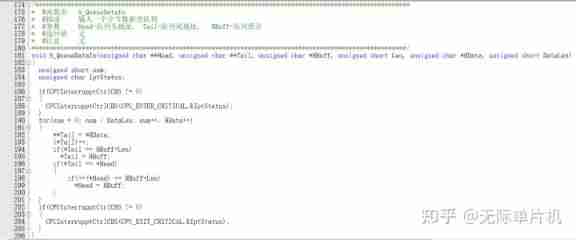
Java virtual machine
summary
Java Official documents https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/index.html
JVM It's a norm , adopt Oracle Java Official documents found JVM Specification review of .Java Virtual machine can be regarded as a virtual computer , Body function bytecode instruction set ( assembly language ) And memory management ( Stack 、 Pile up 、 Method area ) etc.
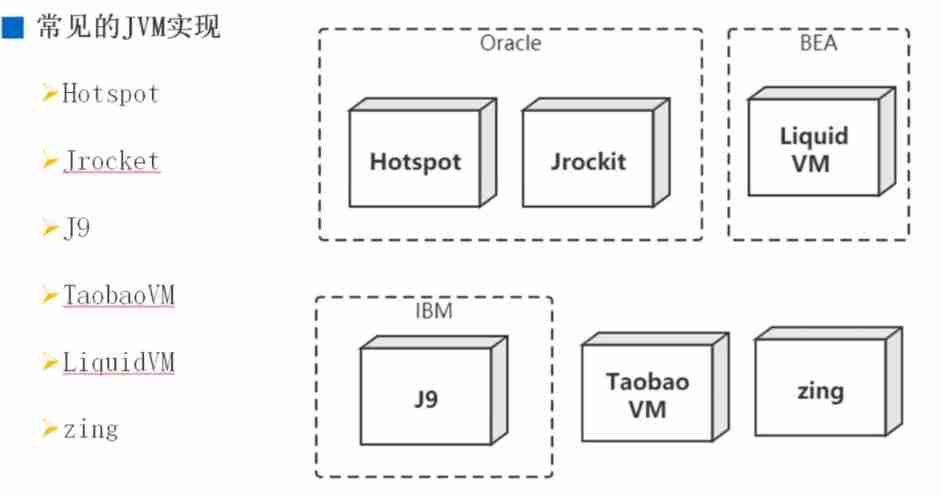
common JVM Realization
- Hotspot: The most widely used Java virtual machine .
- Jrocket: Originally belongs to BEA company , Once known as the fastest in the world JVM, After being Oracle Company purchase , Merge in Hotspot
- J9: IBM Have their own java Virtual machine implementation , It's called J9. Mainly for IBM product (IBM WebSphere and IBM Of AIX On the platform )
- TaobaoVM: Only a certain volume 、 Only manufacturers of a certain scale will develop their own virtual machines , For example, Taobao has its own VM, It's actually Hotspot Customized version of , It's specially prepared for Taobao , Ali 、 God Cats use this virtual machine .
- LiquidVM: It is a virtual machine for hardware , There is no operating system under it ( No Linux Neither windows), The following is the hardware , The operation efficiency is relatively high .
- zing: It belongs to zual This company , Very good , It's a commercial product , Very expensive ! Its garbage collection speed is very fast (1 In milliseconds ), It is the industry benchmark . One of its garbage collection algorithms was later Hotspot Absorption makes the present ZGC.
Architecture
What we usually call JDK, In fact, it means Java Development kit , It contains Java Tool set used in development .
- JDK Architecture
- Java Running environment (JRE) And development tools ( compiler , The debugger ,javadoc etc. ).
- JRE: from JVM,Java Runtime class library , Dynamic link library, etc ; It's for Java Provides the operating environment , One of the most important links is through JVM Interpret bytecode as executable machine code .
- JDK The compiler Javac[.exe], Will Java Code compiled into bytecode (.class file ). The compiled bytecode has the same content on any platform , So we say Java Language is a cross platform language ;Writeonce, run anywhere.
- Java Running environment (JRE) And development tools ( compiler , The debugger ,javadoc etc. ).
