当前位置:网站首页>PostgreSQL基本结构——表
PostgreSQL基本结构——表
2022-07-04 20:57:00 【华为云】
如何在PostgreSQL中执行等效于Oracle DESCRIBE TABLE的命令(使用psql命令)?
#1楼
DESCRIBE TABLE的psql等效项是\\d table 。
有关更多详细信息,请参见PostgreSQL手册的psql部分。
#2楼
您可以使用psql斜杠命令执行此操作:
\d myTable describe table它也适用于其他对象:
\d myView describe view \d myIndex describe index \d mySequence describe sequence资料来源: faqs.org
#3楼
试试看(在psql命令行工具中):
\d+ tablename有关更多信息,请参见手册 。
#4楼
除了PostgreSQL方式(\\ d'something'或\\ dt'table'或\\ ds'sequence'等)
SQL标准的方式,如图所示在这里 :
select column_name, data_type, character_maximum_lengthfrom INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS where table_name = '<name of table>';许多数据库引擎都支持它。
#5楼
如果要从查询而不是psql获取它,则可以查询目录架构。 这是一个执行此操作的复杂查询:
SELECT f.attnum AS number, f.attname AS name, f.attnum, f.attnotnull AS notnull, pg_catalog.format_type(f.atttypid,f.atttypmod) AS type, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'p' THEN 't' ELSE 'f' END AS primarykey, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'u' THEN 't' ELSE 'f' END AS uniquekey, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN g.relname END AS foreignkey, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN p.confkey END AS foreignkey_fieldnum, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN g.relname END AS foreignkey, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN p.conkey END AS foreignkey_connnum, CASE WHEN f.atthasdef = 't' THEN d.adsrc END AS defaultFROM pg_attribute f JOIN pg_class c ON c.oid = f.attrelid JOIN pg_type t ON t.oid = f.atttypid LEFT JOIN pg_attrdef d ON d.adrelid = c.oid AND d.adnum = f.attnum LEFT JOIN pg_namespace n ON n.oid = c.relnamespace LEFT JOIN pg_constraint p ON p.conrelid = c.oid AND f.attnum = ANY (p.conkey) LEFT JOIN pg_class AS g ON p.confrelid = g.oid WHERE c.relkind = 'r'::char AND n.nspname = '%s' -- Replace with Schema name AND c.relname = '%s' -- Replace with table name AND f.attnum > 0 ORDER BY number;它非常复杂,但是它确实向您展示了PostgreSQL系统目录的功能和灵活性,并且应该使您逐渐掌握pg_catalog ;-)。 确保更改查询中的%s。 第一个是模式,第二个是表名。
#6楼
您可以使用星号 \\d *search pattern *来查找与您感兴趣的搜索模式匹配的表。
#7楼
您可以使用:
SELECT attname FROM pg_attribute,pg_class WHERE attrelid=pg_class.oid AND relname='TableName' AND attstattarget <>0; #8楼
除了已经找到的命令行\\d+ <table_name> ,您还可以使用info -schema通过info_schema.columns查找信息。
SELECT *FROM info_schema.columnsWHERE table_schema = 'your_schema'AND table_name = 'your_table'#9楼
使用以下SQL语句
SELECT DATA_TYPE FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS WHERE table_name = 'tbl_name' AND COLUMN_NAME = 'col_name'如果替换tbl_name和col_name,它将显示您要查找的特定列的数据类型。
#10楼
您也可以使用以下查询进行检查
Select * from schema_name.table_name limit 0;示例:我的表有2列名称和密码。 提供以下屏幕截图。
*使用PG admin3
#11楼
Use this command \d table namelike \d queuerecords Table "public.queuerecords" Column | Type | Modifiers-----------+-----------------------------+----------- id | uuid | not null endtime | timestamp without time zone | payload | text | queueid | text | starttime | timestamp without time zone | status | text |#12楼
描述表的最佳方法,例如列,类型,列的修饰符等。
\d+ tablename or \d tablename#13楼
/ dt是逗号,它列出了数据库中存在的所有表。 使用
/ d命令和/ d +我们可以获取表的详细信息。 该系统将像
* / d table_name(或)\\ d + table_name
#14楼
查询的这种变化(如其他答案所述)对我有用。
SELECT COLUMN_NAMEFROM information_schema.COLUMNSWHERE TABLE_NAME = 'city';此处详细介绍: http : //www.postgresqltutorial.com/postgresql-describe-table/
#15楼
我为获取表模式制定了以下脚本。
'CREATE TABLE ' || 'yourschema.yourtable' || E'\n(\n' ||array_to_string(array_agg(' ' || column_expr), E',\n') || E'\n);\n'from(SELECT ' ' || column_name || ' ' || data_type || coalesce('(' || character_maximum_length || ')', '') || case when is_nullable = 'YES' then ' NULL' else ' NOT NULL' end as column_exprFROM information_schema.columnsWHERE table_schema || '.' || table_name = 'yourschema.yourtable'ORDER BY ordinal_position) column_list;#16楼
在MySQL中 ,DESCRIBE table_name
在PostgreSQL中 ,\\ d table_name
或者,您可以使用以下长命令:
