当前位置:网站首页>Implementation of knowledge consolidation source code 2: TCP server receives and processes half packets and sticky packets
Implementation of knowledge consolidation source code 2: TCP server receives and processes half packets and sticky packets
2022-07-06 04:17:00 【yun6853992】
1: Background introduction
1.1: Processing tcp When connecting to receive data , Want to consider recv when ( When reading data ), Half packet of data , Stick package problem
===》tcp Is reliable streaming , Means for each connection ,tcp Sure According to the order , Reliably receive peer messages .
===》 understand : For each connection (fd Corresponding to five tuples ),tcp The bottom layer of the protocol stack maintains a send buffer and a receive buffer .
=====》 For a connection , Corresponding to its own receive buffer , A series of data , It is pushed into the buffer in sequence ,recv Just take data from it .
=====》 about recv Get the receive buffer data , Need some strategy (1: You may get more than one package at a time ( Sticky package ) 2: Probably recv Insufficient parameter settings , Took half a bag ( Half pack ))
1.2: Processing half package , Stick package problem
There are two points to consider in the problem of half package sticking package :
1:recv When fetching data , Pay attention to strategy
2: When the user layer needs to send data , Define certain agreements .
===》 programme 1: When sending data , Data constructs specific headers / tail , After receiving, it is temporarily stored in the buffer and processed logically ( Here, a memory is used to simulate the buffer )
===》 programme 2: When sending data , A specific byte identifies the length of data sent + actual data
2: Test code
According to my understanding of the logic of dealing with half packets and sticky packets , The two processing schemes use test code to simulate :
/************************************************ info: As tcp The service side , Sticky package of data , Half a pack problem , Expect to deal with it data: 2022/02/10 author: hlp ************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//tcp Is reliable streaming We can guarantee its reliability , Receive in sequence , This is where you put it tcp In the receive buffer of
// But put it in the buffer , Our scheme of getting data , It needs to be controlled , To identify specific different packages .( Some bags are very small , Some bags are big , Pay attention when getting data )
// Summary : We fetch data from the cache , Pay attention to the integrity of data , Whether you can get the complete package at one time .
int exec_one_data(char* data, int len);
void check_buff(char * ringbuff, int *ops, int buff_size);// The third parameter is used for emptying after successful processing
void recv_data_by_specific_tail_symbol(int fd);
void recv_data_by_length_and_data(int fd);
int main()
{
// To solve the integrity problem of identification data We need to adapt user layer protocols Specific bytes / Specific terminator / length +data
int fd = 0;
// Specific terminator + Buffer processing Here I am the project is required to use this complex head and tail logo , Just demonstrate In fact, as long as the tail can also be guaranteed
recv_data_by_specific_tail_symbol(fd);
// According to the length +data Our scheme is also a reliable scheme , First receive the length of a specific byte , Then receive data .