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-2vmjOtk2-1644747481396)(http://www.itxiaoshen.com:3001/assets/1644552030402KQTxi6TP.png)]****
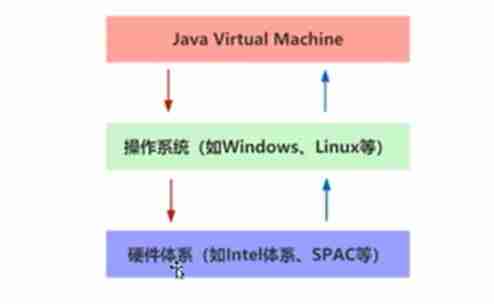
- JVM Relationship with operating system
- introduce Java After the language virtual machine ,Java The language does not need to be recompiled when it runs on different platforms .Java Language use Java Virtual machines block information about specific platforms , bring Java Language compilers only need to be generated in Java Target code running on virtual machine ( Bytecode ), It can run unmodified on multiple platforms .
- In the runtime environment ,JVM Will Java Bytecode is interpreted as machine code . Machine code and platform related ( Different hardware environments 、 Different operating systems , The generated machine code is different ), therefore JVM There are different implementations on different platforms . at present JDK The default implementation is Hotspot VM.
- JVM framework :Java Virtual machine is mainly divided into five modules : Class loader subsystem 、 Run time data area 、 Execution engine 、 Local method interface and garbage collection module .
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-Ut6GY2lN-1644747481400)(http://www.itxiaoshen.com:3001/assets/16445520369994chXCWt4.png)]
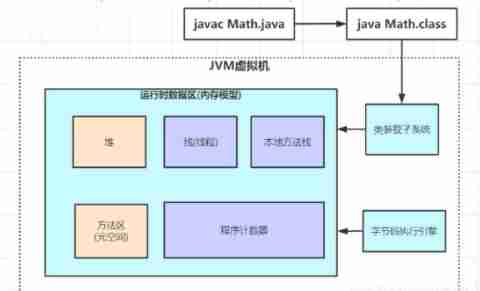
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-2TtOAZ9M-1644747481409)(http://www.itxiaoshen.com:3001/assets/1644641759500Hs1z7mMd.png)]
Escape analysis (Escape Analysis)
summary
- Escape analysis is the dynamic scope of an object ,2 In this case
- The way to escape : Object is passed to another method through parameters .
- Thread escape feature : Object has another thread access .
- The purpose of escape analysis is to confirm whether an object can only be accessed by the current thread .
- Escape analysis can lead to a certain degree of performance optimization . But escape analysis itself also needs a series of complex analysis , This is also a relatively time-consuming process .
- JIT(Just In Time Compiler) Just in time compilation technology , During instant compilation JVM We may do some optimization to our code, such as escape analysis .
Optimization strategy
There are three main optimization strategies for escape analysis : Objects may be allocated on the stack 、 Detach object or scalar substitution 、 Eliminate synchronization lock .
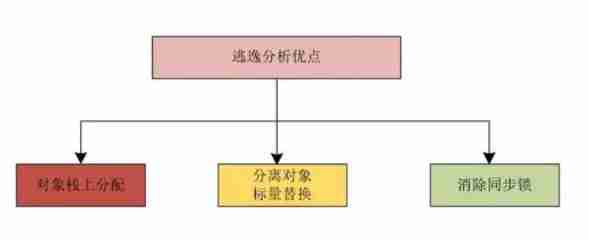
- Objects may be allocated on the stack :JVM Through escape analysis , Analyze the scope of use of the new object , It is possible to allocate objects on the stack . Stack allocation can quickly create and destroy objects on stack frames , No longer allocate objects to heap space , Can effectively reduce JVM The pressure of recycling .
- Detach object or scalar substitution : When JVM Through escape analysis , When you decide to assign an object to the stack , Just in time compilation can break up objects , Replace the object with a small local variable , We call this process of fragmentation scalar substitution . Replace the object with a local variable , It is very convenient to allocate on the stack . Scalars are variables that can no longer be divided , Such as Java Basic data type .
- Synchronous lock elimination : If JVM Through escape analysis , It is found that an object can only be accessed from one thread , When accessing this object , Can not add synchronization lock . If used in the program synchronized lock , be JVM Will synchronized Lock elimination .
