignment must be displayed
Generally, we put final Decorated static variables are called constants ,public static final data type Variable name = value ;
1.3 How to use it? 


2 polymorphic
2.1 What is it?
Parent class reference Point to a subclass object
Parent class reference : refer to Referential variables declared with a parent type
Point to : Which object can be found by memory address
Subclass object :new Subclass Created heap memory object
Subclass Variable = new Subclass ();
Cat c = new Cat();
Parent type Variable name = new Subclass ();
Animal a = new Cat();
2.2 Related knowledge
Six principles of software design :
1 Principle of single responsibility : Single function , Embrace only one change
2 Richter's principle of substitution : When the parent class can be used , You must be able to use subclasses
Because inheritance , Functions of parent class , Subclasses have
3 The principle of Dependence Inversion : Details should depend on abstraction , And abstraction should not depend on details
4 Interface isolation principle : I don't care
5 Dimitar's law : Minimum knowledge principle , And other classes or objects , Know as little as possible
6 Opening and closing principle : Turn off for changes , Open to expansion
2.3 advantage :
Same operation , Scope different objects , There can be different explanations , It produces different results , It's polymorphism
When there are many different ways to implement something , We choose to rely on the top , To embrace variety
The essence is to reduce the coupling between classes and details
2.4 shortcoming
Missing subclass specific properties
2.5 Applicable grammar 




Type conversion exception 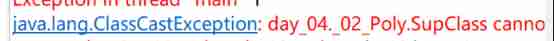
2.6 Several forms of polymorphism 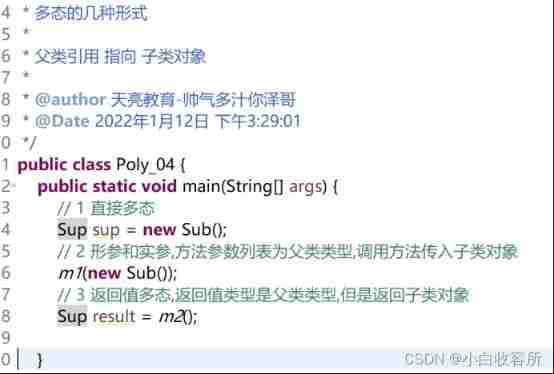
2.7 Instanceof
3.abstract
3.1 What is it?
abstract: Modifier Modified class Abstract class , The decorated method is abstract method
Abstract classes cannot instantiate objects
Abstract methods have no method bodies , Define only the functions , No functional implementation , And the abstract method must be in the abstract class
conversely , In an abstract class There can be no abstract methods
abstract Unable to join final At the same time
3.2 Use the syntax 
4. Interface (Interface)
4.1 What is it?
Interface It can be understood as a completely abstract class , There are only abstract methods and constants
But from 1.8 Start , Allow to appear Static methods and default methods
grammar Modifier interface The interface name {}
Abstract methods in interfaces , No need to add abstract modification , Method The default is public abstract
Interface , No variables , Constant only , also public static final It can be omitted
Between classes and interfaces , No longer an inheritance relationship , It becomes an implementation relationship , from extends Instead of implements
The interface name Variable = new Subclass implementation () Polymorphism also occurs
One class Only one class can be inherited , however Can achieve N Interface , Separated by commas , It can solve the problem of weak single inheritance function
class Class name implements Interface 1 , Interface 2, Interface 3....{}
Interface and interface , It's multi inheritance , Multiple Separated by commas
interface The interface name extends Parent interface name 1, Parent interface name 2,...{}
One class If you implement an interface , Then you must implement all the abstract methods in the interface ,. Otherwise, it is necessary to add abstract modification
An abstract class , Implement an interface , Can achieve 0~N Abstract methods
1.7 There can only be abstract methods
1.8 There can be static methods , There can be default Method ( It can be understood as a member method )
Static methods , Call with the interface name
default Method needs to be called by the sub implementation class , You can also override
1.9 Start Support private Method
4.2 Usage method 



5 Object
5.1 Equals
Object Is the ancestor of all classes , yes java The root class provided in
When a class does not show that it inherits from another class , Default inheritance object
Object xx = new xxx(); Polymorphism can occur
==: When comparing basic types , Compare the size of the value , But when comparing reference types , Compare memory addresses
*
- Compare memory addresses , It has no value , We usually compare the attribute values of two objects , Is it consistent , Instead of comparing whether the addresses of two objects are consistent
*equals(): The method is designed for , Used to compare whether two objects are equal , But the default comparison address - java in Object Inside equals Method , Default compare memory address (==) We need to rewrite according to the requirements
5.2Finalize
finalize : This method will be called automatically when the garbage is collected , Unordered programmers manually call
The garbage : Be an object , When there are no more references to it , This object is treated as garbage data ( Is to create an object , No one can find him )
protected void finalize() throws Throwable { }
Object Medium finalize Method , Nothing has been done , You need to rewrite it according to your needs
5.3toString
toString: Represents the string representation of the current object
When we print a reference variable , Will automatically call the toString Method
and Object In the default toString Method Is to print the memory address of the object (hash value )
边栏推荐
- DOM parsing XML error: content is not allowed in Prolog
- leetcode刷题:二叉树21(验证二叉搜索树)
- [Q&A]AttributeError: module ‘signal‘ has no attribute ‘SIGALRM‘
- sql-lab (54-65)
- Session
- Utiliser la pile pour convertir le binaire en décimal
- leetcode刷题:二叉树24(二叉树的最近公共祖先)
- Idea 2021 Chinese garbled code
- Processing strategy of message queue message loss and repeated message sending
- Epp+dis learning path (1) -- Hello world!
猜你喜欢

Attack and defense world - PWN learning notes
【PyTorch实战】图像描述——让神经网络看图讲故事

Several ways to clear floating
金融数据获取(三)当爬虫遇上要鼠标滚轮滚动才会刷新数据的网页(保姆级教程)
Several methods of checking JS to judge empty objects
Common knowledge of one-dimensional array and two-dimensional array
About IPSec
消息队列消息丢失和消息重复发送的处理策略
![[pytorch practice] write poetry with RNN](/img/91/a6d3f348ff099b7c44eb185921b1b6.png)
[pytorch practice] write poetry with RNN
Attack and defense world ----- summary of web knowledge points
随机推荐
The left-hand side of an assignment expression may not be an optional property access. ts(2779)
SQL lab 1~10 summary (subsequent continuous update)
牛客网刷题网址
Processing strategy of message queue message loss and repeated message sending
Cookie
@What happens if bean and @component are used on the same class?
NGUI-UILabel
MPLS experiment
Solve server returns invalid timezone Go to ‘Advanced’ tab and set ‘serverTimezone’ property manually
(待会删)yyds,付费搞来的学术资源,请低调使用!
Object. Simple implementation of assign()
SQL Lab (46~53) (continuous update later) order by injection
普乐蛙小型5d电影设备|5d电影动感电影体验馆|VR景区影院设备
[deep learning] image multi label classification task, Baidu paddleclas
Pule frog small 5D movie equipment | 5D movie dynamic movie experience hall | VR scenic area cinema equipment
JS to convert array to tree data
Solutions to cross domain problems
Realize all, race, allsettled and any of the simple version of promise by yourself
Inverted index of ES underlying principle
金融数据获取(三)当爬虫遇上要鼠标滚轮滚动才会刷新数据的网页(保姆级教程)