当前位置:网站首页>CompletableFuture使用详解
CompletableFuture使用详解
2022-07-07 03:00:00 【鬼罚olo】
CompletableFuture使用详解
Future的局限性,他没法直接对多个任务进行链式组合等处理,需要借助并发工具类才能完成,实现逻辑比较复杂
而CompletableFutures是对Future的扩展和增强,CompltableFuture实现Future接口,并在此基础上进行了丰富的扩展,完美弥补了Future的局限性,同时CompletableFuture实现了对任务的编排的能力。借助这项能力,可以轻松的组织不同任务的运行顺序,规则以及方式,从某种程序上说,这项能力时他的核心能力。而在以往,虽然通过CountDownlatch等工具类也可以实现任务的编排,但需要复杂的逻辑处理
ComplatableFuture的基础结构如下
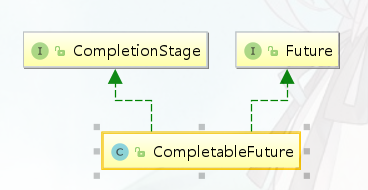
CompletionStage接口定义了任务编排的方法,执行某一阶段,可以向下执行后续阶段。异步执行的
默认线程池是**ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),但为了业务之间互不影响,且便于定位问题,强烈推荐使用自定义线程池**。
CompletableFuture中默认线程池如下:
// 根据commonPool的并行度来选择,而并行度的计算是在ForkJoinPool的静态代码段完成的
private static final boolean useCommonPool =
(ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism() > 1);
private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?
ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
ForkJoinPool中初始化commonPool的参数
static {
// initialize field offsets for CAS etc
try {
U = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class<?> k = ForkJoinPool.class;
CTL = U.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("ctl"));
RUNSTATE = U.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("runState"));
STEALCOUNTER = U.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("stealCounter"));
Class<?> tk = Thread.class;
……
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
commonMaxSpares = DEFAULT_COMMON_MAX_SPARES;
defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory =
new DefaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory();
modifyThreadPermission = new RuntimePermission("modifyThread");
// 调用makeCommonPool方法创建commonPool,其中并行度为逻辑核数-1
common = java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged
(new java.security.PrivilegedAction<ForkJoinPool>() {
public ForkJoinPool run() { return makeCommonPool(); }});
int par = common.config & SMASK; // report 1 even if threads disabled
commonParallelism = par > 0 ? par : 1;
}
功能
常用方法
依赖关系
- thenApply():把前面任务的执行结果,交给后面的Function
- thenCompose():用来连接两个依赖关系的任务,结果由第二个任务返回
and集合关系
- thenCombine():合并任务,有返回值、
- thenAcceptBoth():两个热播我要执行完成后,将结果交给thenAcceptBotj处理,无返回值
- runAfterBoth();两个任务都执行完成后,执行下一步操作
or聚合关系
applyToEither():两个任务哪个执行的快,就使用哪一个结果,有返回值acceptEither():两个任务哪个执行的快,就消费哪一个结果,无返回值runAfterEither():任意一个任务执行完成,进行下一步操作(Runnable类型任务)
并行执行
allOf():当所有给定的 CompletableFuture 完成时,返回一个新的 CompletableFutureanyOf():当任何一个给定的CompletablFuture完成时,返回一个新的CompletableFuture
结果处理
- whenComplete:当任务完成时,将使用结果(或 null)和此阶段的异常(或 null如果没有)执行给定操作
- exceptionally:返回一个新的CompletableFuture,当前面的CompletableFuture完成时,它也完成,当它异常完成时,给定函数的异常触发这个CompletableFuture的完成
异步操作
CompletableFuture提供了四个静态方法创建一个异步操作
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
四个方法的区别
- runAsync()以Runnable函数接口类型为参数,没有返回结果,supplyAsync()以Supplier函数式接口类型未参数,返回结果类型未U;Supplier接口的get()是由返回值会阻塞
- 使用没有指定Executor的方法时,内部使用Fork Join Pool。commonPool()作为他的线程池执行异步代码。如果没有指定线程池,则使用指定的线程池运行
- 默认情况下CompletableFuture会使用公共的ForkJoinPool线程池,这个线程池默认创建的线程数是 CPU 的核数(也可以通过 JVM option:-Djava.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism 来设置ForkJoinPool线程池的线程数)。如果所有CompletableFuture共享一个线程池,那么一旦有任务执行一些很慢的 I/O 操作,就会导致线程池中所有线程都阻塞在 I/O 操作上,从而造成线程饥饿,进而影响整个系统的性能。所以,强烈建议你要根据不同的业务类型创建不同的线程池,以避免互相干扰
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Runnable runnable = ()-> System.out.println("无返回结果任务");
CompletableFuture.runAsync(runnable);
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("有返回值的异步任务");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello world";
});
String result = future.get();
System.out.println();
}
获取结果(join&get)
join()和get()方法都是用来获取CompletableFuture异步之后的返回值,join()方法抛出的是uncheck异常