Escape analysis switch
Escape analysis is not a new concept , As early as 1999 In, a paper proposed this technology . But in Java It is a novel and foreword Optimization Technology , from JDK1.6 Just started introducing this technology ,JDK1.7 Start with escape analysis enabled by default , It can also be controlled by a switch
- -XX:+DoEscapeAnalysis Open escape analysis
- -XX:-DoEscapeAnalysis Close escape analysis
- -XX:+EliminateAllocations Turn on scalar substitution
- -XX:-EliminateAllocations Close scalar substitution
- -XX:+EliminateLocks Open lock to eliminate
- -XX:-EliminateLocks Close the lock to eliminate
- Turn on scalar substitution or lock elimination The escape analysis switch must be turned on
Common interview questions
Will all objects and arrays allocate space in heap memory ? not always , As long as you master the principle of escape analysis , Then you know clearly Java Objects in are not necessarily allocated on the heap , because JVM Through escape analysis , Be able to analyze the scope of use of a new object , And use this to determine whether to allocate this object to the heap .
Is the code lock with lock bound to take effect ? not always
JVM Operation mode
- Explain the pattern (Interpreted Mode): Just use the interpreter (-Xint mandatory JVM Use the interpretive pattern ), Execute a row JVM Bytecode compiles a line of machine code
- Compile mode (Compiled Mode): Just use the compiler (-Xcomp JVM Use compile mode ), First of all JVM Bytecode is compiled into machine code at a time , Then execute all machine codes at once
- Mixed mode (Mixed Mode):(-Xmixed Set up JVM Use mixed mode ) Still use interpretation mode to execute code , But for some “ hotspot ” The code is executed in compiler mode , The machine code corresponding to these hotspot codes will be cached , There is no need to compile next time .JVM In general, mixed mode is used to execute code
| JVM Operation mode | advantage | Applicable scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Explain the pattern | Fast start | Just execute part of the code , And most of the code will be executed only once |
| Compile mode | Slow start , But the execution speed is fast in the later stage , Compare memory usage 1 | Suitable for scenarios where code may be executed repeatedly |
| Mixed mode | commonly JVM The default mode |
Java Start parameter classification
- Standard parameters (-), be-all JVM The implementation must realize the function of these parameters , And backward compatibility ;
- Nonstandard parameters (-X), Default jvm Realize the function of these parameters , But there is no guarantee that all jvm The realization is satisfied , And there is no guarantee of backward compatibility ;jvm Key points of parameter tuning
- Not Stable Parameters (-XX), Each of these parameters jvm The implementation will be different , It may be cancelled at any time in the future , It needs to be used carefully ;jvm Key points of parameter tuning . Can pass java -XX:+PrintFlagsFinal -version Get support parameter options .
Class loading
Class loading process
Class loading : Class loader will class The file is loaded into the memory of the virtual machine
Class 7 Life cycles : load -> verification -> Get ready -> analysis -> initialization -> Use -> uninstall
load : Find it on the hard disk and go through IO Read in bytecode file
Connect : Execution verification 、 Get ready 、 Parsing steps
- verification : Check the correctness of bytecode file , It's not necessary , You can turn off verification to improve the speed of virtual machine loading classes
- Get ready : Allocating memory to static variables of a class , And give default values
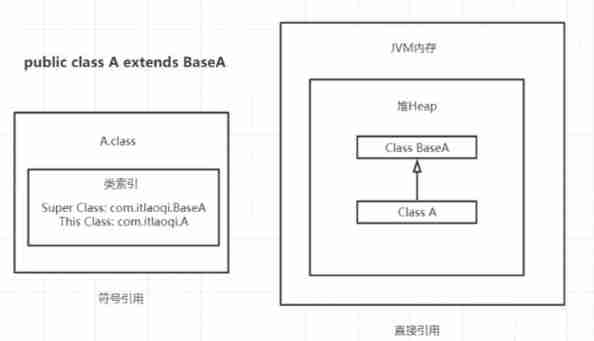
- analysis : Replace symbol references with direct references ; adopt javap -v Disassemble the bytecode file into a more readable file , Image class , Methods and other literal quantities are converted into symbolic references #1...N. Including class parsing , Field analytical , Method resolution , Interface analysis . That is, the static literal Association of bytecode ( character string , static state ) Convert to JVM Dynamic pointer Association in memory ( The pointer , dynamic ).
