当前位置:网站首页>C语言多角度帮助你深入理解指针(1. 字符指针2. 数组指针和 指针数组 、数组传参和指针传参3. 函数指针4. 函数指针数组5. 指向函数指针数组的指针6. 回调函数)
C语言多角度帮助你深入理解指针(1. 字符指针2. 数组指针和 指针数组 、数组传参和指针传参3. 函数指针4. 函数指针数组5. 指向函数指针数组的指针6. 回调函数)
2022-07-07 18:26:00 【朱C.】
目录
1. 字符指针:
字符指针,顾名思义,指向字符型数据的指针,也是本文介绍的最简单的一类指针,但是有几点易错的注意点,所以借此机会详解一下。下面是字符指针最简单的用法
int main()
{
char ch = 'w';
char *pc = &ch;
*pc = 'w';
return 0; }除此之外,我们常会遇到字符指针指向字符串的情况:
int main()
{
const char* pstr = "hello world.";
printf("%s\n", pstr);
return 0; }这里是把一个字符串放到pstr指针变量里了吗?
显然不是,但是为什么能打印出来这个字符串呢?
原因是,字符指针存放了字符串首元素的地址,然后printf函数中%s凭借着首元素地址向下找,打印出整个字符串。所以,事实上,字符指针只存放了字符串首元素的地址。
下面我们出一道题目,巩固一下字符指针最要注意的地方:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char str1[] = "hello world.";
char str2[] = "hello world.";
const char* str3 = "hello world.";//3 4常量字符串,不能被改,在只读数据区
const char* str4 = "hello world.";
if (str1 == str2)//数组名是首元素地址,
//1 和 2是两个独立的数组,所以首地址不一样
printf("str1 == str2\n");
else
printf("str1 != str2\n");
if (str3 == str4)//说明str3和str4指向同一字符串,都是a的地址
printf("str3 == str4\n");
else
printf("str3 != str4\n");
return 0;
}
2.数组指针和指针数组:
深入了解指针可就避免不了分清指针数组和数组指针并学会应用。
首先明确的是数组指针是指针!而指针数组是存放指针的数组!
//指针数组:
int *p1[10];
//数组指针:
int (*p2)[10];对于数组指针的解释:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {0};
printf("%p\n", arr);
printf("%p\n", &arr);
return 0; }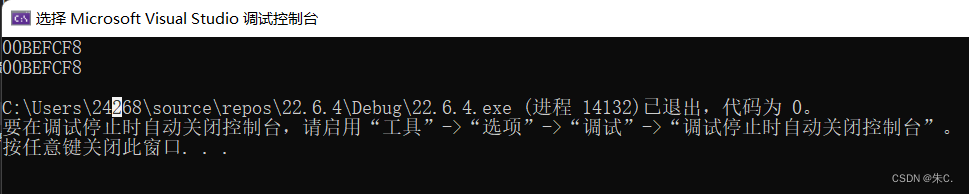
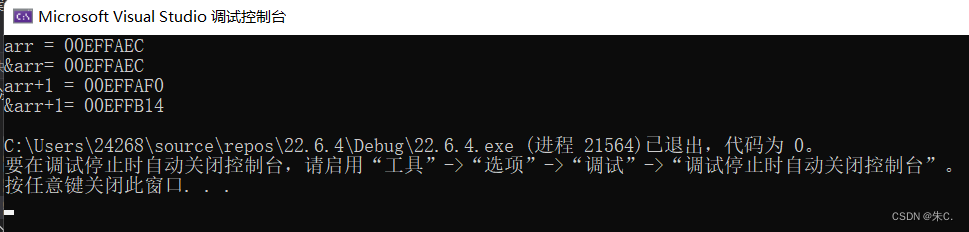
这里我们就发现了,&arr表示的其实arr整个数组的地址,+1后跳过整个数组的长度。
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0};
int (*p)[10] = &arr;//把数组arr的地址赋值给数组指针变量p
//但是我们一般很少这样写代码
return 0; }#include <stdio.h>
void print_arr1(int arr[3][5], int row, int col) {
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<row; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<col; j++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void print_arr2(int (*arr)[5], int row, int col) {
int i = 0;
for(i=0; i<row; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<col; j++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[3][5] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
print_arr1(arr, 3, 5);
//数组名arr,表示首元素的地址
//但是二维数组的首元素是二维数组的第一行
//所以这里传递的arr,其实相当于第一行的地址,是一维数组的地址
//可以数组指针来接收
print_arr2(arr, 3, 5);
return 0; }在第二段代码的传参中就用到了数组指针,大家注意区别两者
3.函数指针:
对于不同的函数,其实我们也可以用指针指向对应的函数,并且通过对函数指针解引用来调用函数,下面看一个简单的例子便于理解:
int Add(int x,int y)
{
return x + y;
}
int main()
{
int arr[5] = { 0 };
int(*p)[5] = &arr;//数组指针
//&函数名 -- 取出的是函数的地址呢?
printf("%p\n", &Add);//函数是有地址的
printf("%p\n", Add);//两种写法没有区别,&函数名和函数名都是函数的地址
int (*pf)(int, int) = &Add;//和数组指针类似
int ret=(*pf)(2, 3);//Add(2,3)
int ret = pf(2, 3);//也可以
printf("%d\n", ret);
return 0;
}我们对比数组指针,把数组指针后的[ ]换成了函数所用的( )大致就是函数指针的雏形了,形如
int(*pf)(int x,int y) 这里的*表示pf是指针,( )表示是指向函数的指针。
#include <stdio.h>
void test()
{
printf("hehe\n");
}
int main()
{
printf("%p\n", test);
printf("%p\n", &test);
return 0; }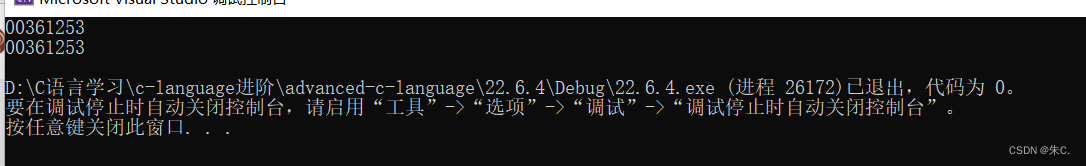
通过这段函数和输出我们发现了其实函数也是有地址的,这也证实了函数指针存在的合理性。初步了解函数指针对下面我们要介绍的三类奠定了基础。
4. 函数指针数组:
函数指针数组,通过上面我们的理解,就是存放函数指针的数组,那么它的形式怎么写呢?下面我们给出:int (*parr1[10])();
其实通过思考我们不难得出,在函数指针的基础上套上数组,这样这个数组就是用来存放函数指针的了。下面我们给出实现计算机的例子来进一步解释一下函数指针数组(该计算器比较简易,意在实现函数指针数组的例子):
#include <stdio.h>
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
int sub(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
int mul(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
int div(int a, int b) {
return a / b;
}
int main()
{
int x, y;
int input = 1;
int ret = 0;
int(*p[5])(int x, int y) = { 0, add, sub, mul, div }; //转移表
while (input)
{
printf("*************************\n");
printf(" 1:add 2:sub \n");
printf(" 3:mul 4:div \n");
printf("*************************\n");
printf("请选择:");
scanf("%d", &input);
if ((input <= 4 && input >= 1))
{
printf("输入操作数:");
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
ret = (*p[input])(x, y);
}
else
printf("输入有误\n");
printf("ret = %d\n", ret);
}
return 0;
}注意中间有一处表示转移表的地方就用到了函数指针数组,可以指向对应的函数实现。