recv_data_by_length_and_data(fd);
return 0;
}
// When sending Specific tail marks + Buffer scheme
// I don't know how much data to get every time , And whether to get the complete data , A buffer must be required
// As a server We have multiple clients fd Connected The best solution is actually every fd The connection should have its own buffer
// Suppose our data can be sent at one time ( There will be no unpacking in business ), Then you can directly parse the sticky packets in a buffer ( There will be problems if you unpack )
void recv_data_by_specific_tail_symbol(int fd)
{
// The buffer can use ringbuffer here demo Just a demonstration. , Used a piece of memory , And all connections share one ( Assume no unpacking , Just verify the idea )
//client send out Suppose the structure sends data Then the client sends it in turn Business does not involve multiple packages
const char * send1_data = "FFFF0D0A<header>my test of send 1. \\<tail>0D0AFEFE";
const char * send2_data = "FFFF0D0A<header>my test of send 2. \\<tail>0D0AFEFE";
const char * send3_data = "FFFF0D0A<header>my test of send 3. \\<tail>0D0AFEFE";
//tcp Is reliable Streaming , Must be in order , Receive a complete package , After the receive is put into the buffer , Just deal with it in turn
//server receive Because of me recv I don't know the length of reception , It is possible to receive a specific len( It may be smaller than a single package , Maybe a packet in the buffer is just truncated )
// therefore Put it in the buffer , Judge the buffer “FFFF0D0A<header><tail>0D0AFEFE” Handle the identification of the head and tail , I judge every time after receiving , Other schemes such as timers can be used
//len = recv(fd, data, 44, 0); memcpy(ringbuff +ops, data, len); check_buff(ringbuff, ops);
// Every fd Using a buffer is the best solution , Here, a piece of memory is used for simple test processing
char * ringbuff = (char *) malloc(1024); // Suppose the buffer size is defined as 1024
memset(ringbuff, 1024, 0);
int ops = 0;