initialization : Class static variables are initialized to the specified values , Execute static code block
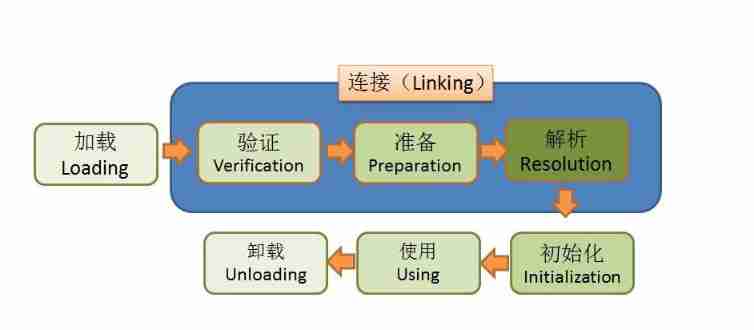
- Use :new Used in the object program
- uninstall : Carry out garbage collection
Class loader
summary
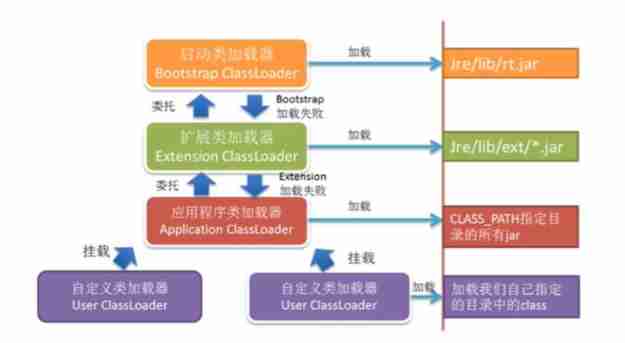
- Start class loader :C Language development , load Java The core library . Based on sandbox mechanism , Load only java、javax、sun Class at the beginning of package .
- Extend the classloader :Java Language writing , from sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader Realization , The upper loader is the boot class loader , Responsible for loading jre/lib/ext Expand... In the directory jar Class package .
- Application class loader :Java Language writing , from sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader Realization , The upper loader is the extension class loader , Is the default class loader . Responsible for loading ClassPath Class package under path , The main thing is to load the classes you write .
- Custom class loaders : Responsible for loading the class package under the user-defined path
- Use scenarios : Bytecode binary streams come from the network , Bytecode file is not in the specified lib、ext、classpath Under the path , You need to process the binary stream to get the bytecode .
- Different class loaders load the same Class After the bytecode file , stay JVM The class objects generated in are different . The same classloader ,Class Examples are in JVM China is the only one .
- stay Java in , A class uses its
Fully qualified class name ( Include package name and class name )As identification ; But in JVM in , A class is uniquely identified by its fully qualified class name and its class loader .
Class loader get example
JVM The predefined class loader is the boot class loader 、 Extend the classloader 、 Application class loader .
package cn.itxs.classloader;
import cn.itxs.entity.User;
public class ClassLoaderMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
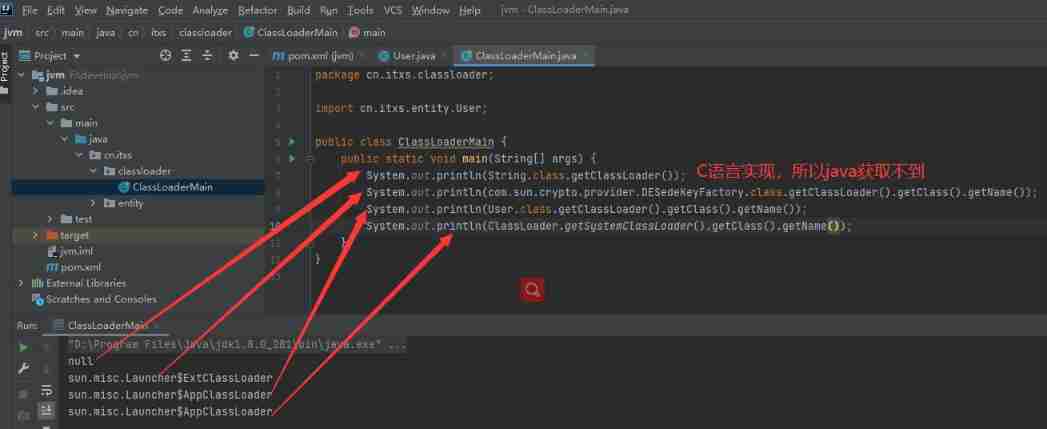
System.out.println(String.class.getClassLoader());
System.out.println(com.sun.crypto.provider.DESedeKeyFactory.class.getClassLoader().getClass().getName());
System.out.println(User.class.getClassLoader().getClass().getName());
System.out.println(ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getClass().getName());
}
}
Custom class loader example
In addition to starting the classloader , All classloaders are ClassLoader Subclasses of , So we can inherit ClassLoader To implement your own classloader .