,不会强制开发者抛出。get()方法抛出的是经过检查的异常,ExecutionException, InterruptedException 需要用户手动处理(抛出或者 try catch)
结果处理
当CompletableFuture的计算结果完成,或者抛出异常的时候,我们可以执行特定的 Action。主要是下面的方法:
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)
- Action的类型是BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable>,它可以处理正常的计算结果,或者异常情况。
- 方法不以Async结尾,意味着Action使用相同的线程执行,而Async可能会使用其它的线程去执行(如果使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)。
- 这几个方法都会返回CompletableFuture,当Action执行完毕后它的结果返回原始的CompletableFuture的计算结果或者返回异常
测试
package ThreadPoolExecultorTest;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @Author lijiaxin
* @Description TODO
* @Date 2022/07/05/9:23
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class CompletableFuture1Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4 ; i++) {
/*开启主线程*/
int finalI = i;
CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
final CompletableFuture<List> listmates = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
List list = null;
if (finalI == 1){
list = test1();
}else if(finalI == 2){
list = test2();
}else if(finalI == 3){
list = test3();
}else {
list = test4();
}
return list;
},threadPoolExecutor());
listmates.thenAcceptAsync(list->{
linkedLists((LinkedList) list);
},threadPoolExecutor());
},threadPoolExecutor());
}
}
public static ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor() {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 1,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(20),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); //任务不能丢弃-同步执行
return executor;
}
public static List<String> test1(){
System.out.println("1");
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add("1");
return list;
}
public static List<String> test2(){
System.out.println("2");
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add("2");
return list;
}
public static List<String> test4(){
System.out.println("4");
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add("4");
return list;
}
public static List<String> test3(){
System.out.println("3");
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add("3");
return list;
}
public static LinkedList<LinkedList<String>> linkedLists(LinkedList linkedList){
System.out.println(linkedList);
LinkedList linkedList1 = null;
linkedList1.add(linkedList);
for (Object list:linkedList1) {
System.out.println(list.toString());
}
return linkedList1;
}
}
边栏推荐
- Get the city according to IP
- Brand · consultation standardization
- Learning notes | data Xiaobai uses dataease to make a large data screen
- from . onnxruntime_ pybind11_ State Import * noqa ddddocr operation error
- 华为机试题素数伴侣
- Postgresql源码(59)分析事务ID分配、溢出判断方法
- ESXI挂载移动(机械)硬盘详细教程
- Programmers' daily | daily anecdotes
- JESD204B时钟网络
- [start from scratch] detailed process of deploying yolov5 in win10 system (CPU, no GPU)
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
2018年江苏省职业院校技能大赛高职组“信息安全管理与评估”赛项任务书第二阶段答案
Apache ab 压力测试
Postgresql中procedure支持事务语法(实例&分析)
如何给目标机器人建模并仿真【数学/控制意义】
联合索引ABC的几种索引利用情况
途家、木鸟、美团……民宿暑期战事将起
【NOI模拟赛】区域划分(结论,构造)
Learning notes | data Xiaobai uses dataease to make a large data screen
健身房如何提高竞争力?
[solution] final app status- undefined, exitcode- 16
MATLAB小技巧(30)非线性拟合 lsqcurefit
dolphinscheduler3. X local startup
Cloudcompare point pair selection
linux系统rpm方式安装的mysql启动失败
libcurl返回curlcode说明
Prime partner of Huawei machine test questions
Stack and queue-p79-10 [2014 unified examination real question]
Tkinter window selects PCD file and displays point cloud (open3d)
Navicat importing 15g data reports an error [2013 - lost connection to MySQL server during query] [1153: got a packet bigger]
MySQL user permissions