// Suppose data is received Put it into the buffer first Here, it is assumed that the data sent by the client is standard , Of course, safety protection should be done
// Suppose I get the data twice "FFFF0D0A<header>my test of send 1. \\<tail>0D0AFEFEFFFF0D0A<header>my test"
// " of send 2. \\<tail>0D0AFEFEFFFF0D0A<header>my test of send 3. \\<tail>0D0AFEFE"
//len = recv(fd, recv1_data, my_len,0); my_len I defined it in advance recv1_data size , This situation should be my_len == len
// for the first time recv extract
const char* recv1_data = "FFFF0D0A<header>my test of send 1. \\<tail>0D0AFEFEFFFF0D0A<header>my test";
memcpy(ringbuff+ops, recv1_data, strlen(recv1_data));
ops += strlen(recv1_data);
// Consumption buffer location modify ops
check_buff(ringbuff, &ops, 1024); // Verify whether there is complete data in the buffer If there is one, deal with Identify the first FFFF0D0A<header> To the next <tail>0D0AFEFE
// The second time recv extract
const char* recv2_data =" of send 2. \\<tail>0D0AFEFEFFFF0D0A<header>my test of send 3. \\<tail>0D0AFEFE";
memcpy(ringbuff+ops, recv2_data, strlen(recv2_data));
ops += strlen(recv2_data);
check_buff(ringbuff, &ops, 1024); // Here is the normal data It should have been all handled
printf("ringbuff length is [%d] \n", ops);
memset(ringbuff, 1024, 0); // Empty it after each treatment It is necessary to Otherwise, there will be problems next time
if(ringbuff)
{
free(ringbuff);
ringbuff = NULL;
}
}
// This function is actually recv after , Put in ringbuff The main parsing logic after
// The processing here is similar to recv The logic of Try to... Once recv Cycle fetch complete , Then every time the data can be processed completely ( Otherwise, in fact, there will be a half bag phenomenon )
void check_buff(char * ringbuff, int *buffops, int buff_size)
{
// Cycle through There should be no such problem But there must be a half package problem
if(*buffops <= strlen("FFFF0D0A<header><tail>0D0AFEFE"))
{
return;
}
printf ("check buff tail is [%s] \n", ringbuff+(*buffops)-strlen("<tail>0D0AFEFE"));
// The comparison terminator is the same before processing Otherwise, leave it to the next time