SELECT a.attname AS Field, t.typname || '(' || a.atttypmod || ')' AS Type, CASE WHEN a.attnotnull = 't' THEN 'YES' ELSE 'NO' END AS Null, CASE WHEN r.contype = 'p' THEN 'PRI' ELSE '' END AS Key, (SELECT substring(pg_catalog.pg_get_expr(d.adbin, d.adrelid), '\'(.*)\'') FROM pg_catalog.pg_attrdef d WHERE d.adrelid = a.attrelid AND d.adnum = a.attnum AND a.atthasdef) AS Default, '' as ExtrasFROM pg_class c JOIN pg_attribute a ON a.attrelid = c.oid JOIN pg_type t ON a.atttypid = t.oid LEFT JOIN pg_catalog.pg_constraint r ON c.oid = r.conrelid AND r.conname = a.attnameWHERE c.relname = 'tablename' AND a.attnum > 0ORDER BY a.attnum#17楼
In postgres \d is used to describe the table structure.e.g. \d schema_name.table_name;this command will provide you the basic info of table such as, columns, type and modifiers.If you want more info about table use\d+ schema_name.table_name;this will give you extra info such as, storage, stats target and description#18楼
为了改进另一个答案的SQL查询(很棒!),这是一个经过修改的查询。 它还包括约束名称,继承信息以及分解为组成部分的数据类型(类型,长度,精度,小数位数)。 它还过滤掉已删除的列(数据库中仍然存在)。
SELECT n.nspname as schema, c.relname as table, f.attname as column, f.attnum as column_id, f.attnotnull as not_null, f.attislocal not_inherited, f.attinhcount inheritance_count, pg_catalog.format_type(f.atttypid,f.atttypmod) AS data_type_full, t.typname AS data_type_name, CASE WHEN f.atttypmod >= 0 AND t.typname <> 'numeric'THEN (f.atttypmod - 4) --first 4 bytes are for storing actual length of data END AS data_type_length, CASE WHEN t.typname = 'numeric' THEN (((f.atttypmod - 4) >> 16) & 65535) END AS numeric_precision, CASE WHEN t.typname = 'numeric' THEN ((f.atttypmod - 4)& 65535 ) END AS numeric_scale, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'p' THEN 't' ELSE 'f' END AS is_primary_key, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'p' THEN p.conname END AS primary_key_name, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'u' THEN 't' ELSE 'f' END AS is_unique_key, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'u' THEN p.conname END AS unique_key_name, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN 't' ELSE 'f' END AS is_foreign_key, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN p.conname END AS foreignkey_name, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN p.confkey END AS foreign_key_columnid, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN g.relname END AS foreign_key_table, CASE WHEN p.contype = 'f' THEN p.conkey END AS foreign_key_local_column_id, CASE WHEN f.atthasdef = 't' THEN d.adsrc END AS default_valueFROM pg_attribute f JOIN pg_class c ON c.oid = f.attrelid JOIN pg_type t ON t.oid = f.atttypid LEFT JOIN pg_attrdef d ON d.adrelid = c.oid AND d.adnum = f.attnum LEFT JOIN pg_namespace n ON n.oid = c.relnamespace LEFT JOIN pg_constraint p ON p.conrelid = c.oid AND f.attnum = ANY (p.conkey) LEFT JOIN pg_class AS g ON p.confrelid = g.oid WHERE c.relkind = 'r'::char AND f.attisdropped = false AND n.nspname = '%s' -- Replace with Schema name AND c.relname = '%s' -- Replace with table name AND f.attnum > 0 ORDER BY f.attnum;#19楼
这应该是解决方案:
SELECT * FROM information_schema.columnsWHERE table_schema = 'your_schema' AND table_name = 'your_table'边栏推荐
- Can be displayed in CAD but not displayed in print
- Master the use of auto analyze in data warehouse
- 类方法和类变量的使用
- numpy vstack 和 column_stack
- A quick start to fastdfs takes you three minutes to upload and download files to the ECS
- At the right time, the Guangzhou station of the city chain science and Technology Strategy Summit was successfully held
- 2021 CCPC Harbin I. power and zero (binary + thinking)
- 为什么说不变模式可以提高性能
- How to use concurrentlinkedqueue as a cache queue
- Compréhension approfondie du symbole [langue C]
猜你喜欢
![[leetcode] 17. Letter combination of telephone number](/img/be/7f456c092f7cda5ebabc2f1cce292e.png)
[leetcode] 17. Letter combination of telephone number
![Compréhension approfondie du symbole [langue C]](/img/4b/26cf10baa29eeff08101dcbbb673a2.png)
Compréhension approfondie du symbole [langue C]

解析steam教育中蕴含的众创空间

MP3是如何诞生的?