5.指向函数指针数组的指针:
有了上面我们理解,我们可以试着写出指向函数指针数组的指针的形式,
下面我们剖析一下:
指向函数指针数组的指针是一个 指针
void test(const char* str) {
printf("%s\n", str);
}
int main()
{
//函数指针pfun
void (*pfun)(const char*) = test;
//函数指针的数组pfunArr
void (*pfunArr[5])(const char* str);
pfunArr[0] = test;
//指向函数指针数组pfunArr的指针ppfunArr
void (*(*ppfunArr)[5])(const char*) = &pfunArr;
return 0; }这里我们进行简单了解,最后我们给出回调函数的实现过程,这是重中之重的例子,也是指针中比较有技术含量实现的经典.
6.回调函数:
定义:
我们借用qsort函数进行讲解,并自己实现qsort函数再来进行回调
//冒泡排序只能排整形数据
//void bubble_sort(int arr[],int sz)
//{
// int i = 0;
// int j = 0;
//for(i=0;i<sz-1;i++)
//{int flag = 1;//假设数组是排好序
// for (j = 0;j<sz-i-1;j++)
// {
//
// if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
// {
// int tmp = arr[j];
// arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
// arr[j + 1] = tmp;
// flag = 0;//
// }
// }
// if(flag==1)
// {
// break;
// }
//}
//}
//qsort库函数 使用快速排序的思想实现的一个排序函数
// 可以排序任意类型的数据
//
//
//void qsort(void* base,//你要排序的数据的起始位置
//size_t num,//待排序的数据元素的个数
//size_t width, //待排序的数据元素的大小
//int(* cmp)(const void* e1, const void* e2)//函数指针,是一个比较函数
//);
//比较两个整形元素
//e1指向一个整数
//e2指向一个整数
int cmp_int(const void* e1, const void* e2)
//{
// if (*(int*)e1 > *(int*)e2)//强制类型转换
// return 1;
// else if (*(int*)e1 == *(int*)e2)
// return 0;
// else
// return -1;
//}
//
{return *(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2; }//强制类型转换
void Swap(char* buf1, char* buf2, int width)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
char tmp = *buf1;
*buf1 = *buf2;
*buf2 = tmp;
buf1++;
buf2++;
}
}
//void*是不能直接解引用的
//void是无具体类型的指针,可以接受任意类型的指针
//无具体类型,所以不能解引用,也不能+-整数
void bubble_sort(void* base, int sz, int width, int(*cmp)(const void* e1, const void* e2))
{
int i = 0;
//趟数
for (i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++)
{
int flag = 1;//假设数组是排好序
//一趟冒泡排序的过程
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < sz - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (cmp((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width) > 0)
{
//交换
Swap((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width, width);
flag = 0;
}
}
if (flag == 1)
{
break;
}
}
}
struct Stu
{
char name[20];
int age;
};
int cmp_stu_by_name(const void* e1,const void* e2)
{
return strcmp(((struct Stu*)e1)->name, ((struct Stu*)e2)->name);
}
void test1()
{
int arr[] = { 9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
//把数组排成升序
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
//bubble_sort(arr, sz);
qsort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp_int);//默认排升序
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
void test2()
{//测试使用qsort来排序结构体数据
struct Stu s[] = { {"zs",15 }, { "ls",30 }, { "ww",25 } };
int sz = sizeof(s) / sizeof(s[0]);
qsort(s, sz, sizeof(s[0]),cmp_stu_by_name);
}
void test3()
{
int arr[] = { 9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0 };
//把数组排成升序
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
//bubble_sort(arr, sz);
bubble_sort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp_int);//默认排升序
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}
void test4()
{
//测试使用qsort来排序结构数据
struct Stu s[] = { {"zhangsan", 15}, {"lisi", 30}, {"wangwu", 25} };
int sz = sizeof(s) / sizeof(s[0]);
bubble_sort(s, sz, sizeof(s[0]), cmp_stu_by_name);
//bubble_sort(s, sz, sizeof(s[0]), cmp_stu_by_age);
}
int main()
{
//test1();
//test2();
test3();
test4();
}这里我们给出了详解代码注释在代码里。这里主要是我们在bubble_sort函数里回调了cmp_XX对应的函数,还请读者仔细理解。
以上就是进阶指针的内容,以后在数据结构里我们更会多次利用这些知识。希望有帮助到您!
边栏推荐
- 微服务远程Debug,Nocalhost + Rainbond微服务开发第二弹
- One click deployment of any version of redis
- 不落人后!简单好用的低代码开发,快速搭建智慧管理信息系统
- POJ 1742 coins (monotone queue solution) [suggestions collection]
- 阿里云有奖体验:如何通过ECS挂载NAS文件系统
- Force buckle 989 Integer addition in array form
- 机械臂速成小指南(十二):逆运动学分析
- Opencv learning notes high dynamic range (HDR) imaging
- 静态测试工具
- [MySQL - Basic] transactions
猜你喜欢
Nebula importer data import practice