if(strcmp("<tail>0D0AFEFE", ringbuff+(*buffops)-strlen("<tail>0D0AFEFE")) !=0)
{
return;
}
// Unpack the received data
int datalen = -1;
char * onedata;
char * ops;
char * temp_data = ringbuff;
// First determine whether there is an ending package Then judge the head for processing
const char * end_str = "<tail>0D0AFEFE";
// Take one tail at a time Then process a package
while((ops = strstr(temp_data, end_str)) != NULL)
{
datalen = ops - temp_data +strlen(end_str);
exec_one_data(temp_data, datalen);
temp_data = ops+strlen(end_str);
}
// There is data left It's impossible because recv It is put in the buffer after the loop fetches
if(temp_data - ringbuff != *buffops)
{
printf("there is loss data: [%ld][%s] \n", strlen(temp_data), temp_data);
}
// Empty processing
memset(ringbuff, 1024, 0);
buffops = 0;
}
// This is a complete send packet FFFF0D0A<header> XXX <tail>0D0AFEFE
int exec_one_data(char* data, int len)
{
const char * start_str = "FFFF0D0A<header>";
char * ops;
ops = strstr(data, start_str);
if(ops == data) // If the middle contains header, Incorrect parsing , But it should be impossible
{
int out_len = len-strlen("FFFF0D0A<header><tail>0D0AFEFE");
char * out_data = NULL;
out_data =(char*)malloc(out_len +1);
memset(out_data, out_len+1, 0);
memcpy(out_data, data + strlen("FFFF0D0A<header>"), out_len);
printf("out_data is [%lu][%s] \n", strlen(out_data), out_data);
if(out_data != NULL)
{
free(out_data);
out_data = NULL;
}
}
if(ops == NULL) // No head found discarded
{
printf("package data is error, not find start data. \n");
}
if(ops != data) // There is abnormal data in front of the head
{
printf("recv package data is error.");
}
return 0;
}
// When sending Specific byte storage data length + actual data
// Personal understanding This takes data according to a specific structure It is guaranteed that no buffer is needed
void recv_data_by_length_and_data(int fd)
{
// Construct the sent data
const char * send_data_str = "my test of send data \\";
unsigned short len = strlen(send_data_str);
printf("vps short is : %lu \n", sizeof(unsigned short)); //vps short is : 2