package cn.itxs.entity;
public class Goods {
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("hello goods!");
}
}
Generate bytecode file Goods.class Post shear ( It's not a copy , Delete the bytecode file under the classpath ) To D:\temp\cn\itxs\entity Under the table of contents
package cn.itxs.classloader;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.Channels;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.WritableByteChannel;
public class ItxsClassLoader extends ClassLoader{
private String classPath;
public ItxsClassLoader(String classPath) {
this.classPath = classPath;
}
private byte[] loadBytes(String name) throws IOException {
name = name.replaceAll("\\.","/");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(classPath+"/"+name+".class");
FileChannel fc = fis.getChannel();
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
WritableByteChannel wbc = Channels.newChannel(baos);
ByteBuffer by = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (true){
int i = fc.read(by);
if (i == 0 || i == -1){
break;
}
by.flip();
wbc.write(by);
by.clear();
}
fis.close();
return baos.toByteArray();
}
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
try {
byte[] bytes = loadBytes(name);
return defineClass(name,bytes,0, bytes.length);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new ClassNotFoundException();
}
}
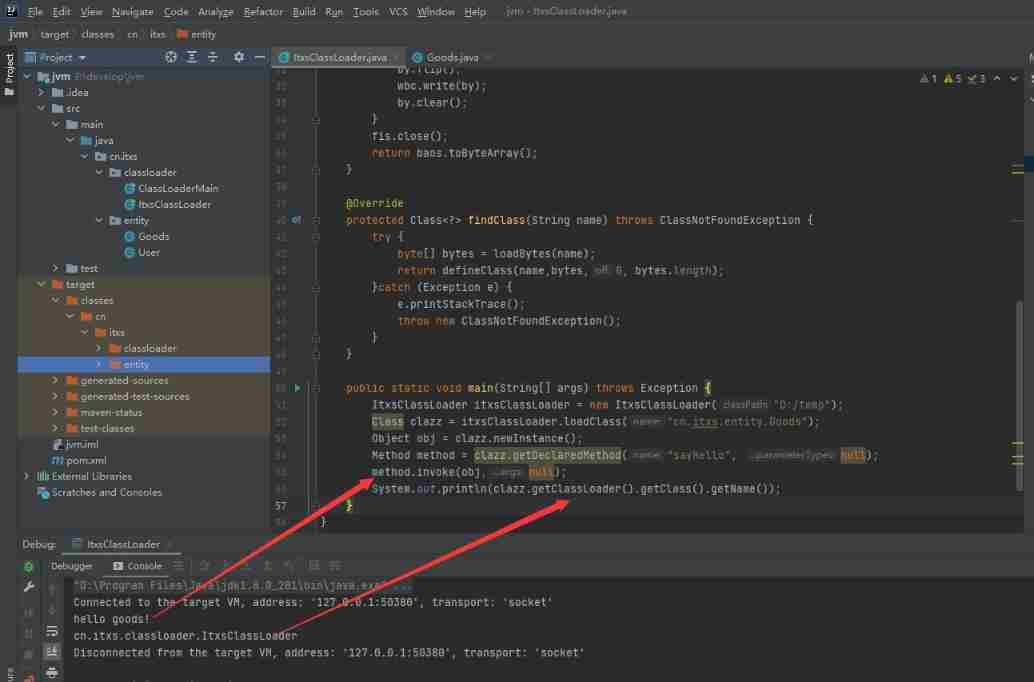
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ItxsClassLoader itxsClassLoader = new ItxsClassLoader("D:/temp");
Class clazz = itxsClassLoader.loadClass("cn.itxs.entity.Goods");
Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("sayHello", null);
method.invoke(obj,null);
System.out.println(clazz.getClassLoader().getClass().getName());
}
}
Parent delegate mechanism
- Parent delegate mechanism : When a class loader receives a class load request , It doesn't load the specified class directly , Instead, delegate the request to your parent loader to load it . Only when the parent loader cannot load this class , The current loader will be responsible for loading the class .