机器学习笔记 - 使用Streamlit探索对象检测数据集

CodeSonar网络研讨会

Measure the height of the building
Micro service remote debug, nocalhost + rainbow micro service development second bullet

Airiot helps the urban pipe gallery project, and smart IOT guards the lifeline of the city

如何满足医疗设备对安全性和保密性的双重需求?
智能软件分析平台Embold
![About cv2 dnn. Readnetfromonnx (path) reports error during processing node with 3 inputs and 1 outputs [exclusive release]](/img/59/33381b8d45401607736f05907ee381.png)
About cv2 dnn. Readnetfromonnx (path) reports error during processing node with 3 inputs and 1 outputs [exclusive release]

使用高斯Redis实现二级索引
随机推荐
Tensorflow2.x下如何运行1.x的代码
Force buckle 1790 Can two strings be equal by performing string exchange only once
上海交大最新《标签高效深度分割》研究进展综述,全面阐述无监督、粗监督、不完全监督和噪声监督的深度分割方法
When easygbs cascades, how to solve the streaming failure and screen jam caused by the restart of the superior platform?
浅尝不辄止系列之试试腾讯云的TUIRoom(晚上有约,未完待续...)
ISO 26262 - 基于需求测试以外的考虑因素
【论文阅读】MAPS: Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning-based Portfolio Management System
凌云出海记 | 赛盒&华为云:共助跨境电商行业可持续发展
Spark judges that DF is empty
[philosophy and practice] the way of program design
Flask1.1.4 werkzeug1.0.1 source code analysis: Routing
With st7008, the Bluetooth test is completely grasped
阿里云有奖体验:如何通过ECS挂载NAS文件系统
字符串中数据排序
Implement secondary index with Gaussian redis
rk3128投影仪lcd显示四周显示不完整解决
如何满足医疗设备对安全性和保密性的双重需求?
Flask1.1.4 Werkzeug1.0.1 源码分析:路由
guava多线程,futurecallback线程调用不平均
Force buckle 599 Minimum index sum of two lists