// use 2 A specific length of bytes +data Structure of data
// Here we need to turn to the network sequence Take it out and turn it back
char * send_data = NULL;
send_data = (char*)malloc(2 +len +1);// A terminator is reserved
memset(send_data, 2+len, 0);
memcpy(send_data, &len, 2);
memcpy(send_data+2, send_data_str, len);
// Here you should print a specific length in hexadecimal last send data is [22][my test of send data \]
printf("last send data is [%u][%s] \n", *((unsigned short *)send_data), send_data+2);
// Receiving end processing You should receive two bytes first Then receive the following data length
// What is sent here is actually send_data The receiving end first receives the length of two bytes , Then receive data of a specific length ( Here we can do the analysis directly )
unsigned short recv_data_len;
memcpy(&recv_data_len, send_data, 2);
printf("recv data is[%d: %s] \n", recv_data_len, send_data+2); //recv data is[22: my test of send data \]
// Pay attention to the sending end data free
if(send_data != NULL)
{
free(send_data);
send_data = NULL;
}
}
3: test result :
Only the logic of analog reception , The actual reception can be based on tcp Logic for reference implementation .
[email protected]:~/220107$ ./tag
check buff tail is [header>my test]
check buff tail is [<tail>0D0AFEFE]
out_data is [20][my test of send 1. \]
out_data is [20][my test of send 2. \]
out_data is [20][my test of send 3. \]
ringbuff length is [150]
vps short is : 2
last send data is [22][my test of send data \]
recv data is[22: my test of send data \]
I started trying to accumulate some common code : Spare in your own code base
More of my knowledge comes from here , I recommend you understand :Linux,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK, Streaming media ,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP, coroutines ,DPDK Etc , Learn now
边栏推荐
- asp. Core is compatible with both JWT authentication and cookies authentication
- asp. Core is compatible with both JWT authentication and cookies authentication
- hashlimit速率控制