- When loading classes , Although user-defined classes will not be used by Bootstrap ClassLoader or Extension ClassLoader load ( Determined by the loading range of the class loader ), But the code implementation will still be delegated until Bootstrap ClassLoader, The upper layer cannot load , Then whether the lower layer can load , If you can't load , It will trigger findClass, Throw out ClassNotFoundException.
- The hierarchical relationship between class loaders does not exist in the form of inheritance , But in combination .
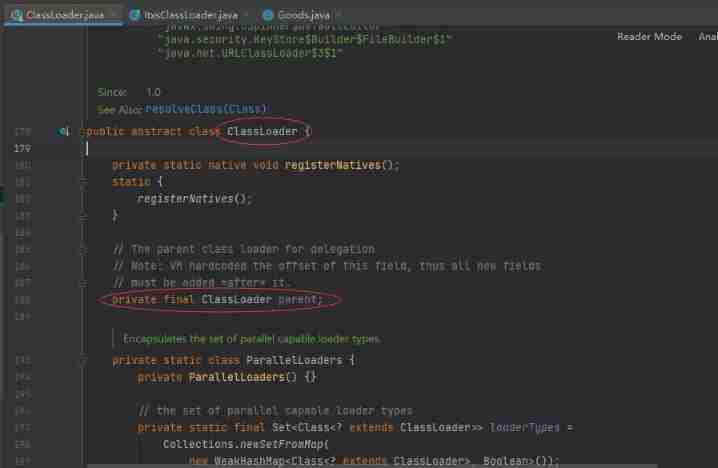
- The parental delegation mechanism is in ClassLoader Inside loadClass Method , If you want to implement the class loader yourself , Inherit ClassLoader After rewriting findClass Method , Load the corresponding class . The implementation process of the source code is as follows :
- First, judge whether the class has been loaded .
- The class is not loaded , If the parent class is not empty , Give it to the parent class to load .
- If the parent class is empty , hand Bootstrap Classloader load .
- If the class still cannot be loaded into , The trigger findClass, Throw out ClassNotFoundException.
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
c = findClass(name);
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
The role of parental delegation mechanism
- It can avoid the repeated loading of classes , When the parent loader has loaded a class , The child loader will not reload the class .
- Safety guaranteed . because Bootstrap ClassLoader When loading , Only... Will be loaded JAVA_HOME Medium jar The class in the bag , Such as java.lang.Integer, This class will not be replaced at will , This can effectively prevent the core Java API Be tampered with .
