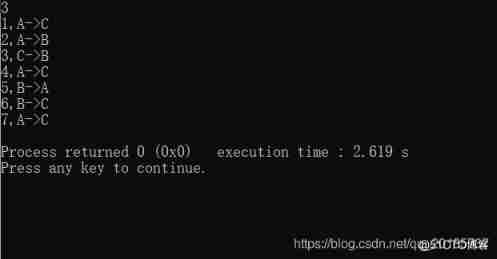
About char[] Array pass scanf Some problems in the use of assignment .
If we have this code
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
char c1[2];
scanf("%s",c1);
char c2[20];
scanf("%s",c2);
printf("%s %s\n",c1,c2);
return 0;
}
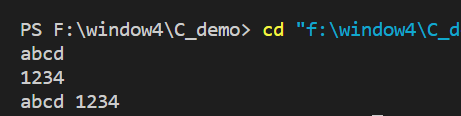
char Type arrays open up their own space in the stack . When we enter data
The result is the data we entered , But the strange thing is that we are here c1 The length of is limited to 2 Why store all the input data and output it ? Because it is stored continuously in memory space , We just used scanf The second parameter of is array c1 The first address , When receiving a set of data , It is stored in sequence according to the continuous memory , And because it is a character array , Therefore, a null character is appended . stay printf The output format in the function is %s, In the reading c1 When the first address above points to the value of the variable , Stop reading when encountering empty characters . So we just entered a length greater than 2 The data of , We can still read the corresponding data , But this behavior is undefined , If there is other data in the later memory, it will cause some errors .
If we exchange c1 and c2 Size of array
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void){
char c1[20];
scanf("%s",c1);
char c2[2];
scanf("%s",c2);
printf("%s %s\n",c1,c2);
return 0;
}
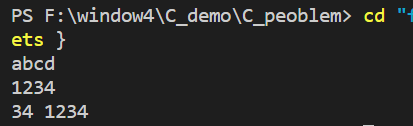
Why is the output different from the previous conclusion ? Similarly, we need to understand the memory space of storage . I hope to help you understand .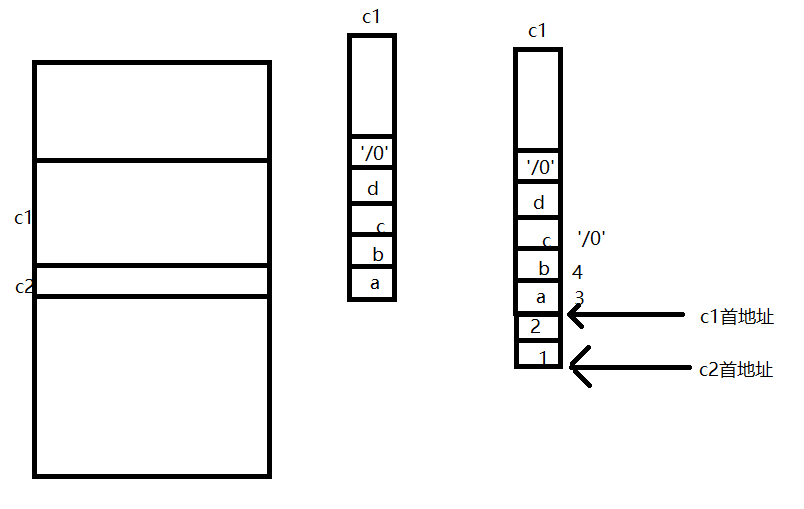
c1 We first store the data of the array in the stack space , Let's start with c1 Assignment of character variables in , Later, c2 Open up space and c2 Spatial continuity of , Give again c2 assignment , It is worth noting that the memory stored here is continuous , So I'm giving c2 When you assign , Because the data we input through the keyboard here is greater than c2 The space occupied by the array is large, so the redundant data will be stored in c1 in , stay printf In the sentence ,printf("%s %s\n",c1,c2); c1 Some values in the array have been overwritten at this time , So the output c1 The value of will not be the data we stored in the first step abcd It is 34.

![Leetcode topic [array] -118 Yang Hui triangle](/img/77/d8a7085968cc443260b4c0910bd04b.jpg)