- SharedPreferences 源码分析
- Class A, B, C networks and subnet masks in IPv4
- 【HBZ分享】ArrayList的增删慢查询快的原因
- About some basic DP -- those things about coins (the basic introduction of DP)
- Global and Chinese markets for medical gas manifolds 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- MySql数据库root账户无法远程登陆解决办法
- pd. to_ numeric
猜你喜欢
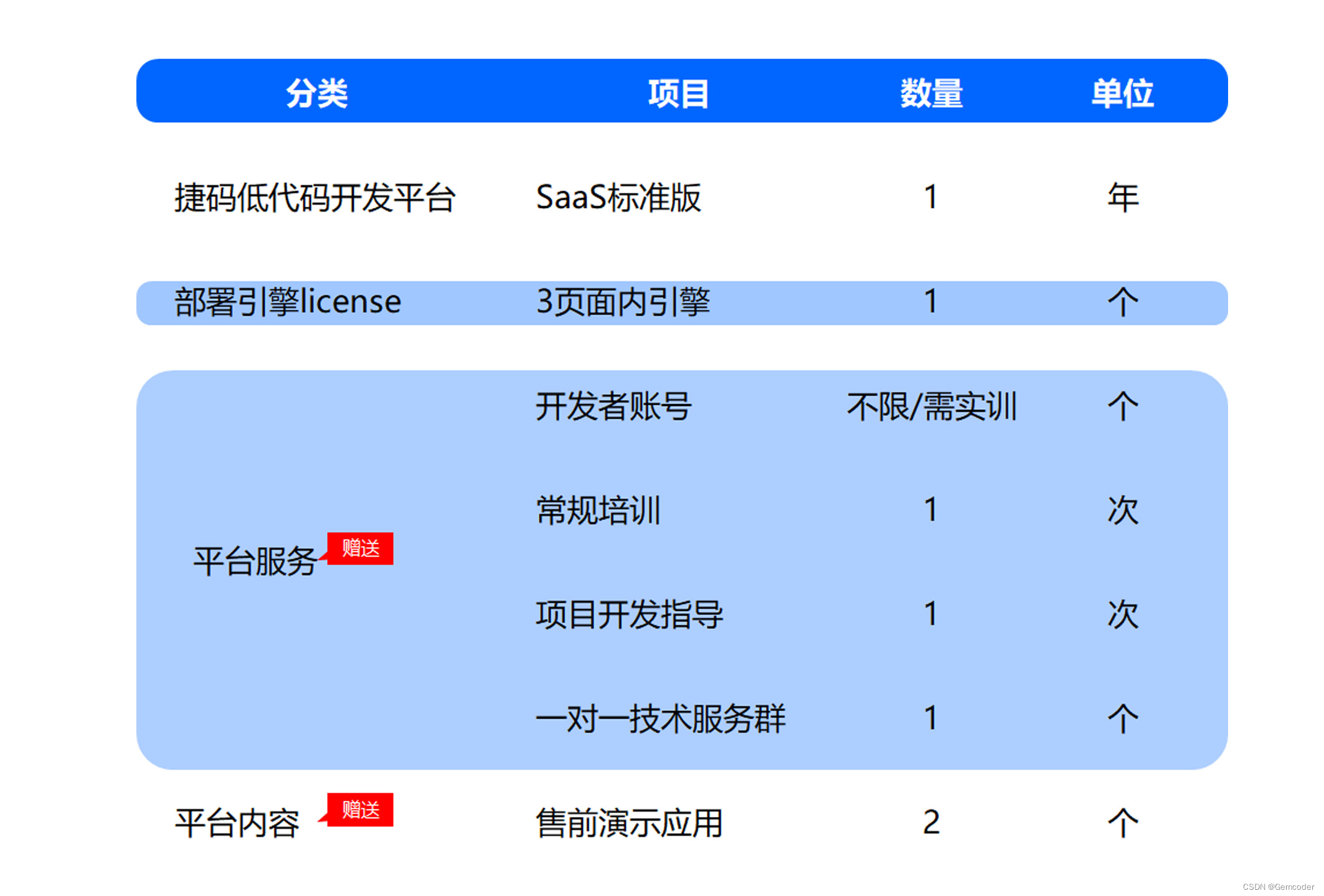
满足多元需求:捷码打造3大一站式开发套餐,助力高效开发

综合能力测评系统
![[introduction to Django] 11 web page associated MySQL single field table (add, modify, delete)](/img/8a/068faf3e8de642c9e3c4118e6084aa.jpg)
[introduction to Django] 11 web page associated MySQL single field table (add, modify, delete)
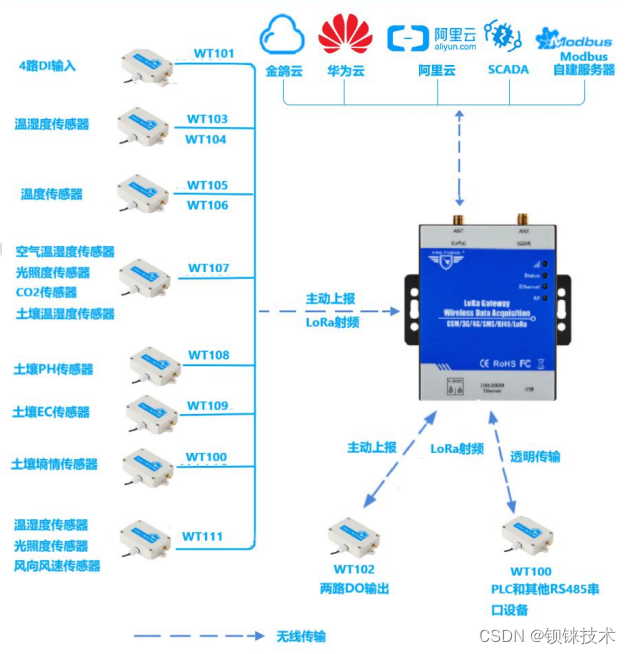
lora网关以太网传输
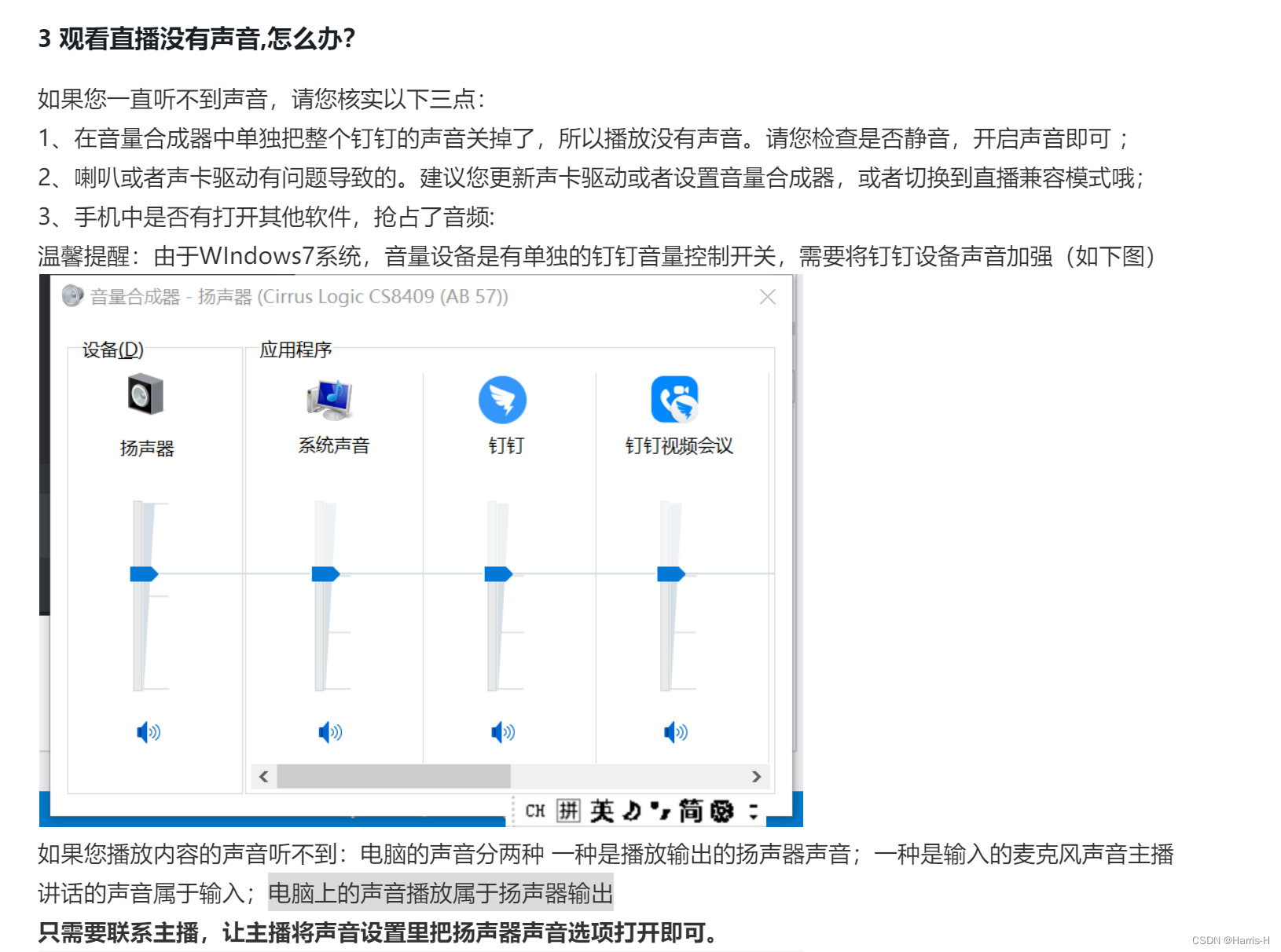
How does computer nail adjust sound
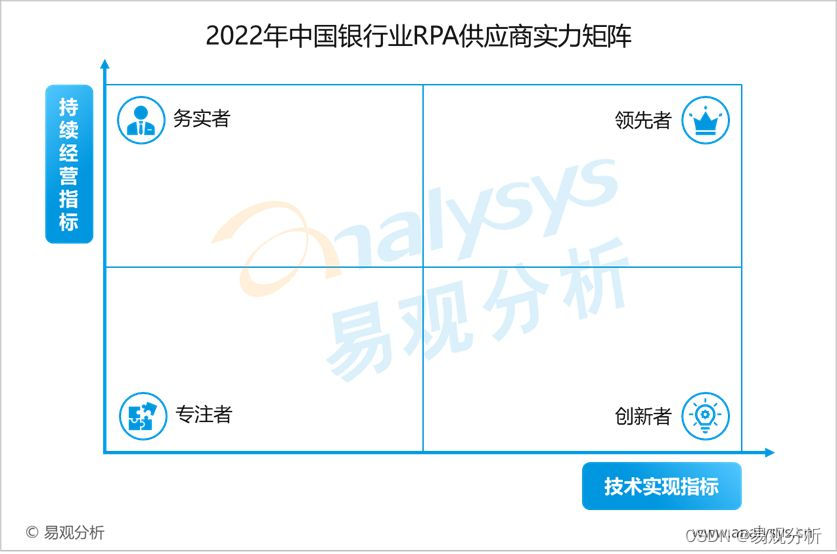
《2022年中国银行业RPA供应商实力矩阵分析》研究报告正式启动

Solution of storage bar code management system in food industry

One question per day (Mathematics)

Recommendation | recommendation of 9 psychotherapy books
20、 EEPROM memory (AT24C02) (similar to AD)
随机推荐
Data processing methods - smote series and adasyn
lora网关以太网传输
电脑钉钉怎么调整声音
10 exemples les plus courants de gestion du trafic istio, que savez - vous?
Global and Chinese markets for otolaryngology devices 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Fedora/rehl installation semanage
查询mysql数据库中各表记录数大小
asp. Core is compatible with both JWT authentication and cookies authentication
Several important classes in unity
MySQL transaction isolation level
[FPGA tutorial case 11] design and implementation of divider based on vivado core
2/12 didn't learn anything
Understanding of processes, threads, coroutines, synchronization, asynchrony, blocking, non blocking, concurrency, parallelism, and serialization
Detailed explanation of serialization and deserialization
In depth MySQL transactions, stored procedures and triggers
Interface idempotency
P2022 有趣的数(二分&数位dp)
Viewing and verifying backup sets using dmrman
DM8 backup set deletion
Explain in simple terms node template parsing error escape is not a function