Break parental delegation
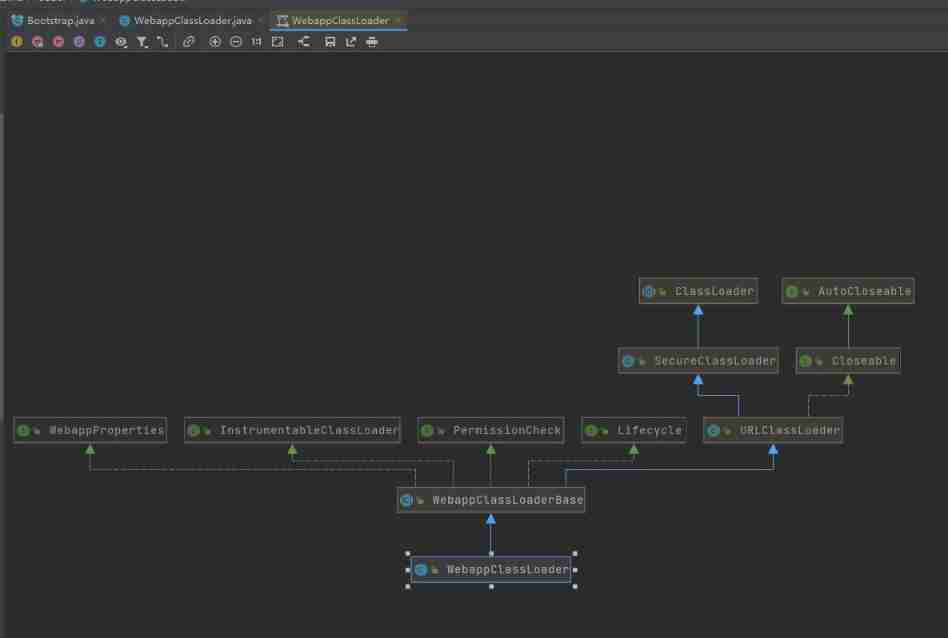
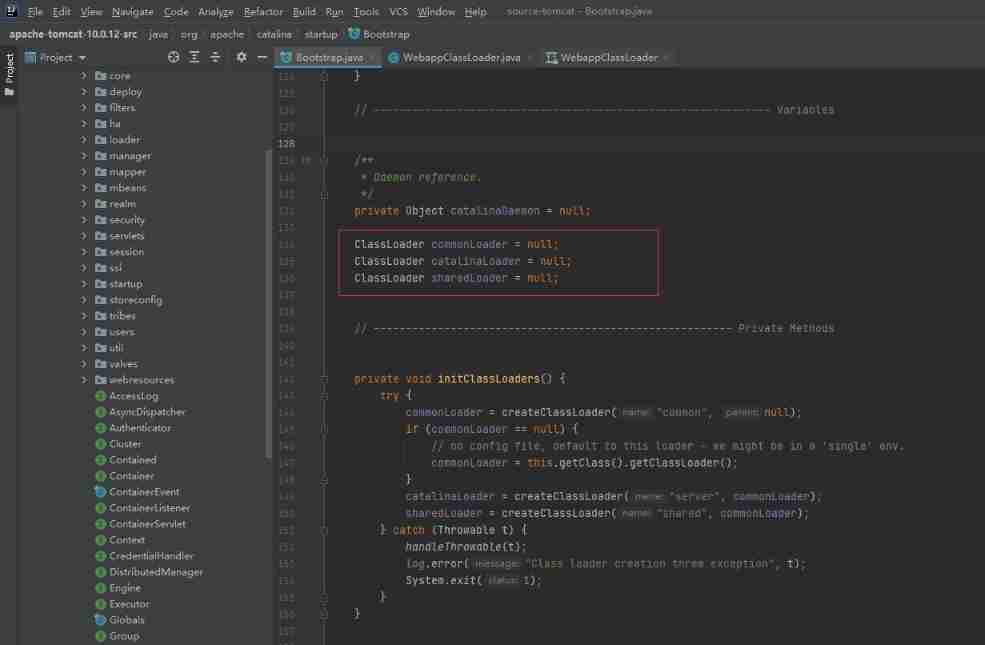
- The parental delegation mechanism is not inevitable . such as Tomcat web There are many applications deployed in the container , The dependent versions of these applications on third-party class libraries are different , And usually the path of these third-party class libraries is the same , If you use the default parental delegation class loading mechanism , You can't load more than one of the same classes . therefore Tomcat Undermining the principle of parental appointment , Provide a mechanism for isolation , For each web The container provides a separate WebAppClassLoader loader .
- Tomcat Class loading mechanism of : To achieve isolation , Priority load Web Apply your own defined classes , Do not follow the appointment of parents , Each application has its own class loader ——WebAppClassLoader Responsible for loading the class file , If you can't load it, give it to CommonClassLoader load .
** My blog website **IT Little god www.itxiaoshen.com


![[research materials] 2021 live broadcast annual data report of e-commerce - Download attached](/img/a6/74da2f44c7b6b22fed2f8e41a55988.jpg)