【C语言】符号的深度理解
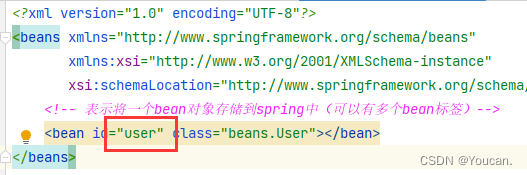
Difference between ApplicationContext and beanfactory (MS)

Analyzing the maker space contained in steam Education
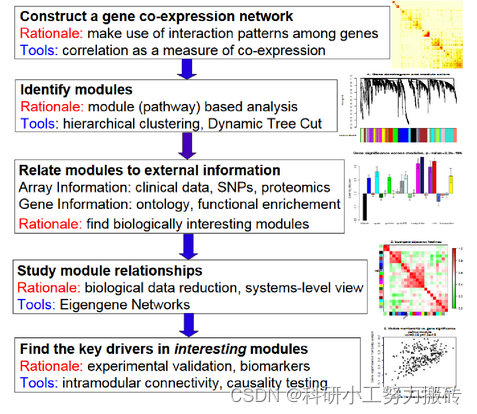
WGCNA analysis basic tutorial summary
Three or two things about the actual combat of OMS system
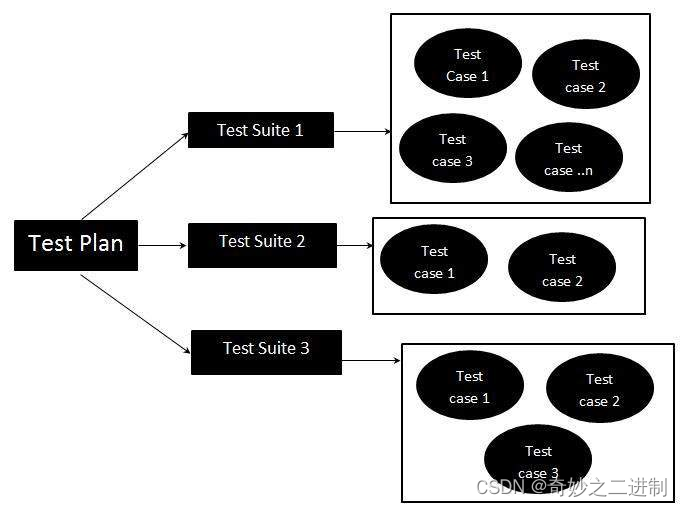
gtest从一无所知到熟练使用(3)什么是test suite和test case
随机推荐
QT—双缓冲绘图
奋斗正当时,城链科技战略峰会广州站圆满召开
Jerry's ad series MIDI function description [chapter]
Why does invariant mode improve performance
Difference between ApplicationContext and beanfactory (MS)
如何借助自动化工具落地DevOps
redis RDB AOF
Go language loop statement (3 in Lesson 10)
Minidom module writes and parses XML
Redis bloom filter
Application practice | Shuhai supply chain construction of data center based on Apache Doris
Redis cache
[C language] deep understanding of symbols
2021 CCPC 哈尔滨 B. Magical Subsequence(思维题)
Drop down selection of Ehlib database records
Master the use of auto analyze in data warehouse
巅峰不止,继续奋斗!城链科技数字峰会于重庆隆重举行
Flink1.13 SQL basic syntax (I) DDL, DML
GTEST from ignorance to proficiency (4) how to write unit tests with GTEST
How to use concurrentlinkedqueue as a cache queue
